Linux内核进程管理子系统有什么第四十三回 —— 进程主结构详解(39)
接前一篇文章:Linux内核进程管理子系统有什么第四十二回 —— 进程主结构详解(38)
本文内容参考:
Linux内核进程管理专题报告_linux rseq-CSDN博客
《趣谈Linux操作系统 核心原理篇:第三部分 进程管理》—— 刘超
《图解Linux内核 基于6.x》 —— 姜亚华 机械工业出版社
setuid系统调用及示例-CSDN博客
setuid函数解析 - HelloMarsMan - 博客园
特此致谢!
进程管理核心结构 —— task_struct
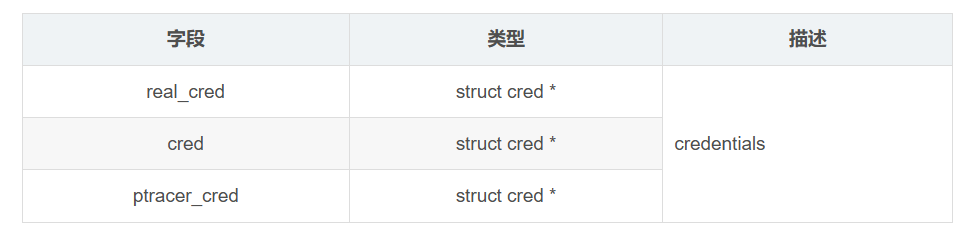
8. 进程权限相关成员
进程权限相关成员包括以下几个:
/* Process credentials: *//* Tracer's credentials at attach: */const struct cred __rcu *ptracer_cred;/* Objective and real subjective task credentials (COW): */const struct cred __rcu *real_cred;/* Effective (overridable) subjective task credentials (COW): */const struct cred __rcu *cred;这几个字段的描述如下:
上一回继续对于struct cred进行解析,本回仍然继续。为了便于理解和回顾,再次贴出struct cred的定义,在include/linux/cred.h中,如下:
/** The security context of a task** The parts of the context break down into two categories:** (1) The objective context of a task. These parts are used when some other* task is attempting to affect this one.** (2) The subjective context. These details are used when the task is acting* upon another object, be that a file, a task, a key or whatever.** Note that some members of this structure belong to both categories - the* LSM security pointer for instance.** A task has two security pointers. task->real_cred points to the objective* context that defines that task's actual details. The objective part of this* context is used whenever that task is acted upon.** task->cred points to the subjective context that defines the details of how* that task is going to act upon another object. This may be overridden* temporarily to point to another security context, but normally points to the* same context as task->real_cred.*/
struct cred {atomic_t usage;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_CREDENTIALSatomic_t subscribers; /* number of processes subscribed */void *put_addr;unsigned magic;
#define CRED_MAGIC 0x43736564
#define CRED_MAGIC_DEAD 0x44656144
#endifkuid_t uid; /* real UID of the task */kgid_t gid; /* real GID of the task */kuid_t suid; /* saved UID of the task */kgid_t sgid; /* saved GID of the task */kuid_t euid; /* effective UID of the task */kgid_t egid; /* effective GID of the task */kuid_t fsuid; /* UID for VFS ops */kgid_t fsgid; /* GID for VFS ops */unsigned securebits; /* SUID-less security management */kernel_cap_t cap_inheritable; /* caps our children can inherit */kernel_cap_t cap_permitted; /* caps we're permitted */kernel_cap_t cap_effective; /* caps we can actually use */kernel_cap_t cap_bset; /* capability bounding set */kernel_cap_t cap_ambient; /* Ambient capability set */
#ifdef CONFIG_KEYSunsigned char jit_keyring; /* default keyring to attach requested* keys to */struct key *session_keyring; /* keyring inherited over fork */struct key *process_keyring; /* keyring private to this process */struct key *thread_keyring; /* keyring private to this thread */struct key *request_key_auth; /* assumed request_key authority */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITYvoid *security; /* LSM security */
#endifstruct user_struct *user; /* real user ID subscription */struct user_namespace *user_ns; /* user_ns the caps and keyrings are relative to. */struct ucounts *ucounts;struct group_info *group_info; /* supplementary groups for euid/fsgid *//* RCU deletion */union {int non_rcu; /* Can we skip RCU deletion? */struct rcu_head rcu; /* RCU deletion hook */};
} __randomize_layout;
上一回在讲 struct cred中的第4组字段kuid_t suid和kgid sgid时,

对于setuid系统调用进行知识补强。没有讲完,本回继续讲解这一知识点,力求讲清楚、讲透彻。
知识补强 —— setuid系统调用
再来回顾一下setuid系统调用的功能细节。


前几回讲的都是理论知识,不是很好理解。下边通过一个示例代码以及其运行结果来加深对于setuid系统调用的理解。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <errno.h>void show_curr_uids(void)
{int ret;uid_t real_uid;uid_t effective_uid;uid_t saved_uid;ret = getresuid(&real_uid, &effective_uid, &saved_uid);printf("Real uid: %d, Effective uid: %d\n", real_uid, effective_uid);printf("Current UIDs:\n");printf("\tReal uid: %d\n\tEffective uid: %d\n\tSaved uid: %d\n", getuid(), geteuid(), (getresuid(&real_uid, &effective_uid, &saved_uid) == 0) ? saved_uid : -1);
}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{int ret;uid_t original_ruid, original_euid, original_suid;uid_t target_uid;//获取并打印初始 UIDif (getresuid(&original_ruid, &original_euid, &original_suid) != 0){perror("getresuid");exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}//检查是否以root权限运行if (geteuid() == 0){printf("\nRunning as ROOT (Privileged User)\n");printf("Before setuid.\n");show_curr_uids();//作为root,可以设置为任意有效的UID//这里我们尝试设置为'nobody' 用户 (通常UID 65534, 但请检查你的系统)target_uid = 65534;printf("\nAttempting to set UID to %d (usually 'nobody' user)...\n", target_uid);ret = setuid(target_uid);if (ret == 0){printf("setuid(%d) succeeded.\n", target_uid);printf("\nAfter setuid.\n");show_curr_uids();printf("Note: All UIDs (Real, Effective, Saved) are now %d.\n", target_uid);printf("The process is now running with 'nobody' privileges.\n");}else{perror("setuid");printf("Failed to set UID to %d.\n", target_uid);}}else{printf("\nRunning as a REGULAR USER (UID: %d)\n", getuid());printf("Before setuid.\n");show_curr_uids();//作为普通用户,只能设置为自己的ruid或suidtarget_uid = original_ruid; //选择设置为自己的真实UID (这不会改变任何东西)printf("\nAttempting to set UID to my Real UID (%d)...\n", target_uid);ret = setuid(target_uid);if (ret == 0){printf("setuid(%d) succeeded (as expected).\n", target_uid);printf("\nAfter setuid.\n");show_curr_uids();}else{perror("setuid");printf("Failed to set UID to %d.\n", target_uid);}
#if 0//尝试设置为一个无效的UID(比如一个不存在的或不属于我的UID)//这通常会失败target_uid = 9999; //假设这是一个无效的或不属于当前用户的UIDprintf("\nAttempting to set UID to an invalid/different UID (%d)...\n", target_uid);ret = setuid(target_uid);if (ret == -1){if (errno == EPERM){printf("setuid(%d) failed with EPERM (Operation not permitted) - as expected for a regular user.\n", target_uid);printf("This is because %d is not my Real UID (%d) or Saved Set-UID (%d).\n", target_uid, original_ruid, original_suid);}else{perror("setuid");}printf("After failed setuid.\n");show_curr_uids();}else{printf("setuid(%d) unexpectedly succeeded.\n", target_uid);printf("After unexpected setuid.\n");show_curr_uids();}
#endif}return 0;
}
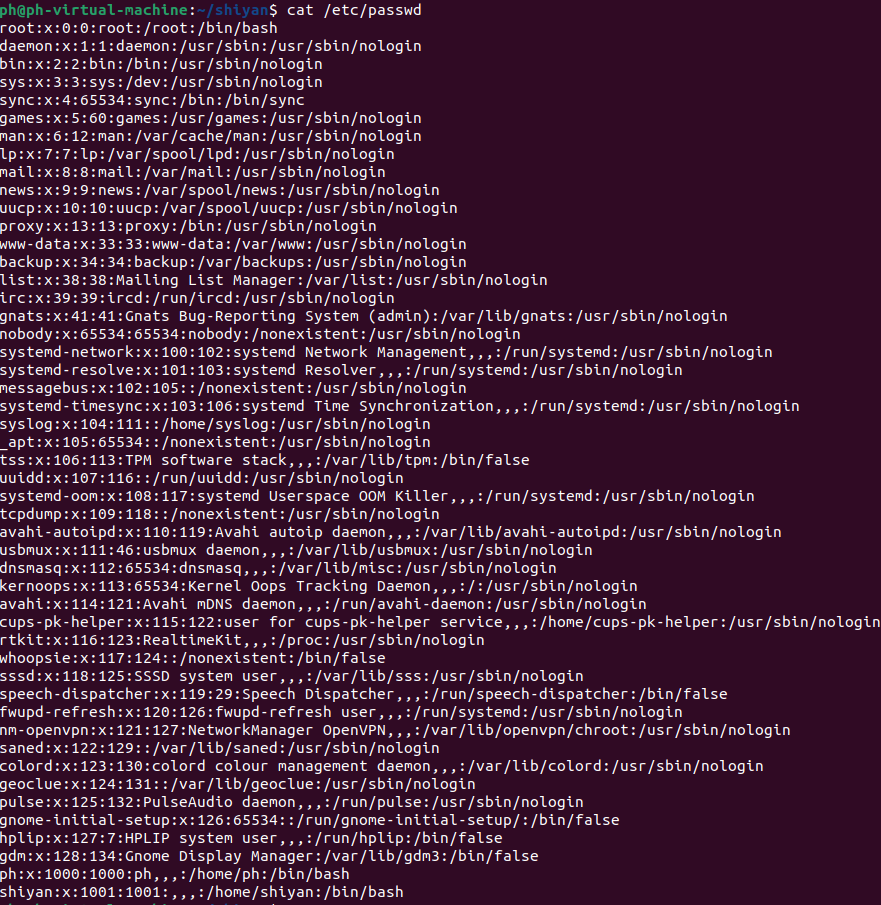
首先说一下,系统中原本有两个用户:root(UID为0)和ph(UID为1000)。为了做本次setuid测试,笔者专门通过adduser命令创建了用户shiyan(UID为1001)。
接下来看setuid在不同权限下的行为:
(1)以超级用户(root)执行程序
实际命令及结果如下:
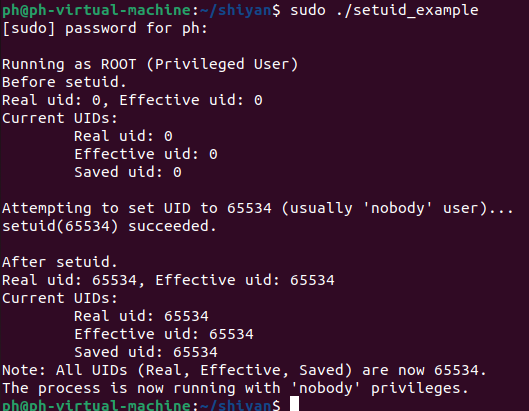
如果进程具有超级用户特权,那么这三个UID都被设置成了uid(setuid函数的参数)的值。这里,uid的值65534,是'nobody'用户的UID。
对应代码片段为:
//检查是否以root权限运行if (geteuid() == 0){printf("\nRunning as ROOT (Privileged User)\n");printf("Before setuid.\n");show_curr_uids();//作为root,可以设置为任意有效的UID//这里我们尝试设置为'nobody' 用户 (通常UID 65534, 但请检查你的系统)target_uid = 65534;printf("\nAttempting to set UID to %d (usually 'nobody' user)...\n", target_uid);ret = setuid(target_uid);if (ret == 0){printf("setuid(%d) succeeded.\n", target_uid);printf("\nAfter setuid.\n");show_curr_uids();printf("Note: All UIDs (Real, Effective, Saved) are now %d.\n", target_uid);printf("The process is now running with 'nobody' privileges.\n");}else{perror("setuid");printf("Failed to set UID to %d.\n", target_uid);}}这就对应的是setuid系统调用的具体行为(功能细节)中的:

setuid系统调用的其余功能细节,下一回进行解析。
