【CVPR2020】GhostNet:从廉价操作中获得更多特征
文章目录
- 一、论文信息
- 二、论文概要
- 三、实验动机
- 四、创新之处
- 五、实验分析
- 六、核心代码
- 七、实验总结
一、论文信息
- 论文题目:GhostNet: More Features from Cheap Operations
- 中文题目:GhostNet:从廉价操作中获得更多特征
- 论文链接:点击跳转
- 代码链接:点击跳转
- 作者:Kai Han (华为技术有限公司)、Yunhe Wang (华为技术有限公司)、Qi Tian (华为技术有限公司)、Jianyuan Guo (北京大学)、Chunjing Xu (华为技术有限公司)、Chang Xu (悉尼大学)
- 单位:华为技术有限公司、北京大学、悉尼大学
- 核心速览:该论文提出了 Ghost模块,通过廉价操作生成更多特征图,从而有效降低计算成本,同时保持较高的性能。基于Ghost模块,提出了 GhostNet,用于图像分类和目标检测任务,实验结果表明GhostNet在准确性和计算效率上超越了其他轻量级模型,如MobileNetV3。
二、论文概要
该论文提出了 Ghost模块,通过廉价操作生成更多特征图,从而有效降低计算成本,同时保持较高的性能。基于Ghost模块,提出了 GhostNet,用于图像分类和目标检测任务,实验结果表明GhostNet在准确性和计算效率上超越了其他轻量级模型,如MobileNetV3。
三、实验动机
-
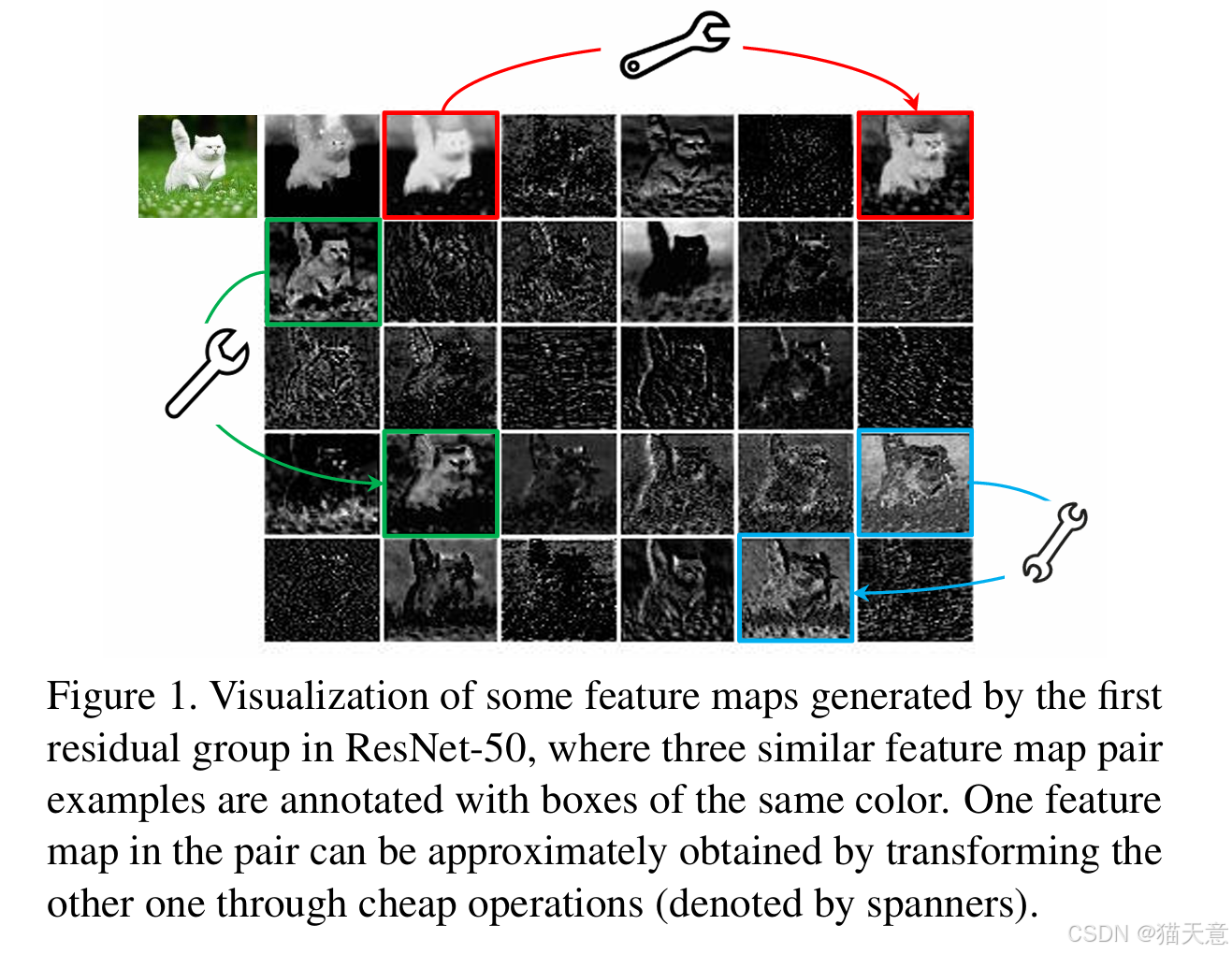
目标:随着深度神经网络的普及,如何在计算和存储资源有限的嵌入式设备上部署高效的神经网络成为一个挑战。为了减小计算资源的消耗,同时保持较高的识别性能,本研究提出了 Ghost模块,利用冗余信息生成更多特征图,从而提高计算效率。
-
动机:充分利用神经网络中的冗余特征图,通过廉价操作生成特征图,减少卷积操作的计算量,提升模型在移动设备上的推理速度和准确性。
四、创新之处
-
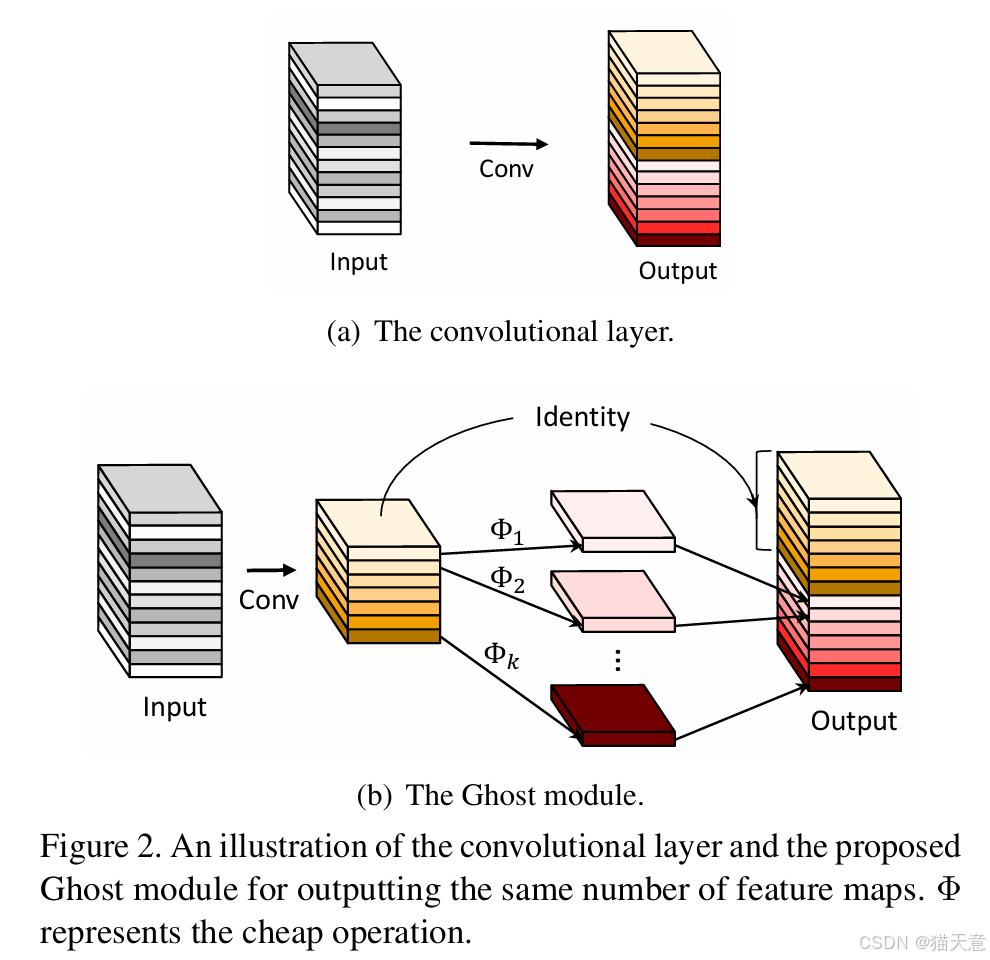
Ghost模块:提出了一种新的模块来生成更多特征图,避免了传统方法中冗余特征图的计算。通过使用少量的基础特征图和简单的线性变换,可以有效提高计算效率。
-
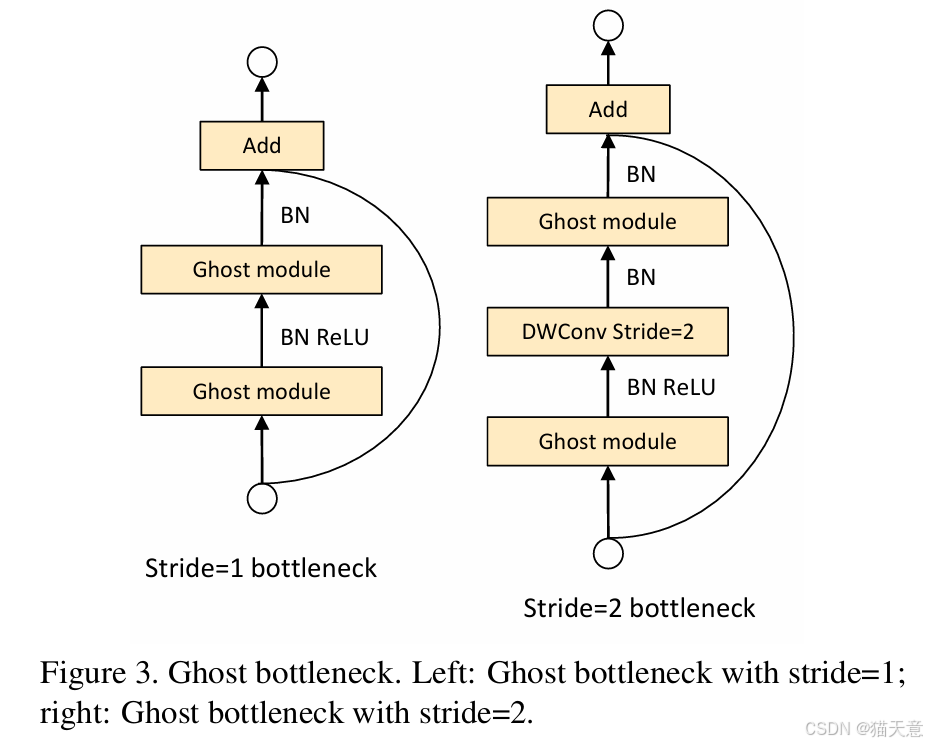
Ghost瓶颈(Ghost Bottleneck):结合Ghost模块设计的瓶颈结构,类似于残差模块,进一步提高了网络的效率。
-
GhostNet架构:通过堆叠Ghost瓶颈模块,设计了一个高效的轻量级网络,适用于各种视觉任务(如图像分类、目标检测等)。
五、实验分析
-
在 ImageNet、CIFAR-10 和 MS COCO 数据集上进行实验,实验结果表明,GhostNet在计算效率和准确性方面均超越了当前一些流行的轻量化网络(如MobileNetV3)。
-
ImageNet 分类任务中,GhostNet在计算复杂度接近的情况下,比MobileNetV3的Top-1准确率提高了0.5%。
-
目标检测任务:在MS COCO数据集上,GhostNet在较低的计算成本下,与MobileNetV2和MobileNetV3相当,甚至表现更好。
六、核心代码
# 2020.06.09-Changed for building GhostNet
# Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. <foss@huawei.com>
"""
Creates a GhostNet Model as defined in:
GhostNet: More Features from Cheap Operations By Kai Han, Yunhe Wang, Qi Tian, Jianyuan Guo, Chunjing Xu, Chang Xu.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.11907
Modified from https://github.com/d-li14/mobilenetv3.pytorch and https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import math__all__ = ['ghost_net']def _make_divisible(v, divisor, min_value=None):"""This function is taken from the original tf repo.It ensures that all layers have a channel number that is divisible by 8It can be seen here:https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/slim/nets/mobilenet/mobilenet.py"""if min_value is None:min_value = divisornew_v = max(min_value, int(v + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)# Make sure that round down does not go down by more than 10%.if new_v < 0.9 * v:new_v += divisorreturn new_vdef hard_sigmoid(x, inplace: bool = False):if inplace:return x.add_(3.).clamp_(0., 6.).div_(6.)else:return F.relu6(x + 3.) / 6.class SqueezeExcite(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_chs, se_ratio=0.25, reduced_base_chs=None,act_layer=nn.ReLU, gate_fn=hard_sigmoid, divisor=4, **_):super(SqueezeExcite, self).__init__()self.gate_fn = gate_fnreduced_chs = _make_divisible((reduced_base_chs or in_chs) * se_ratio, divisor)self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)self.conv_reduce = nn.Conv2d(in_chs, reduced_chs, 1, bias=True)self.act1 = act_layer(inplace=True)self.conv_expand = nn.Conv2d(reduced_chs, in_chs, 1, bias=True)def forward(self, x):x_se = self.avg_pool(x)x_se = self.conv_reduce(x_se)x_se = self.act1(x_se)x_se = self.conv_expand(x_se)x = x * self.gate_fn(x_se)return x class ConvBnAct(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_chs, out_chs, kernel_size,stride=1, act_layer=nn.ReLU):super(ConvBnAct, self).__init__()self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_chs, out_chs, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False)self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_chs)self.act1 = act_layer(inplace=True)def forward(self, x):x = self.conv(x)x = self.bn1(x)x = self.act1(x)return xclass GhostModule(nn.Module):def __init__(self, inp, oup, kernel_size=1, ratio=2, dw_size=3, stride=1, relu=True):super(GhostModule, self).__init__()self.oup = oupinit_channels = math.ceil(oup / ratio)new_channels = init_channels*(ratio-1)self.primary_conv = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(inp, init_channels, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(init_channels),nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),)self.cheap_operation = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(init_channels, new_channels, dw_size, 1, dw_size//2, groups=init_channels, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(new_channels),nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),)def forward(self, x):x1 = self.primary_conv(x)x2 = self.cheap_operation(x1)out = torch.cat([x1,x2], dim=1)return out[:,:self.oup,:,:]class GhostBottleneck(nn.Module):""" Ghost bottleneck w/ optional SE"""def __init__(self, in_chs, mid_chs, out_chs, dw_kernel_size=3,stride=1, act_layer=nn.ReLU, se_ratio=0.):super(GhostBottleneck, self).__init__()has_se = se_ratio is not None and se_ratio > 0.self.stride = stride# Point-wise expansionself.ghost1 = GhostModule(in_chs, mid_chs, relu=True)# Depth-wise convolutionif self.stride > 1:self.conv_dw = nn.Conv2d(mid_chs, mid_chs, dw_kernel_size, stride=stride,padding=(dw_kernel_size-1)//2,groups=mid_chs, bias=False)self.bn_dw = nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_chs)# Squeeze-and-excitationif has_se:self.se = SqueezeExcite(mid_chs, se_ratio=se_ratio)else:self.se = None# Point-wise linear projectionself.ghost2 = GhostModule(mid_chs, out_chs, relu=False)# shortcutif (in_chs == out_chs and self.stride == 1):self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()else:self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_chs, in_chs, dw_kernel_size, stride=stride,padding=(dw_kernel_size-1)//2, groups=in_chs, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(in_chs),nn.Conv2d(in_chs, out_chs, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_chs),)def forward(self, x):residual = x# 1st ghost bottleneckx = self.ghost1(x)# Depth-wise convolutionif self.stride > 1:x = self.conv_dw(x)x = self.bn_dw(x)# Squeeze-and-excitationif self.se is not None:x = self.se(x)# 2nd ghost bottleneckx = self.ghost2(x)x += self.shortcut(residual)return xclass GhostNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, cfgs, num_classes=1000, width=1.0, dropout=0.2):super(GhostNet, self).__init__()# setting of inverted residual blocksself.cfgs = cfgsself.dropout = dropout# building first layeroutput_channel = _make_divisible(16 * width, 4)self.conv_stem = nn.Conv2d(3, output_channel, 3, 2, 1, bias=False)self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(output_channel)self.act1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)input_channel = output_channel# building inverted residual blocksstages = []block = GhostBottleneckfor cfg in self.cfgs:layers = []for k, exp_size, c, se_ratio, s in cfg:output_channel = _make_divisible(c * width, 4)hidden_channel = _make_divisible(exp_size * width, 4)layers.append(block(input_channel, hidden_channel, output_channel, k, s,se_ratio=se_ratio))input_channel = output_channelstages.append(nn.Sequential(*layers))output_channel = _make_divisible(exp_size * width, 4)stages.append(nn.Sequential(ConvBnAct(input_channel, output_channel, 1)))input_channel = output_channelself.blocks = nn.Sequential(*stages) # building last several layersoutput_channel = 1280self.global_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))self.conv_head = nn.Conv2d(input_channel, output_channel, 1, 1, 0, bias=True)self.act2 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)self.classifier = nn.Linear(output_channel, num_classes)def forward(self, x):x = self.conv_stem(x)x = self.bn1(x)x = self.act1(x)x = self.blocks(x)x = self.global_pool(x)x = self.conv_head(x)x = self.act2(x)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)if self.dropout > 0.:x = F.dropout(x, p=self.dropout, training=self.training)x = self.classifier(x)return xdef ghostnet(**kwargs):"""Constructs a GhostNet model"""cfgs = [# k, t, c, SE, s # stage1[[3, 16, 16, 0, 1]],# stage2[[3, 48, 24, 0, 2]],[[3, 72, 24, 0, 1]],# stage3[[5, 72, 40, 0.25, 2]],[[5, 120, 40, 0.25, 1]],# stage4[[3, 240, 80, 0, 2]],[[3, 200, 80, 0, 1],[3, 184, 80, 0, 1],[3, 184, 80, 0, 1],[3, 480, 112, 0.25, 1],[3, 672, 112, 0.25, 1]],# stage5[[5, 672, 160, 0.25, 2]],[[5, 960, 160, 0, 1],[5, 960, 160, 0.25, 1],[5, 960, 160, 0, 1],[5, 960, 160, 0.25, 1]]]return GhostNet(cfgs, **kwargs)if __name__=='__main__':model = ghostnet()model.eval()print(model)input = torch.randn(32,3,320,256)y = model(input)print(y.size())
七、实验总结
GhostNet通过使用Ghost模块和Ghost瓶颈显著提高了计算效率,特别适合在移动设备上进行快速推理。实验结果表明,GhostNet在保证较低计算复杂度的同时,能够提供与传统卷积网络相媲美甚至更好的性能,适用于移动端和嵌入式设备。
