Langchain入门:对话式RAG
我们现在有在 Lilian Weng 的博客文章 中构建的 Q&A 应用程序(本系列上篇)
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(openai_api_base = "https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1/",openai_api_key = os.environ['siliconflow'],model_name = "Qwen/Qwen3-8B", # 模型名称
)
import bs4
from langchain import hub
from langchain.chains import create_retrieval_chain
from langchain.chains.combine_documents import create_stuff_documents_chain
from langchain_chroma import Chroma
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter# 1. Load, chunk and index the contents of the blog to create a retriever.
loader = WebBaseLoader(web_paths=("https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",),bs_kwargs=dict(parse_only=bs4.SoupStrainer(class_=("post-content", "post-title", "post-header"))),
)
docs = loader.load()text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=200)
splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(documents=splits, embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(openai_api_base="https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1/",openai_api_key=os.environ["siliconFlow"],model="Qwen/Qwen3-Embedding-8B"))
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()# 2. Incorporate the retriever into a question-answering chain.
system_prompt = ("You are an assistant for question-answering tasks. ""Use the following pieces of retrieved context to answer ""the question. If you don't know the answer, say that you ""don't know. Use three sentences maximum and keep the ""answer concise.""\n\n""{context}"
)prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", system_prompt),("human", "{input}"),]
)question_answer_chain = create_stuff_documents_chain(llm, prompt)
rag_chain = create_retrieval_chain(retriever, question_answer_chain)
添加聊天历史
我们构建的链直接使用输入查询来检索相关上下文。但在对话环境中,用户查询可能需要对话上下文才能被理解。
我们需要更新我们现有应用的两个方面:
提示词: 更新我们的提示词以支持历史消息作为输入。
上下文化问题: 添加一个子链,获取最新的用户问题,并在聊天历史的上下文中重新表述它。这可以简单地理解为构建一个新的“历史感知”检索器。
简而言之,做如下升级:
- 查询 -> 检索器 (原来)
- (查询, 聊天历史) -> 大型语言模型 -> 重新表述的查询 -> 检索器(现在)
首先,我们需要定义一个子链,该子链获取历史消息和最新的用户问题,并在引用历史信息时重新表述问题。
我们将使用一个提示词,其中包含名为“chat_history”的 MessagesPlaceholder 变量。这允许我们使用“chat_history”输入键将消息列表传递给提示词,这些消息将在系统消息之后和包含最新问题的人类消息之前插入。
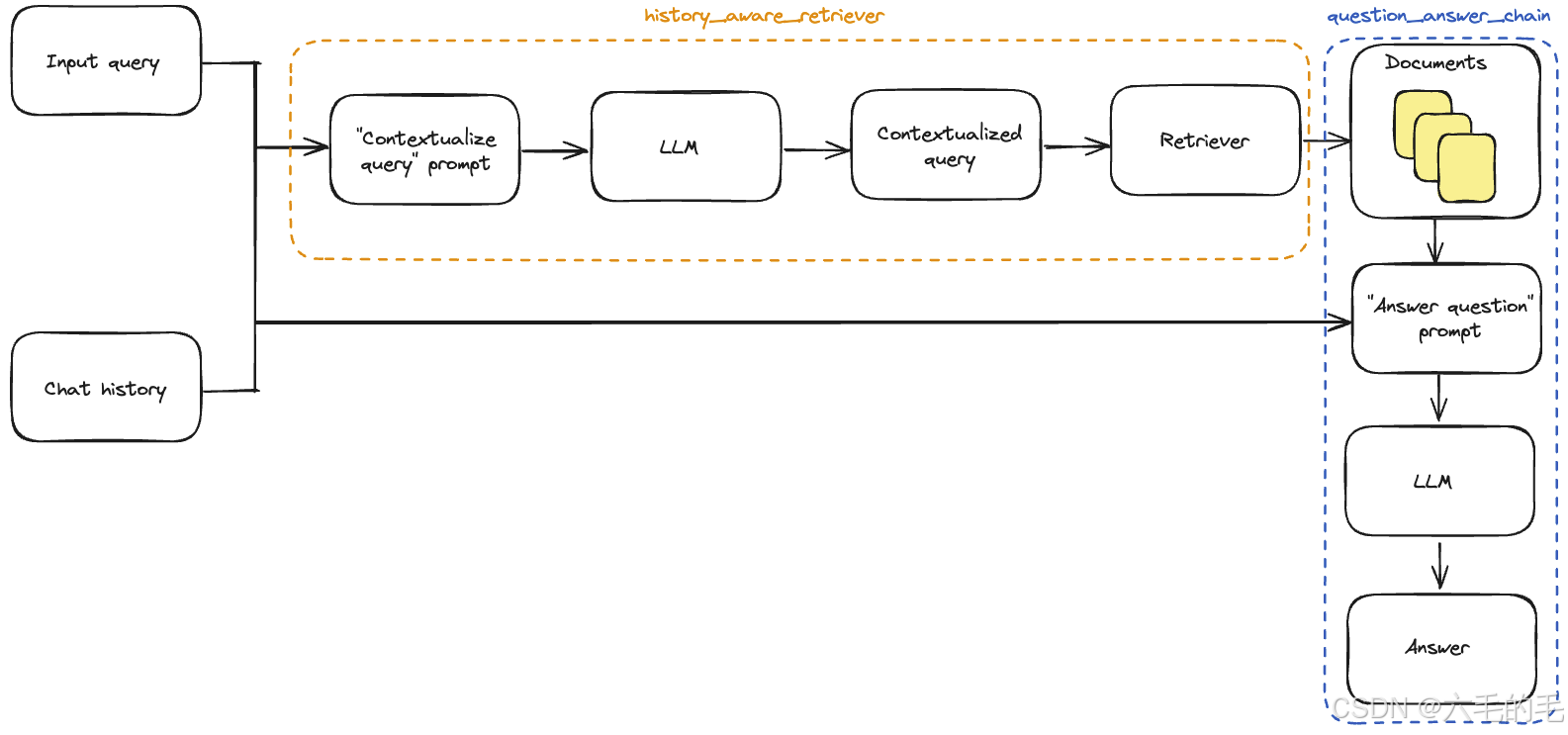
请注意,我们利用一个辅助函数 create_history_aware_retriever 来处理这一步,该函数管理 chat_history 为空的情况,否则按顺序应用 提示词 | 大型语言模型 | 输出解析器() | 检索器。
create_history_aware_retriever 构建一个接受 输入 和 聊天历史 作为输入的链,并具有与检索器相同的输出模式。
create_history_aware_retriever 的作用是创建一个具有历史对话感知能力的检索器,它能够理解对话上下文并将用户的问题重新表述为独立的、可理解的查询。
from langchain.chains import create_history_aware_retriever
from langchain_core.prompts import MessagesPlaceholdercontextualize_q_system_prompt = ("Given a chat history and the latest user question ""which might reference context in the chat history, ""formulate a standalone question which can be understood ""without the chat history. Do NOT answer the question, ""just reformulate it if needed and otherwise return it as is."
)contextualize_q_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", contextualize_q_system_prompt),MessagesPlaceholder("chat_history"),("human", "{input}"),]
)history_aware_retriever = create_history_aware_retriever(llm, retriever, contextualize_q_prompt
)
现在我们可以构建完整的问答链。这只需将检索器更新为我们的新 history_aware_retriever。
同样,我们将使用 create_stuff_documents_chain 来生成一个 question_answer_chain,输入键为 context、chat_history 和 input——它接受检索到的上下文以及对话历史和查询以生成答案
我们使用 create_retrieval_chain 构建最终的 rag_chain。该链按顺序应用 history_aware_retriever 和 question_answer_chain,保留中间输出,例如检索到的上下文,以便于使用。它的输入键为 input 和 chat_history,输出中包括 input、chat_history、context 和 answer。
from langchain.chains import create_retrieval_chain
from langchain.chains.combine_documents import create_stuff_documents_chainqa_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", system_prompt),MessagesPlaceholder("context"),("human", "{input}"),]
)question_answer_chain = create_stuff_documents_chain(llm, qa_prompt)
rag_chain = create_retrieval_chain(history_aware_retriever, question_answer_chain)
下面我们提出一个问题和一个需要上下文化的后续问题,以返回合理的响应。因为我们的链包括一个 “chat_history” 输入,调用者需要管理聊天历史。我们可以通过将输入和输出消息附加到列表来实现这一点:
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, AIMessagechat_history = []question = "What is Task Decomposition?"
ai_msg_1 = rag_chain.invoke({"input": question, "chat_history": chat_history})
chat_history.extend([HumanMessage(content=question),AIMessage(content=ai_msg_1["answer"]),]
)second_question = "What are common ways of doing it?"
ai_msg_2 = rag_chain.invoke({"input": second_question, "chat_history": chat_history})print(ai_msg_2["answer"])
在这里,我们已经讨论了如何添加应用逻辑以纳入历史输出,但我们仍在手动更新聊天历史并将其插入到每个输入中。在一个真实的问答应用中,我们希望有某种方式来持久化聊天历史,以及某种方式来自动插入和更新它。
为此,我们可以使用:
- BaseChatMessageHistory:存储聊天历史。
- RunnableWithMessageHistory: LCEL链和BaseChatMessageHistory的包装器,处理将聊天历史注入输入并在每次调用后更新它。
我们实现第二种选项的简单示例,其中聊天历史存储在一个简单的字典中。LangChain管理与Redis等技术的内存集成,以提供更强大的持久性。
RunnableWithMessageHistory的实例为您管理聊天历史。它们接受一个配置,其中包含一个键(默认为"session_id"),指定要获取并预先添加到输入中的对话历史,并将输出附加到相同的对话历史。
from langchain_core.chat_history import BaseChatMessageHistory
from langchain_core.runnables.history import RunnableWithMessageHistorystore = {}def get_session_history(session_id: str) -> BaseChatMessageHistory:if session_id not in store:store[session_id] = BaseChatMessageHistory()return store[session_id]conversational_rag_chain = RunnableWithMessageHistory(rag_chain,get_session_history,input_messages_key="input",history_messages_key="chat_history",output_messages_key="answer",
)
RunnableWithMessageHistory 是 LangChain 中的一个包装器,用于为任何 Runnable 对象自动管理聊天历史,让原本无状态的链条变成有状态的对话系统。
conversational_rag_chain.invoke({"input": "What is Task Decomposition?"},config={"configurable": {"session_id": "abc123"}},
)["answer"]
可以在store字典中检查对话历史:
for message in store["abc123"].messages:if isinstance(message, AIMessage):prefix = "AI"else:prefix = "User"print(f"{prefix}: {message.content}\n")
代理
代理利用大型语言模型的推理能力在执行过程中做出决策。使用代理可以将一些对检索过程的自由裁量权转移出去。尽管它们的行为比链更不可预测,但在这种情况下它们提供了一些优势:
- 代理直接生成检索器的输入,而不一定需要我们像上面那样明确构建上下文;
- 代理可以执行多个检索步骤以服务于查询,或者完全不执行检索步骤(例如,响应用户的通用问候时)。
代理可以访问“工具”并管理它们的执行。在这种情况下,我们将把检索器转换为一个LangChain工具,由代理使用:
from langchain.tools.retriever import create_retriever_tooltool = create_retriever_tool(retriever,"blog_post_retriever", # 工具名称(Agent 调用时使用)"Searches and returns excerpts from the Autonomous Agents blog post." # 工具描述
)tools = [tool]
工具是LangChain 可运行的,并实现了通常的接口:
tool.invoke("task decomposition")
现在我们已经定义了工具和大型语言模型,我们可以创建代理。我们将使用LangGraph来构建代理。 目前我们正在使用高级接口来构建代理,但LangGraph的好处在于,这个高级接口是由一个低级的、高度可控的API支持的,以防你想修改代理逻辑。
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agentagent_executor = create_react_agent(llm, tools)
我们现在可以试一试。请注意,到目前为止它是无状态的(我们仍然需要添加内存)
query = "What is Task Decomposition?"for s in agent_executor.stream({"messages": [HumanMessage(content=query)]}
):print(s)print("----")
LangGraph内置了持久性,因此我们不需要使用ChatMessageHistory!相反,我们可以直接将检查点传递给我们的LangGraph代理
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySavermemory = MemorySaver()agent_executor = create_react_agent(llm, tools, memory=memory)
如果我们输入一个不需要检索步骤的查询,代理不会执行检索:
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "abc123"}}for s in agent_executor.stream({"messages": [HumanMessage(content="Hi! I'm Bob.")]}, config=config
):print(s)print("----")
进一步地,如果我们输入一个需要检索步骤的查询,代理会生成工具的输入:
query = "What is Task Decomposition?"for s in agent_executor.stream({"messages": [HumanMessage(content=query)]}, config=config
):print(s)print("----")
同样的原则允许代理在必要时使用对话的上下文:
uery = "What according to the blog post are common ways of doing it? redo the search"for s in agent_executor.stream({"messages": [HumanMessage(content=query)]}, config=config
):print(s)print("----")
