回溯算法经典题目+详细讲解+图示理解
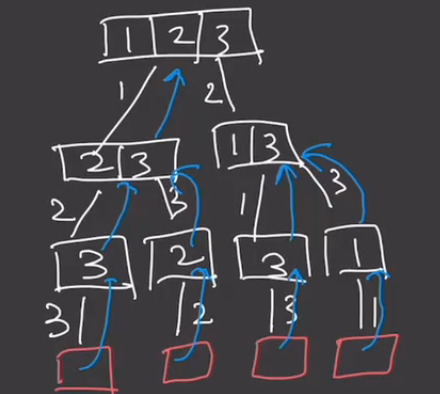
46.全排列
https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations/description/
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();dfs(res, nums, tmp);return res;}private void dfs(List<List<Integer>> res, int[] nums, List<Integer> tmp) {if (tmp.size() == nums.length) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));return;}// 找到tmp与nums中不同的第一个元素for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {int j;for (j = 0; j < tmp.size(); j++) {if (nums[i] == tmp.get(j)) break;}// 从这个元素开始进行递归if (j == tmp.size()) {tmp.add(nums[i]);dfs(res, nums, tmp);tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);}}}
}解题思路:这道题其实就是通过递归加回溯来实现,每一层递归就找到第一个不在tmp中的元素,然后先加入到tmp中,直到把所有的都加入到tmp中就会记录到res中
这里就是枚举所有的情况
47.全排列 II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations-ii/description/
class Solution {boolean[] used;public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();used = new boolean[nums.length];Arrays.sort(nums);dfs(res, nums, tmp);return res;}private void dfs(List<List<Integer>> res, int[] nums, List<Integer> tmp) {if (tmp.size() == nums.length) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));return;}// 找到tmp中不存在的nums[i]for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {// 判断当前元素是否被使用过if (used[i]) continue;// 如果当前元素和上一个元素一样且上一个元素未被使用if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]) continue;// 未被使用过就直接加入tmp.add(nums[i]);used[i] = true; // 标记已使用dfs(res, nums, tmp); // 找下一个// 回溯used[i] = false; tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);}}
}解题思路:这道题其实和上一道(46)有点像,只不过这里需要加入去重的逻辑对于全排列的通用做法就是用一个数组来记录被一个位置是否访问过,并且通过dfs加回溯进行解决,这里加入去重其实就是先对数组进行排序,然后后面遍历的时候通过if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]) continue;保证相同的元素在同一层中只被扩展一次
77. 组合
https://leetcode.cn/problems/combinations/description/
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {// 每次取出k个数,进行排列List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();dfs(1, n, k, res, new ArrayList<>());return res;}private void dfs(int start, int n, int k, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> tmp) {// 已经达到要求的数量了if (tmp.size() == k) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));return;}for (int i = start; i <= n; i++) {tmp.add(i);dfs(i+1, n, k, res, tmp);tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);}}
}解题思路:这道题其实就是通过回溯法来进行实现,其实和回溯的模板是差不多的,就是每次dfs进来都判断一下是否已经凑够需要的数量了,如果是的话就直接加入到要返回的那个集合中,否则就是进行遍历回溯。
然后这里因为是组合,不是排列,所以我们不用关心顺序,也就用不上used数组来进行标记了,我们是用一个start进行存储,严格控制了每次只能去i的下一位,避免了乱序的情况
39. 组合总和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum/description/
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();dfs(0, candidates, target, new ArrayList<>(), res);return res;}private void dfs(int start, int[] candidates, int target, List<Integer> tmp, List<List<Integer>> res) {if (target == 0) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));return;}if (target < 0) return;for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {tmp.add(candidates[i]);dfs(i, candidates, target - candidates[i], tmp, res);tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);}}
}解题思路:这道题就是经典的回溯,不过因为同一个数字是可以重复选择的,所以每次进行递归的位置都是从当前位置开始,具体的直接看代码就行,简单易懂
40.组合总和II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-ii/description/
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();Arrays.sort(candidates);dfs(0, candidates, target, new ArrayList<>(), res);return res;}private void dfs(int start, int[] candidates, int target, List<Integer> tmp, List<List<Integer>> res) {if (target < 0) return;if (target == 0) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));return;}for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {// 避免出现重复的子集if (i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i-1]) continue;tmp.add(candidates[i]);// 从i+1开始是为了保证每一个数都只会试用一次dfs(i+1, candidates, target - candidates[i], tmp, res);tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);}}
}解题思路:这道题其实和39有点像,不过这道题因为可能存在重复的元素,并且要求了每个元素都是不能重复使用的,所以我们我们需要多加两步判断,就是每次进行递归的时候不能从当前元素开始,而是要从当前元素的下一位开始,这样就做到了避免重复使用当前元素的情况,然后就是避免出现重复的子集,因为加入存在两个1,那么125(取第一个1)和125(取第二个1)的结果是一样的,要避免这种情况,所以直接判断到当前层中有重复的就直接跳过,其实原理就是保证同一层中只保留重复元素中的一个,不过要注意需要先进行排序,具体的直接看代码就行了
216. 组合总和 III
https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-iii/description/
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();dfs(1, k, n, new ArrayList<>(), res);return res;}private void dfs(int start, int k, int n, List<Integer> tmp, List<List<Integer>> res) {// 判断当前元素的个数是否已经够了if (k == tmp.size()) {// 达到要求if (n == 0) res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));// 否则就是不符合了直接返回return;}// 开始继续寻找(每个数字都只能是1~9)for (int i = start; i <= 9; i++) {tmp.add(i);dfs(i+1, k, n - i, tmp, res);// 回溯tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);}}
}解题思路:这道题的解题思路就还是回溯的模板,题目说了重复的数字只能使用一个并且对于重复的子集也是只能保留一份的,所以我们可以每一次都是从start开始进行遍历,然后递归的时候都是从下一个数开始,这样子就能保证上面要的这两点
78.子集
https://leetcode.cn/problems/subsets/description/
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {int len = nums.length;List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();res.add(new ArrayList<>());for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++) {dfs(0, i, nums, res, new ArrayList<>());}return res;}private void dfs(int start, int len, int[] nums, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> tmp) {if (tmp.size() == len) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));return;}for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {tmp.add(nums[i]);dfs(i + 1, len, nums, res, tmp);tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);}}
}解题思路:这道题依旧是回溯,不过这里需要我们额外判断的点其实就是那个长度的判断,因为长度可以从0到len,所以我们可以用一个for来调用,覆盖到所有长度大小类型,然后dfs的逻辑就和回溯的模板没什么区别了,依旧是从start开始,这样避免了出现同一组合重复问题,每一次递归调用都是从下一个位置开始,因为同一数字不可重复使用
90.子集II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/subsets-ii/description/
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {int len = nums.length;List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();Arrays.sort(nums);dfs(0, 0, nums, res, new ArrayList<>());return res;}private void dfs(int start, int len, int[] nums, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> tmp) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {if (i > start && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue;tmp.add(nums[i]);dfs(i + 1, len, nums, res, tmp);tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);}}
}解题思路:每次进来都是直接添加到res中,不过就要在进行递归调用的时候让下一层从当前数的下一个位置开始进行取数,这样子就不会出现重复。
然后避免出现相同数就是先排序,然后跳过相同数就行了
491.递增子序列
https://leetcode.cn/problems/non-decreasing-subsequences/description/
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();if (nums.length < 2) return res;boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length];dfs(0, nums, new ArrayList<>(), res);return res;}private void dfs(int start, int[] nums, List<Integer> tmp, List<List<Integer>> res) {if (tmp.size() > 1) res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));// 同一层中,值相同的只选择一个Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {if (set.contains(nums[i])) continue;if (tmp.isEmpty() || tmp.get(tmp.size() - 1) <= nums[i]) {set.add(nums[i]);tmp.add(nums[i]);} else continue;dfs(i + 1, nums, tmp, res);tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);}}
}解题思路:直接通过回溯进行解决,只要判断到tmp的大小已经大于等于2就意味着可以添加到res中了,但是这道题在这里不能直接return掉,因为还可以有更多
然后这里会开一个set,用来对每一层进行去重,就是只要是同一层中,值相同的只能取其他的一个,避免了出现重复序列的情况
接着值要不要添加到tmp中就是判断一下这个值是不是tmp的第一个元素,或者是不是比tmp中的最后一个元素小,如果满足其中的一个都能直接添加到tmp中
最后就是正常的回溯逻辑了
129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/description/
class Solution {private int res;public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {res = 0;dfs(root, 0l);return res;}private void dfs(TreeNode node, Long num) {if (node == null) return;num = num * 10 + node.val;if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {res += num;} else {if (node.left != null) dfs(node.left, num);if (node.right != null) dfs(node.right, num);}// 回溯num = (num - node.val) / 10;}
}解题思路:这道题其实很明显就是使用回溯,然后每次都是先将节点的值加到当前路径中,然后判断一下当前节点是否已经到叶子节点了,如果到的话就需要进行累加操作,否则就是继续进行递归,最后需要进行回溯,否则会出现逻辑混乱
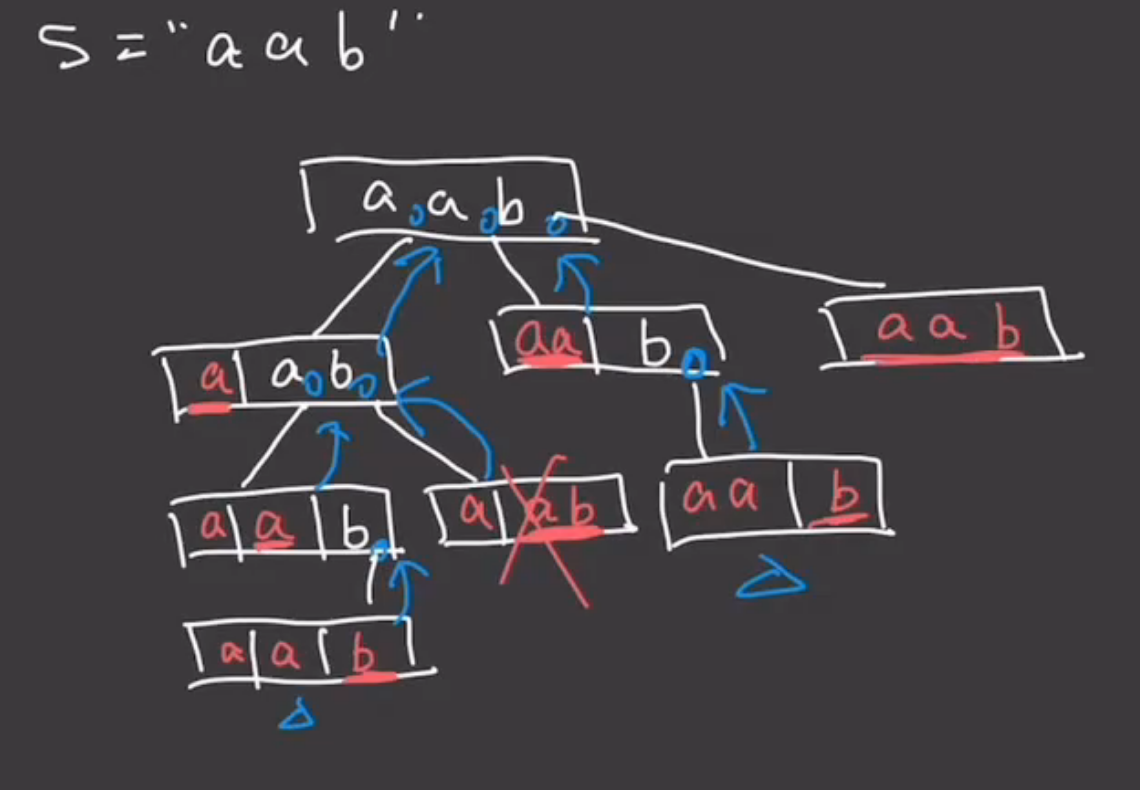
131.分割回文串
https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-partitioning/description/
class Solution {public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();int len = s.length();boolean[][] dp = new boolean[len][len];dfs(s, 0, res, new ArrayList<>(), dp);return res;}private void dfs(String s, int start, List<List<String>> res, List<String> tmp, boolean[][] dp) {int len = s.length();if (start >= len) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));return;}for (int i = start; i < len; i++) {String sub = s.substring(start, i + 1);if (isHW(s, start, i, dp)) {tmp.add(sub);dfs(s, i + 1, res, tmp, dp);tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);}}}private boolean isHW(String s, int left, int right, boolean[][] dp) {if (dp[left][right]) return true;while (left < right) {if (s.charAt(left++) != s.charAt(right--)) return false;}dp[left][right] = true;return true;}
}解题思路:这道题其实就是不断的模拟分割的点,然后判断截取出来的这部分是不是一个回文串,如果是的话就继续分割下去,否则就停止分割
93.复原IP地址
https://leetcode.cn/problems/restore-ip-addresses/description/
class Solution {public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();if (s.length() < 4 || s.length() > 12) return res;if (!containsSpecialCharacters(s)) return res;dfs(0, 0, s, res, new StringBuilder());return res;}private void dfs(int start, int cnt, String s, List<String> res, StringBuilder tmp) {int len = s.length();// 第四层,并且已经遍历完整个字符串if (cnt == 4) {if (start == len) {res.add(tmp.substring(1)); // 去掉第一个“.”}return;}// 剩下的字符串必需够分且不会操作剩下层数*3int remain = len - start;if (remain < (4 - cnt) || remain > (4 - cnt) * 3) return;int num = 0;// 每个位置最多选3个for (int i = start; i < start + 3 && i < len; i++) {num = num * 10 + (s.charAt(i) - '0');if (num > 255) break; // 如果这部分大于255直接跳出if (i > start && s.charAt(start) == '0') break; // 这部分的开头是0也要跳过int lenBefore = tmp.length(); // 记录长度tmp.append(".").append(s, start, i + 1);dfs(i + 1, cnt + 1, s, res, tmp);tmp.setLength(lenBefore);}}// 是否包含特殊字符private boolean containsSpecialCharacters(String s) {for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {if (!(s.charAt(i) <= '9' && s.charAt(i) >= '0')) return false;}return true;}
}解题思路:通过递归(回溯)来实现解答。
首先就是每一层递归进来之后要判断一下当前是否是在处理第四部分,如果是的画就是判断一下当前的索引是否遍历到最后一个字符,因为我们在下面进行递归的时候是直接限制死每个位置最多就只能拼接三个字符的。
然后需要进行判断的就是,
1. 当前剩余的字符数量是否够给剩下的层数分以及加入每个层数都分到3个字符,能否分完。
2. 统计每一部分大小并判断是否超过255
3. 如果当前构建的这部分已经不只一个数字,那么开头数字是否是0
最后就是直接通过递归和回溯就行了,并且我们一开始的时候就要先判断一下这个字符串的字符是否都是合法的
注意:如果是用String来进行保存每一部分的话,是不需要进行手动回溯的,因为每次调用的都是扔一个新的对象进去,旧对象自己保留在原来的栈中了,但是如果是StringBuilder就需要手动回溯,因为这个是直接修改原来的值,不会变成一个新对象
最后的最后就是直接看代码吧,代码应该是写的比较清晰的,但是我表达的可能没那么清晰。
51. N皇后
https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-queens/description/
class Solution {public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();char[] broad = new char[n];Arrays.fill(broad, '.');dfs(n, 0, res, new ArrayList<>(), new HashSet<>(), new HashSet<>(), new HashSet<>(), broad);return res;}private void dfs(int n, int row, List<List<String>> res, List<String> tmp, Set<Integer> colSet, Set<Integer> subSet, Set<Integer> addSet, char[] broad) {// 当前行是最后一行if (row == n) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));return;}// 开始进行遍历for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// 先判断这个位置可以取吗if (colSet.contains(i) || subSet.contains(row - i) || addSet.contains(row + i)) continue;// 标记一下这些位置已经被使用了colSet.add(i);subSet.add(row - i);addSet.add(row + i);broad[i] = 'Q';tmp.add(new String(broad));broad[i] = '.';dfs(n, row + 1, res, tmp, colSet, subSet, addSet, broad);// 回溯colSet.remove(i);subSet.remove(row - i);addSet.remove(row + i);tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);}}
}解题思路:题目的意思就是说主要一个位置有皇后,那么这个位置的横坐标和纵坐标以及两条对角线都是不能放的。
这道题我们没有别的办法在,只能通过枚举的方式不断的尝试出所有的情况,我们是通过分行来处理,每一行都会取尝试所有的列,如果发现都不行就会回溯到上一行,让上一行去选择新的位置。
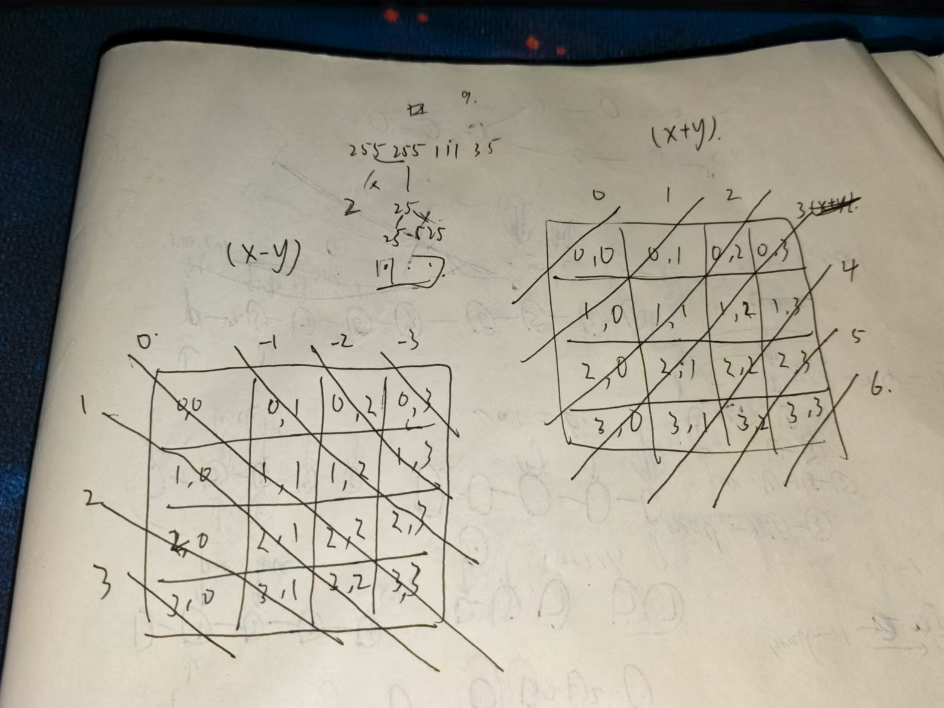
然后要记录纵坐标以及两条对角线的使用情况,所以需要开set记录,横坐标就不用记录了,应该我们是一行一行处理。列坐标的记录比较简单,主要是对角线的记录,正对角线上的坐标,只要x和y进行相加,可以发现正对角线上的值都是相同的,反对角线就是x-y,也是相等的。
具体可以看下面这张图进行理解。
37. 解数独
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sudoku-solver/description/
class Solution {public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {boolean[][] cols = new boolean[9][9], rows = new boolean[9][9]; // 记录第n行/列是否存在数字x ,[n][x]boolean[][][] cells = new boolean[3][3][9]; // 记录第 i行第j个小宫格是否有数字x ,[i][j][x]// 初始化for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {if (board[i][j] != '.') {int x = board[i][j] - '1';rows[i][x] = true;cols[j][x] = true;cells[i / 3][j / 3][x] = true;}}}// 递归dfs(board, rows, cols, cells, 0, 0);}private boolean dfs(char[][] board, boolean[][] rows, boolean[][] cols, boolean[][][] cells, int row, int col) {// 当前行遍历完了,开始下一行if (col == 9) {row++;col = 0;}// 所有行遍历完了if (row == 9) return true;// 判断是否要进行构造if (board[row][col] != '.') return dfs(board, rows, cols, cells, row, col+1);for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {// 可以构造if (rows[row][i] || cols[col][i] || cells[row / 3][col / 3][i]) continue;board[row][col] = (char) (i + '1');rows[row][i] = cols[col][i] = cells[row / 3][col / 3][i] = true;// 进行递归if (dfs(board, rows, cols, cells, row, col + 1)) return true;// 返回false说明构造失败,需要回溯board[row][col] = '.';rows[row][i] = cols[col][i] = cells[row / 3][col / 3][i] = false;}return false;}
}解题思路:这道题就是通过回溯来确定的,其实只要处理好几个点就行了,首先就是判断好同一列、同一行以及九宫格内不重复,这一点通过数组记录就行了,然后就是通过直接返回布尔类型的方式,这样子就能实现只要找到一个符合条件的答案就会一直返回,然后结束掉,如果是返回void的话就需要搜索所有情况才会结束
22. 括号生成
https://leetcode.cn/problems/generate-parentheses/description/
class Solution {public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();char[] path = new char[n * 2];build(n, 0, 0, path, res);return res;}private void build(int n, int l, int r, char[] path, List<String> res) {if (r == n) {res.add(new String(path));return;}// 如果左括号没用完,可以填左括号if (l < n) {path[l + r] = '(';build(n, l + 1, r, path, res);}// 如果右括号比较少,可以填右括号if (r < l) {path[l + r] = ')';build(n, l, r + 1, path, res);}}
}解题思路:这道题就是用构造回溯法,用一个数组来记录每一个位置选择的括号的类型,那么这道题其实就变成判断每一个位置选与不选了,只要判断到右边的括号已经用完了就可以记录下这一次构造的结果
如果发现左边括号没用完就优先使用左边的括号,然后才是发现右边括号剩的比较多,就用右边的,就是这种优先使用左边的括号就能避免说出现右边括号使用的比左边括号使用得多的情况发生,避免无效组合
然后这里其实是隐式回溯,我们主要是通过l和r来进行判定构造的位置,path我们是采取直接覆盖的方式(int 类型是基本类型)
79. 单词搜索
https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-search/description/
class Solution {public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {char c = word.charAt(0);for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < board[i].length; j++) {if (c == board[i][j]) {if (find(board, word, 0, i, j)) return true;}}}return false;}private boolean find(char[][] board, String word, int index, int i, int j) {if (index == word.length()) return true;// 越界判断if (i >= board.length || i < 0 || j >= board[0].length || j < 0) return false;char tmp = board[i][j];if (word.charAt(index) != tmp) return false;// 标记一下当前位置已经访问过了board[i][j] = '#';// 向四周去找boolean res = find(board, word, index + 1, i + 1, j) || find(board, word, index + 1, i - 1, j)|| find(board, word, index + 1, i, j + 1) || find(board, word, index + 1, i, j - 1);// 回溯board[i][j] = tmp;return res;}}解题思路:这道题的解题思路就是你先从原来的那个数组中找到和word首字母一样的那个位置开始进行查找,每次都是查找四周,看看是否有呢index指向的那个字符相同的,如果发现不相同就会进行剪枝,然后每次遍历过的位置就会标记一下,最后才回溯回来
需要注意的就是主函数查找的时候可能有多个位置,所以通过for循环找到所有符合第一个字符的位置
