【C++】string 的使用(初步会用 string,看这一篇文章就够了)
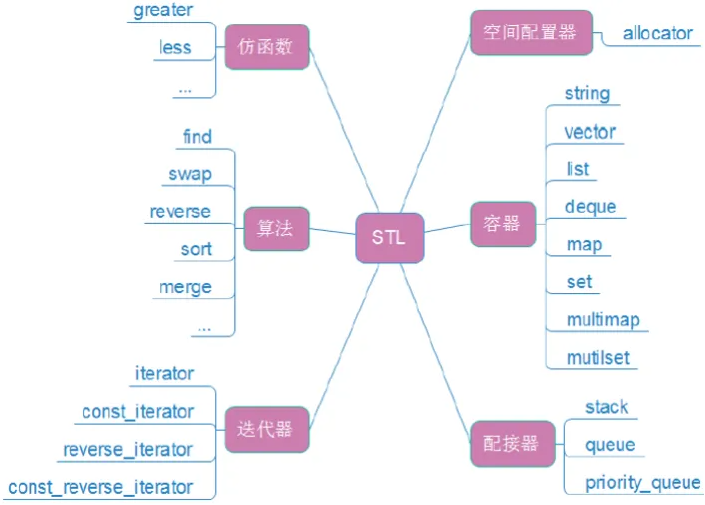
STL 简介
标准模板库,是C++标准库的重要组成部分。主要是数据结构和算法的库。
io流 是C++库里的东西
六大组件:
string 简介
<string> - C++ Reference
string 是管理字符串的类,是管理字符数组是顺序表,现实中的复杂类型都是通过字符串来表达的
标准库的东西都放在std这个命名空间里,如果std没有展开,就要 std::string
C语言也有管理字符串:<string.h>里strxxx系列的库函数
string 的使用
注意:以下的 pos 是下标,从 0 开始!!!
构造函数 (constructor)
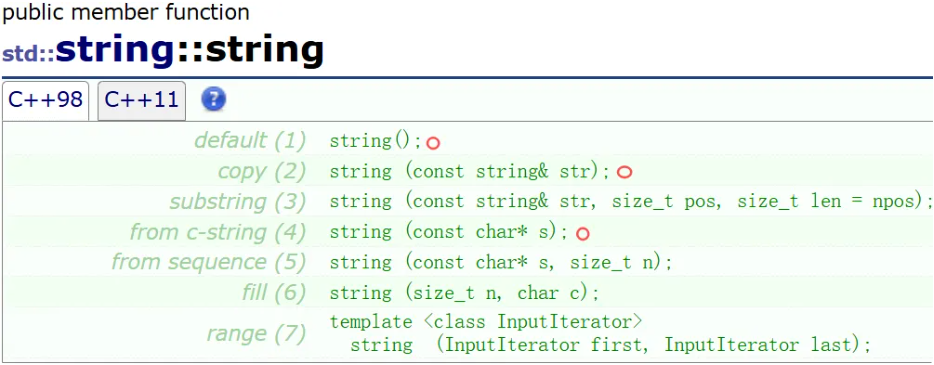
(1):无参的构造
(2):拷贝构造
(3):复制从字符位置 pos 开始并跨越 len 字符的 str 部分(如果 str 太短或 len 是 string::npos,则复制到 str 的末尾)
(4):用常量字符串初始化
(5):拷贝s数组的前n个进行初始化
(6):用n个字符初始化
(7):
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
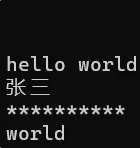
{string s1;string s2(s1); // (const string& str)string s3("hello world"); // (const char* s)string s4("张三");string s5(10, '*'); // (size_t n, char c)cout << s1 << endl; // 在 string类 外面重载了流插入、留提取,可以直接使用// 省略打印 s2 - s5 的代码string s6(s3, 6, 5); // (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos)cout << s6 << endl;return 0;
}
为什么 string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos); 给了缺省参数?

npos 是 string 这个类里公共的静态成员常量,给的-1是整型的最大值
string s7(s3, 6);cout << s7 << endl; // worldstring s8(s3, 6, 100);cout << s8 << endl; // world没给第三个参数:代表给了个很大的值(4G),长度远超后面的
析构函数 (destructor)
不管,对象出了作用域自动调用
operator= 赋值

后两个不支持也可以,没多大意义
s1 = s4;cout << s1 << endl; // 张三s1 = "000001";cout << s1 << endl; // 000001s1 = '2';cout << s1 << endl; // 22. 修改操作 (Modifiers)
push_back

append 追加

(1):追加string对象
(2):追加string对象从subpos下标位置开始的sublen个字符
(3):追加常量字符串
(4):追加常量字符串的前n个
(5):追加n个字符
(6):
// 增string s1("hello");// 尾插入一个字符s1.push_back(' ');// 尾插一个字符串s1.append("world");cout << s1 << endl; // hello worldC语言中字符串追加:strcat
缺点:效率低,每次先找到 '\0' 再追加;不能自动扩容,你先要自己开够空间,否则报错
string 只管插入,空间不够?交给对象s1,s1其实就是管理字符数组的顺序表
class string
{operator+=(char ch) // 调push_backoperator+=(const char* str) // 调appendprivate:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;
};operator+=

string s1("hello");s1 += ' ';s1 += "world";cout << s1 << endl; // hello worldassign 赋值
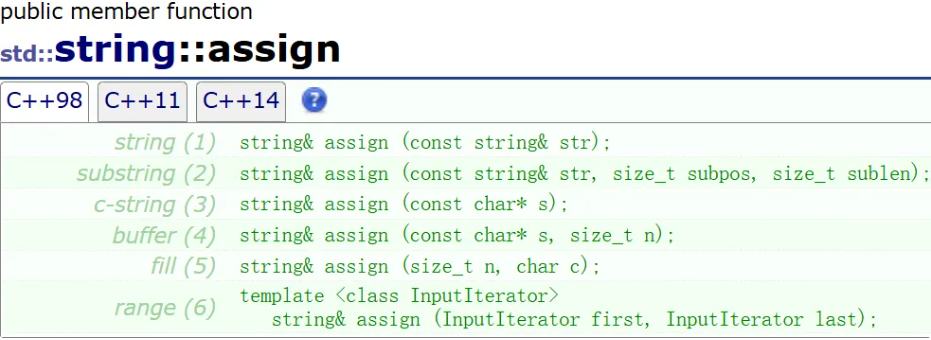
为字符串分配一个新值,替换其当前内容。很少用
string s1("hello world");s1.assign("ssssss");cout << s1 << endl; // ssssssinsert 插入
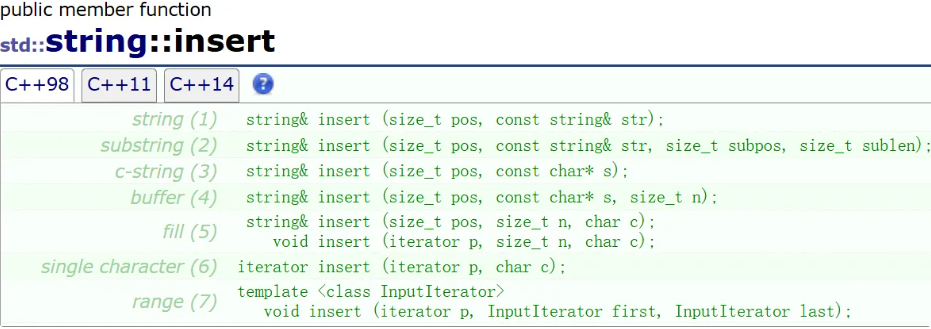
插入字符串。尽量少用,有效率问题
string s1("000001");s1.insert(0, "hello");cout << s1 << endl; // hello000001s1.insert(5, "world");cout << s1 << endl; // helloworld000001s1.insert(0, 3, 'x');cout << s1 << endl; // xxxhelloworld000001s1.insert(s1.begin() + 10, 3, 'y');cout << s1 << endl; // xxxhellowoyyyrld000001erase 删除

(1):删除从 pos 位置开始,并跨越 len 长的字符。len 给大或不给,删完
(2):擦除 p 指向的字符
(3):擦除范围 [first,last] 中的字符序列
string s1("hello world");s1.erase(5, 1);cout << s1 << endl; // helloworlds1.erase(5);cout << s1 << endl; // hellostring s2("hello world");s2.erase(0, 1);cout << s2 << endl; // ello worlds2.erase(s2.begin());cout << s2 << endl; // llo worldreplace 替换
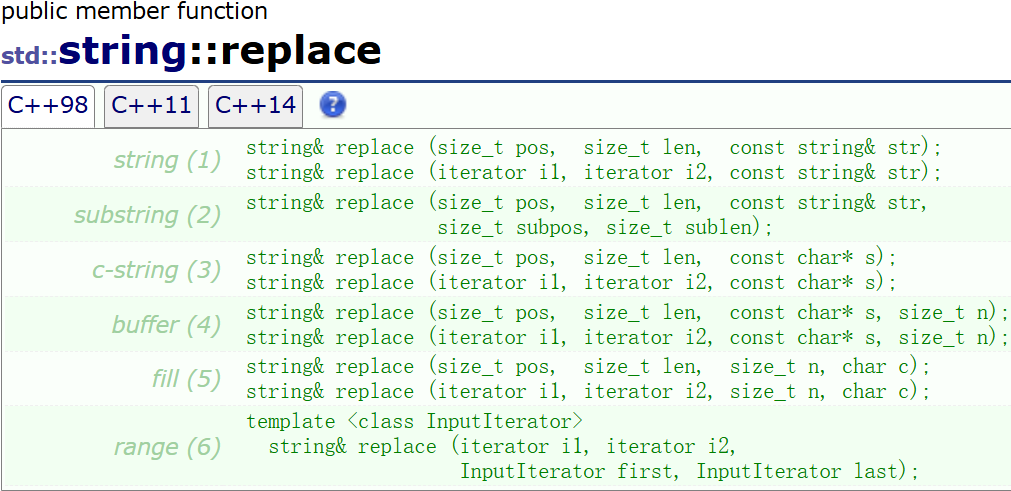
// world替换成 xxxxxxxxxxstring s1("hello world hello C++");s1.replace(6, 5, "xxxxxxxxxx");cout << s1 << endl; // hello xxxxxxxxxx hello C++s1.replace(6, 10, "yyyyy");cout << s1 << endl; // hello yyyyy hello C++// 所有空格替换成20%string s2("hello world hello C++");string s3;for (auto ch : s2){if (ch != ' ')s3 += ch;elses3 += "20%";}s2 = s3;cout << s2 << endl;3. 容量 (Capacity)
size 数据个数
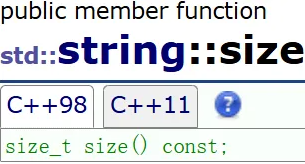 建议用 size
建议用 size
length 长度
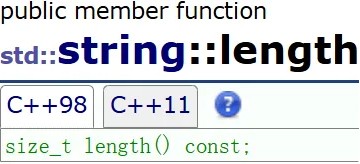
string s1("hello world");cout << s1.size() << endl; // 11cout << s1.length() << endl; // 11历史:最开始 string 用的很多,就在标准库里写了个 string。单有 string 肯定不够,开发了 STL,后来发现 string 应该放到 STL 里面。
 string 不属于 STL,但他们是同类;把 string 归到 STL 里也合适
string 不属于 STL,但他们是同类;把 string 归到 STL 里也合适
C语言用的 strlen;C++ string 最开始用的是 length-长度,STL 出来以后被迫加上 size(统一性)
顺序表、链表等线性表可以叫 length-长度;树、哈希等非线性叫 size
max_size
返回字符串可以达到的最大长度
不同编译器下结果不同,没用
capacity
返回当前为字符串分配的存储空间的大小,以字节表示
不同编译器下结果不同,没用
clear 清理数据
擦除字符串的内容,该字符串将变为空字符串(长度为 0 个字符)。但不释放空间
string s1("hello world");cout << s1.size() << endl;cout << s1.capacity() << endl;size_t old = s1.capacity();for (size_t i = 0; i < 100; i++){s1 += 'x';if (old != s1.capacity()){cout << "扩容:" << s1.capacity() << endl;old = s1.capacity();}}cout << s1.size() << endl;cout << s1.capacity() << endl;s1.clear();cout << s1.size() << endl;cout << s1.capacity() << endl;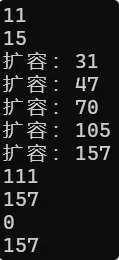
reserve 请求更改容量

应用场景:知道要开多少空间,提前一把开好,避免慢慢扩容的代价
单纯开空间,只改变 capacity,不改变 size
n > 容量:扩,且扩的 >= n
n < 容量:执行不具约束力的请求,去缩小 string 的 capacity:容器自行优化,允许 string 的 capacity > n
string s;s.reserve(100); // 知道string要插入100个cout << s.capacity() << endl;size_t old = s.capacity();for (size_t i = 0; i < 100; i++){s += 'x';if (old != s.capacity()){cout << "扩容:" << s.capacity() << endl;old = s.capacity();}}//s.clear();//cout << s.capacity() << endl;s.reserve(10);cout << s.capacity() << endl;不放开屏蔽的代码:![]() 放开屏蔽的代码:
放开屏蔽的代码:![]()
resize 开空间 + 填值初始化

开空间 + 填值初始化
n > size:则通过在末尾插入所需字符数来扩展当前内容,以达到 n 的大小。指定 c,用 c;没指定用 '\0'
n < size:缩短为其前 n 个字符,删除第 n个字符之外的字符
缩容是有代价的,很少会缩空间(以时间换空间)
string s1("hello world");s1.reserve(100);cout << s1.size() << endl;cout << s1.capacity() << endl;// s1.resize(200);s1.resize(200, 'x');cout << s1.size() << endl;cout << s1.capacity() << endl;s1.resize(20);cout << s1.size() << endl;cout << s1.capacity() << endl;s1.resize(0);cout << s1.size() << endl;cout << s1.capacity() << endl;![]()
shrink_to_fit 请求缩容至合适

这个请求不具约束力:容器自行优化,允许 string 的 capacity > size
不建议缩
4. 元素访问 (Element access)
operator[ ]
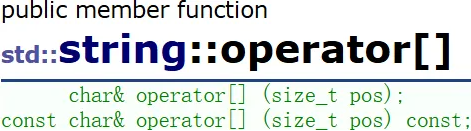
返回的是第pos位置字符的引用,所以能被修改
string、vector重载了[ ],可以像数组一样使用
string s1("hello world");cout << s1 << endl; cout << s1.size() << endl;for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++){s1[i]++;}s1[0]--;// 遍历stringfor (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++){cout << s1[i];}cout << endl;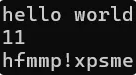
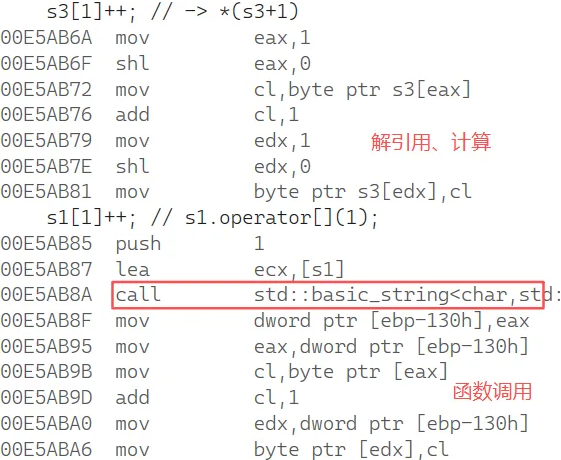
string s1("hello world"):常量字符串是无法改变的。所以底层是在堆上开一个数组,最后面加\0
char s3[] = "hello world";s3[1]++; // -> *(s3+1)s1[1]++; // s1.operator[](1);自定义类型用这个 [ ] 运算符变成调用operator,1作为参数传过去
表达式读,读的是函数调用的返回值
5. 迭代器 (Iterators)
iterators 提供一种统一的方式 访问和修改 容器的数据
iterators 是像指针的类型,不一定是指针
iterators 属于 string 这个类域
string 的底层就是指针;其他容器不一定是指针,有可能是封装的自定义类型。eg:链表
string 迭代器不好用,建议用 下标 + [ ]
begin 正向迭代器
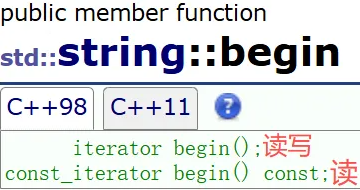
返回开始位置
end
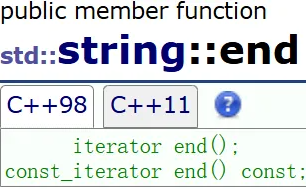
返回最后一个数据的下一个位置
string s1("hello world");string::iterator it = s1.begin();while (it != s1.end()){(*it)--; // 写:迭代器可以修改++it;}cout << endl;it = s1.begin();while (it != s1.end()){cout << *it; // 读:gdkknvnqkc++it;}cout << endl;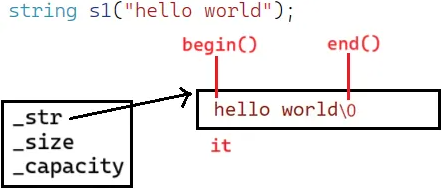
string 不喜欢用迭代器。迭代器的 3 个意义:
1. 第三种访问 string 的方式:范围for(最爱)
语法上:依次取 s1 的数据,赋值给 ch 变量
范围 for 底层就是迭代器;不支持迭代器,就不支持范围for(栈先进先出,不支持遍历,不支持迭代器,不支持范围for)
范围for 只能正着遍历,不能倒着遍历。只有反向迭代器能倒着遍历
string s1("hello world");// for (char ch : s1) 错:ch是每个字符的拷贝,ch的改变不影响string里的for (auto& ch : s1){ch--;}cout << endl;for (char ch : s1){cout << ch; // gdkknvnqkc}cout << endl;2. 任何容器都支持迭代器,并且用法是类似
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);vector<int>::iterator vit = v.begin();while (vit != v.end()){cout << *vit << " ";++vit;}cout << endl;return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;int main()
{list<int> lt;lt.push_back(10);lt.push_back(20);lt.push_back(30);lt.push_back(40);list<int>::iterator lit = lt.begin();while (lit != lt.end()){cout << *lit << " ";++lit;}cout << endl;return 0;
}3. 迭代器和算法配合
算法要作用到数据上面去,数据在容器里一般被封装为私有,不能直接访问
算法可以通过迭代器,去处理容器中的数据

逆置是通用的,链表、数组……都可以逆置
一个底层是数组,一个底层是链表,但对我来说用法一样
#include <algorithm>
// 意义2的2个代码reverse(lt.begin(), lt.end()); // 要逆置链表,就传链表的迭代器区间……reverse(v.begin(), v.end());for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;for (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;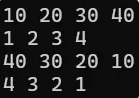
rbegin 反向迭代器
rend
string s1("hello world");// string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();auto rit = s1.rbegin(); // 有了迭代器,auto的价值体现出来了while (rit != s1.rend()){(*rit) += 3;cout << *rit;++rit;}cout << endl;cout << s1 << endl;![]()
const 对象不能用普通的迭代器,要用 const 迭代器
否则报错,相当于权限放大的问题
仔细看 2、4、14、15 行
// void Func(string s) 会调用拷贝构造(深拷贝,代价极大)。如果不改变,最好加 const
void Func(const string& s)
{string::const_iterator it = s.begin();while (it != s.end()){// *it += 2; 报错,*it是常量cout << *it << " "; // h e l l o w o r l d ++it;}cout << endl; //string::const_reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();auto rit = s.rbegin();while (rit != s.rend()){// (*rit) += 3; 报错cout << *rit << " "; // d l r o w o l l e h ++rit;}
}int main()
{string s1("hello world");Func(s1);return 0;
}6. 字符串操作 (String operations)
c_str

获取底层的 C 字符串。返回 C 形式指向字符数组(包函 \0)的指针
意义:和 C 的一些接口函数配合
class string
{
private:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;
}; string s1("hello world");cout << s1 << endl; // 调string的流插入cout << s1.c_str() << endl; // 识别成 char* string filename = "test.cpp";filename += ".zip";// FILE* fout = fopen(filename, "r"); 报错// FILE *fopen(const char *,const char *)”: // 无法将参数 1 从“std::string”转换为“const char *”FILE* fout = fopen(filename.c_str(), "r");substr
把子字符串复制给另一对象
find

搜索由参数指定的序列第一次出现的位置
找到了返回:第一个匹配的第一个字符的位置;没找到返回:string::npos
(1):要搜索的 string 中,从 pos 位开始搜索 str
(2):……从 pos 位开始搜索字符数组。到第一个 '\0' 还没找到,结束搜索
(3):……从 pos 位开始搜索字符数组。到第一个 '\0' 或 搜索 n 个字符后,还没找到,结束搜索
(4):……从 pos 位开始搜索字符c
若 pos > size,永远找不到
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string url = "ftp://www.baidu.com/?tn=65081411_1_oem_dg";// string url = "http://www.baidu.com/?tn=65081411_1_oem_dg"// string url = "https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/";// 协议 域名 资源名size_t pos1 = url.find("://");string protocol;if (pos1 != string::npos){protocol = url.substr(0, pos1);}cout << protocol << endl;string domain;string uri;size_t pos2 = url.find('/', pos1 + 3);if (pos2 != string::npos){domain = url.substr(pos1 + 3, pos2 - (pos1 + 3));uri = url.substr(pos2 + 1);}cout << domain << endl;cout << uri << endl;return 0;
}rfind
在字符串中搜索 由参数指定的序列最后一次出现的位置
查找最后一个单词的长度;查找一个文件的后缀:test.cpp.zip
find_first_of
在字符串中搜索 由其参数指定的序列中任一字符匹配的第一个字符
std::string str("Please, replace the vowels in this sentence by asterisks.");std::size_t found = str.find_first_of("aeiou"); // 给元音字母都改成 *while (found != std::string::npos){str[found] = '*';found = str.find_first_of("aeiou", found + 1);}std::cout << str << '\n';// Pl**s*, r*pl*c* th* v*w*ls *n th*s s*nt*nc* by *st*r*sks.find_last_of
在字符串中搜索 由其参数指定的序列中任一字符匹配的最后一个字符
find_first_not_of
在字符串中搜索 由其参数指定的序列中任一字符都不匹配的第一个字符
find_last_not_of
在字符串中搜索 由其参数指定的序列中任一字符都不匹配的最后一个字符
7. 非成员函数
getline
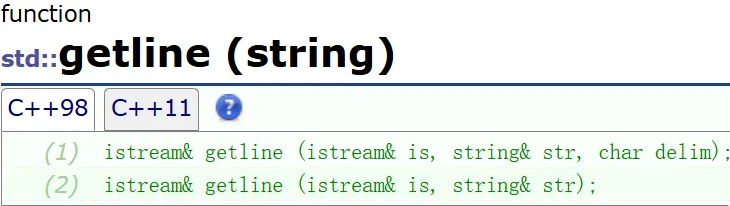
从 is 中提取字符并将它们存储到 str 中,直到找到分隔符 delim 或 换行
scanf / cin 有时要求连续输入多值,不论什么类型,多值之间规定 空格 / 换行 表示间隔
遇见 空格 / 换行 就认为当前读值结束。无法读有空格的字符串
string name;// cin >> str; 无法读有空格的字符串cout << "Please, enter your full name: ";getline(cin, name);cout << "Hello, " << name << "!\n";8. 字符串相互转换
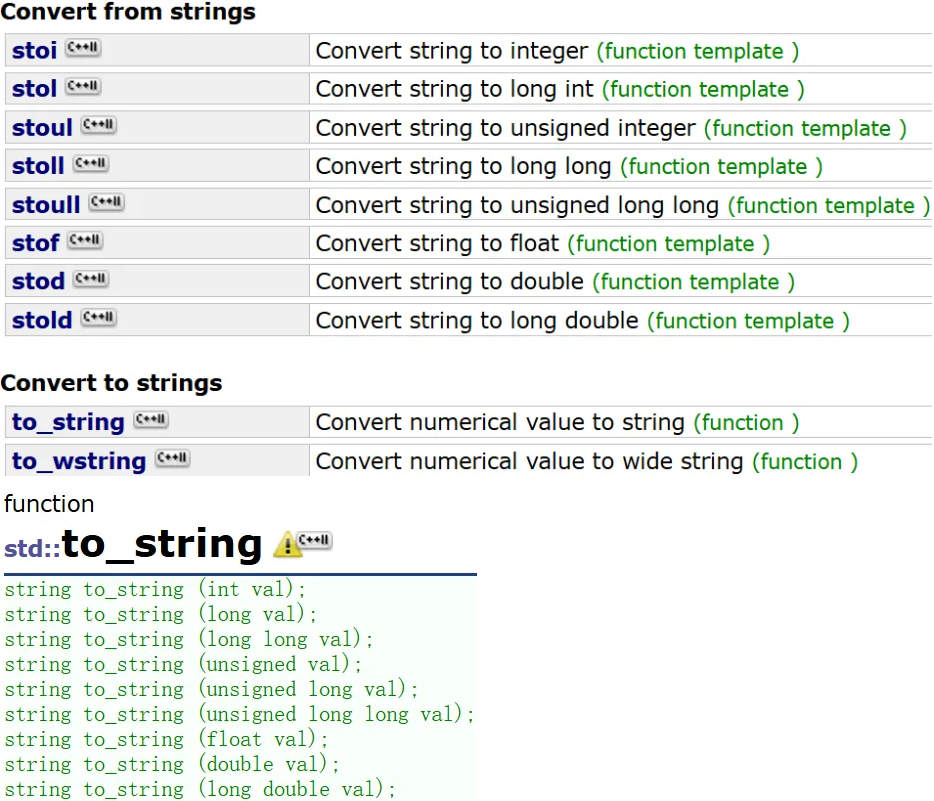
为什么要写成模板?要兼容其他字符类型字符串的管理
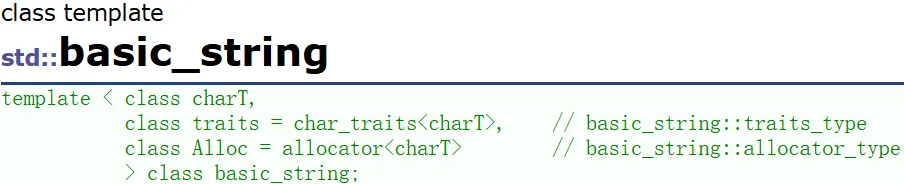
string 是被 typedef 了,只是它里面传的是 <char>1字节
string 的本源类是 basic_string
除了 string ,还有 wstring:<wchar_t>2字节、us16string:<char16_t>2字节、us32string:<char32_t>4字节

和编码有关。
编码表也叫映射表,值和符号的一一对应关系表
例如ASCII表:英文1字节(8比特位)2^8=256,足够表示所有符号了;
ASCII不能显示中文。中国自己有 gbk;国际上有 unicode 万国码
一般1个中文2字节(16比特位)2^16=65536
本篇的分享就到这里了,感谢观看,如果对你有帮助,别忘了点赞+收藏+关注。
小编会以自己学习过程中遇到的问题为素材,持续为您推送文章
