Java学习day_13之API(常用API对象克隆)
一、Math
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public static int abs(int a) | 获取参数绝对值 |
| public static double ceil(double a) | 向上取整 |
| public static double floor(double a) | 向下取整 |
| public static int round(float a) | 四舍五入 |
| public static int max(int a,int b) | 获取两个int值中的较大值 |
| public static double pow(double a,double b) | 返回a的b次方幂的值 |
| public static double random() | 返回值为double的随机值,范围[0.0,1.0) |
public class MathDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {//获取参数绝对值System.out.println(Math.abs(88));//88System.out.println(Math.abs(-88));//88//向上取整System.out.println(Math.ceil(11.1));//12.0System.out.println(Math.ceil(-11.1));//-11.0//向下取整System.out.println(Math.floor(12.3));//12.0System.out.println(Math.floor(-13.4));//-14.0//四舍五入System.out.println(Math.round(13.2));//13System.out.println(Math.round(13.5));//14//Math.round(x) 实际上等价于 (long)Math.floor(x + 0.5):System.out.println(Math.round(-13.2));//-13System.out.println(Math.round(-13.5));//-13System.out.println(Math.round(-13.6));//-14//获取两个int值中的较大值、较小值System.out.println(Math.max(5, 100));//100System.out.println(Math.min(5, 100));//5//返回a的b次幂的值System.out.println(Math.pow(5, 2));//25.0System.out.println(Math.pow(4, 0.5));//2.0//返回值为double的随机值,范围[0.0,1.0)for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(Math.random());}}
}

二、System
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public static void exit(int status) | 终止当前的Java虚拟机 |
| public static long currentTimeMillis() | 返回当前系统的时间,毫秒值 |
| public static void arraycopy(数据源数组,起始索引,目的地数组,起始索引,拷贝个数) | 数组拷贝 |
public class SystemDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {//自幂数,一个n位自然数等于自身各个数位上数字的n次幂之和long start = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 100; i <= 10000; i++) {if(isnumber(i)){System.out.println(i + "是自幂数");}}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();//获取程序运行的总时间System.out.println(end - start);//毫秒//拷贝数组//细节//1.如果数据源数组和目的数组都是基本数据类型,那么两者的类型必须保持一致,否则会报错//2.在拷贝的时候需要考虑数组的长度,超出范围也会报错int[] arr1 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};int[] arr2 = new int[10];System.arraycopy(arr1,0,arr2,0,5);for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {System.out.print(arr2[i] + " ");}}private static boolean isnumber(int i) {int count = 0;int x = i;int sum = i;int result = 0;while (x > 0){x = x/10;count++;}while (i > 0){result = (int) (result + Math.pow(i % 10,count));i = i/10;}if (result == sum){return true;}else {return false;}}
}

三、Runtime
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public static Runtime getRuntime() | 当前系统的运行环境对象 |
| public void exit(int status) | 停止虚拟机 |
| public int availableProcessors() | 获得CPU的线程数 |
| public long maxMemory() | JVM能从系统中获取总内存大小 |
| public long totalMemory() | JVM已经从系统中获取总内存大小 |
| public long freeMemory() | JVM剩余内存大小 |
| public Process exec(String command) | 运行cmd命令 |
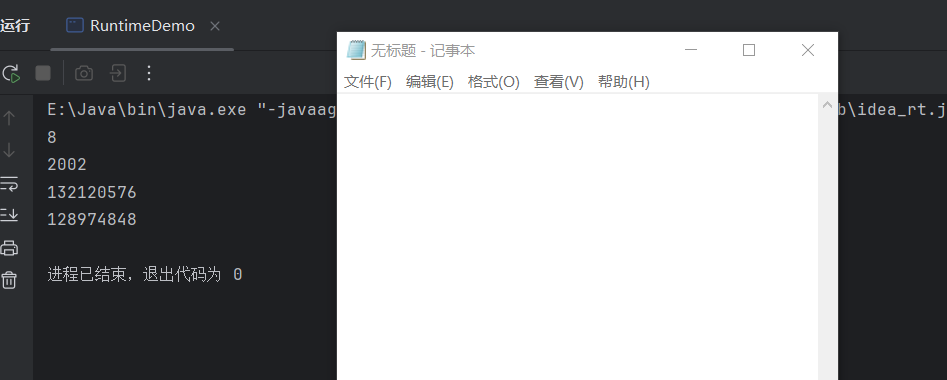
public class RuntimeDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.获取Runtime对象//Runtime r1 = Runtime.getRuntime();//2.exit 停止虚拟机//Runtime.getRuntime().exit(0);//3.获得CPU的线程数System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());//4.总内存大小,单位byte字节System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory()/1024 /1024);//5.已经获取的总内存大小,单位byte字节System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().totalMemory());//6.剩余内存大小System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory());//7.运行cmd命令Runtime.getRuntime().exec("notepad");}
}
四、Object
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public String toString() | 返回对象的字符串表示形式 |
| public boolean equals(Object obj) | 比较两个对象是否相等 |
| protected Object clone(int a) | 对象克隆 |
public class ObjectDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Object obj = new Object();String str1 = obj.toString();System.out.println(str1);//toString方法的结论//如果我们打印一个对象,想要看到属性值的话,那么就重写toString方法Student stu = new Student("zxp",23);System.out.println(stu);}
}public String toString() {return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";}

public class ObjectDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {Student stu1 = new Student("zhangsan",23);Student stu2 = new Student("zhangsan",23);boolean result = stu1.equals(stu2);System.out.println(result);//true//结论//1.如果没有重新equals方法,那么默认使用Object中的方法进行比较,比较的是地址值是否相等//2.重写之后比较的就是对象内部的属性值了}
}
public class ObjectDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "abc";StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("abc");System.out.println(s.equals(sb));//false//String 类的 equals() 方法实现中,首先会检查参数是否为 String 类型的实例。// 如果不是(比如这里是 StringBuilder),会直接返回 false,即使两者包含的字符内容完全相同。System.out.println(sb.equals(s));//false//StringBuilder 类没有重写 Object 类的 equals() 方法,它使用的是父类 Object 的默认实现。// Object 的 equals() 方法比较的是对象的内存地址(即是否为同一个对象),而不是内容。}
}
对象克隆
把A对象的属性值完全拷贝给B对象
浅克隆:不管对象内部的属性是基本数据类型还是引用数据类型,都完全拷贝
//1.创建对象int[] data = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};User u1 = new User(1,"zhangsan","0526","girl",data);//2.克隆对象/*细节方法在底层会帮我们创建一个对象,并把原对象中的数据拷贝过去书写细节:1.重新Object中的clone方法2.让javabean类实现Cloneable接口3.创建原对象并调用clone就可以了*/User u2 = (User) u1.clone();int[] arr = u1.getData();arr[0] = 100;System.out.println(u1);System.out.println(u2);

深克隆:基本数据类型拷贝过来,字符串复用,引用数据类型会重新创建新的 需额外重新clone方法
@Overrideprotected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {//调用父类的clone方法//相当于让Java帮我们克隆一个对象,并把克隆之后的对象返回出去//深克隆//先把被克隆对象中的数组获取出来int[] data = this.data;//创建新的数组int[] newData = new int[data.length];//拷贝数组中的数据for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {newData[i] = data[i];}//调用父类中的方法克隆对象User u = (User) super.clone();//因为父类中的克隆方法是浅克隆,替换克隆出来对象中的数组地址值u.data = newData;return u;}

五、Objects
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public static boolean equals(Object a ,Object b) | 先做非空判断,比较两个对象 |
| public static boolean isNull(Object obj) | 判断对象是否为null,为null返回true ,反之false |
| public static boolean nonNull(Object obj) | 判断对象是否为null,为null返回false ,反之true |
public class ObjectsDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {Student stu1 = null;Student stu2 = new Student("zhangsan",23);boolean result = Objects.equals(stu1,stu2);System.out.println(result);//false/*1.方法的底层会判断stu1是否为null,为null则返回false2.如果stu1不为null,那么就利用stu1再次调用equals方法3.此时stu1是student类型,所以最终会调用student的equals方法如果没有重写,比较地址值,如果重写,比较属性值*/System.out.println(Objects.isNull(stu1));//trueSystem.out.println(Objects.isNull(stu2));//falseSystem.out.println(Objects.nonNull(stu1));//falseSystem.out.println(Objects.nonNull(stu2));//true}
}
六、BigInteger
BigInteger构造方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public BigInteger(int num,Random rnd) | 获取随机大整数,范围:[0~2的num次方-1] |
| public BigInteger(String val) | 获取指定的大整数 |
| public BigInteger(String val,int radix) | 获取指定进制的大整数 |
| public static BigInteger(long val) | 静态方法获取BigInteger的对象,内部有优化 |
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Random;public class BigIntegerDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//获取随机大整数BigInteger bd1 = new BigInteger(4,new Random());System.out.println(bd1);//获取指定大整数BigInteger bd2 = new BigInteger("123456789");System.out.println(bd2);//123456789//获取指定进制的大整数BigInteger bd3 = new BigInteger("100",2);System.out.println(bd3);//4/*静态方法获取BigInteger的对象,内部有优化1.能表示范围比较小,只能在long的取值范围之内,如果超出long的范围就不行2.提前把-16~16 先创建好BigInteger对象,如果多次获取不会重新创建新的*/BigInteger bd4 = BigInteger.valueOf(16);BigInteger bd5 = BigInteger.valueOf(16);System.out.println(bd5 == bd4);//trueBigInteger bd6 = BigInteger.valueOf(17);BigInteger bd7 = BigInteger.valueOf(17);System.out.println(bd6 == bd7);//false}
}
注意
- 如果BigInteger表示的数字没有超出long的范围,可以用静态方法获取
- 如果BigInteger表示的超出long范围,可以用构造方法获取
- 对象一旦创建,BigInteger内部记录的值不能发生改变
- 只有进行计算都会产生一个新的BigInteger对象
BigInteger成员方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public BigInteger add(BigInteger val) | 加法 |
| public BigInteger subtract(BigInteger val) | 减法 |
| public BigInteger multiply(BigInteger val) | 乘法 |
| public BigInteger divide(BigInteger val) | 除法,获取商 |
| public BigInteger[] divideAndRemainder(BigInteger val) | 除法,获取商和余数 |
| public boolean equals(Object x) | 比较是否相同 |
| public BigInteger pow(int exponent) | 次幂 |
| public BigInteger max/min(BigInteger val) | 返回较大值/较小值 |
| public int intValue(BigInteger val) | 转为int类型整数,超出范围报错 |
public class BigIntegerDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建两个BigInteger对象BigInteger bd1 = BigInteger.valueOf(10);BigInteger bd2 = BigInteger.valueOf(2);//加法BigInteger bd3 = bd1.add(bd2);System.out.println(bd3);//12//减法BigInteger bd4 = bd1.subtract(bd2);System.out.println(bd4);//8//乘法BigInteger bd5 = bd1.multiply(bd2);System.out.println(bd5);//20//除法,获取商BigInteger bd6 = bd1.divide(bd2);System.out.println(bd6);//5//除法,获取商和余数BigInteger[] bd7 = bd1.divideAndRemainder(bd2);System.out.println(bd7[0]);//5System.out.println(bd7[1]);//0//比较是否相同boolean result = bd1.equals(bd2);System.out.println(result);//false//次幂计算BigInteger bd8 = bd1.pow(2);System.out.println(bd8);//100//返回最值BigInteger bd9 = bd1.max(bd2);BigInteger bd10 = bd1.min(bd2);System.out.println(bd9);//10System.out.println(bd10);//2//转为int类型int bd = bd1.intValue();System.out.println(bd);//10}
}
