ChipCamp探索系列 -- 1. Soft-Core RISC-V on FPGA
一个多月的时间,Chisel芯片开发入门系列阶段性小结一下,要看看下一步的探索方向了。本篇尝试新开一个系列,就叫“ChipCamp探索系列”,本篇为第一篇。
Chisel也好Verilog也好,芯片敏捷开发往下一步工程化普及化必然涉及到CPU/MCU的“落地”,去流个片固然可以有成就感但毕竟很浪费也不敏捷,不是“学习”所应该付出的代价,那么Soft-Core RISC-V on FPGA就是一个较为合适的必然选择了。
Soft-core RISC-V on FPGA:
https://www.eevblog.com/forum/fpga/amdxilinx-announced-their-own-risc-v-soft-core/
--AMD/Xilinx announced their own RISC-V soft-core. posted on: November 03 2023.
--MicroSemi have been offering both RISC-V soft cores since 2017 and hard cores (PolarFire SoC, in e.g. the new BeagleBoard Fire, Icicle) since late 2020.
--Lattice announced their first official RISC-V soft core in I think June 2020 (collab with SiFive announced December 2019), and improved versions e.g. an 800 LUT core in mid 2021.
--Intel/Altera introduced RISC-V soft-core on Nios V in October 2021
--Xilinx is a little late to the party.
soft-core RISC-V by xilinx:
https://www.amd.com/en/products/software/adaptive-socs-and-fpgas/microblaze-v.html
The AMD MicroBlaze V processor is a soft-core RISC-V processor IP for AMD adaptive SoCs and FPGAs.
The MicroBlaze V processor is based on the RISC-V instruction set architecture (ISA).
It allows developers to leverage the open-source RISC-V software ecosystem, is hardware compatible with the classic MicroBlaze processor, and is fully integrated in the AMD Vivado and Vitis tools design flow.
The AMD MicroBlaze V processor is designed to be highly modular with a configurable architecture suitable for embedded systems applications.
soft-core RISC-V by Altera:
https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/content-details/835599/altera-extends-its-multi-platform-risc-v-support-by-partnering-with-prominent-risc-v-tools-provider-ashling-white-paper.html
https://cdrdv2-public.intel.com/835599/nios-v-multi-platform-risc-v-white-paper.pdf
In the case of FPGAs, one or more soft-core processors can be instantiated in the device’s programmable fabric.
soft-core RISC-V by Lattice:
https://www.latticesemi.com/products/designsoftwareandip/intellectualproperty/ipcore/ipcores04/riscvmccpu
The Lattice Semiconductor RISC-V MC CPU soft IP contains a 32-bit RISC-V processor core and optional submodules – Timer and Programmable Interrupt Controller (PIC).
soft-core RISC-V by MicroChip:
https://www.microchip.com/en-us/products/fpgas-and-plds/system-on-chip-fpgas/mi-v/soft-cpus
https://github.com/Mi-V-Soft-RISC-V/
https://www.hackster.io/pablotrujillojuan/creating-a-risc-v-system-with-an-fpga-80d726
The Libero SoC Design Suite and SoftConsole development environments provide all the required tools to integrate Mi-V soft CPUs in our FPGAs and develop, test and debug embedded firmware.
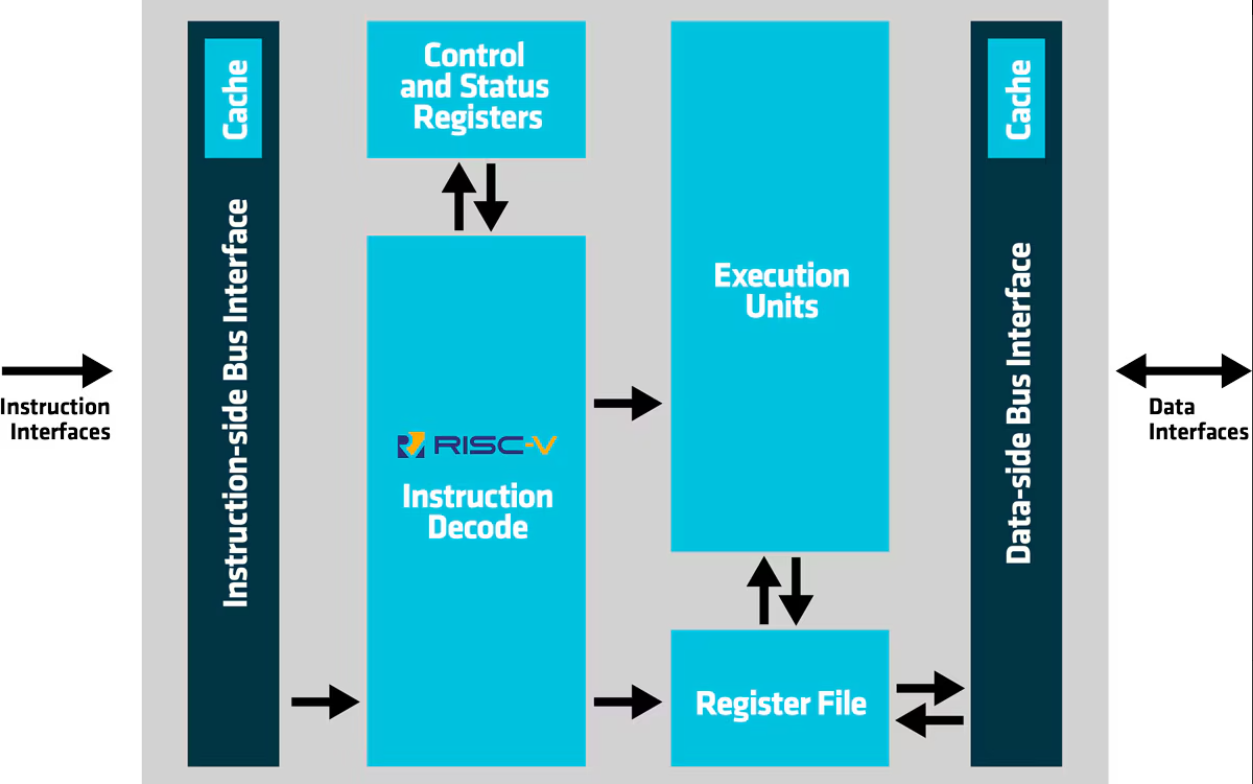
附图1:来自上面AMD MicroBlaze V soft-core RISC-V processor IP!
----启发:这个架构图给出外部视角的RISC-V处理器(指令接口和数据接口)。
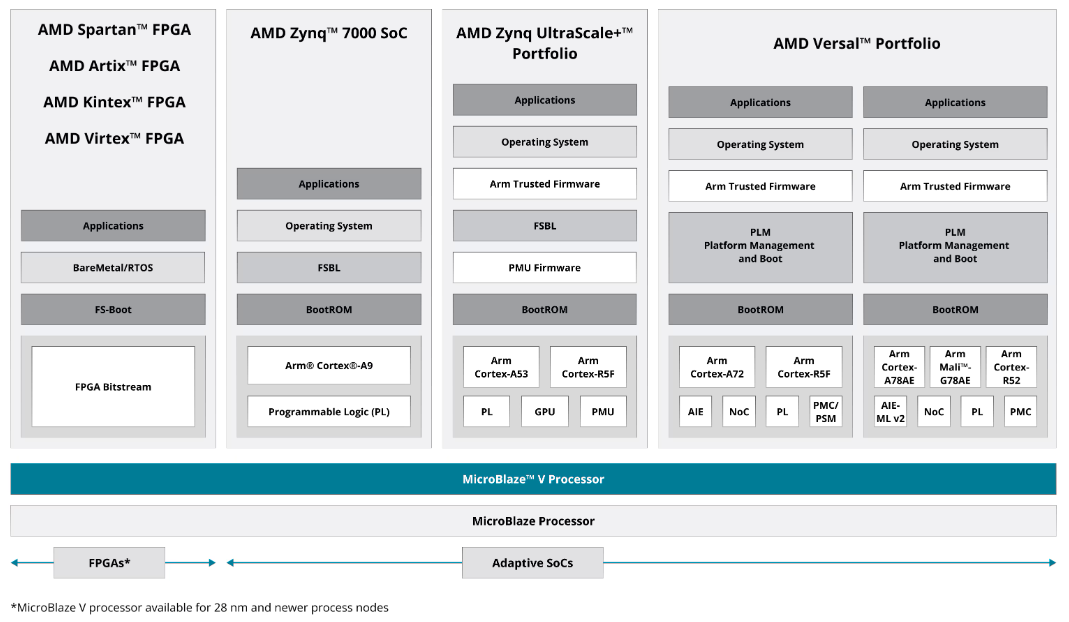
附图2:来自上面AMD MicroBlaze V soft-core RISC-V processor IP!
----启示:世界第一Xilinx的FPGA系列从Spartan-Artix-Kintex-Virtex到Zynq再到Versal。
----启示:从纯FPGA到Soc FPGA/SoPC的Zynq = PL+PS。
附图3:来自上面Intel Altera的Nios V RISC-V Whitepaper!
----启示:这个Nios系列FPGA够强的,2004年开始的Nios 2就是soft-core processor的理想选择!
----启示:手头的这本《EDA技术使用教程--Verilog HDL版》(2010年第四版) 潘松-黄继业-潘明编著,就在第11章专门讲解Nios II并把它称为SoPC:SoPC系统开发技术最早是由Altera公司提出来的,即将嵌入式处理器、I/O口、存储器以及各类功能模块集成到一个FPGA器件上,SoPC Builder是Nios 2嵌入式处理器开发软件包。

图4:来自上面的Lattice的官方网页的图片:
----启示:CPU核的外部接口,以指令接口和数据接口为主要两个。和图一的启示类似。
----启示:其中的数据接口会通过数据总线AHB和外部连接,而指令接口可以孤立独享。
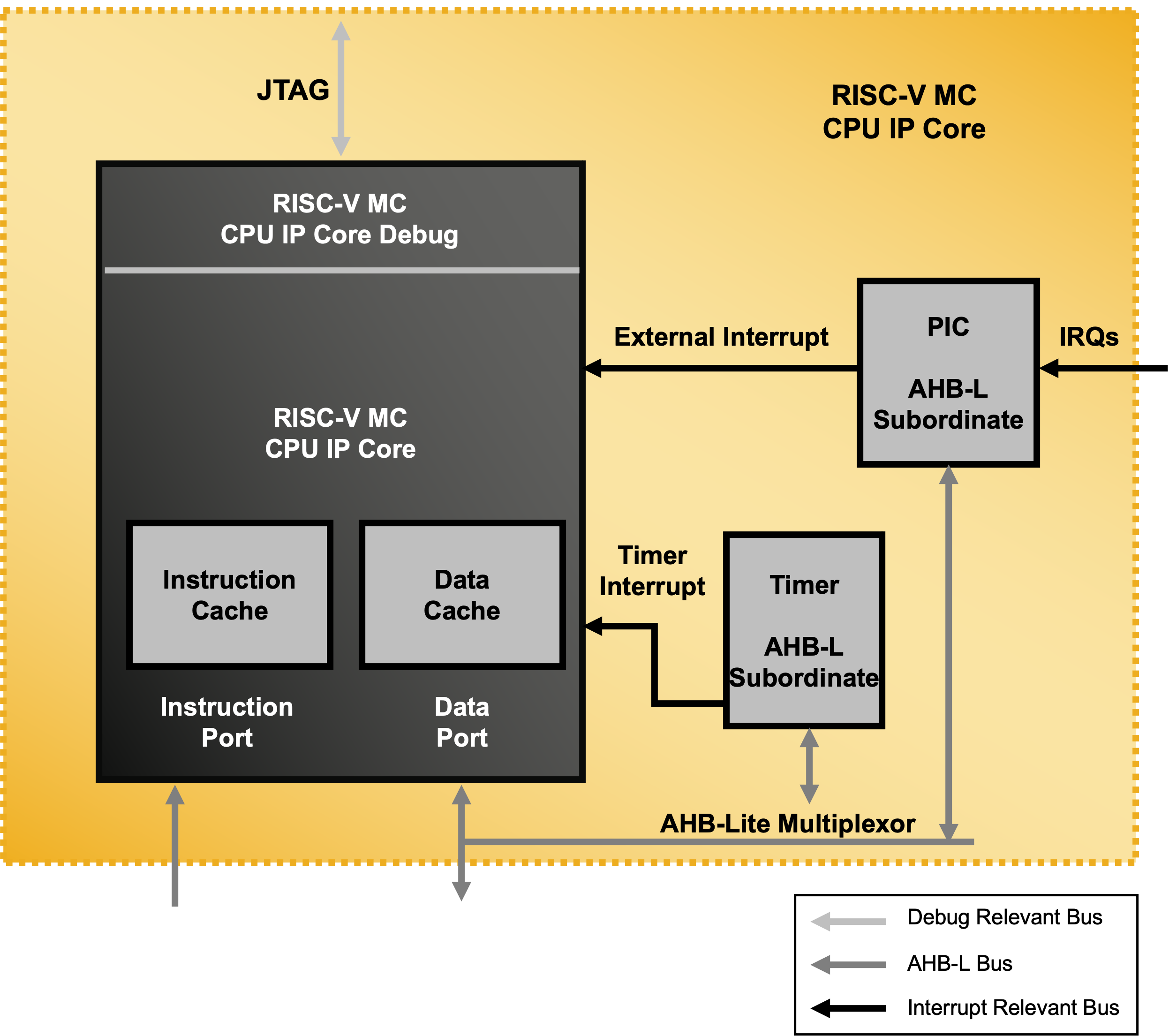
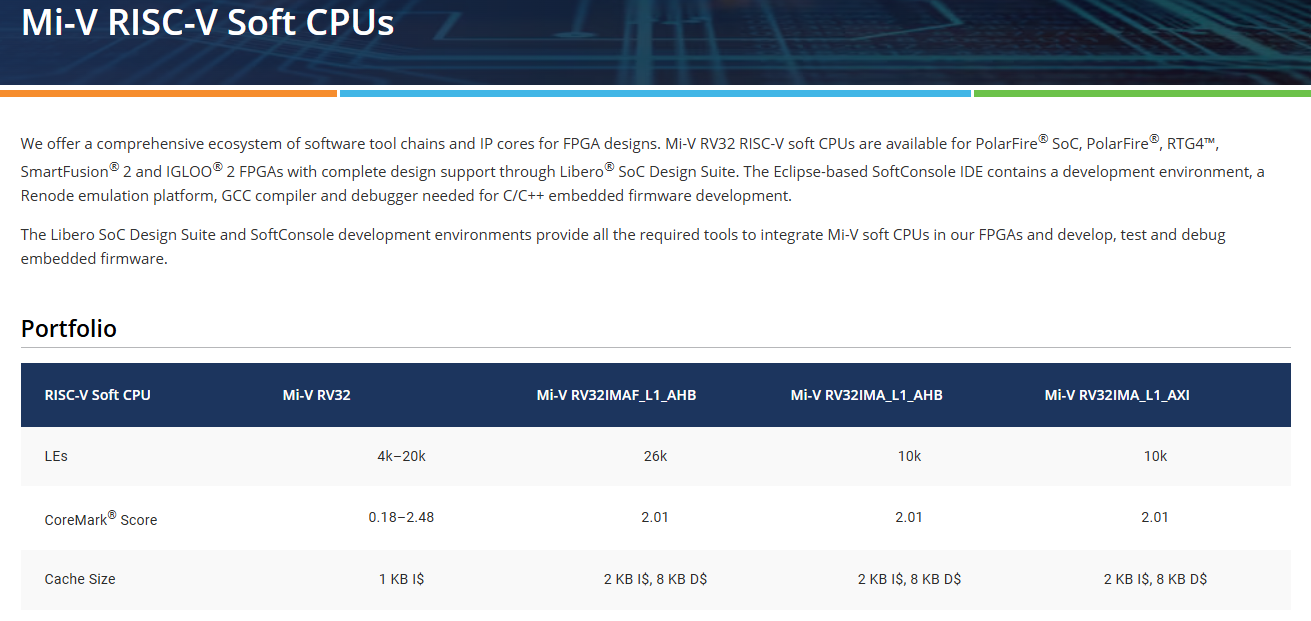
图5:来自上面MicroChip的Mi-V RISC-V Soft CPU的介绍。
----启示1:MicroChip的FPGA系列,包括PolarFire-RTG4-SmartFusion-IGLOO2等。
----启示2:MicroChip的软件叫Libero SoC Design Suite。
----启示3:MicroChip的软核IP有5个形成的系列,而不是单个。
PS1:夏宇闻老师的《Verilog数字系统设计教程》(2008年第2版)关注到了软核和硬核的概念,其1.5.4节的标题就叫“软核、固核和硬核的概念及其重用”!
----把功能经过验证的、可综合的、实现后电路结构总门数在5000门以上的Verilog HDL模型称之为“软核”。
----把在某一种FPGA器件上实现的、经过验证是正确的、5000门以上的电路结构编码文件称为“固核”。
----把在某一种ASIC器件上实现的、经过验证是正确的、5000门以上的电路结构版图掩膜称为“硬核”。
PS2:FPGA上可以通过软核实现RISC-V,但更主要的趋势是FPGA芯片上集成硬核(ARM或RISC-V)、形成所谓的SoC FPGA或SoPC。也有在SoPC的概念上纠结、认为SoPC是软核、SoC FPGA才是硬核,但这个争论意义并不大,区分清楚软核和硬核即可,特此提示。
