接口自动化测试大全(python+pytest+allure)
文章目录
- 一、requests模块(用于发送请求)
- 1、环境配置
- 1. 下载reqeusts/pytest模块
- 2. requests模块的第一个接口测试
- 2、requests模块说明
- 简介
- API使用
- 示例1
- 示例2
- 二、pytest(用于组织和管理用例)
- 常见命令
- pytest.ini
- 三、前后置
- 四、参数化(mark.parametrize)
- 五、函数上下文管理(fixture)
- fixture基本使用
- yield与fixture结合
- fixture的参数
- 与conftest.py文件配合
- 六、yml与JSON Schema
- yml
- JSON Schema
- 数据类型
- 字符串特殊校验
- 数组约束
- 对象约束
- 必需属性
- 依赖关系
- 代码示例
- 七、日志模块
- logging
- logger
- FileHandel
- 八、Allure
- 安装
- 使用
一、requests模块(用于发送请求)
1、环境配置
1. 下载reqeusts/pytest模块
这个模块可以发送请求到指定接口,并且可以配置请求中的参数/解析响应值,进而实现接口自动化。
控制台输入下面的命令:
pip install requests==2.31.0
pip install pytest==8.3.2
2. requests模块的第一个接口测试
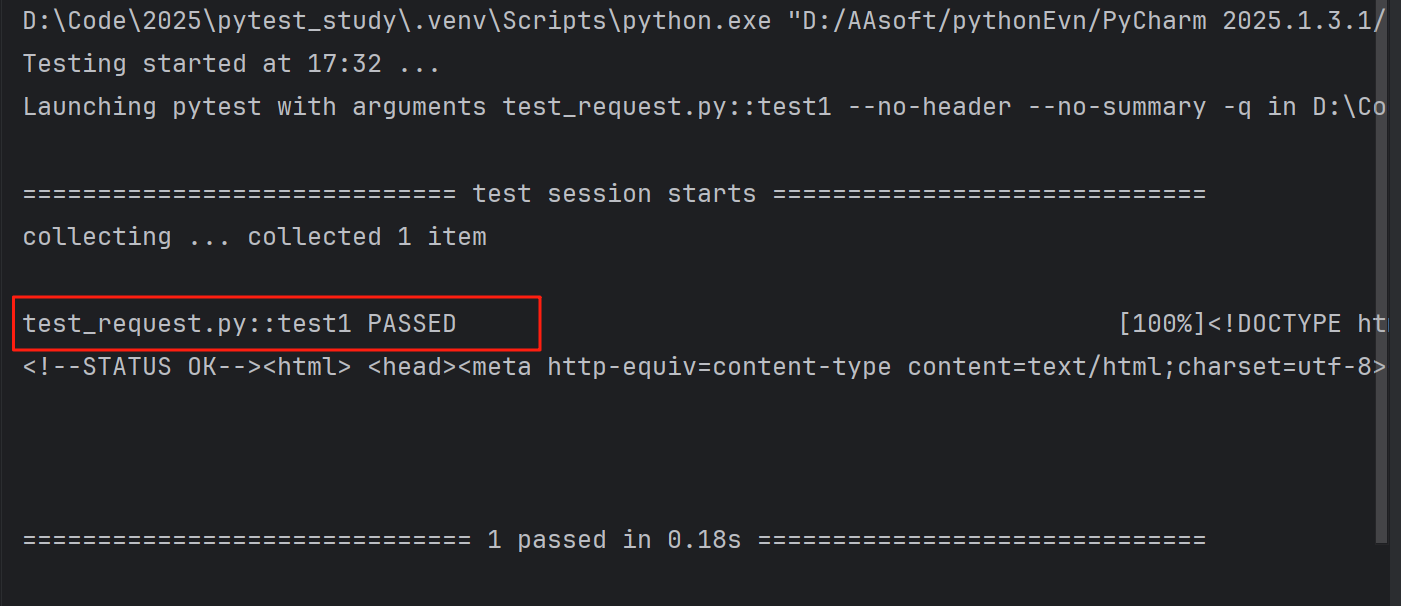
我们通过代码的方式,判断百度网址是否运行正常:
import requestsdef test1():request=requests.request(method="GET", url="http://www.baidu.com")assert request.status_code==200print(request.text)执行结果通过:
2、requests模块说明
简介
requests库是一个非常流行的HTTP客户端库。它可以发送http请求给到指定url,并且返回一个Response对象,这个对象包含对应url返回的所有信息
API使用
requests模块常用的请求方法:
# 发起get请求
def get(url, params=None, **kwargs):pass # 函数体省略# 发起post请求
def post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs):pass # 函数体省略# 支持不同请求方式,method: 指定请求方法,(底层实际就是调用上述的原子方法)
# 支持 `get`, `OPTIONS`, `HEAD`, `post`, `PUT`, `PATCH`, or `DELETE`
def request(method, url, **kwargs):pass # 函数体省略
通过request获取请求后可以得到一个Response对象,对象中返回的信息如下:
| 属性/方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
r.status_code | 响应状态码 |
r.content | 字节方式的响应体,会自动解码gzip和deflate压缩 |
r.headers | 以字典对象存储服务器响应头,若键不存在则返回None |
r.json() | Requests中内置的JSON解析方法,将响应体解析为JSON格式 |
r.url | 获取实际请求的URL |
r.encoding | 编码格式,根据响应头部的字符编码确定 |
r.cookies | 获取服务器设置的cookies |
r.raw | 返回原始响应体,不进行任何处理 |
r.text | 字符串方式的响应体,会自动根据响应头部的字符编码进行解码 |
r.raise_for_status() | 失败请求(非200响应)抛出异常 |
示例1
import requestsurl = "http://localhost:8090/blog/getBlogDetail"# 定义查询参数
params = {"blogId": 9773
}# 定义请求头信息
header = {"user_token_header": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJpZCI6MSwidXNlcm5hbWUiOiJ6aGFuZ3NhbiIsImV4cCI6MTczNTU1ODk2Mn0.72oh-gQ-5E6_aICLsjotWL4ZHmgy0jF1794JDE-uUkg","x-requested-with": "XMLHttpRequest"
}r = requests.post(url=url, params=params, headers=header)
print(r.json())
示例2
import requestsurl = "http://localhost:8090/user/login"# 定义要发送的数据
data = {"username": "dd","password": "111"
}r = requests.post(url=url, data=data)
print(r.json())
二、pytest(用于组织和管理用例)
常见命令
使用下面的命令,可以按照我们指定的方式,获取到被执行测试的用例结果:
| 命令 | 描述 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
pytest | 在当前目录及其子目录中搜索并进行测试。 | |
pytest -v | 增加输出的详细程度。 | |
pytest -s | 显示测试中的 print 语句。 | |
pytest test_module.py | 运行指定的测试模块。 | |
pytest test_dir/ | 运行指定目录下的所有测试。 | |
pytest -k <keyword> | 只运行测试名包含指定关键字的测试。 | |
pytest -m <marker> | 只运行标记为指定标记的测试。 | |
pytest -q | 减少输出的详细程度。 |
pytest.ini
我们安装完pytest后,如果项目中的文件按照下面的命名规范,pytest就会认为它们是一个的测试用例:
| 元素 | 命名规范 |
|---|---|
| 测试文件 (文件名) | 以 test_ 开头 或 以 _test.py 结尾 |
| 测试函数 (函数名) | 以 test_ 开头 |
| 测试类 (类名) | 以 Test 开头 (且无 __init__ 方法) |
| 测试方法 (类中的方法名) | 以 test_ 开头 |
例如:
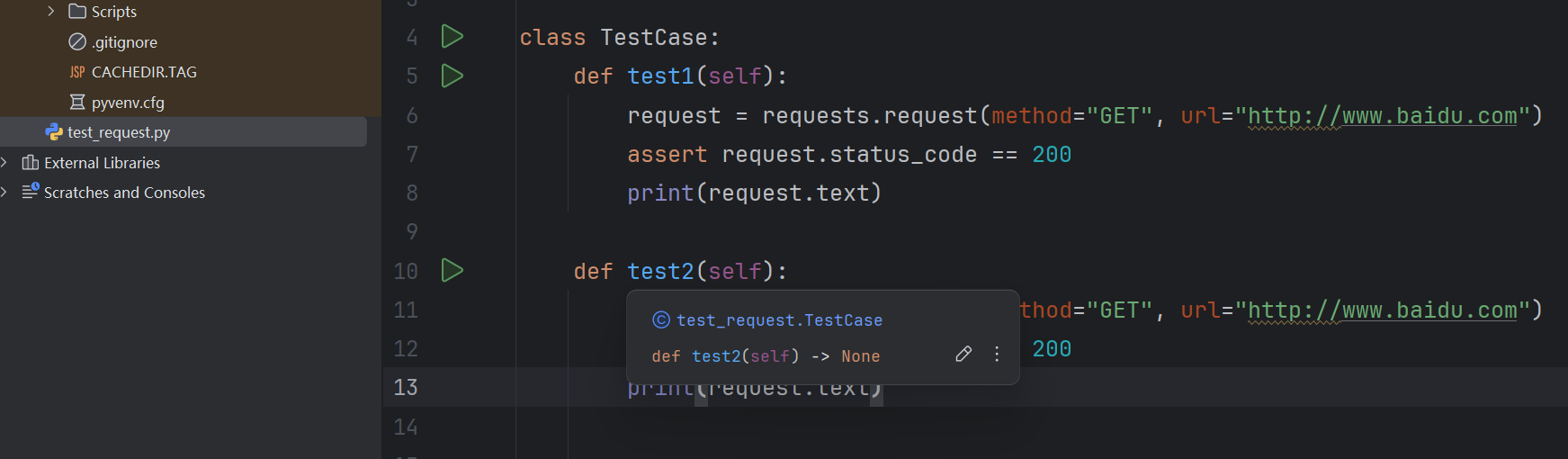
我们使用命令行,运行pytest命令,test1和test2就会被pytest执行:
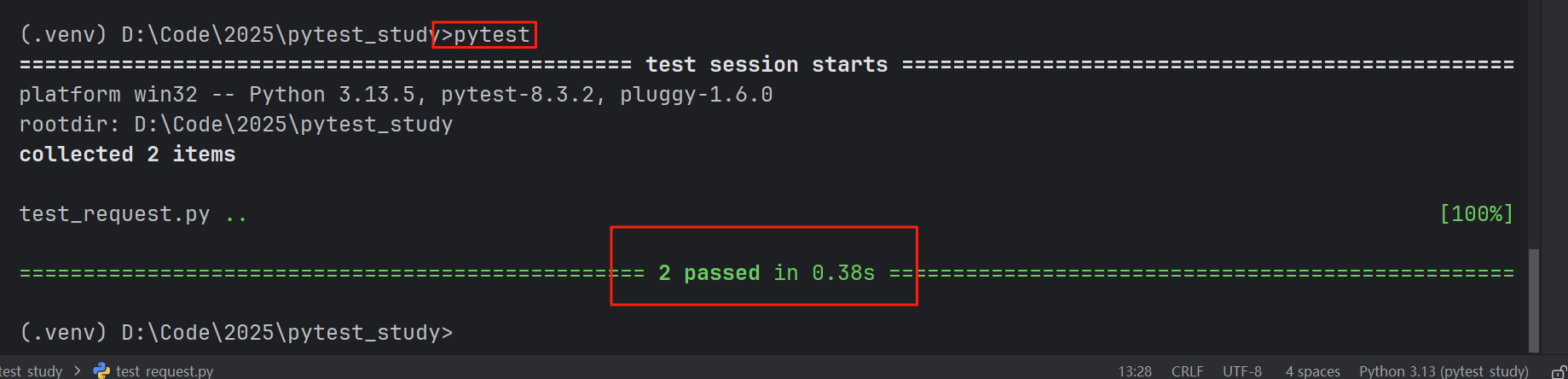
以上是默认的命名规范,我们可以通过pytest.ini配置文件进行自定义的命名规范,让pytest按章我们的想法去筛选需要测试的文件、类、方法:
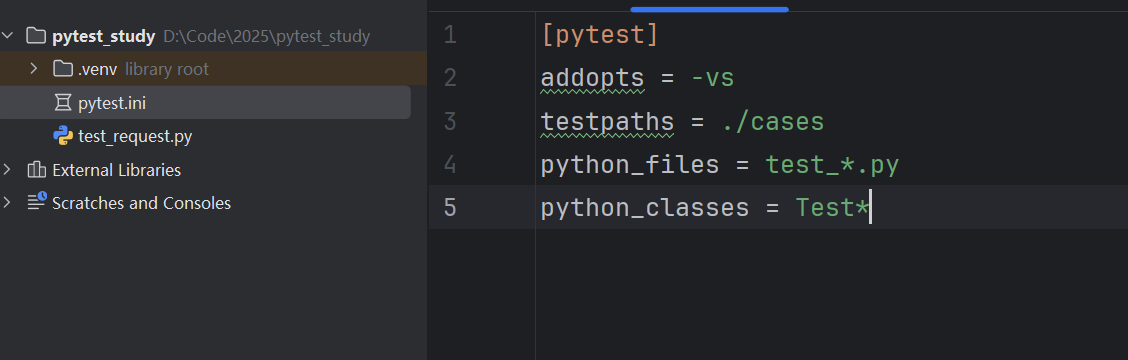
| 配置项 | 示例值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
addopts | -vs | 设置默认的命令行参数。 |
testpaths | ./cases | 指定执行测试的目录。 |
python_files | test_*.py | 自定义测试文件的匹配规则。 |
python_classes | Test* | 自定义测试类的匹配规则。 |
*是通配符,可以代表任意字符,宝库口但不限于空- addopts 配置后直接使用pytest命令后面就不用加 -vs就会有-vs的效果
三、前后置
pytest框架提供了三种前后置方法:
setup_method和teardown_method:用于每个测试方法的前后置setup_class和teardown_class:用于一个测试类的前后置fixtrue前后置(fixture不止于前后置,有很强大的功能,后面中的那介绍)
演示(前置方法和函数必须在类中定义才会生效):
import pytestclass Test:def setup_method(self):print("方法初始化")def teardown_method(self):print("方法关闭资源")def setup_class(self):print("类初始化")def teardown_class(self):print("类关闭资源")def test1(self):print("test1")def test2(self):print("test2")
四、参数化(mark.parametrize)
看下面这个测试函数:
def test3(self, a, b):print("test3")print(a)print(b)
如果a和b需要输入多个用例作为参数测试多组数据怎么办?
这时候我们可以通过pytest的注解,手动定义多组参数:
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b",[(1,2),(3,4)])def test3(self, a, b):print("test3")print(a)print(b)此方法执行了两次:
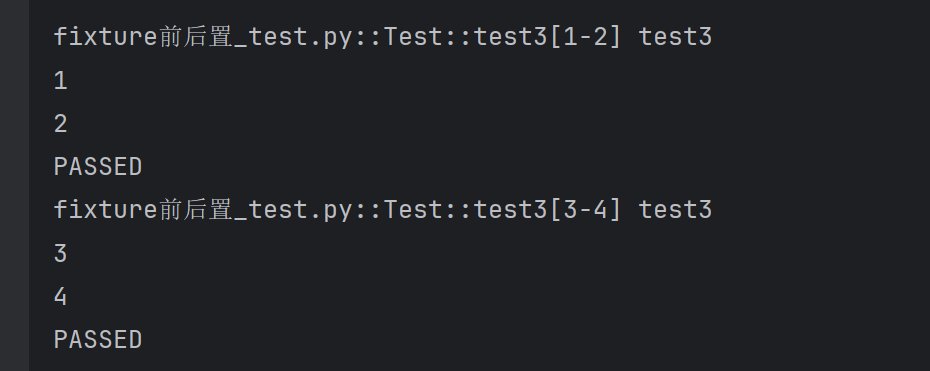
五、函数上下文管理(fixture)
fixture基本使用
被@pytest.fixture修饰的方法可以被其他测试方法当作参数使用(被修饰方法就是参数名):
@pytest.fixturedef fixture1(self):print("fixture1------")return "fd"def test4(self,fixture1):print("fixture1返回的参数",fixture1)print("test4------")
@pytest.fixture的特性是如果test4方法把fixture1当作参数(方法签名中声明),那么方法执行前默认调用一次fixture1方法,并且test4方法可以使用fixture1方法的返回值
此外@pytest.fixture修饰的方法可以嵌套使用:
@pytest.fixturedef fixture1(self):print("调用f1")return "返回f1"@pytest.fixturedef fixture2(self,fixture1):print("调用f2")return "返回f2"@pytest.fixturedef fixture3(self,fixture2):print("调用f3")return "返回f3"def test5(self,fixture3):print("fixture3------",fixture3)yield与fixture结合
yield关键字在python中常见的用法有三种:
1.节省内存的生成器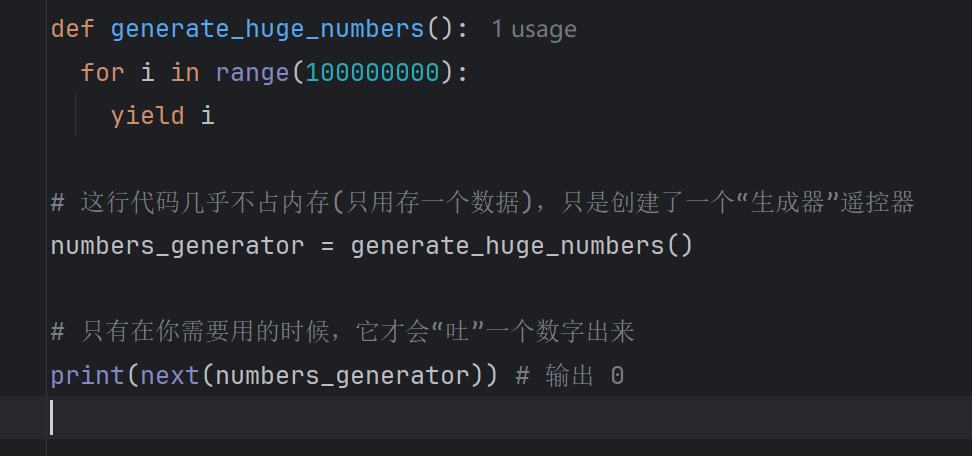
2. 异步编程
3. 配合@pytest.fixture实现前后置(重点)
fixture+yield可以灵活的进行前后置操作:
@pytest.fixturedef fixture4(self):with open("haha.jpg","w") as f:print("打开资源")yield fprint("文件关闭")def test6(self,fixture4):print("文件对象:",fixture4)
fixture的参数
fixture可以不传任何参数,如上文演示便是。也可以传递参数,让测试用例的执行更加灵活
pytest.fixture(scope='', params='', autouse='', ids='', name='')
- scope: 限定fixture方法的作用范围
- funtion(默认):测试方法声明了fixture就会调用一次
- class: 同一个测试类中,只会调用一次
- module:同一个模块(一个.py文件)调用一次
- session:执行一次pytest命令调用一次
- autouse: 默认是False,如果设置True,每个测试方法都会调用一次该fixture方法
- params: 参数用于参数化fixture,支持列表传入。每个参数值都会使fixture执行一次,类似于for循环
- ids: 参数与 params 配合使用,为每个参数化实例指定可读的标识符(给参数取名字)
- name: 参数用于为fixture显式设置一个名称。如果使用了 name ,则在测试函数中需要使用这个
名称来引用 fixture (给fixture取名字)
与conftest.py文件配合
conftest.py是一个特殊的文件,我们在这里面可以配置fixture函数
当我们配置了一个fixture在conftest.py文件中:
import pytest@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
def open_close_file():with open(".\哈哈.txt","w+") as f:print("打开文件")print()print(f.read())yield fprint()print("关闭文件")配置完后,别的模块就可以调用这个fixture:
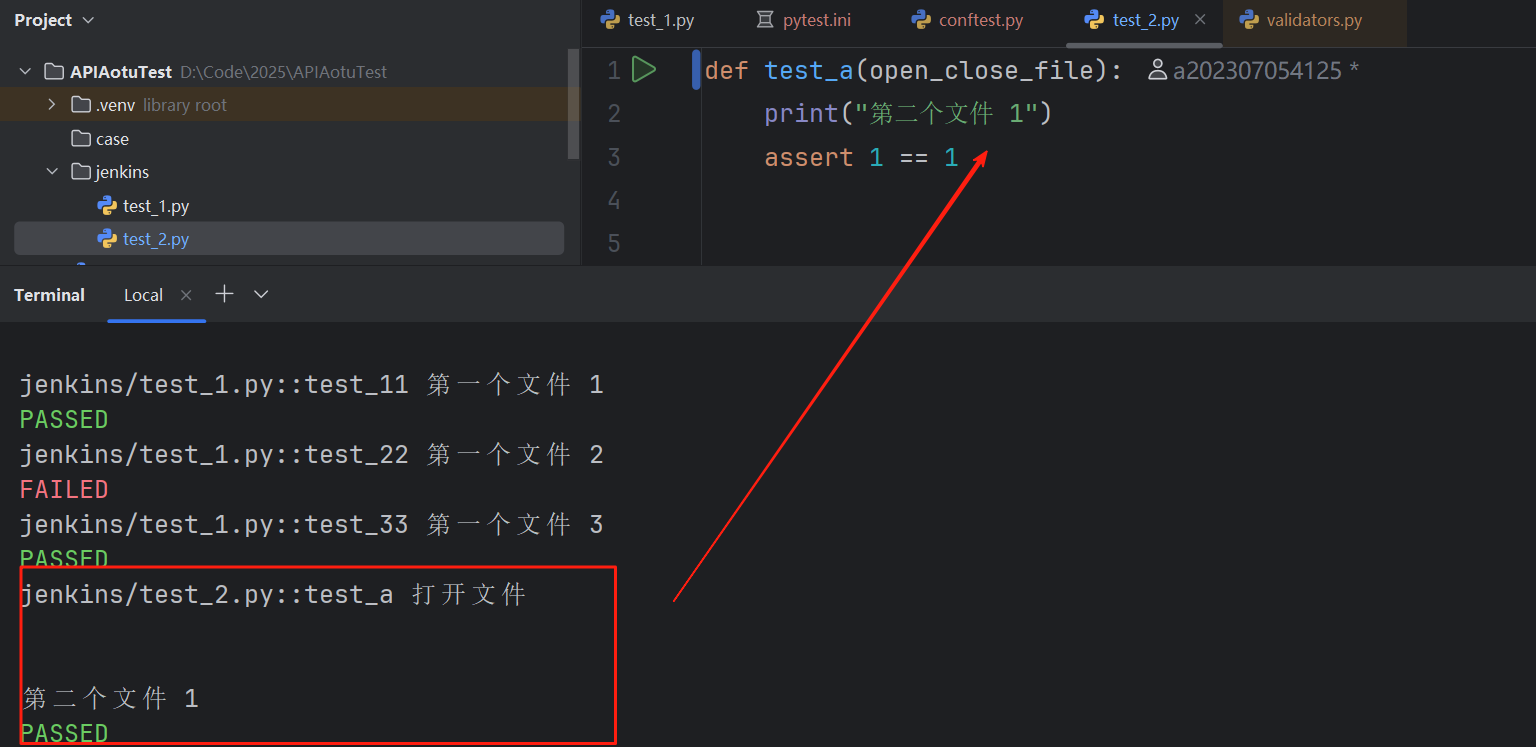
六、yml与JSON Schema
yml
简述:
在实际项目中yml文件用的应该是比较多的,它可以进行文件的配置,并且阅读比较直观。
在测试过程中,我们需要根据不同的测试需求去更改yml配置文件,python提供了yaml库来通过代码来进行自动配置。
用法:
使用前需要安装:
pip install pip install PyYAML==6.0.1
import yaml# 追加写
def write_yml_a(filename,data):with open(filename,mode='a+',encoding="utf-8") as f:yaml.dump(data,f)# 安全读
def read_yml(filename,key):with open(filename,mode='r',encoding="utf-8") as f:data=yaml.safe_load(f)return data[key]#示例
def test():data=read_yml("test.yml","ss")print(data)print(data["arr"]['a'])
JSON Schema
JSON Schema用于校验/定义JSON数据格式。定义一个Schema类型的字符串,就可以知道一个JSON数据它的属性、类型、必传属性等等信息。
数据类型
好的,这是从图片内容转换成的 Markdown 表格。
| type | 解释 |
|---|---|
string | 字符串类型,用于文本数据。 |
number | 数字类型,用于表示浮点数。 |
integer | 整数类型,用于表示整数。 |
boolean | 布尔类型,值为 true 或 false。 |
object | 对象类型,用于嵌套的 JSON 对象。 |
array | 数组类型,用于列表或集合。 |
null | 空值类型。 |
示例
{"type": "object","properties": {"name": { "type": "string" },"age": { "type": "integer" }}
}
- type=object,表示这个jsion数据是一个对象
- properties描述了该对象有哪些属性
字符串特殊校验
pattern: 使用正则表达式来验证字符串是否符合特定的模式。
{"type": "object","properties": {"email": {"type": "string"},"username": {"type": "string","pattern": "\\S+"}}
}
数组约束
minItems和maxItems:指定数组的最小和最大长度。uniqueItems:确保数组中的元素是唯一的。items:定义数组中每个元素的类型和约束。
代码块:
{"type": "object","properties": {"tags": {"type": "array","items": { "type": "string" },"minItems": 1,"uniqueItems": true}}
}
对象约束
minProperties和maxProperties:指定对象的最小和最大属性数量。additionalProperties:控制是否允许对象中存在未在properties中定义的额外属性,默认为True。
代码块:
{"type": "object","properties": {"name": { "type": "string" }},"minProperties": 1,"additionalProperties": false
}
必需属性
通过 required 关键字,JSON Schema 可以指定哪些属性是必需的。如果 JSON 实例中缺少这些必需属性,验证将失败。
示例:
代码块:
{"type": "object","properties": {"name": { "type": "string" },"email": { "type": "string" }},"required": ["name", "email"]
}
依赖关系
dependentRequired 可以定义属性之间的依赖关系。例如,如果某个属性存在,则必须存在另一个属性。
示例:
代码块:
{"type": "object","properties": {"creditCard": { "type": "string" },"billingAddress": { "type": "string" }},"dependentRequired": {"creditCard": ["billingAddress"]}
}
代码示例
from jsonschema.validators import validateif __name__ == "__main__":json = {"product_id": "451","product_name": "Wireless Mouse","price": 29.99,"in_stock": True}schema = {"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#","title": "Simple Product","description": "A basic schema for a product","type": "object","properties": {"product_id": {"description": "The unique identifier for the product.","type": "integer"},"product_name": {"description": "The name of the product.","type": "string"},"price": {"description": "The price of the product.","type": "number","minimum": 0},"in_stock": {"description": "Indicates if the product is currently in stock.","type": "boolean"}},"required": ["product_id","product_name","price"]}# 校验失败会抛出jsonschema.exceptions.ValidationError异常validate(json, schema)运行后报错:

七、日志模块
logging 是 Python 标准库中的一个模块,它提供了灵活的日志记录功能。
logging
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.ERROR)
logger=logging.getLogger(__name__)
- 通过logging我们可以过滤整体日志的级别,大于等于
ERROR的日志才会被处理 - 获取logger用于输出日志,并且指定这个日志输出工具的名字
- __name__表示以使用logger进行日志输出的模块名字进行命名
logger
logger可以指定日志输出的级别并且输入日志
import logging
import syslogging.basicConfig(level=logging.ERROR)if __name__ == "__main__":logger=logging.getLogger(__name__)logger.setLevel(logging.ERROR)logger.error("heihei")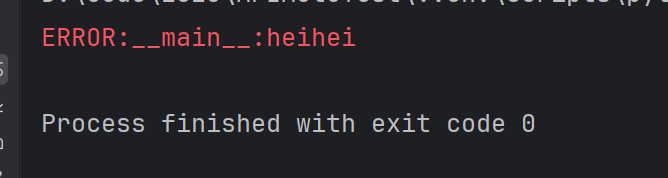
FileHandel
handel是专门处理日志的输出位置和输出形式的。
import logginglogging.basicConfig(level=logging.ERROR)if __name__ == "__main__":logger=logging.getLogger(__name__)# 指定输出到test.log,没有则创建handle=logging.FileHandler(filename="test.log",encoding="utf-8")# 指定日志输出格式handle.setFormatter(logging.Formatter("%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s"))logger.setLevel(logging.ERROR)# handle可以添加多个logger.addHandler(handle)logger.error("heihei")八、Allure
allure是一个流行的用于生成可视化测试报告的开源工具
安装
-
下载allure-pytest包
pip install allure-pytest==2.13.5 -
把allure安装的bin路径设置到环境变量
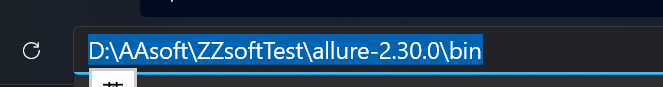
-
在控制台输入 allure --version,如果出现版本信息就OK了
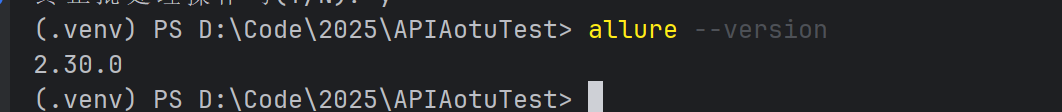
如果还是不行,把allure的环境变量上移一点
使用
1、这个命令会自动执行pytest 然后生成报告到指定文件夹,如果没有则创建(生成的报告都是json文件)
pytest --alluredir=results_dir
2、直接在浏览器打开可视化的html文件(不会保存)
allure serve .\allure-results\
此外可以指定端口号
allure serve --port 8787 .\allure-results\
3、 生成json元数据放到\allure-results\ 中,然后生成allure-report用于保存可视化的html文件 并且清理之前在allure-report中的遗留数据
allure generate .\allure-results\ -o .\allure-report --clean
