webrtc弱网-LossBasedBweV2类源码分析与算法原理
1. 核心功能
LossBasedBweV2是WebRTC Google Congestion Control (GoogCC) 算法套件中的第二代基于丢包的带宽估计器。它的核心功能是:
带宽估计: 根据网络数据包的丢失情况,估算当前网络路径可用的带宽上限。其核心假设是:当发送速率超过网络容量时,将出现拥塞,表现为数据包丢失。通过分析丢包模式,它可以反向推断出这个容量瓶颈。
状态输出: 不仅输出一个带宽估计值(
DataRate),还输出一个状态(LossBasedState)。这个状态用于指导上层控制器(如GoogCCNetworkController)的行为,例如:kIncreasing/kIncreaseUsingPadding: 建议可以尝试增加发送速率,后者暗示可以使用填充数据来探测。kDecreasing: 估计值正在因丢包而下降,应减少发送速率。kDelayBasedEstimate: 当前未处于丢包受限状态,应优先使用基于延迟的估计结果。
多源信息融合: 它并非孤立工作,而是融合了多种信息源:
丢包信息: 主要输入,来自
RTCP Receiver Reports或传输反馈。延迟基于估计值: 来自
DelayBasedBwe的另一个估计值,用作上限或候选值。确认速率: 当前网络的吞吐量测量值,用作参考和下限。
配置参数: 通过字段试验(Field Trials)提供大量可调参数,用于控制算法行为。
2. 核心算法原理
LossBasedBweV2的核心算法基于最大似然估计(Maximum Likelihood Estimation, MLE),其基本原理可以概括为:
建立丢包模型: 算法假设一个信道模型,其中包丢失概率由两部分组成:
固有丢失(
inherent_loss): 代表与拥塞无关的随机丢包(如无线链路错误)。拥塞丢失: 当发送速率(
sending_rate)超过信道的“丢包受限带宽”(loss_limited_bandwidth)时,按一定比例((sending_rate - loss_limited_bandwidth) / sending_rate)产生额外丢包。
总的丢包概率函数为:loss_probability = inherent_loss + (1 - inherent_loss) * max(0, (sending_rate - loss_limited_bandwidth) / sending_rate)
定义似然函数: 给定一组观测到的包接收/丢失情况,计算在这组信道参数(
inherent_loss,loss_limited_bandwidth)下,观察到这组结果的似然度(Likelihood)。似然度是模型参数的函数。最大化似然函数: 算法的目标是找到一组参数(
inherent_loss,loss_limited_bandwidth),使得观察到的数据的似然度最大。这组参数就是最可能产生当前观测数据的信道状态,其中的loss_limited_bandwidth就是最终的带宽估计值。牛顿法优化: 为了高效地找到使似然函数最大化的参数,算法对
inherent_loss参数使用了牛顿法(Newton's Method)进行迭代优化。GetDerivatives()函数计算似然函数的一阶和二阶导数,NewtonsMethodUpdate()根据导数更新inherent_loss的值。高带宽偏好: 为了防止算法在存在随机丢包(高
inherent_loss)时过于保守,似然函数中引入了一个高带宽偏置项(high_bandwidth_bias)。该项会随着候选带宽的增加而增加,从而让算法更倾向于选择高带宽的估计,即使它需要假设一个更高的固有丢包率来解释观测到的丢包。GetHighBandwidthBias()和AdjustBiasFactor()负责计算这个偏置。
3. 关键数据结构
LossBasedBweV2::Config:作用: 包含所有可配置的实验参数,通过字段试验字符串(如
WebRTC-Bwe-LossBasedBweV2)解析而来。这些参数控制着算法的几乎所有方面,包括观察窗口大小、候选因子、牛顿法迭代次数、各种阈值和开关等。其有效性由IsConfigValid()函数验证。重要性: 使得算法行为高度可调,便于A/B测试和算法迭代。
LossBasedBweV2::ChannelParameters:作用: 表示信道模型的一个候选参数集。
loss_limited_bandwidth: 待评估的带宽估计值。inherent_loss: 对应的固有丢包率估计。
重要性: MLE优化过程的核心操作对象。
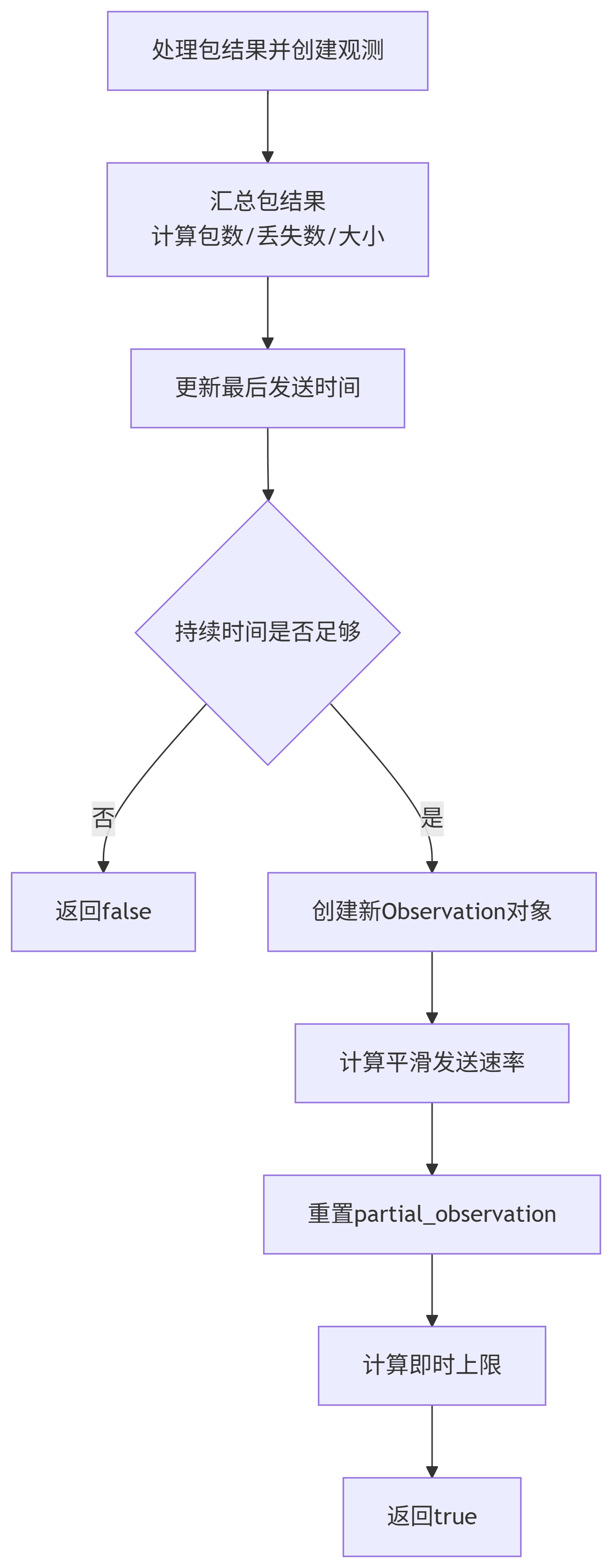
LossBasedBweV2::Observation:作用: 存储一个时间窗口内的丢包观测结果。由多次
UpdateBandwidthEstimate调用中积累的PacketResult汇总而成,直到持续时间满足observation_duration_lower_bound。num_packets,num_lost_packets,num_received_packetssize,lost_size(字节数,use_byte_loss_rate为true时使用)sending_rate: 该观测窗口内的平均发送速率(经过平滑处理)。id: 观测的唯一ID,用于时间加权。
重要性: 是似然计算的基础数据单元。
LossBasedBweV2::Result:作用: 算法的输出结果。
bandwidth_estimate: 最终计算出的基于丢包的带宽估计值。state: 估计器的状态(Increasing/Decreasing/DelayBasedEstimate),用于指导拥塞控制行为。
HoldInfo和PaddingInfo:作用: 用于实现状态保持(Hold)和填充(Padding)逻辑。
HoldInfo: 在估计减少后,暂时限制估计值的增长幅度和持续时间,避免过快回升再次引发丢包。PaddingInfo: 当状态为kIncreaseUsingPadding时,记录用于判断是否持续进行填充探测的速率和时间戳。
重要性: 这些是增强算法稳定性和主动探测能力的机制。
4. 核心方法详解
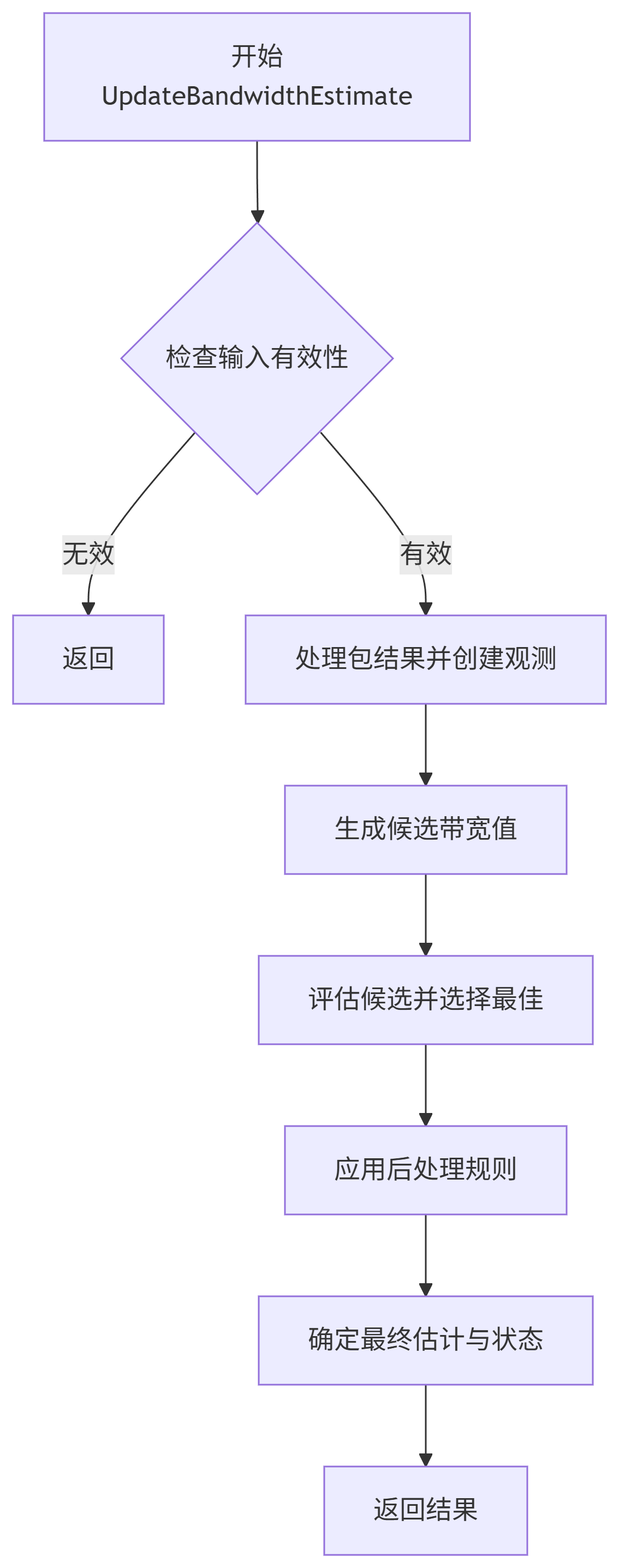
UpdateBandwidthEstimate:入口方法。接收新的包反馈信息(
packet_results)、当前的延迟估计值(delay_based_estimate)和是否在应用限制区域(in_alr)的标志。流程:
更新观测值: 调用
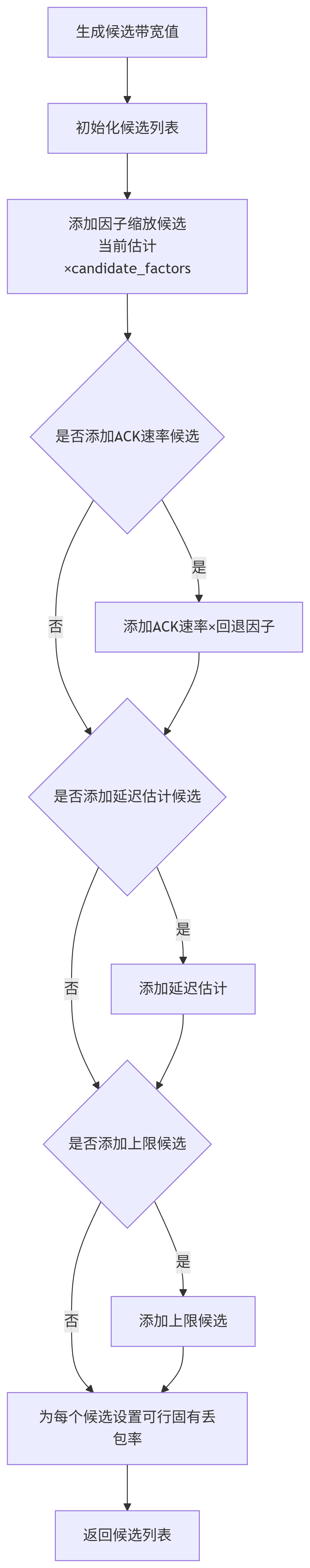
PushBackObservation将新的包结果汇总到当前部分观测中,如果持续时间足够,则创建一个新的Observation并加入环形缓冲区。生成候选: 调用
GetCandidates生成一组待评估的ChannelParameters候选。候选来自:当前估计乘以配置的
candidate_factors(如1.02, 1.0, 0.95)。确认速率(
acknowledged_bitrate_)。延迟估计值(
delay_based_estimate_)。即时上限(
GetInstantUpperBound(),在ALR状态下)。
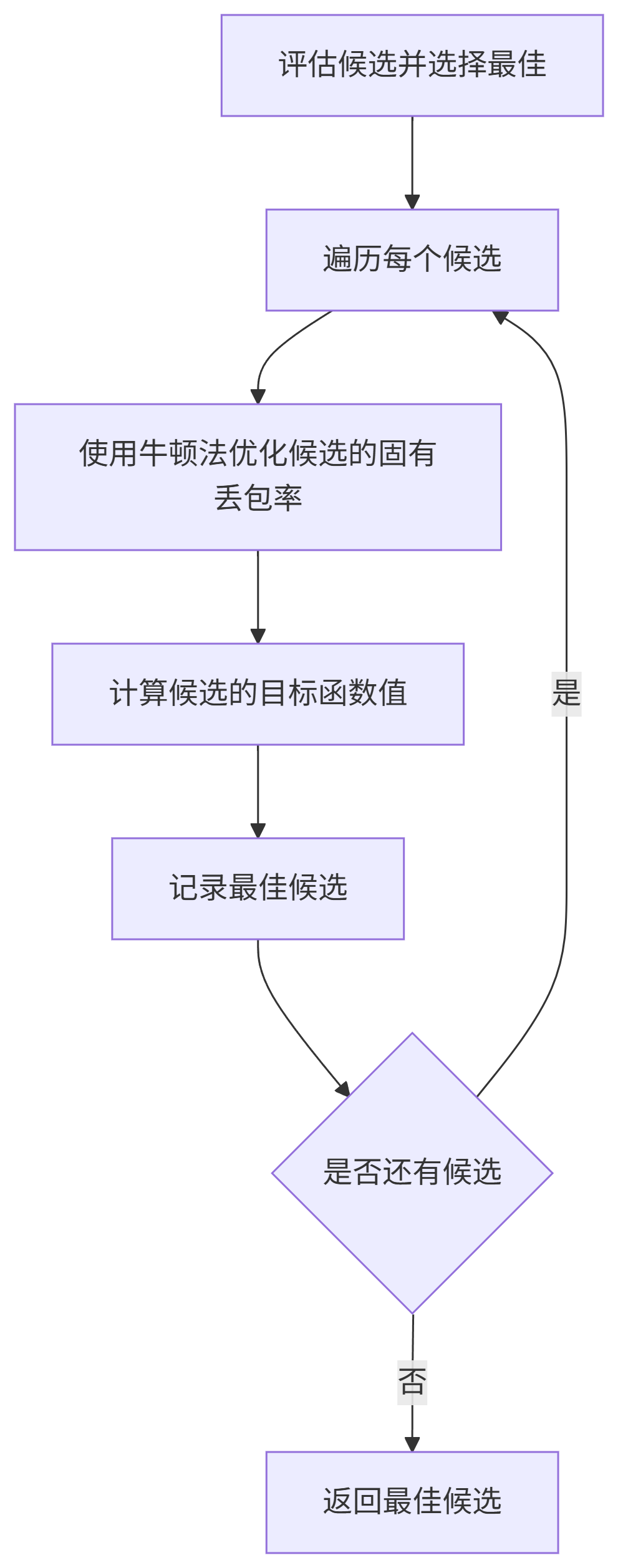
评估候选: 对每个候选,使用牛顿法优化其
inherent_loss(NewtonsMethodUpdate),然后计算其似然函数值加上高带宽偏置后的目标函数值(GetObjective)。选择最佳候选: 选择目标函数值最大的候选作为
best_candidate。应用约束和规则:
平均丢失检查: 如果平均上报丢包率大于最佳候选的固有丢包率,可能禁止增加(
not_increase_if_inherent_loss_less_than_average_loss)。延迟增加窗口: 在刚减少带宽后的一段时间(
delayed_increase_window)内,限制增长上限(bandwidth_limit_in_current_window)。确认速率约束: 在丢包受限状态下,如果估计要增加,则其上限受
acknowledged_bitrate_乘以一个因子约束。
最终边界处理: 将最佳候选的带宽与即时下限(
GetInstantLowerBound,主要来自确认速率)、即时上限(GetInstantUpperBound,基于平均丢包率计算)和延迟估计值进行比对,得到最终的bounded_bandwidth_estimate。状态机更新: 根据最终估计值的变化、与延迟估计的关系以及Hold/Padding的状态,决定新的
LossBasedState。更新内部状态: 设置
current_best_estimate_、loss_based_result_、last_hold_info_、last_padding_info_等。
GetCandidates:根据配置和当前状态,生成一系列带宽候选值,然后为每个带宽值创建一个
ChannelParameters结构体,并为其设置一个可行的初始inherent_loss(GetFeasibleInherentLoss)。
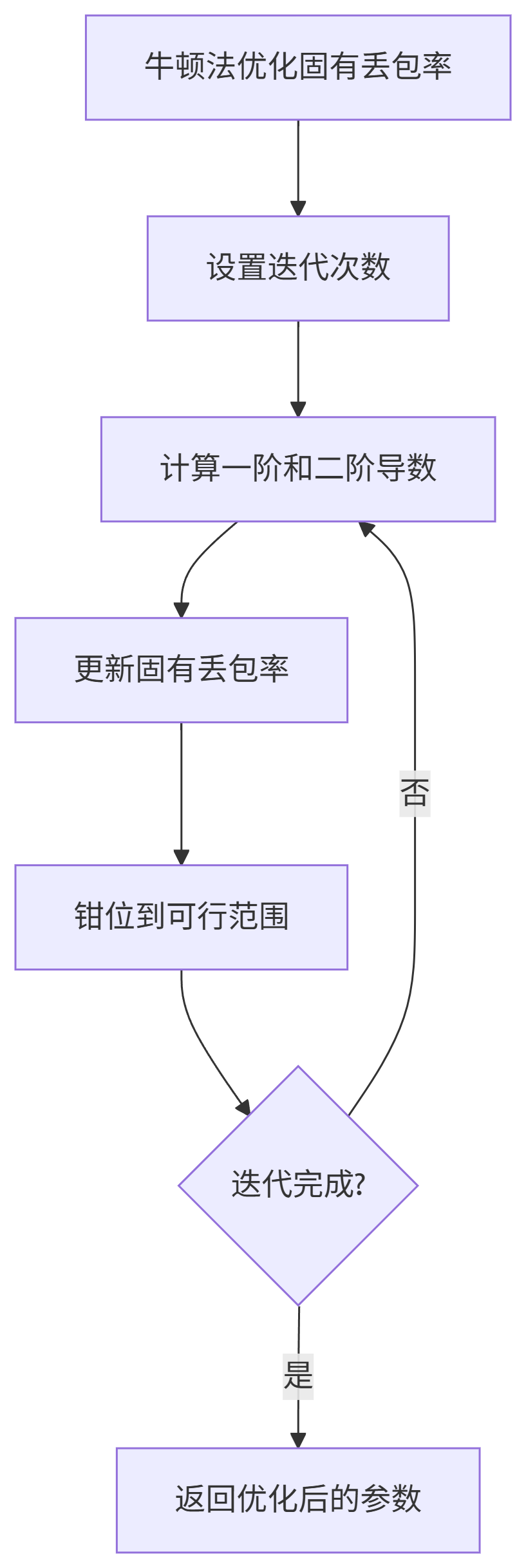
GetDerivatives和NewtonsMethodUpdate:MLE优化的核心。
GetDerivatives计算当前参数下似然函数对inherent_loss的一阶和二阶导数。NewtonsMethodUpdate根据牛顿迭代公式inherent_loss -= step_size * (first_derivative / second_derivative)更新参数,并将结果钳位到可行范围内[inherent_loss_lower_bound, GetInherentLossUpperBound]。
GetObjective:计算候选参数的目标函数值,即对数似然值 + 高带宽偏置。算法目标是最大化该函数。
GetInstantUpperBound和CalculateInstantUpperBound:基于近期平均丢包率计算一个带宽上限。其模型为:
instant_upper_bound = bandwidth_balance / (average_loss - loss_offset)。如果平均丢包率很低,这个上限会很高(max_bitrate_),丢包率越高,这个上限越低。
GetInstantLowerBound和CalculateInstantLowerBound:计算带宽下限,通常取
max(min_bitrate_, acknowledged_bitrate_ * factor)。确保估计值不会低于当前网络的实际吞吐量太多。
5. 设计亮点
基于模型的MLE方法: 相比于简单的丢包阈值法(如
SendSideBandwidthEstimation中使用的),V2版本采用了更严谨的概率模型和优化方法,理论上能更准确地反映网络状态。灵活可配置性: 通过大量的字段试验参数暴露了算法的核心旋钮,使得算法可以快速迭代和调优,无需修改代码。
多候选评估: 不是只做一次优化,而是生成多个候选点并评估,避免陷入局部最优,并能融合其他估计源(如延迟估计、确认速率)。
状态机与控制逻辑: 输出的
State为上层控制器提供了丰富的语义信息,使得拥塞控制策略可以更精细,例如区分“可用填充数据探测”的增加和普通增加。时间加权: 对观测窗口内的历史数据使用指数衰减加权(
temporal_weights_),更重视近期的网络状况。Hold机制: 在带宽下降后引入一个“冷静期”,防止估计过快反弹,提高稳定性。
区分包丢失率和字节丢失率: 通过
use_byte_loss_rate开关,可以选择是基于包计数还是基于字节计数来计算丢包率,以适应不同的场景。
6. 典型工作流程
初始化: 创建
LossBasedBweV2对象,通过字段试验解析并验证配置(CreateConfig,IsConfigValid)。初始化观察窗口、权重向量等。初始状态为未就绪。设置初始值: 通常由上层控制器调用
SetBandwidthEstimate或通过UpdateBandwidthEstimate传入的第一个delay_based_estimate来设置初始带宽估计。持续更新:
上层控制器定期(如每次收到传输反馈时)调用
UpdateBandwidthEstimate。该方法汇总包反馈,形成观测点。
生成多个候选带宽值。
对每个候选,优化其固有丢包率,并计算目标函数。
选择最佳候选。
应用各种约束和规则(Hold、ACK速率约束等)得到最终估计。
根据最终估计值的变化和与其他估计值的关系,更新状态机。
返回
Result(带宽+状态)。
控制决策: 上层控制器(如
GoogCCNetworkController)根据返回的Result中的state和bandwidth_estimate,结合其他模块(如延迟基于BWE、探测器)的输出,最终决定目标码率、是否发起探测等控制命令。
7. LossBasedBweV2 核心算法流程图
7.1.总体流程图
7.2.处理包结果并创建观测
7.3.生成候选带宽值
7.4.评估候选并选择最佳
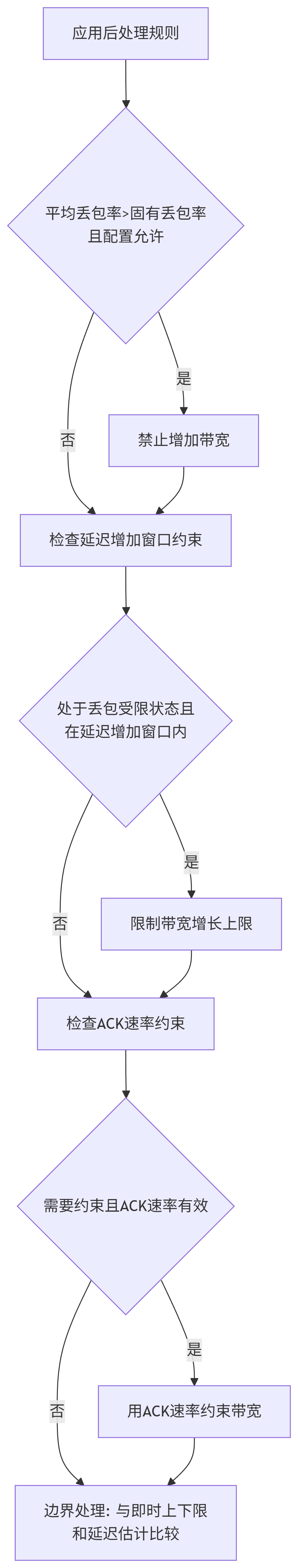
7.5.应用后处理规则
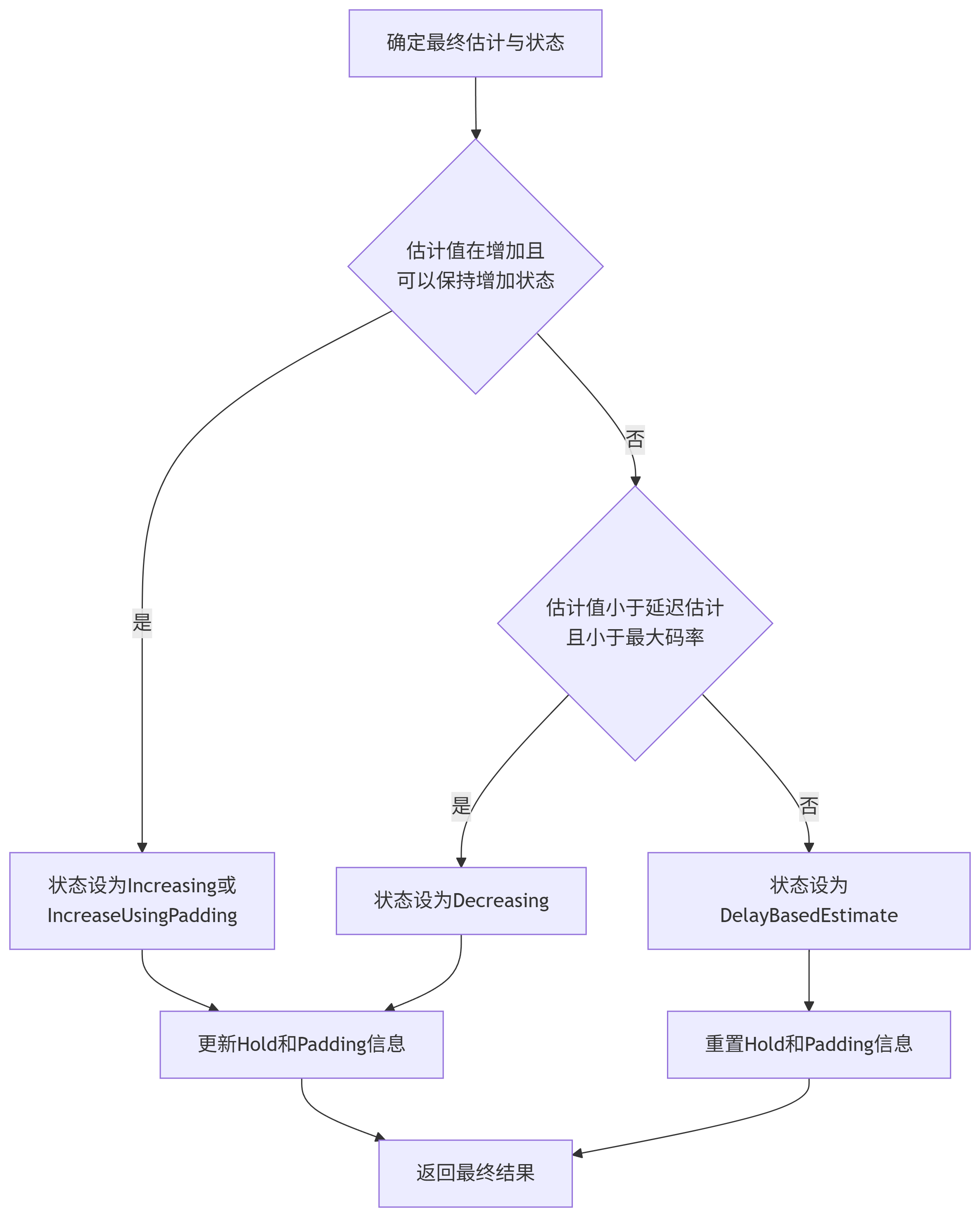
7.6.确定最终估计与状态
7.7.牛顿法优化过程
8.核心算法精解
void LossBasedBweV2::UpdateBandwidthEstimate(rtc::ArrayView<const PacketResult> packet_results,DataRate delay_based_estimate,bool in_alr) {// 存储延迟基于的带宽估计值,用于后续比较和约束delay_based_estimate_ = delay_based_estimate;// 检查估计器是否已启用if (!IsEnabled()) {RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "The estimator must be enabled before it can be used.";return;}// 检查是否有包结果数据if (packet_results.empty()) {RTC_LOG(LS_VERBOSE) << "The estimate cannot be updated without any loss statistics.";return;}// 处理包结果并创建观测数据if (!PushBackObservation(packet_results)) {return;}// 如果当前最佳估计尚未初始化,使用延迟基于的估计进行初始化if (!IsValid(current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth)) {if (!IsValid(delay_based_estimate)) {RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "The delay based estimate must be finite: " << ToString(delay_based_estimate);return;}current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth = delay_based_estimate;loss_based_result_ = {.bandwidth_estimate = delay_based_estimate,.state = LossBasedState::kDelayBasedEstimate};}// 初始化最佳候选为当前最佳估计ChannelParameters best_candidate = current_best_estimate_;double objective_max = std::numeric_limits<double>::lowest();// 生成并评估所有候选带宽值for (ChannelParameters candidate : GetCandidates(in_alr)) {// 使用牛顿法优化候选的固有丢包率参数NewtonsMethodUpdate(candidate);// 计算候选的目标函数值const double candidate_objective = GetObjective(candidate);// 选择目标函数值最大的候选if (candidate_objective > objective_max) {objective_max = candidate_objective;best_candidate = candidate;}}// 如果估计值减少了,记录减少时间if (best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth <current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth) {last_time_estimate_reduced_ = last_send_time_most_recent_observation_;}// 如果平均丢包率大于当前固有丢包率,且配置允许,禁止增加估计值if (GetAverageReportedLossRatio() > best_candidate.inherent_loss &&config_->not_increase_if_inherent_loss_less_than_average_loss &¤t_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth <best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth) {best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth =current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth;}// 如果处于丢包受限状态,应用额外的约束if (IsInLossLimitedState()) {// 在延迟增加窗口内限制估计值的增长if (recovering_after_loss_timestamp_.IsFinite() &&recovering_after_loss_timestamp_ + config_->delayed_increase_window >last_send_time_most_recent_observation_ &&best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth >bandwidth_limit_in_current_window_) {best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth =bandwidth_limit_in_current_window_;}// 检查估计是否在丢包受限状态下增加bool increasing_when_loss_limited = IsEstimateIncreasingWhenLossLimited(/*old_estimate=*/current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth,/*new_estimate=*/best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth);// 如果估计在增加且确认速率有效,使用确认速率约束估计值if (increasing_when_loss_limited && IsValid(acknowledged_bitrate_)) {double rampup_factor = config_->bandwidth_rampup_upper_bound_factor;// 如果在保持状态下,使用不同的增长因子if (IsValid(last_hold_info_.rate) &&acknowledged_bitrate_ <config_->bandwidth_rampup_hold_threshold * last_hold_info_.rate) {rampup_factor = config_->bandwidth_rampup_upper_bound_factor_in_hold;}// 应用确认速率约束best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth =std::max(current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth,std::min(best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth,rampup_factor * (*acknowledged_bitrate_)));// 如果状态为减少但估计值未变,稍微增加以确保状态切换if (loss_based_result_.state == LossBasedState::kDecreasing &&best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth ==current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth) {best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth =current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth +DataRate::BitsPerSec(1);}}}// 应用最终边界约束DataRate bounded_bandwidth_estimate = DataRate::PlusInfinity();if (IsValid(delay_based_estimate_)) {bounded_bandwidth_estimate =std::max(GetInstantLowerBound(),std::min({best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth,GetInstantUpperBound(), delay_based_estimate_}));} else {bounded_bandwidth_estimate = std::max(GetInstantLowerBound(), std::min(best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth,GetInstantUpperBound()));}// 如果配置要求约束最佳候选,并且约束后的估计小于最佳候选,重置估计if (config_->bound_best_candidate &&bounded_bandwidth_estimate < best_candidate.loss_limited_bandwidth) {RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Resetting loss based BWE to " << bounded_bandwidth_estimate.kbps()<< "due to loss. Avg loss rate: " << GetAverageReportedLossRatio();current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth = bounded_bandwidth_estimate;current_best_estimate_.inherent_loss = 0;} else {current_best_estimate_ = best_candidate;// 确保估计不低于确认速率的下限if (config_->lower_bound_by_acked_rate_factor > 0.0) {current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth =std::max(current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth,GetInstantLowerBound());}}// 处理保持状态下的估计约束if (loss_based_result_.state == LossBasedState::kDecreasing &&last_hold_info_.timestamp > last_send_time_most_recent_observation_ &&bounded_bandwidth_estimate < delay_based_estimate_) {// 确保确认速率是保持速率的下限if (config_->lower_bound_by_acked_rate_factor > 0.0) {last_hold_info_.rate =std::max(GetInstantLowerBound(), last_hold_info_.rate);}// 带宽估计不允许超过保持速率loss_based_result_.bandwidth_estimate =std::min(last_hold_info_.rate, bounded_bandwidth_estimate);return;}// 确定最终状态if (IsEstimateIncreasingWhenLossLimited(/*old_estimate=*/loss_based_result_.bandwidth_estimate,/*new_estimate=*/bounded_bandwidth_estimate) &&CanKeepIncreasingState(bounded_bandwidth_estimate) &&bounded_bandwidth_estimate < delay_based_estimate_ &&bounded_bandwidth_estimate < max_bitrate_) {// 设置增加状态,可能使用填充数据进行探测if (config_->padding_duration > TimeDelta::Zero() &&bounded_bandwidth_estimate > last_padding_info_.padding_rate) {last_padding_info_.padding_rate = bounded_bandwidth_estimate;last_padding_info_.padding_timestamp =last_send_time_most_recent_observation_;}loss_based_result_.state = config_->padding_duration > TimeDelta::Zero()? LossBasedState::kIncreaseUsingPadding: LossBasedState::kIncreasing;} else if (bounded_bandwidth_estimate < delay_based_estimate_ &&bounded_bandwidth_estimate < max_bitrate_) {// 设置减少状态if (loss_based_result_.state != LossBasedState::kDecreasing &&config_->hold_duration_factor > 0) {RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << this << " " << "Switch to HOLD. Bounded BWE: "<< bounded_bandwidth_estimate.kbps()<< ", duration: " << last_hold_info_.duration.ms();last_hold_info_ = {.timestamp = last_send_time_most_recent_observation_ +last_hold_info_.duration,.duration =std::min(kMaxHoldDuration, last_hold_info_.duration *config_->hold_duration_factor),.rate = bounded_bandwidth_estimate};}last_padding_info_ = PaddingInfo();loss_based_result_.state = LossBasedState::kDecreasing;} else {// 重置保持和填充信息,使用延迟基于的估计last_hold_info_ = {.timestamp = Timestamp::MinusInfinity(),.duration = kInitHoldDuration,.rate = DataRate::PlusInfinity()};last_padding_info_ = PaddingInfo();loss_based_result_.state = LossBasedState::kDelayBasedEstimate;}// 设置最终带宽估计值loss_based_result_.bandwidth_estimate = bounded_bandwidth_estimate;// 更新延迟增加窗口和带宽限制if (IsInLossLimitedState() &&(recovering_after_loss_timestamp_.IsInfinite() ||recovering_after_loss_timestamp_ + config_->delayed_increase_window <last_send_time_most_recent_observation_)) {bandwidth_limit_in_current_window_ =std::max(kCongestionControllerMinBitrate,current_best_estimate_.loss_limited_bandwidth *config_->max_increase_factor);recovering_after_loss_timestamp_ = last_send_time_most_recent_observation_;}
}LossBasedBweV2是WebRCC中一个设计复杂、高度可配置的第二代基于丢包的带宽估计器。它采用最大似然估计原理,结合了信道模型、优化算法、多源信息融合和状态机逻辑,旨在更准确、更稳定地从丢包事件中推断网络带宽,并为拥塞控制决策提供丰富的依据。
