MySQL-day2_02
MySQL-day2
- (四)排序
- (五)聚合函数
- 一、count 总记录数
- 二、max 最大值
- 三、min 最小值
- 四、sum 求和
- 五、avg 平均值
- (六)数据分组
- 一、分组
- 二、分组后的数据筛选
- (七)数据分页显示
- 一、获取部分行
- 二、分页
(四)排序
- 为了方便查看数据,可以对数据进行排序;
select * from 表名;
order by 字段1 asc|desc, 字段2 asc|desc, ...
- 将行数据按照字段1 进行排序,如果某些字段1 的值相同时,则按照字段2 排序,以此类推;
- 默认按照字段值从小到大排序;
- asc(默认值)从小到大排序,升序;
- desc 从大到小排序,降序;
例1:查询所有学生记录,按 age 从小到大排序
select * from students order by age;
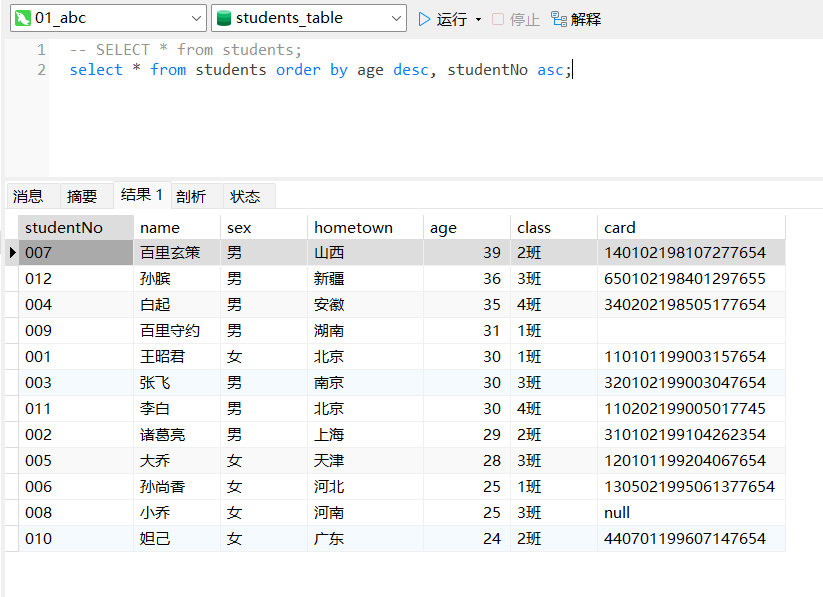
例2:查询所有学生记录,按 age 从大到小排序,
年龄相同时,再按 studentNo 从小到大排序。
select * from students order by age desc, studentNo asc;
▲ where 结合 order by:
select * from 表名 where 条件 order by 字段1, 字段2;
(五)聚合函数
为了快速得到统计数据,经常会用到如下 5 个聚合函数。
🔺注意:聚合函数不能在 where 后面的条件中使用!!!
一、count 总记录数
count(*) 表示计算总记录数,括号中写 * 与字段名,结果是相同的。
例1:查询学生总数(学生总数就是 students 表中记录的总数)
select count(*) from students;
select count(name) from students;
例2:查询性别 sex 为 ‘女’ 的学生总数
select count(*) from students where sex='女';
二、max 最大值
max(字段)表示求此字段的最大值。
例3:查询最大 age
select max(age) from students;
例4:查询性别sex 为’女’ 的最大年龄 age
select max(age) from students where sex='女';
🔺聚合函数不能在 where 后面的条件中使用。
🔺聚合函数不能与普通字段同时出现在查询结果中。
三、min 最小值
min(字段)表示求此字段的最小值。
例7:查询学生最小年龄 age
select min(age) from students;
例8:查询 class 班级为 ‘1班’ 的最小年龄 age
select min(age) from students where class='1班';
四、sum 求和
sum(字段) 表示求此字段的和。
例9:查询学生 age 年龄总和
select sum(age) from students;
例10:查询 hometown 为 ‘北京’ 的学生 age 总和
select sum(age) from students where hometown='北京';
五、avg 平均值
avg(字段) 表示求此字段的平均值。
例11:查询学生平均年龄
select avg(age) from students;
例12:查询 sex 为 ‘男’ 的平均年龄
select avg(age) from students where sex='男';
如果有null,忽略null。
比如三个年龄分别是:10,20,null
avg 计算结果是:(10+20)/2=15
(六)数据分组
一、分组
- 按照字段分组,表示此字段相同的数据会被放到一个组中。
- 分组的目的是配合聚合函数,聚合函数会对每一组的数据分布进行统计。
select 字段1, 字段2, 聚合函数... from 表名 group by 字段1, 字段2 ...
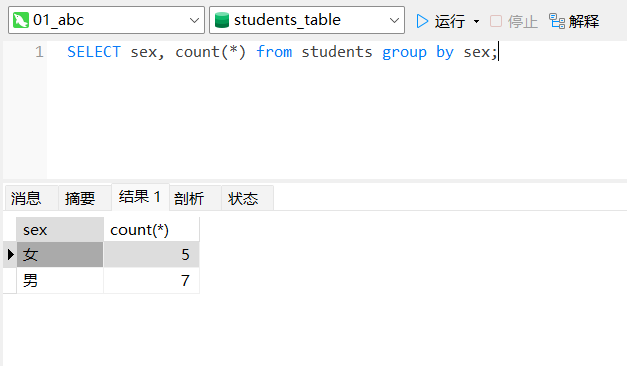
例1:查询各种 sex 性别的人数
select sex, count(*) from students group by sex;
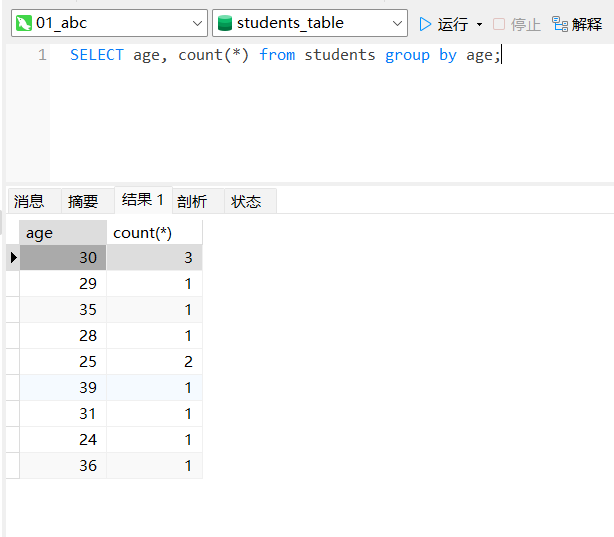
例2:查询各年龄 age 的人数
SELECT age, count(*) from students group by age;
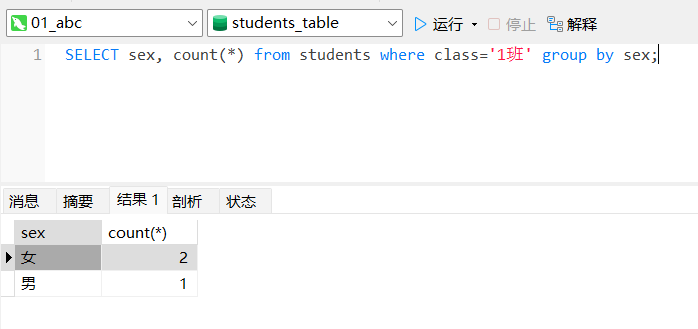
例3:分别查询 ‘1班’ 不同性别学生数量
SELECT sex, count(*) from students where class='1班' group by sex;
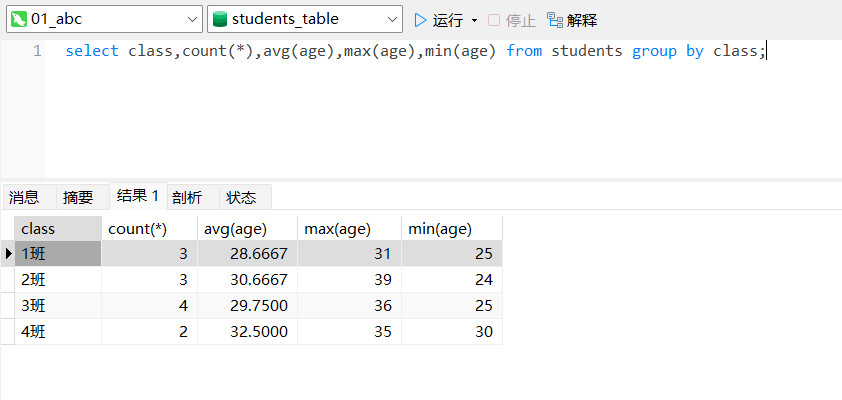
例4:用数据分组方法,统计各个班级学生总数、平均年龄、最大年龄、最小年龄。
select class,count(*),avg(age),max(age),min(age) from students group by class;
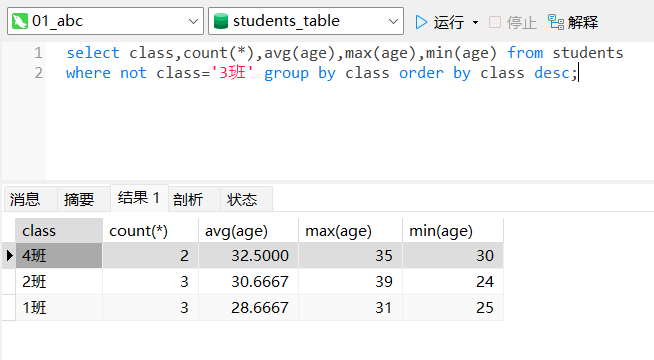
例5:用数据分组方法,统计各个班级学生总数、平均年龄、最大年龄、最小年龄。
但不统计 ‘3班’,统计结果按班级名称从大到小排序。
select class,count(*),avg(age),max(age),min(age) from students
where not class='3班' group by class order by class desc;
二、分组后的数据筛选
select 字段1, 字段2, 聚合... from 表名
group by 字段1, 字段2, 字段3...
having 字段1,...聚合...
▲ having 后面的条件运算符与 where 的相同。
例1:使用 where 子句,查询男生总人数
select count(*) from students where sex='男';
例2:使用 having 子句,查询男生总人数
select sex, count(*) from students group by sex having sex='男';
例3:求班级人数大于3人的班级名字
select class from students group by class having count(*)>3;
例4:用 having 子句,查询除了 ‘1班’ 以外,其他各个班级学生的平均年龄、最大年龄、最小年龄;
select class, avg(age),max(age),min(age) from students
group by class having not class='1班';
★ where 和 having:
- where是对 from 后面指定的表进行数据筛选,属于对原始数据的筛选;
- having是对 group by 的结果进行筛选;
- having 后面的条件中可以用聚合函数,where后面的条件不可以使用聚合函数。
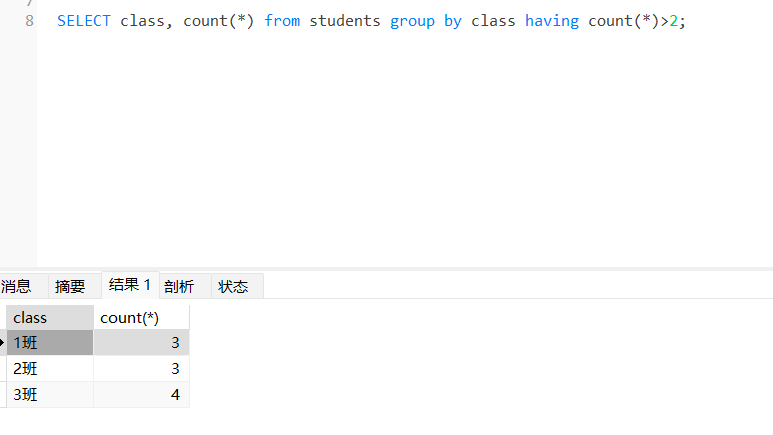
练习1:查询班级总人数大于2人的班级名称以及班级对应的总人数。
SELECT class, count(*) from students group by class
having count(*)>2;
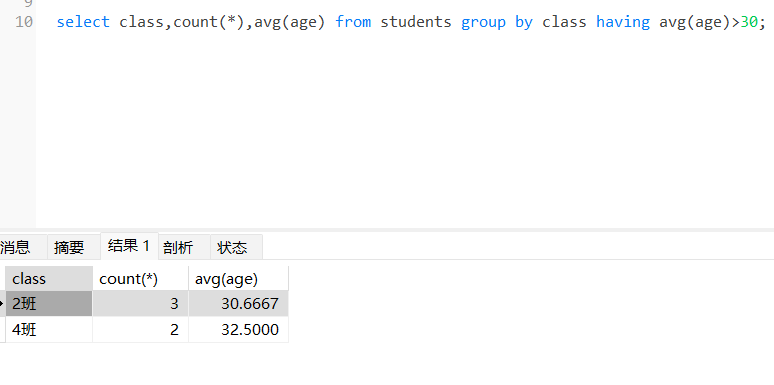
练习2:查询平均年龄大于30岁id班级名称和班级总人数。
select class,count(*),avg(age) from students
group by class having avg(age)>30;
(七)数据分页显示
一、获取部分行
当数据量过大时,在一页中查看数据是一件非常麻烦的事情。
语法:limit 开始行, 获取行数;
select * from 表名 limit start, count
- 从 start 开始,获取 count 条数据;
- start 索引从 0 开始,如省略 start 默认从 0 开始。
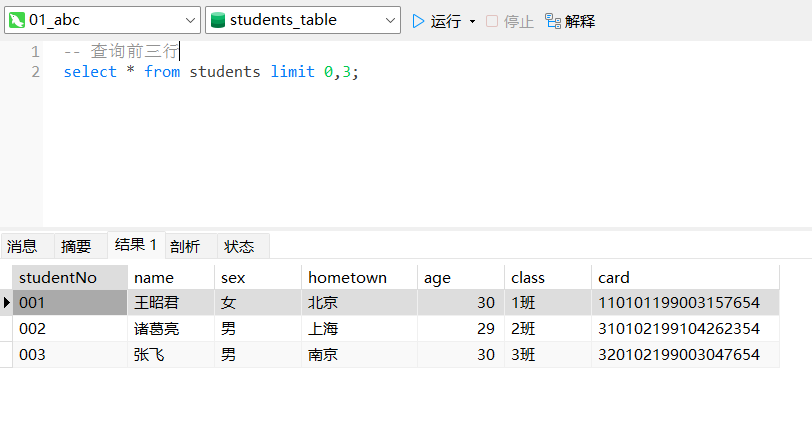
例1:查询前 3 行学生记录。
select * from students limit 0,3;
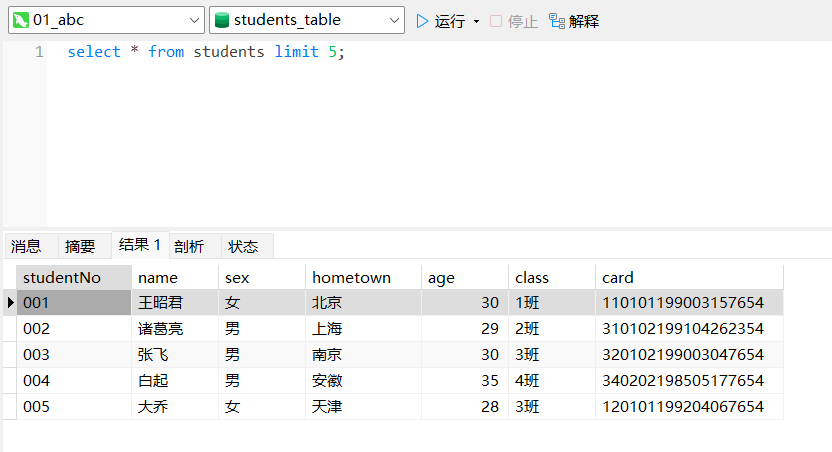
例2:省略 start ,查询前 5 行学生记录
select * from students limit 5;
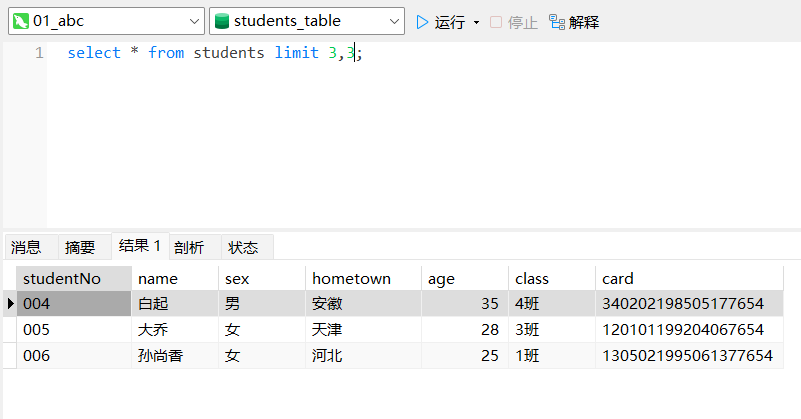
例3:查询从第 4 行开始的 3 条学生记录
select * from students limit 3,3;
例4:查询年龄最大的同学的name
select name from students order by age desc limit 1;
例5:查询年龄最小的女同学信息
select * from students where sex='女' order by age limit 1;
二、分页
当一张表记录特别多的时候,就需要用到分页显示。
已知:每页显示 m 条数据,求:查询第 n 页的数据。
select * from students limit (n-1)*m,m
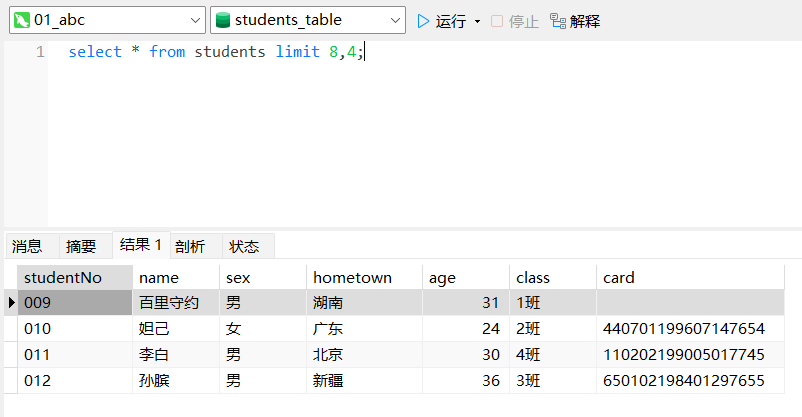
例1:每页显示 4 条记录,查询第 3 页的数据。
m = 4,n = 3;
(n-1)*m = (3-1)*4 = 8;
select * from students limit 8,4;
例2:查询 students 表,每页显示 5 条记录,求总页数。
- 查询记录总条数 a;
- 使用 a 除以每页显示条数 5,得到 b;
- 如果 b 为整数,则 b 为总页数。
- 如果 b 不为整数,则 b+1 为总页数。
| 操作 | 说明 | |
|---|---|---|
| 第一步 | select count(*) from students | 得到 students 表的总条数,结果为:12 |
| 第二步 | 12 / 5 = 2.4 | 不能整除 |
| 第三步 | 2 + 1 = 3 | 总页数为 3 页 |
