动态 SQL 标签对比表
动态 SQL 标签对比表
| 标签 | 用途 | 关键属性 | 默认行为 |
|---|---|---|---|
<if> | 条件判断 | test | 条件成立则拼接 |
<where> | 处理 WHERE | 无 | 去除 AND/OR 开头,加 WHERE |
<set> | 处理 SET | 无 | 去除末尾逗号,加 SET |
<foreach> | 遍历集合 | collection, item, separator | 无默认,必须指定 |
<choose>/<when>/<otherwise> | 多路选择 | test | 只执行第一个匹配 |
<trim> | 自定义修剪 | prefix, suffix, prefixOverrides | 灵活控制前后缀 |
<bind> | 创建变量 | name, value | 执行 OGNL 表达式 |
<sql> + <include> | 代码复用 | id, refid | 抽取公共 SQL |
✅ 最佳实践建议
优先使用
<where>和<set>:避免手动处理AND和逗号。<foreach>必须注意collection命名:单参数List是list,数组是array,多参数用@Param。复杂逻辑用
<trim>:比<where>和<set>更灵活。避免过度嵌套:动态 SQL 层级不要太深,否则难以维护。
使用
<sql>复用字段列表:避免重复写SELECT *或字段名。<bind>用于模糊查询:避免在 Java 层拼接%。
🛠️ 常见错误排查
| 问题 | 原因 | 解决方案 |
|---|---|---|
Mapped Statements collection does not contain... | 方法名与 XML id 不匹配 | 检查命名、namespace |
A different statement with this id already exists | 多个 Mapper 有相同 id | 确保 namespace + id 唯一 |
Collection 'xxx' not found | collection 写错 | 检查 list/array/@Param |
SQL 报 AND ... 错误 | <where> 未正确使用 | 用 <where> 或 <trim> |
| 批量插入报错 | <foreach> separator 缺失 | 加 separator="," |
一.select
1.select的属性
id 用来引入这条语句,例如和接口名相同,用于实现接口
parameterType 传来参数的类型
resultMap:适合使用返回值是自定义实体类的情况(用于多表)
resultType:适合使用返回值得数据类型是非自定义的,即jdk的提供的类型(用于单表)
2.select——传递单个参数
User getUserById(Integer id);
<select id="getUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.fzy.entity.User">
select * from user where id=#{id}</select>单个参数不需要@parm
2.select——传递list、数组、map
用foreach遍历,foreach的属性有
tem表示集合中每一个元素进行迭代时的别名,
index指定一个名字,用于表示在迭代过程中,每次迭代到的位置,
open表示该语句以什么开始,
separator表示在每次进行迭代之间以什么符号作为分隔符,
close表示以什么结束,
collection属性
1、如果传入的是单参数且参数类型是一个List的时候,collection属性值为list。
List<User> getUserList(List<Integer> ids);
<select id="getUserList" resultType="com.fzy.entity.User">select * from user where id in<foreach collection="list" item="uid" index="1" separator="," open="(" close=")">#{uid}</foreach>
</select>2、如果传入的是单参数且参数类型是一个Array数组的时候,collection的属性值为array 。
List<User> getUserArray(int[] array);
<select id="getUserArray" resultType="com.fzy.entity.User">select * from user where id in<foreach collection="array" item="uid" index="1" separator="," open="(" close=")">#{uid}</foreach>
</select>3、如果传入的参数是多个的时候,我们就需要把它们封装成一个Map了,当然单参数也可以封装成map,实际上如果你在传入参数的时候,在MyBatis里面也是会把它封装成一个Map的,map的key就是参数名,所以这个时候collection属性值就是传入的List或Array对象在自己封装的map里面的key。
List<User> getUserMap(Map<String,String> map);
<select id="getUserMap" resultType="com.fzy.entity.User">select * from user where username=#{username} and password= #{password}
</select>3.select——模糊查询
SELECT * FROM table WHERE name LIKE CONCAT('%', #{text},'%');
SELECT * FROM tableName WHERE name LIKE '%${_parameter}%';
#{}和${}
在之前的默认情况下,使用#{}格式的语法会通知MyBatis创建预处理语句属性并安全地设置值(比如通过?占位符)。这样做更安全,更迅速,通常也是首选做法,不过有时只是想直接在 SQL语句中插入一个不改变的字符串。
比如,像 ORDER BY,可以这样来使用: ORDER BY ${columnName}
#{}通过占位符的方式在sql执行前进行预编译,给占位符赋值,安全性更高;
${}通过拼接的方式给sql赋值,可能会一起sql注入的问题,安全性降低;
sql注入
Select * from user where name=”zhansgan “ or ” and pwd=”123456”
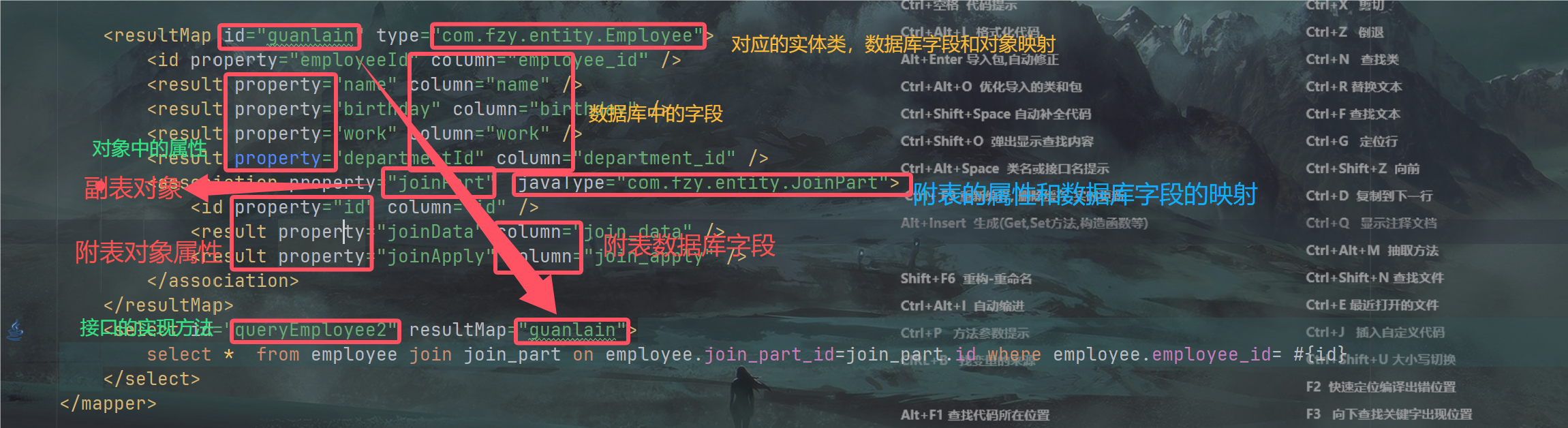
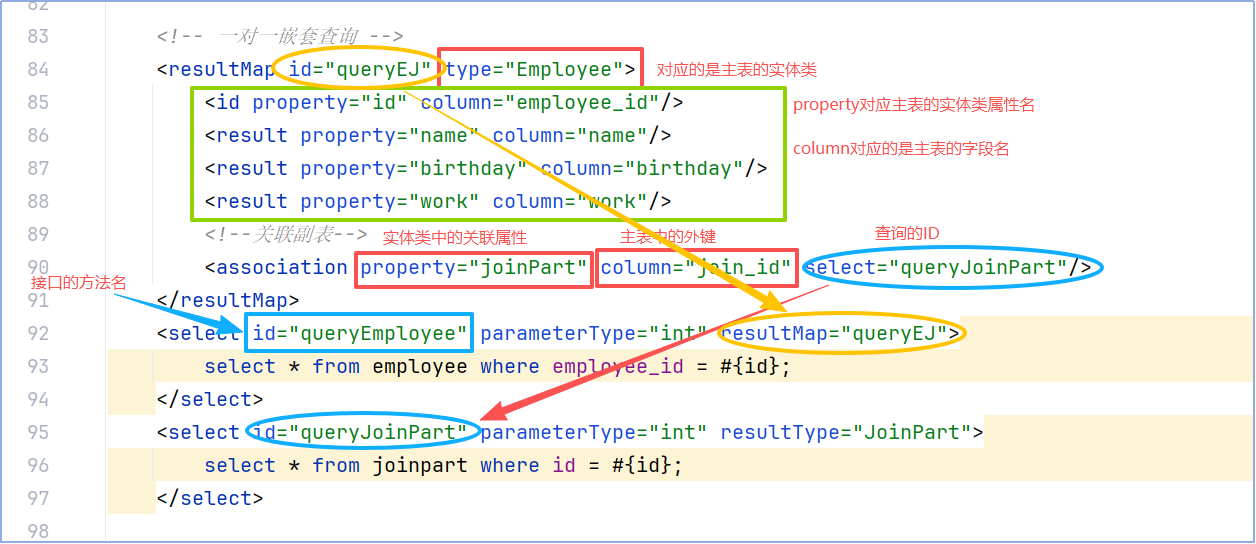
4.select——resultMap
esultMap的设计目标就是为复杂语句通过配置文件描述数据库表结果和Java实体类的关系(OR映射)