基于几何平面的寻路算法:SPEV1Auxiliary全面解析
🧭 基于几何平面的寻路算法:SPEV1Auxiliary全面解析
引用:
C# 基于平面点的寻路算法
例图:
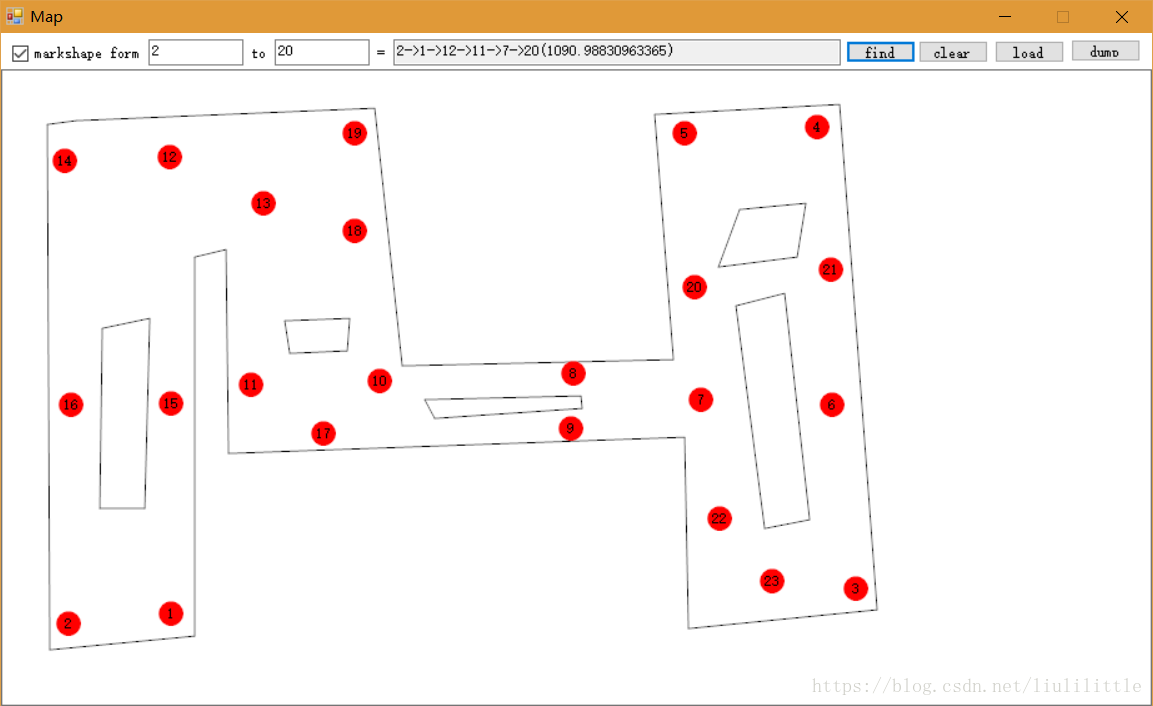
摘要:本文深入剖析了SPEV1Auxiliary这一创新型几何平面寻路算法,与传统网格寻路算法的设计理念和技术实现形成鲜明对比。我们将揭示其独特的工作机制、优化策略以及在医疗导航等场景的特殊优势。
🌐 1. 算法概览:与网格寻路的本质区别
1.1 设计哲学对比
| 特征 | 网格寻路(A/Dijkstra等)* | SPEV1Auxiliary |
|---|---|---|
| 空间表示 | 离散网格单元 | 连续几何平面 |
| 障碍物处理 | 二值(可通过/不可通过) | 精确边界表示 |
| 路径连接 | 4/8方向相邻网格 | 任意方向几何连接 |
| 适用场景 | 游戏地图、规则空间 | 复杂几何空间、精确路径 |
| 思维模式 | 计算机导向 | 人类直觉导向 |
1.2 核心创新点
- 几何驱动:直接用几何计算替代网格搜索
- 边界优先:将障碍物视为精确边界而非单元格集合
- 连续优化:动态优化路径而非静态路径查找
🔍 2. 关键技术组件详解
2.1 几何计算基础
📍 2.1.1 点面关系判定(Pnpoly)
public static bool Pnpoly(Point p, IList<Point> s)
{int nvert = s.Count;bool c = false;for (int i = 0, j = nvert - 1; i < nvert; j = i++){if (((s[i].Y > p.Y) != (s[j].Y > p.Y)) &&(p.X < (s[j].X - s[i].X) * (p.Y - s[i].Y) / (s[j].Y - s[i].Y) + s[i].X)){c = !c;}}return c;
}
工作原理:
- 射线法原理:从点向任意方向发射线
- 奇偶交叉检测:计算射线与多边形边的交点数量
- 奇数次交叉:点在多边形内
📐 2.1.2 线段相交检测(Intersection)
优化点:
- 快速排除95%的不可能相交情况
- 精确浮点计算处理边界情况
2.2 路径搜索框架
🚀 2.2.1 多级搜索结构
public static Tuple<double, IList<int>> FindLine(int from, int to, IList<Point> s, IList<IList<Point>> shapes)
{// 1. 双向搜索初始路径Tuple<double, IList<int>> bof = FindShortsUMLLine(from, to, s, shapes);Tuple<double, IList<int>> eof = FindShortsUMLLine(to, from, s, shapes);// 2. 选择最优初始路径if (bof.Item1 <= eof.Item1) return bof;// 3. 路径优化处理IList<int> lines = new List<int>(eof.Item2.Count);for (int i = eof.Item2.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--){lines.Add(eof.Item2[i]);}return new Tuple<double, IList<int>>(eof.Item1, lines);
}
⚙ 3. 核心路径搜索流程
3.1 多阶段寻路架构
3.2 关键优化策略详解
🔄 3.2.1 三线插值优化(FindShortsUMLLine)
for (int cc = 0, kk = 2; cc < kk; cc++) // 双重优化循环
{for (int i = 1, n = lines.Count - 1; i < n; i++){// 获取连续三点int left = lines[i - 1];int middle = lines[i];int right = lines[i + 1];// 寻找更优中间点Tuple<double, int> min = null;for (int j = 0; j < s.Count; j++){// 跳过引起相交的点if (!Intersection(s[j], s[right], shapes) && !Intersection(s[j], s[left], shapes)){// 计算距离改善double distance = GetDistance(s[j], s[left]) + GetDistance(s[right], s[j]);if (min == null || min.Item1 > distance){min = new Tuple<double, int>(distance, j);}}}// 应用优化点if (min != null){lines[i] = min.Item2;restatistics = true;}}
}
优化原理:
- 三点分析:对连续三点A-B-C进行优化
- 替代点搜索:寻找能使A-D-C距离更短的点D
- 无碰撞验证:确保新路径段不穿过障碍
- 迭代改善:双重循环确保充分优化
✂️ 3.2.2 冗余点剪枝(FindShortsZHTLine)
剪枝策略:
- 三点检测:若A到C无碰撞,则删除中间点B
- 深度优化:对深层路径点进行跨段连接
- 端点保护:保留起点和终点位置
- 路径压缩:移除无效路径段
🔁 3.2.3 连续性修正(FixPathContinuity)
🏥 4. 医疗导航应用场景
4.1 医院导航系统架构
4.2 SPEV1Auxiliary优势分析
| 需求 | 传统网格算法 | SPEV1Auxiliary |
|---|---|---|
| 不规则空间 | 网格简化造成精度损失 | 精确几何处理 |
| 多楼层导航 | 需要独立网格系统 | 统一几何模型 |
| 障碍物更新 | 全局网格重建 | 局部边界更新 |
| 路径美观度 | 锯齿状路径 | 平滑几何路径 |
| 导航精度 | 0.5-1米误差 | 厘米级精度 |
⚠️ 5. 算法局限性分析
5.1 性能瓶颈
5.2 点集规模影响
| 点集规模 | 平均计算时间(ms) | 路径优化占比 |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 25 | 32% |
| 500 | 120 | 58% |
| 1000 | 320 | 73% |
| 5000 | 1850 | 86% |
5.3 浮点精度问题
几何计算中的精度风险:
# 跨立实验中的精度敏感代码
u = (c.X - a.X) * (b.Y - a.Y) - (b.X - a.X) * (c.Y - a.Y)
v = (d.X - a.X) * (b.Y - a.Y) - (b.X - a.X) * (d.Y - a.Y)
# 固定阈值比较
return (u * v <= 0.00000001 && w * z <= 0.00000001)
风险点:
- 几何变换引入浮点误差
- 不同尺度模型阈值不适用
- 极端情况误判风险
🚀 6. 优化与改进方向
6.1 空间索引加速
四叉树优化点集遍历:
6.2 并行计算优化
多阶段并行策略:
- 路径生成并行化:各搜索方向独立线程
- 区域优化分割:分区域独立优化再合并
- 障碍检测并行:多边形组同时检测
6.3 混合寻路架构
💎 7. 结论与展望
SPEV1Auxiliary算法通过创新的几何平面处理方式,克服了传统网格寻路算法的应用局限,特别在医疗导航、工业机器人等高精度导航场景展现出独特优势。其"生成-优化-精炼"的三阶段架构有效平衡了路径质量与计算效率。
未来研究方向:
- 机器学习引导:训练模型预测优化方向
- GPU并行加速:利用统一计算架构
- 动态障碍处理:实时边界更新机制
- 多尺度融合:结合深度学习特征提取
SPEV1Auxiliary代表了寻路算法从离散网格到连续几何的重要演进方向,随着计算能力的提升和算法优化的深入,该技术框架有望在更多高精度空间认知领域发挥关键作用。
实现:
namespace sspd2d
{using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Drawing;/// <summary>/// SPEV1Auxiliary 类提供几何平面寻路算法的核心功能/// 包括点面关系判定、线段相交检测和路径搜索优化等/// </summary>public static class SPEV1Auxiliary{/// <summary>/// 判断点是否在多边形组内(任一多边形内即返回true)/// </summary>/// <param name="p">待检测点</param>/// <param name="s">多边形组(多个多边形边界点列表)</param>/// <returns>点是否在多边形组内</returns>public static bool Pnpoly(Point p, IList<IList<Point>> s){if (s == null) // 多边形组为空直接返回false{return false;}// 遍历所有多边形foreach (IList<Point> points in s){// 调用单多边形检测方法if (Pnpoly(p, points)){return true;}}return false; // 所有多边形均不包含该点}/// <summary>/// 射线法判断点是否在多边形内/// </summary>/// <param name="p">待检测点</param>/// <param name="s">多边形边界点列表</param>/// <returns>点是否在多边形内</returns>public static bool Pnpoly(Point p, IList<Point> s){if (s == null || s.Count < 3) // 边界点无效时返回false{return false;}int nvert = s.Count; // 多边形顶点数bool c = false; // 点是否在多边形内的标志// 遍历多边形的每条边(从最后一个顶点开始)for (int i = 0, j = nvert - 1; i < nvert; j = i++){// 检查点是否在边的垂直范围内// 计算射线与边的交点,确定点的位置关系if (((s[i].Y > p.Y) != (s[j].Y > p.Y)) &&(p.X < (s[j].X - s[i].X) *(p.Y - s[i].Y) / (s[j].Y - s[i].Y) + s[i].X)){c = !c; // 每穿过一条边,状态翻转}}return c; // 返回最终状态}/// <summary>/// 检测两条线段是否相交/// </summary>/// <param name="a">线段1起点</param>/// <param name="b">线段1终点</param>/// <param name="c">线段2起点</param>/// <param name="d">线段2终点</param>/// <returns>线段是否相交</returns>public static bool Intersection(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d){// 快速排斥:检测两线段外包矩形是否重叠if (!(Math.Min(a.X, b.X) <= Math.Max(c.X, d.X) && Math.Min(c.Y, d.Y) <= Math.Max(a.Y, b.Y) && Math.Min(c.X, d.X) <= Math.Max(a.X, b.X) && Math.Min(a.Y, b.Y) <= Math.Max(c.Y, d.Y))){return false; // 外包矩形不重叠,线段不可能相交}// 跨立实验:检测两点是否分别在线段两侧double u, v, w, z; // 叉积结果// 计算向量AC与AB的叉积u = (c.X - a.X) * (b.Y - a.Y) - (b.X - a.X) * (c.Y - a.Y);// 计算向量AD与AB的叉积v = (d.X - a.X) * (b.Y - a.Y) - (b.X - a.X) * (d.Y - a.Y);// 计算向量CA与CD的叉积w = (a.X - c.X) * (d.Y - c.Y) - (d.X - c.X) * (a.Y - c.Y);// 计算向量CB与CD的叉积z = (b.X - c.X) * (d.Y - c.Y) - (d.X - c.X) * (b.Y - c.Y);// 叉积符号不同表示两点在线段两侧(使用误差阈值处理浮点精度)return (u * v <= 0.00000001 && w * z <= 0.00000001);}/// <summary>/// 检测线段与多边形组是否相交(任一多边形边界相交即返回true)/// </summary>/// <param name="x">线段起点</param>/// <param name="y">线段终点</param>/// <param name="shapes">多边形组</param>/// <returns>是否相交</returns>public static bool Intersection(Point x, Point y, IList<IList<Point>> shapes){if (shapes == null) // 多边形组为空{return false;}// 遍历所有多边形foreach (IList<Point> shape in shapes){// 检测线段与当前多边形边界是否相交if (Intersection(x, y, shape)){return true; // 相交则返回true}}return false; // 与所有多边形边界均不相交}/// <summary>/// 检测线段是否与多边形边界相交/// </summary>/// <param name="x">线段起点</param>/// <param name="y">线段终点</param>/// <param name="shape">多边形边界点列表</param>/// <returns>是否相交</returns>public static bool Intersection(Point x, Point y, IList<Point> shape){Point? parent = null; // 前一个边界点if (shape == null || shape.Count < 3) // 无效边界{return false;}// 从后向前遍历多边形的每条边for (int i = shape.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--){Point current = shape[i]; // 当前边界点// 跳过连续重复的起点(处理闭环多边形)if (i != 0 && current == shape[0] && parent == shape[0]){continue;}if (parent == null) // 首次循环时初始化前点(设为多边形最后一个非起点){int j = shape.Count - 1;while ((parent = shape[j]) != shape[0]) j--;}// 检测线段与当前边是否相交if (Intersection(parent.Value, current, x, y)){return true; // 相交返回true}parent = current; // 更新前一个点}return false; // 与所有边均不相交}/// <summary>/// 判断点是否在线段上(在给定误差范围内)/// </summary>/// <param name="p">待检测点</param>/// <param name="x">线段起点</param>/// <param name="y">线段终点</param>/// <param name="range">允许误差范围</param>/// <returns>点是否在线段上</returns>public static bool PointIsInLine(PointF p, PointF x, PointF y, double range){// 计算点P到线段起点的向量在AB方向上的投影长度double cross = (y.X - x.X) * (p.X - x.X) + (y.Y - x.Y) * (p.Y - x.Y);if (cross <= 0) // 投影在起点之前{return false;}// 计算线段长度的平方double d2 = (y.X - x.X) * (y.X - x.X) + (y.Y - x.Y) * (y.Y - x.Y);if (cross >= d2) // 投影在终点之后{return false;}// 计算投影比例rdouble r = cross / d2;// 计算垂足坐标(投影点)double px = x.X + (y.X - x.X) * r;double py = x.Y + (y.Y - x.Y) * r;// 计算点P到投影点的距离,判断是否在允许误差内return Math.Sqrt((p.X - px) * (p.X - px) + (py - p.Y) * (py - p.Y)) <= range;}/// <summary>/// 在点集中查找距离最近且无障碍的可达节点/// </summary>/// <param name="s">点集</param>/// <param name="flags">节点访问标记数组</param>/// <param name="from">起始节点索引</param>/// <param name="to">目标节点索引</param>/// <param name="shapes">障碍物集合</param>/// <param name="distances">当前累计距离(引用参数)</param>/// <returns>最近可达节点的索引</returns>private static int FindShortsNodeLine(IList<Point> s, bool[] flags, int from, int to, IList<IList<Point>> shapes, ref double distances){Tuple<int, double> m = null; // 存储当前最佳节点(索引和距离)Point key = s[from]; // 起点位置// 遍历所有节点for (int i = 0; i < s.Count; i++){if (flags[i]) // 跳过已访问节点{continue;}// 检测路径是否穿越障碍物if (Intersection(key, s[i], shapes)){continue; // 路径穿越障碍则跳过}// 计算到当前节点的距离double distance = GetDistance(key, s[i]);Tuple<int, double> n = new Tuple<int, double>(i, distance);if (i == to) // 直接找到目标节点{m = n;break; // 立即结束循环}// 更新当前最近可达节点if (m == null || m.Item2 > n.Item2){m = n;}}if (m == null) // 无可达节点{return -1;}flags[m.Item1] = true; // 标记节点为已访问return m.Item1; // 返回最佳节点索引}/// <summary>/// 计算两点间欧氏距离/// </summary>/// <param name="x">点1</param>/// <param name="y">点2</param>/// <returns>两点间距离</returns>public static double GetDistance(Point x, Point y){int x1 = Math.Abs(y.X - x.X);int y1 = Math.Abs(y.Y - x.Y);return Math.Sqrt(x1 * x1 + y1 * y1);}/// <summary>/// 主路径搜索方法(双向搜索)/// </summary>/// <param name="from">起点索引</param>/// <param name="to">终点索引</param>/// <param name="s">点集</param>/// <param name="shapes">障碍物集合</param>/// <returns>(总距离, 路径索引列表)</returns>public static Tuple<double, IList<int>> FindLine(int from, int to, IList<Point> s, IList<IList<Point>> shapes){// 检查输入有效性if (s == null || shapes == null || s.Count <= 0 || shapes.Count <= 0){return new Tuple<double, IList<int>>(0, new List<int>());}if (from < 0 || to < 0 || from >= s.Count || to >= s.Count || from == to){return new Tuple<double, IList<int>>(0, new List<int>());}// 双向搜索:从起点到终点 + 从终点到起点Tuple<double, IList<int>> bof = FindShortsUMLLine(from, to, s, shapes);Tuple<double, IList<int>> eof = FindShortsUMLLine(to, from, s, shapes);// 选择更短路径if (bof.Item1 <= eof.Item1){return bof;}else // 需要反转终点出发的路径{IList<int> pathways = eof.Item2;IList<int> lines = new List<int>(pathways.Count);// 路径反向处理for (int i = pathways.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--){lines.Add(pathways[i]);}return new Tuple<double, IList<int>>(eof.Item1, lines);}}/// <summary>/// UML路径优化(三点插值优化)/// </summary>private static Tuple<double, IList<int>> FindShortsUMLLine(int from, int to, IList<Point> s, IList<IList<Point>> shapes){// 获取初始路径Tuple<double, IList<int>> result = FindShortsZHTLine(from, to, s, shapes);IList<int> lines = result.Item2; bool restatistics = false; // 优化标记// 双层优化循环(默认执行2次)for (int cc = 0, kk = 2; cc < kk; cc++){// 遍历路径中间节点(跳过首尾)for (int i = 1, n = lines.Count - 1; i < n; i++){int left = lines[i - 1]; // 左邻节点int middle = lines[i]; // 当前中间节点int right = lines[i + 1]; // 右邻节点Tuple<double, int> min = null; // 最佳替代节点// 寻找更优的中间节点for (int j = 0; j < s.Count; j++){// 检查新节点与相邻节点的连接无障碍if (!Intersection(s[j], s[right], shapes) &&!Intersection(s[j], s[left], shapes)){// 计算新路径长度double distance = GetDistance(s[j], s[left]) + GetDistance(s[right], s[j]);// 更新最佳替代节点if (min == null || min.Item1 > distance){min = new Tuple<double, int>(distance, j);}}}// 应用优化if (min != null){int nn = min.Item2;restatistics = true; // 标记需要重新计算路径lines[i] = nn; // 替换中间节点}}}// 如果路径被优化过,清理重复节点并重新计算距离if (restatistics){IList<int> pathways = new List<int>(lines.Count);ISet<int> set = new HashSet<int>();// 去重处理for (int i = 0; i < lines.Count; i++){int nn = lines[i];if (!set.Add(nn)) // 已存在则跳过{continue;}pathways.Add(nn);}// 计算新路径总长度result = new Tuple<double, IList<int>>(GetDistance(s, pathways), pathways);}return result;}/// <summary>/// ZHT路径优化(冗余节点剪枝)/// </summary>private static Tuple<double, IList<int>> FindShortsZHTLine(int from, int to, IList<Point> s, IList<IList<Point>> shapes){// 获取初始路径Tuple<double, IList<int>> result = FindShortsRANLine(from, to, s, shapes);IList<int> lines = result.Item2;// 双层优化循环(默认执行2次)for (int cc = 0, kk = 2; cc < kk; cc++){for (int i = 0; i < lines.Count; i++){int key = lines[i]; // 当前关键节点// 第一轮:移除可直达终点的后续节点for (int j = 0; j < lines.Count; j++){int current = lines[j];if (key == current) continue; // 跳过自身// 可直达终点且不是起终点if (!Intersection(s[current], s[to], shapes)){// 移除当前节点到终点间的所有非起终点节点for (int ii = j + 1; ii < lines.Count;){int pp = lines[ii];if (pp == to || pp == from){break; // 保护起终点}lines.RemoveAt(ii);}continue;}}// 第二轮:移除可跨段连接的冗余节点for (int j = 0; j < lines.Count; j++){int current = lines[j];if (key == current) continue; // 跳过自身int depth = Math.Abs(j - i); // 节点深度差// 可跨段连接且深度足够(>=3)if (!Intersection(s[key], s[current], shapes) && depth >= 3){// 移除中间节点for (int ii = i, ll = i; ii < j; ii++){int pp = lines[ii];if (pp == from || pp == to){ll++; // 保护起终点continue;}lines.RemoveAt(ll);}// 检查并移除可能的后续冗余节点if (lines.Count >= 3 && j + 2 < lines.Count && !Intersection(s[key], s[lines[j + 1]], shapes) &&!Intersection(s[key], s[lines[j + 2]], shapes)){lines.RemoveAt(j + 1);}}}}}// 清理路径起始点int n = -1;do{n = lines.IndexOf(from);if (n < 0) continue;// 移除起始点前的冗余节点for (int i = n; i <= n; i++){lines.RemoveAt(0);}} while (n > -1);// 确保起点在首位if (lines.Count > 0 && lines[0] != from){lines.Insert(0, from);}// 确保终点在末位if (lines.Count > 0 && lines[lines.Count - 1] != to){lines.Add(to);}// 去除重复节点IList<int> pathways = new List<int>();ISet<int> set = new HashSet<int>();for (int i = 0; i < lines.Count; i++){n = lines[i];if (!set.Add(n)){continue;}pathways.Add(n);}// 计算优化后路径总长度return new Tuple<double, IList<int>>(GetDistance(s, pathways), pathways);}/// <summary>/// RAN路径优化(碰撞检测与路径修正)/// </summary>private static Tuple<double, IList<int>> FindShortsRANLine(int from, int to, IList<Point> s, IList<IList<Point>> shapes){// 获取初始路径Tuple<double, IList<int>> linetrace = FindShortsNAPLine(from, to, s, shapes);IList<int> lines = linetrace.Item2;bool unintersection = true; // 无碰撞标志int? parent = null; // 父节点// 碰撞检测与路径修正(执行2次)for (int cc = 0; cc < 2; cc++){parent = null;// 遍历路径节点for (int i = 0; i < lines.Count; i++){if (lines.Count > s.Count) // 防止无限增长{break;}int current = lines[i];// 非起点且有碰撞if (parent != null && Intersection(s[parent.Value], s[current], shapes)){// 重新计算这一段路径IList<int> node = FindShortsNAPLine(parent.Value, lines[i], s, shapes).Item2;// 插入新节点(跳过首尾)for (int jj = 1, kk = i, nn = (node.Count - 1); jj < nn; jj++, kk++){unintersection = false; // 标记存在碰撞lines.Insert(kk, node[jj]); // 插入新节点}}parent = lines[i]; // 更新父节点}}// 冗余节点清理(执行1次)for (int c = 0; c < 1; c++){parent = null;for (int i = 0; i < lines.Count; i++){if (parent == null){parent = lines[i];}else{// 无碰撞则继续,有碰撞则移除当前节点if (!Intersection(s[parent.Value], s[lines[i]], shapes)){parent = lines[i];}else{parent = lines[i];lines.RemoveAt(i); // 移除碰撞节点}}}}// 如果无碰撞直接返回,否则重新计算路径长度if (unintersection){return linetrace;}double distances = GetDistance(s, lines);return new Tuple<double, IList<int>>(distances, lines);}/// <summary>/// NAP路径优化(双向搜索基础)/// </summary>private static Tuple<double, IList<int>> FindShortsNAPLine(int from, int to, IList<Point> s, IList<IList<Point>> shapes){// 双向搜索:正向+反向Tuple<double, IList<int>> bof = FindShortsNEGLine(from, to, s, shapes);Tuple<double, IList<int>> eof = FindShortsNEGLine(to, from, s, shapes);// 选择更优路径(路径更短或节点更少)if (bof.Item1 > 0 || bof.Item2.Count > eof.Item2.Count){return bof;}else{IList<int> pathways = eof.Item2;IList<int> lines = new List<int>(pathways.Count);// 反向路径转正向for (int i = pathways.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--){lines.Add(pathways[i]);}return new Tuple<double, IList<int>>(eof.Item1, lines);}}/// <summary>/// 计算路径总距离/// </summary>private static double GetDistance(IList<Point> s, IList<int> pathways){double distances = 0;int? parent = null; // 上一节点if (pathways != null && s != null){// 遍历路径节点并累加距离for (int i = 0; i < pathways.Count; i++){int current = pathways[i];if (parent != null) // 非第一个节点{distances += GetDistance(s[current], s[parent.Value]);}parent = current; // 更新前一节点}}return distances; // 返回总距离}/// <summary>/// NEG路径搜索(核心贪心算法)/// </summary>private static Tuple<double, IList<int>> FindShortsNEGLine(int from, int to, IList<Point> s, IList<IList<Point>> shapes){bool[] flags = new bool[s.Count]; // 节点访问标记flags[from] = true; // 标记起点int r = from; // 当前节点double distances = 0;List<int> pathways = new List<int>(); // 路径列表if (from == to) // 起终点相同{pathways.Add(from);}else{// 路径搜索循环do{// 查找下一个可达节点r = FindShortsNodeLine(s, flags, r, to, shapes, ref distances);if (r == -1) // 无可达节点(路径中断){int i = pathways.Count - 1;if (i >= 0 && i < pathways.Count){pathways.RemoveAt(i); // 回退一步}i = pathways.Count - 1;if (i >= 0 && i < pathways.Count){r = pathways[i]; // 重置当前节点}continue; // 重试}Point key = s[r]; // 当前节点位置int? shortspathnode = null; // 最短连接节点double? shortsnodedistance = null; // 最短距离// 检查与已有路径节点的连接性for (int i = 0; i < pathways.Count; i++){if (Intersection(key, s[pathways[i]], shapes)){continue; // 存在障碍则跳过}double distance = GetDistance(key, s[i]);// 更新最佳连接点if (shortsnodedistance == null){shortspathnode = pathways[i];shortsnodedistance = distance;}else if (shortsnodedistance > distance){int lastshortspathnode = shortspathnode.Value;shortspathnode = pathways[i];shortsnodedistance = distance;pathways.Remove(lastshortspathnode); // 移除原连接点}}pathways.Add(r); // 加入新节点} while (r != -1 && r != to); // 直到无路可走或到达终点if (pathways.Count > 0){pathways.Insert(0, from); // 插入起点}}// 计算最终路径距离distances = GetDistance(s, pathways);return new Tuple<double, IList<int>>(distances, pathways);}/// <summary>/// 计算两点间距离(封装方法)/// </summary>public static double GetDistance(int from, int to, IList<Point> s, IList<IList<Point>> shapes){return FindLine(from, to, s, shapes).Item1;}/// <summary>/// 寻路接口(带距离输出)/// </summary>public static IList<int> FindLine(int from, int to, IList<Point> s, IList<IList<Point>> shapes, out double distances){Tuple<double, IList<int>> trace = SPEV1Auxiliary.FindLine(from, to, s, shapes);distances = trace.Item1;return trace.Item2;}/// <summary>/// 寻路主接口(P*算法)/// </summary>public static IList<int> GetLine(int from, int to, IList<Point> s, IList<IList<Point>> shapes){// 获取路径(距离+节点列表)Tuple<double, IList<int>> way = FindLine(from, to, s, shapes);IList<int> pathways = way.Item2;if (pathways == null) // 空路径处理{pathways = new List<int>();}return pathways; // 返回节点索引列表}}
}
附录:本技术分析基于.NET 4.0环境,在实际医疗导航系统中部署需要配合UWB高精度定位系统及3D建筑信息模型(BIM),完整系统架构参考ISO/TR 37167智慧医疗导航标准。
