Groovy学习篇章一之—— GDK 探秘:Groovy如何给Java对象“开外挂”,让String也能“跑命令”!
Groovy学习
一 介绍
Groovy第一个版本发布于2007年,是一种用于Java虚拟机的敏捷地动态语言,同时也是一门面向对象语言。即可以作为编程语言,也可以作为纯粹的脚本语言。
动态语言与静态语言:
动态语言,是在运行时确定数据类型的语言,变量在使用前无需声明类型,类型会根据赋值动态推断。例如,Python、JavaScript 和 PHP 都属于动态语言。动态语言的特点是灵活性高,开发者可以专注于业务逻辑,而不需要过多关注类型声明。
静态语言,则是在编译时确定数据类型的语言。变量在使用前必须显式声明类型,且类型在程序生命周期内通常不会改变。例如,C、C++ 和 Java 都是静态语言。静态语言的优势在于编译器可以在编译阶段捕获类型错误,从而提高代码的安全性和稳定性。
二 Groovy与Java的关系
java代码文件修改后缀为.groovy后,可以直接作为groovy文件运行,即使其内部的代码仍为java代码,这体现了groovy与java语言本身的互通性。
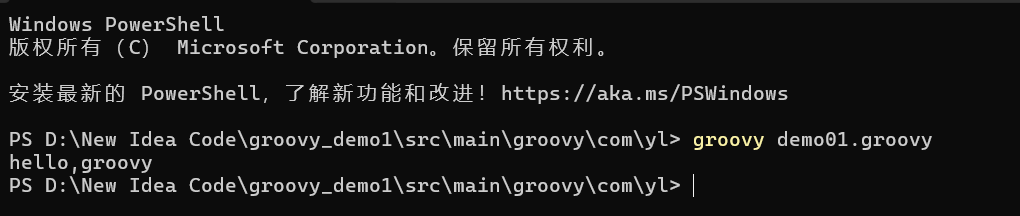
当我们对demo01.groovy文件中的代码进行简化,去掉类名、方法体等之后,其仍能得到与java一样的运行结果,这体现了groovy语言相较于java语言的简洁性和轻量性。

三 GDK
和Java相似,Java有JDK,Groovy也有自己的GDK,但GDK其实是依赖于JDK的,因为其是在不修改JDK源码的情况下,通过MetaClass 和 扩展模块(Extension Modules)机制,在运行时为 JDK 的类“注入”了额外的功能,故可以说Groovy扩展了JDK,这些扩展形成了GDK(Groovy JDK)。
1. GDK是JDK的扩展
举一个例子:
在java中,当我们需要与系统进行交互时,我们可以使用java.lang.process包下的类来进行,比如说在控制台打印执行“git help”命令的内容,java实现如下:
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("git help");BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));String line;while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {System.out.println(line);}bufferedReader.close();}
}
//执行结果如下:
/*
usage: git [-v | --version] [-h | --help] [-C <path>] [-c <name>=<value>][--exec-path[=<path>]] [--html-path] [--man-path] [--info-path][-p | --paginate | -P | --no-pager] [--no-replace-objects] [--bare][--git-dir=<path>] [--work-tree=<path>] [--namespace=<name>][--config-env=<name>=<envvar>] <command> [<args>]
These are common Git commands used in various situations:
start a working area (see also: git help tutorial)clone Clone a repository into a new directoryinit Create an empty Git repository or reinitialize an existing one
work on the current change (see also: git help everyday)add Add file contents to the indexmv Move or rename a file, a directory, or a symlinkrestore Restore working tree filesrm Remove files from the working tree and from the index
examine the history and state (see also: git help revisions)bisect Use binary search to find the commit that introduced a bugdiff Show changes between commits, commit and working tree, etcgrep Print lines matching a patternlog Show commit logsshow Show various types of objectsstatus Show the working tree status
grow, mark and tweak your common historybranch List, create, or delete branchescommit Record changes to the repositorymerge Join two or more development histories togetherrebase Reapply commits on top of another base tipreset Reset current HEAD to the specified stateswitch Switch branchestag Create, list, delete or verify a tag object signed with GPG
collaborate (see also: git help workflows)fetch Download objects and refs from another repositorypull Fetch from and integrate with another repository or a local branchpush Update remote refs along with associated objects
'git help -a' and 'git help -g' list available subcommands and some
concept guides. See 'git help <command>' or 'git help <concept>'
to read about a specific subcommand or concept.
See 'git help git' for an overview of the system.
*/而在groovy中,只需要一句即可实现同java一样的效果:
println "git help".execute().text
//执行结果同样为:
/*
usage: git [-v | --version] [-h | --help] [-C <path>] [-c <name>=<value>][--exec-path[=<path>]] [--html-path] [--man-path] [--info-path][-p | --paginate | -P | --no-pager] [--no-replace-objects] [--bare][--git-dir=<path>] [--work-tree=<path>] [--namespace=<name>][--config-env=<name>=<envvar>] <command> [<args>]
These are common Git commands used in various situations:
start a working area (see also: git help tutorial)clone Clone a repository into a new directoryinit Create an empty Git repository or reinitialize an existing one
work on the current change (see also: git help everyday)add Add file contents to the indexmv Move or rename a file, a directory, or a symlinkrestore Restore working tree filesrm Remove files from the working tree and from the index
examine the history and state (see also: git help revisions)bisect Use binary search to find the commit that introduced a bugdiff Show changes between commits, commit and working tree, etcgrep Print lines matching a patternlog Show commit logsshow Show various types of objectsstatus Show the working tree status
grow, mark and tweak your common historybranch List, create, or delete branchescommit Record changes to the repositorymerge Join two or more development histories togetherrebase Reapply commits on top of another base tipreset Reset current HEAD to the specified stateswitch Switch branchestag Create, list, delete or verify a tag object signed with GPG
collaborate (see also: git help workflows)fetch Download objects and refs from another repositorypull Fetch from and integrate with another repository or a local branchpush Update remote refs along with associated objects
'git help -a' and 'git help -g' list available subcommands and some
concept guides. See 'git help <command>' or 'git help <concept>'
to read about a specific subcommand or concept.
See 'git help git' for an overview of the system.
*/这是为什么呢?让我们进入GDK的源码进行查看
(1).按住ctrl,鼠标单击 execute()方法
public static Process execute(String self) throws IOException {return Runtime.getRuntime().exec(self);
}(2).按住ctrl,鼠标单击 text :
public static String getText(Process self) throws IOException {String text = IOGroovyMethods.getText(new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(self.getInputStream())));closeStreams(self);return text;}上面两个方法都存在于ProcessGroovyMethods类中的。
可以看到,GDK的源码是Java编写的。
前面说过Groovy是面向对象的编程语言,那么"git help".execute()的含义应该是调用String类中的execute()方法,但是我们进入源码查看却发现,String类中并不存在execute()方法,且GDK 中的String类源码和JDK中的String源码是一模一样的,这就验证了Groovy是没有修改JDK源码的。
但GDK中的String类并不存在execute()方法,为何我们编译时不会报错,运行时也不会报错呢?首先,因为Groovy是一门动态语言,故其在编译时并不会严格检查当前对象是否能调用这个方法;其次,Groovy拥有MetaClass(元类)和扩展模块机制。
MetaClass(元类)是 Groovy 中一个核心的运行时机制,可以理解为每个 Groovy 对象都附带的一个“行为控制器”或“方法查找器”,且MetaClass会知晓其对应的类中所有的信息(即JDK中的定义的方法和属性)。
扩展模块(比如 DefaultGroovyMethods)中定义的静态方法,在运行时会被注册到对应类(需要它的类)的 MetaClass 中,从而让这些静态方法看起来就像是原始类的实例方法一样。
故而,在执行"git help".execute()代码时,就可以理解为是Groovy在运行时动态地将ProcessGroovyMethods类中的方法装载到了String类对应的MetaClass中,使String类“看起来”拥有了execute()方法,故而不会报错,且可正确执行,最终返回一个Process对象。
同理,可以理解,在执行.text代码时,虽然Process类中并不存在getText()方法,但通过Groovy的MetaClass 和扩展模块机制,可以在运行时动态地将ProcessGroovyMethods类中的方法装载到了 Process类MetaClass中,最终就可以得到我们需要的 字符串结果。
最后通过 println 方法,将结果打印出来。
从上面,这个例子,就可以看出,GDK中将一些常用的功能提前封装为一些模块中的方法(如ProcessGroovyMethods类中的getText(Process self)方法,将java中的读取输入流中的字符串和关闭流提前一起封装了),通过MetaClass(元类)和扩展模块机制,在运行时实现为某些类动态扩展一些方法,使得Groovy的代码的编写更为简洁。
2. 扩展模块(类)的内部机制
那当Groovy在运行时是如何知道要将扩展模块中的每个方法扩展到哪个到对应的类的
MetaClass中的呢?例如:如何知道要将
ProcessGroovyMethods类中的getText(Process self)方法需要在运行时扩展到String类的MetaClass中
1.什么是扩展模块
Groovy中的“扩展模块”本质上是 Groovy 运行时默认加载的静态方法集合,它们通过约定静态方法的第一个参数类型就是被扩展的类,Groovy 运行时会根据这个约定将方法注入到被扩展的类的MetaClass(元类)中。
也就是说,我们上面说的ProcessGroovyMethods类就可视为Groovy中的一个扩展模块,其中的方法:
public static Process execute(String self) throws IOException {return Runtime.getRuntime().exec(self);
}其中第一个参数类型为String,Groovy在运行时就会将此方法注册添加到String类的MetaClass中。
在Groovy中,当我们调用方法时,都会到其对应的 metaClass 保存的信息中查找,如果找到就会调用。故当执行String对象.execute(String self)时,Groovy会到String 类的 MetaClass 类中查找并调用execute(String self)方法。
2. GDK 中的主要扩展模块(类)
DefaultGroovyMethods (DGM):
作用: 这是 GDK 中最核心、最庞大的扩展类。它为几乎所有基本的 Java 类型(如
Object、String、Integer、List、Map、File、Date等)提供了大量的通用方法。例子:
"hello".each { println it }(为String添加each迭代方法)[1, 2, 3].collect { it * 2 }(为List添加collect转换方法)new File("test.txt").text = "Hello"(为File添加text属性读写)1.plus(2)(为Integer添加plus方法,虽然通常直接用+)
StringGroovyMethods:
作用: 专门为
java.lang.String类提供了更多字符串操作的便捷方法。虽然很多字符串方法也在 DGM 中,但这个类会包含一些更专业的字符串处理。例子:
"hello".capitalize()(将首字母大写)"foo".padLeft(5, '*')(左侧填充)
ProcessGroovyMethods:
作用: 正如我们之前讨论的,它专门为
java.lang.Process类提供了增强方法,简化了外部进程的输入输出处理和管理。例子:
"ls -l".execute().text(执行命令并直接获取输出文本)process.waitForProcessOutput()(等待进程输出并避免阻塞)
IOGroovyMethods:
作用: 为
java.io.File、java.io.InputStream、java.io.OutputStream等I/O相关的类提供了大量简化文件和流操作的方法。例子:
new File("data.txt").eachLine { line -> println line }(按行读取文件)inputStream.eachByte { byte -> ... }(按字节处理流)
DateGroovyMethods / TimeCategory:
作用: 增强了
java.util.Date和java.util.Calendar等日期时间类,提供了更直观的日期时间计算和操作方法。例子:
(new Date()) + 1.day(日期加一天)use(TimeCategory) { 1.hour.from.now }(更灵活的时间计算)
