02 流程流转
审批流程图
如下图,在此流程图中,存在两个UserTask节点,第一个节点是主管审批,第二个节点是产品经理审批,两个节点中间有一个排他网关,此网关用来对主管审批的结果进行判断,如果主管审批通过,则流程走到产品经理审批节点,如果主管审批拒绝,则流程走到结束节点。
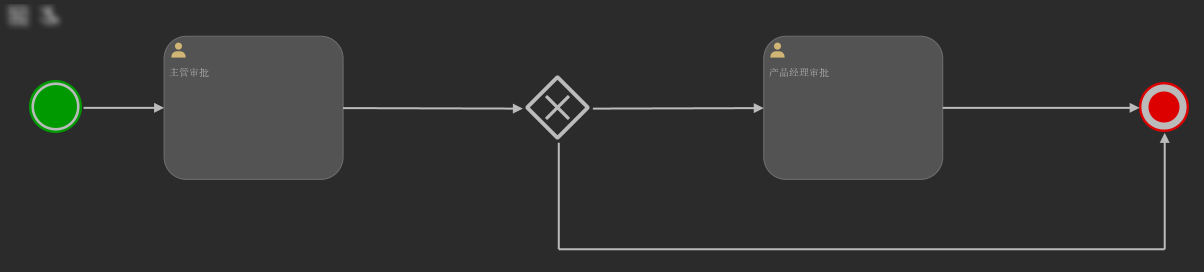
主管审批节点通过UEL表达式${assignManager}动态赋值,产品经理审批节点通过UEL表达式${assignProductLineManager}动态赋值,网关节点通过UEL表达式${isPass}动态赋值。
流程流转
上文 《01 启动流程实例》 讲到在完成流程实例的启动后,流程将通过commandContext.getAgenda().planContinueProcessOperation(execution)流转到下一个节点。本文将以此代码为入口,研究流程如何流转到下一个节点。
上面的代码中,getAgent 方法返回来一个 ActivitiEngineAgenda 接口,此接口的实现类是DefaultActivitiEngineAgenda,它的内部成员属性如下,operations 在这里充当 FIFO 队列,用来存储将要执行的 AbstractOperation (本质上是一个 Runnable 接口)操作,而 CommandContext 则是命令上下文。
public class DefaultActivitiEngineAgenda implements ActivitiEngineAgenda {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DefaultActivitiEngineAgenda.class);protected LinkedList<Runnable> operations = new LinkedList<Runnable>();protected CommandContext commandContext;public DefaultActivitiEngineAgenda(CommandContext commandContext) {this.commandContext = commandContext;}// 省略部分代码
}ContinueProcessOperation 操作(第一次)
构造 ContinueProcessOperation
planContinueProcessOperation(execution) 在 DefaultActivitiEngineAgenda 中的实现如下,把传入的 execution 和 commandContext 构造一个 ContinueProcessOperation 实例,并放入了 operations 队列中,
@Override
public void planContinueProcessOperation(ExecutionEntity execution) {planOperation(new ContinueProcessOperation(commandContext, execution));
}@Override
public void planOperation(Runnable operation) {// 将 operation 任务放到 operations 队列中,等待定时任务从队列中取出任务并执行operations.add(operation);if (operation instanceof AbstractOperation) {ExecutionEntity execution = ((AbstractOperation) operation).getExecution();if (execution != null) {// 这里添加的内容,在 org/activiti/engine/impl/interceptor/CommandInvoker的execute(CommandConfig, Command<T>) // 中有使用,目的是告诉 CommandInvoker 有待执行的 AbstractOperationcommandContext.addInvolvedExecution(execution);}}logger.debug("Operation {} added to agenda", operation.getClass());
}ContinueProcessOperation 类定义如下:
public abstract class AbstractOperation implements Runnable {// 省略部分代码
}public class ContinueProcessOperation extends AbstractOperation {// 省略部分代码
}执行 ContinueProcessOperation
由异步任务执行器 org/activiti/engine/impl/asyncexecutor/DefaultAsyncJobExecutor 中的 AcquireAsyncJobsDueRunnable 调用 DefaultActivitiEngineAgenda 的 getNextOperation 来取出 operations 队列中的 AbstractOperation 任务,然后由 CommandInvoker 来执行(异步任务执行器 DefaultAsyncJobExecutor 是在我们调用 ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine() 创建 ProcessEngine 阶段完成的初始化)。
CommandInvoker 中执行 AbstractOperation 任务的代码是下面这一段
protected void executeOperations(final CommandContext commandContext) {// 任务不是空的while (!commandContext.getAgenda().isEmpty()) {// 取出任务Runnable runnable = commandContext.getAgenda().getNextOperation();// 执行任务executeOperation(runnable);}
}public void executeOperation(Runnable runnable) {// ContinueProcessOperation 继承 AbstractOperation,所以这个if条件的值是true,进入此if内部逻辑// 除了 ContinueProcessOperation 外, 其它继承 AbstractOperation 的Operation类都能进入这个if逻辑if (runnable instanceof AbstractOperation) {AbstractOperation operation = (AbstractOperation) runnable;// Execute the operation if the operation has no execution (i.e. it's an operation not working on a process instance)// or the operation has an execution and it is not endedif (operation.getExecution() == null || !operation.getExecution().isEnded()) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Executing operation {} ", operation.getClass());}// 直接调用 ContinueProcessOperation(Runnable)的run方法,// 会不会开启异步线程?不会,直接调用run方法,就是调用一个普通的方法runnable.run();}} else {// 直接调用 Runnable 的run方法,会不会开启异步线程?不会,直接调用run方法,就是调用一个普通的方法runnable.run();}
}执行 ContinueProcessOperation 的 run() 方法后,来到了 ContinueProcessOperation 中
public class ContinueProcessOperation extends AbstractOperation {// 省略部分代码/*** 当 ContinueProcessOperation 操作被执行时,以 run 方法作为入口*/@Overridepublic void run() {// 第一次执行这个逻辑,取出来的 currentFlowElement 是一个 StartEvent,StartEvent 是 FlowNode 的子类FlowElement currentFlowElement = getCurrentFlowElement(execution);if (currentFlowElement instanceof FlowNode) {// 继续执行 FlowNode 类型的类,StartEvent会走这个方法continueThroughFlowNode((FlowNode) currentFlowElement);} else if (currentFlowElement instanceof SequenceFlow) {// 继续执行 SequenceFlow 类型的类continueThroughSequenceFlow((SequenceFlow) currentFlowElement);} else {throw new ActivitiException("Programmatic error: no current flow element found or invalid type: " + currentFlowElement + ". Halting.");}}protected void continueThroughFlowNode(FlowNode flowNode) {// Check if it's the initial flow element. If so, we must fire the execution listeners for the process tooif (flowNode.getIncomingFlows() != null&& flowNode.getIncomingFlows().size() == 0&& flowNode.getSubProcess() == null) {executeProcessStartExecutionListeners();}// For a subprocess, a new child execution is created that will visit the steps of the subprocess// The original execution that arrived here will wait until the subprocess is finished// and will then be used to continue the process instance.if (flowNode instanceof SubProcess) {createChildExecutionForSubProcess((SubProcess) flowNode);}if (flowNode instanceof Activity && ((Activity) flowNode).hasMultiInstanceLoopCharacteristics()) {// the multi instance execution will look at asyncexecuteMultiInstanceSynchronous(flowNode);} else if (forceSynchronousOperation || !flowNode.isAsynchronous()) {// 同步执行,StartEvent走的是这里executeSynchronous(flowNode);} else {// 异步执行executeAsynchronous(flowNode);}}/*** 同步执行* @param flowNode*/protected void executeSynchronous(FlowNode flowNode) {// 调用HistoryManager记录流程活动开始了,这里并不是单单指StartEvent活动,而是所有活动commandContext.getHistoryManager().recordActivityStart(execution);// Execution listener: event 'start'// 执行 StartEvent 上的监听器,发布 Start 的 Event 事件if (CollectionUtil.isNotEmpty(flowNode.getExecutionListeners())) {executeExecutionListeners(flowNode, ExecutionListener.EVENTNAME_START);}// Execute any boundary events, sub process boundary events will be executed from the activity behaviorif (!inCompensation && flowNode instanceof Activity) { // Only activities can have boundary events// 获取节点上的边界事件,如果有,就执行List<BoundaryEvent> boundaryEvents = ((Activity) flowNode).getBoundaryEvents();if (CollectionUtil.isNotEmpty(boundaryEvents)) {executeBoundaryEvents(boundaryEvents, execution);}}// Execute actual behavior// 取出节点上的行为ActivityBehavior activityBehavior = (ActivityBehavior) flowNode.getBehavior();// 当 activityBehavior 不为空,走此方法,此方法后续也会调用 planTakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation// activityBehavior 表示一个节点上拥有的行为// StartEvent 节点的行为是 NoneStartEventActivityBehavior,没有做其它业务,仅仅是过度// UserTask 节点的行为是 UserTaskActivityBehavior,这个行为会把任务写入到数据库后,等待用户完成任务,流程才会继续走下去if (activityBehavior != null) {// 执行节点上的行为,StartEvent后走的是这里,executeActivityBehavior(activityBehavior, flowNode);} else {logger.debug("No activityBehavior on activity '{}' with execution {}", flowNode.getId(), execution.getId());// StartEvent后不走这里,计划执行 TakeOutgoingSequenceFlows 操作,这个操作是一个连线行为,第一步先找出当前节点的出口,第二步从出口走到下一个节点。Context.getAgenda().planTakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation(execution, true);}}/*** 执行节点上的行为* @param activityBehavior* @param flowNode*/protected void executeActivityBehavior(ActivityBehavior activityBehavior,FlowNode flowNode) {logger.debug("Executing activityBehavior {} on activity '{}' with execution {}",activityBehavior.getClass(),flowNode.getId(),execution.getId());if (Context.getProcessEngineConfiguration() != null && Context.getProcessEngineConfiguration().getEventDispatcher().isEnabled()) {Context.getProcessEngineConfiguration().getEventDispatcher().dispatchEvent(ActivitiEventBuilder.createActivityEvent(ActivitiEventType.ACTIVITY_STARTED,flowNode.getId(),flowNode.getName(),execution.getId(),execution.getProcessInstanceId(),execution.getProcessDefinitionId(),flowNode));}try {// 这方法里面后续会执行 planTakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation// 执行 StartEvent 的 NoneStartEventActivityBehavior 行为activityBehavior.execute(execution);} catch (RuntimeException e) {if (LogMDC.isMDCEnabled()) {LogMDC.putMDCExecution(execution);}throw e;}}
}
执行 NoneStartEventActivityBehavior
因为 NoneStartEventActivityBehavior 是空实现,但它继承自 FlowNodeActivityBehavior ,拥有了父类的能力,所以 activityBehavior.execute(execution) 实际执行的是父类FlowNodeActivityBehavior 的 execute(DelegateExecution) 方法。
public class NoneStartEventActivityBehavior extends FlowNodeActivityBehavior {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;// Nothing to see here.// The default behaviour of the BpmnActivity is exactly what// a none start event should be doing.}在 execute(DelegateExecution) 方法中调用了 leave(execution) 方法,详情见代码
public abstract class FlowNodeActivityBehavior implements TriggerableActivityBehavior {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;protected BpmnActivityBehavior bpmnActivityBehavior = new BpmnActivityBehavior();/*** Default behaviour: just leave the activity with no extra functionality.* NoneStartEventActivityBehavior 自己没有实现 execute 方法,所以会调用父类* FlowNodeActivityBehavior 的 execute 方法*/public void execute(DelegateExecution execution) {leave(execution);}/*** Default way of leaving a BPMN 2.0 activity: evaluate the conditions on the outgoing sequence flow and take those that evaluate to true.* 离开 BPMN 2.0 activity的默认方式:评估 Outgoing sequence 流上的条件,并选取那些评估为 true 的条件*/public void leave(DelegateExecution execution) {// 走到 bpmnActivityBehavior 中的 performDefaultOutgoingBehavior 方法bpmnActivityBehavior.performDefaultOutgoingBehavior((ExecutionEntity) execution);}
}BpmnActivityBehavior 的 performDefaultOutgoingBehavior 内部调用 Context.getAgenda().planTakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation(ExecutionEntity, boolean) 方法,这里的 Context.getAgenda() 获取到的 Agenda 和上面的 Agenda 是同一个,取到 Agenda后,调用了它的 planTakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation(ExecutionEntity, boolean) 方法,此方法将产生连线行为,将 StartEvent 根据 Process 流程模型的定义连接到下一个节点。
public class BpmnActivityBehavior implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;/*** Performs the default outgoing BPMN 2.0 behavior, which is having parallel paths of executions for the outgoing sequence flow.* <p>* More precisely: every sequence flow that has a condition which evaluates to true (or which doesn't have a condition), is selected for continuation of the process instance. If multiple sequencer* flow are selected, multiple, parallel paths of executions are created.*/public void performDefaultOutgoingBehavior(ExecutionEntity activityExecution) {performOutgoingBehavior(activityExecution,true,false);}/*** Actual implementation of leaving an activity.* @param execution The current execution context* @param checkConditions Whether or not to check conditions before determining whether or not to take a transition.* @param throwExceptionIfExecutionStuck If true, an {@link ActivitiException} will be thrown in case no transition could be found to leave the activity.* 最后在这个方法里调用了 planTakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation 方法,用于走出当前就节点,走到下一个节点*/protected void performOutgoingBehavior(ExecutionEntity execution,boolean checkConditions,boolean throwExceptionIfExecutionStuck) {Context.getAgenda().planTakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation(execution,true);}
}TakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation 操作
构造 TakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation
DefaultActivitiEngineAgenda 的 planTakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation 方法如下,将 ExecutionEntity 封装成 TakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation,再放入 operations 队列中。
public class DefaultActivitiEngineAgenda implements ActivitiEngineAgenda {@Overridepublic void planTakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation(ExecutionEntity execution, boolean evaluateConditions) {planOperation(new TakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation(commandContext, execution, evaluateConditions));}
}执行 TakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation
TakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation 也和 ContinueProcessOperation 一样是 AbstractionOperation 的子类,同样也是由定时任务通过 CommandInvoker 来调用 TakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation 中的 run() 方法。
public class TakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation extends AbstractOperation {// 省略部分代码@Overridepublic void run() {FlowElement currentFlowElement = getCurrentFlowElement(execution);// Compensation checkif ((currentFlowElement instanceof Activity)&& (((Activity) currentFlowElement)).isForCompensation()) {cleanupCompensation();return;}// When leaving the current activity, we need to delete any related execution (eg active boundary events)// 清除当前节点的一些附属信息cleanupExecutions(currentFlowElement);// 当前 currentFlowElement 是一个 StartEvent,StartEvent 是 FlowNode 的子类if (currentFlowElement instanceof FlowNode) {// 处理 FlowNode 流节点handleFlowNode((FlowNode) currentFlowElement);} else if (currentFlowElement instanceof SequenceFlow) {// 处理 SequenceFlow 系列流handleSequenceFlow();}}/*** uai 处理流节点* @param flowNode*/protected void handleFlowNode(FlowNode flowNode) {// 记录 StartEvent 活动结束handleActivityEnd(flowNode);if (flowNode.getParentContainer() != null&& flowNode.getParentContainer() instanceof AdhocSubProcess) {handleAdhocSubProcess(flowNode);} else {// StartEvent走这里, 离开流节点leaveFlowNode(flowNode);}}/*** 离开流节点* @param flowNode*/protected void leaveFlowNode(FlowNode flowNode) {// 省略部分代码String defaultSequenceFlowId = null;if (flowNode instanceof Activity) {defaultSequenceFlowId = ((Activity) flowNode).getDefaultFlow();} else if (flowNode instanceof Gateway) {defaultSequenceFlowId = ((Gateway) flowNode).getDefaultFlow();}// Determine which sequence flows can be used for leaving// 声明 List<SequenceFlow> 实例,用来存储符合外出流条件的 SequenceFlowList<SequenceFlow> outgoingSequenceFlows = new ArrayList<SequenceFlow>();// 获取 StartEvent 节点可以外出的顺序流,并放到外出顺序流集合 outgoingSequenceFlows 中for (SequenceFlow sequenceFlow : flowNode.getOutgoingFlows()) {String skipExpressionString = sequenceFlow.getSkipExpression();// 通过 isSkipExpressionEnabled 判断 execution 是否开启了跳过表达式if (!SkipExpressionUtil.isSkipExpressionEnabled(execution, skipExpressionString)) {if (!evaluateConditions || (evaluateConditions && ConditionUtil.hasTrueCondition(sequenceFlow, execution)&& (defaultSequenceFlowId == null || !defaultSequenceFlowId.equals(sequenceFlow.getId())))) {// 符合外出流条件的放入到 outgoingSequenceFlowsoutgoingSequenceFlows.add(sequenceFlow);}} else if (flowNode.getOutgoingFlows().size() == 1 || SkipExpressionUtil.shouldSkipFlowElement(commandContext,execution,skipExpressionString)) {// The 'skip' for a sequence flow means that we skip the condition, not the sequence flow.// 符合外出流条件的放入到 outgoingSequenceFlowsoutgoingSequenceFlows.add(sequenceFlow);}}// Check if there is a default sequence flowif (outgoingSequenceFlows.size() == 0 && evaluateConditions) { // The elements that set this to false also have no support for default sequence flowif (defaultSequenceFlowId != null) {for (SequenceFlow sequenceFlow : flowNode.getOutgoingFlows()) {if (defaultSequenceFlowId.equals(sequenceFlow.getId())) {// 符合外出流条件的放入到 outgoingSequenceFlowsoutgoingSequenceFlows.add(sequenceFlow);break;}}}}// No outgoing found. Ending the execution// 如果没有当前节点没有可以外出的顺序流,则流程到当前节点后,设置为结束。StartEvent不走这里if (outgoingSequenceFlows.size() == 0) {if (flowNode.getOutgoingFlows() == null || flowNode.getOutgoingFlows().size() == 0) {logger.debug("No outgoing sequence flow found for flow node '{}'.", flowNode.getId());// 当前节点没有可以外出的顺序流,走向结束节点Context.getAgenda().planEndExecutionOperation(execution);} else {throw new ActivitiException("No outgoing sequence flow of element '" + flowNode.getId() + "' could be selected for continuing the process");}} else {// Leave, and reuse the incoming sequence flow, make executions for all the others (if applicable)ExecutionEntityManager executionEntityManager = commandContext.getExecutionEntityManager();List<ExecutionEntity> outgoingExecutions = new ArrayList<ExecutionEntity>(flowNode.getOutgoingFlows().size());// 当前节点有多个可以外出的出口顺序流,取出第一个SequenceFlow sequenceFlow = outgoingSequenceFlows.get(0);// Reuse existing one/*** uai* 给已经存在的execution(ExecutionEntity)实例更新状态,表示流程走到了 sequenceFlow 这个节点.* Process流程模型可以理解为一条高速公路,execution(ExecutionEntity)理解为一辆车,高速公路上有多个服务区,每个服务区是一个 sequenceFlow。* 现有一辆货车,我们规定它每走到一个服务区时车辆要加油或者司机要休息一下,在加油或者休息时司机需要把当前所在的服务区(sequenceFlow)告诉他的老板,让* 老板知道货运到哪里了(也就是在整个审批流程中,setCurrentFlowElement这一操作,让我们知道流程走到哪里了)*/// 将 execution 中的 CurrentFlowElement 从之前的 StartEvent 更新为 SequenceFlowexecution.setCurrentFlowElement(sequenceFlow);execution.setActive(true);// 将从 StartEvent 中出发的 execution 实例放入到 outgoingExecutions 链表中outgoingExecutions.add((ExecutionEntity) execution);// Executions for all the other one// 有多条出口,我的审批流程图中,StartEvent 只有一条外出流,所以不进入这个 if 语句if (outgoingSequenceFlows.size() > 1) {for (int i = 1; i < outgoingSequenceFlows.size(); i++) {// 如果当前 execution 有 parent,则大家共用这个 parent,// 如果当前 execution 没有 parent,则用当前 execution 作为 parent,ExecutionEntity parent = execution.getParentId() != null ? execution.getParent() : execution;// 根据 父ExecutionEntity 信息,创建 子ExecutionEntity 实例,相当于高速公里有分叉路ExecutionEntity outgoingExecutionEntity = commandContext.getExecutionEntityManager().createChildExecution(parent);SequenceFlow outgoingSequenceFlow = outgoingSequenceFlows.get(i);// 给 子ExecutionEntity 实例设置当前节点为 outgoingSequenceFlowoutgoingExecutionEntity.setCurrentFlowElement(outgoingSequenceFlow);// 存储到数据库executionEntityManager.insert(outgoingExecutionEntity);outgoingExecutions.add(outgoingExecutionEntity);}}// Leave (only done when all executions have been made, since some queries depend on this)// 把 outgoingExecution 放入到 Agenda 的队列中,计划离开当前节点,前往下一个节点// 这里可能有多个节点,所以通过遍历走所有的外出流,当前的审批流程图中,只有一条外出流,所以 outgoingExecutions 的大小是1for (ExecutionEntity outgoingExecution : outgoingExecutions) {// 准备执行 ContinueProcessOperation 操作Context.getAgenda().planContinueProcessOperation(outgoingExecution);}}}
}上面这个代码,最重要的是从 StartEvent 节点的信息中找到了外出流 (SequenceFlow),随即调用 execution 的 setCurrentFlowElement 把活跃节点从之前的 StartEvent 更新为 SequenceFlow,这个操作表示流程从 StartEvent 走到了 SequenceFlow 这里。后续将从 SequenceFlow 继续走到下个节点。
分析上面代码发现流程最终又走到了 Context.getAgenda().planContinueProcessOperation(ExecutionEntity) 方法去执行 ContinueProcessOperation 中的业务,是不是重复执行了?
表面上看是重复执行了,但实际上有一些微妙的变化,这个变化是:传给 planContinueProcessOperation 方法的 execution 实例,它的 currentFlowElement 从 StartEvent 变成了 SequenceFlow。这个变化就会使得流程进入到 ContinueProcessOperation 的 else if 语句中,而不是第一次刚进来的 if 语句。
public class ContinueProcessOperation extends AbstractOperation {// 省略部分代码/*** 当 ContinueProcessOperation 操作被执行时,以 run 方法作为入口*/@Overridepublic void run() {// 第一次执行这个逻辑,取出来的 currentFlowElement 是一个 StartEvent,StartEvent 是 FlowNode 的子类FlowElement currentFlowElement = getCurrentFlowElement(execution);if (currentFlowElement instanceof FlowNode) {// 继续执行 FlowNode 类型的类,StartEvent会走这个方法continueThroughFlowNode((FlowNode) currentFlowElement);} else if (currentFlowElement instanceof SequenceFlow) {// 继续执行 SequenceFlow 类型的类continueThroughSequenceFlow((SequenceFlow) currentFlowElement);} else {throw new ActivitiException("Programmatic error: no current flow element found or invalid type: " + currentFlowElement + ". Halting.");}}
}ContinueProcessOperation 操作(第二次)
构造 ContinueProcessOperation
忽略阐述此重复内容。
执行 ContinueProcessOperation
接上面的内容,流程进入到 ContinueProcessOperation 的 else if 语句中,而不是第一次刚进来的 if 语句。
else if 语句中调用的方法是 continueThroughSequenceFlow(SequenceFlow)。
/*** 执行 SequenceFlow 逻辑* @param sequenceFlow*/
protected void continueThroughSequenceFlow(SequenceFlow sequenceFlow) {// Execution listener. Sequenceflow only 'take' makes sense ... but we've supported all three since the beginning// 执行 SequenceFlow 上的监听器if (CollectionUtil.isNotEmpty(sequenceFlow.getExecutionListeners())) {executeExecutionListeners(sequenceFlow,ExecutionListener.EVENTNAME_START);executeExecutionListeners(sequenceFlow,ExecutionListener.EVENTNAME_TAKE);executeExecutionListeners(sequenceFlow,ExecutionListener.EVENTNAME_END);}// Firing event that transition is being takenif (Context.getProcessEngineConfiguration() != null && Context.getProcessEngineConfiguration().getEventDispatcher().isEnabled()) {FlowElement sourceFlowElement = sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement();FlowElement targetFlowElement = sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement();Context.getProcessEngineConfiguration().getEventDispatcher().dispatchEvent(ActivitiEventBuilder.createSequenceFlowTakenEvent((ExecutionEntity) execution,ActivitiEventType.SEQUENCEFLOW_TAKEN,sequenceFlow.getId(),sourceFlowElement != null ? sourceFlowElement.getId() : null,sourceFlowElement != null ? (String) sourceFlowElement.getName() : null,sourceFlowElement != null ? sourceFlowElement.getClass().getName() : null,sourceFlowElement != null ? ((FlowNode) sourceFlowElement).getBehavior() : null,targetFlowElement != null ? targetFlowElement.getId() : null,targetFlowElement != null ? targetFlowElement.getName() : null,targetFlowElement != null ? targetFlowElement.getClass().getName() : null,targetFlowElement != null ? ((FlowNode) targetFlowElement).getBehavior() : null));}// 获取 sequenceFlow 的下一个节点FlowElement targetFlowElement = sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement();// 更新 execution 当前所处的节点,前面更新过两次,第一次设置为 StartEvent,第二次设置为 SequenceFlow,当前第三次更新为审批流程图中的UserTaskexecution.setCurrentFlowElement(targetFlowElement);logger.debug("Sequence flow '{}' encountered. Continuing process by following it using execution {}",sequenceFlow.getId(),execution.getId());// 继续前往下个节点,在这里又执行了一次 planContinueProcessOperationContext.getAgenda().planContinueProcessOperation(execution);
}上面代码中,最后一行又是 Context.getAgenda().planContinueProcessOperation(ExecutionEntity) 方法,此方法去执行 ContinueProcessOperation 中的业务。这一次传给 planContinueProcessOperation 方法的 execution 实例,它的 currentFlowElement 从 SequenceFlow 变成了 UserTask。
ContinueProcessOperation 操作(第三次)
构造 ContinueProcessOperation
忽略阐述此重复内容。
执行 ContinueProcessOperation
UserTask 和 StartEvent 一样,它也是 FlowNode 的子类,因此在 ContinueProcessOperation 的 run 方法中,流程进入到 if 语句 中。
public class ContinueProcessOperation extends AbstractOperation {// 省略部分代码/*** 当 ContinueProcessOperation 操作被执行时,以 run 方法作为入口*/@Overridepublic void run() {// 第一次执行这个逻辑,取出来的 currentFlowElement 是一个 StartEvent,StartEvent 是 FlowNode 的子类FlowElement currentFlowElement = getCurrentFlowElement(execution);if (currentFlowElement instanceof FlowNode) {// 继续执行 FlowNode 类型的类,StartEvent会走这个方法continueThroughFlowNode((FlowNode) currentFlowElement);} else if (currentFlowElement instanceof SequenceFlow) {// 继续执行 SequenceFlow 类型的类continueThroughSequenceFlow((SequenceFlow) currentFlowElement);} else {throw new ActivitiException("Programmatic error: no current flow element found or invalid type: " + currentFlowElement + ". Halting.");}}
}进入后,大致逻辑和 StartEvent 相似,但不同的点在于 UserTask 上的节点行为是 UserTaskActivityBehavior,此行为不像 StartEvent 的 NoneStartEventActivityBehavior 行为,UserTaskActivityBehavior 它定义了这个 UserTask 上的具体行为。在经过这个行为后,流程会暂时停在 UserTask 节点上,等待用户审批完成才会继续走下去。UserTask 节点的具体的行为见下一篇文章03 节点行为。下面这个代码和前面是重复的,为方便观察,所以粘贴一份。
/*** 同步执行* @param flowNode*/
protected void executeSynchronous(FlowNode flowNode) {// 调用HistoryManager记录流程活动开始了,这里并不是单单指StartEvent活动,而是所有活动commandContext.getHistoryManager().recordActivityStart(execution);// Execution listener: event 'start'// 执行 StartEvent 上的监听器,发布 Start 的 Event 事件if (CollectionUtil.isNotEmpty(flowNode.getExecutionListeners())) {executeExecutionListeners(flowNode, ExecutionListener.EVENTNAME_START);}// Execute any boundary events, sub process boundary events will be executed from the activity behaviorif (!inCompensation && flowNode instanceof Activity) { // Only activities can have boundary events// 获取节点上的边界事件List<BoundaryEvent> boundaryEvents = ((Activity) flowNode).getBoundaryEvents();if (CollectionUtil.isNotEmpty(boundaryEvents)) {executeBoundaryEvents(boundaryEvents, execution);}}// Execute actual behavior// 执行实际的行为,UserTask对应的behavior是UserTaskActivityBehavior,这个UserTaskActivityBehavior里面会把task写入到act_ru_taskActivityBehavior activityBehavior = (ActivityBehavior) flowNode.getBehavior();// 当 activityBehavior 不为空,走此方法,此方法后续也会调用 planTakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation// activityBehavior 表示一个节点上拥有的行为// StartEvent 节点的行为是 NoneStartEventActivityBehavior,没有做其它业务,仅仅是过度// UserTask 节点的行为是 UserTaskActivityBehavior,这个行为会把任务写入到数据库后,等待用户完成任务,流程才会继续走下去if (activityBehavior != null) {executeActivityBehavior(activityBehavior, flowNode);} else {logger.debug("No activityBehavior on activity '{}' with execution {}", flowNode.getId(), execution.getId());// 计划执行 TakeOutgoingSequenceFlows 操作,这个操作是一个连线行为,第一步先找出当前节点的出口,第二步从出口走到下一个节点。Context.getAgenda().planTakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation(execution, true);}
}总结
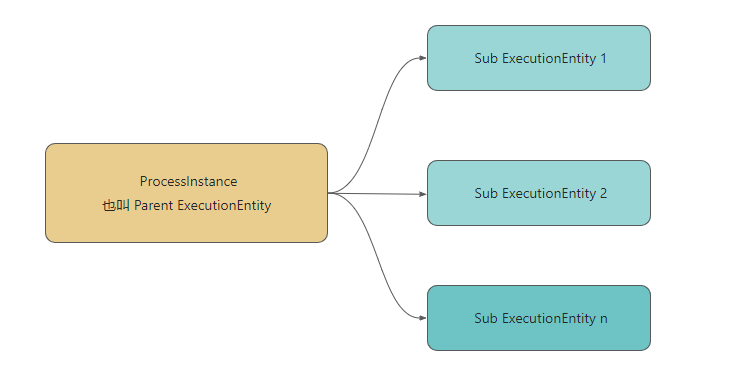
本章节内容有点绕也有点复杂,下面画个简图辅助理解。图中的 ExecutionEntity 是 ProcessInstance 接口的实现类,所以 ExecutionEntity 本身就是 ProcessInstance 的一个实例,这个实例叫 流程实例。一个流程实例至少有一个或多个 ExecutionEntity 实例,流程实例本身称之为 Parent ExecutionEntity,而流程实例下的一个或多个 ExecutionEntity 称之为 Sub ExecutionEntity, 它们之间属于父子关系。像本章开头的审批流程图,因没有并行分支,所以只会产生一个 Sub ExecutionEntity。
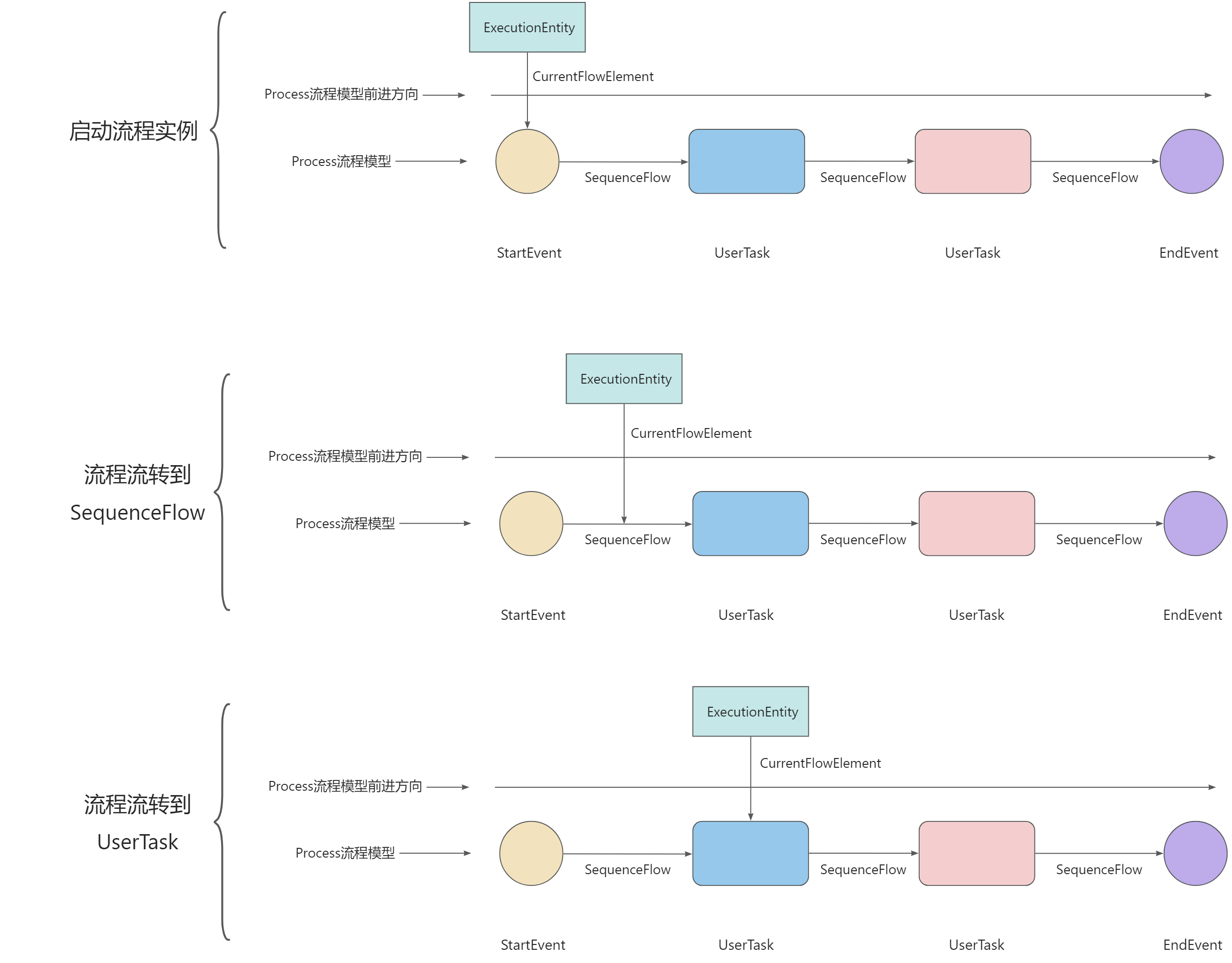
- 启动流程实例:创建 ExecutionEntity 的实例,并将此实例的 CurrentFlowElement 指向 StartEvent。
- 流程流转到SequenceFlow:ExecutionEntity 流转到 SequenceFlow,此时将 CurrentFlowElement 指向 SequenceFlow。
- 流程流转到UserTask:ExecutionEntity 流转到 UserTask,此时将 CurrentFlowElement 指向 UserTask。
- 以此类推,当 ExecutionEntity 流转到 EndEvent 时,将 CurrentFlowElement 指向 EndEvent,标记此流程实例结束。