Qt C++实现KD树
一、什么是KD树?
1、KD树(K-Dimension Tree)是一种对K维空间中的实例点进行存储,以便对其进行快速检索的树形数据结构。
2、KD树是一种二叉树,表示对K维空间的一个划分,构造KD树相当于不断地用垂直于坐标轴的超平面将K维空间切分,构成一系列的K维超矩形区域,KD树的每个结点对应于一个K维超巨型区域。
3、采用中位数切分超平面,确保左右子树数据量平衡,实例点存储在切分超平面上对应的结点,左右子结点都是左小右大。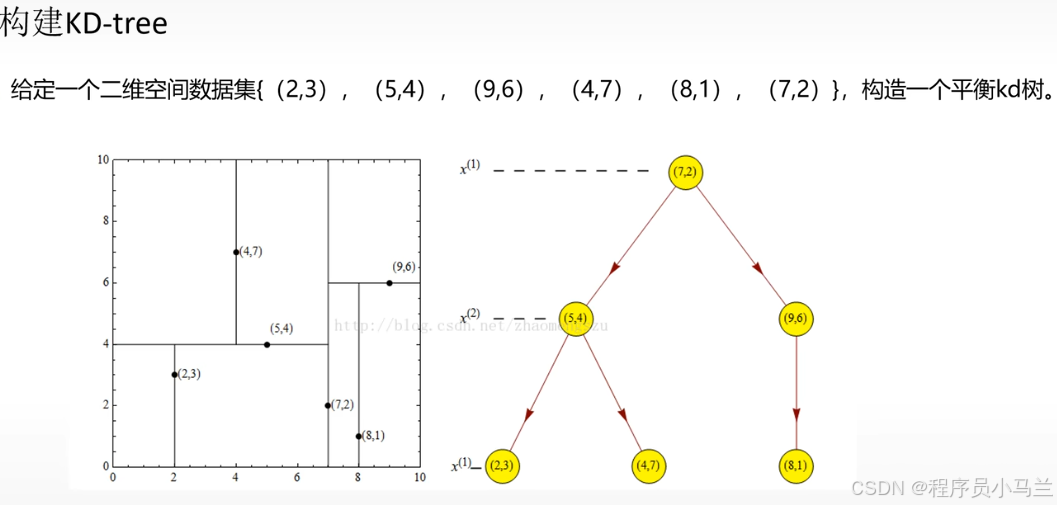
4、利用KD树可以省去对大部分数据点的搜索(通过超球面相交判断实现剪枝),从而减少搜索的计算量。
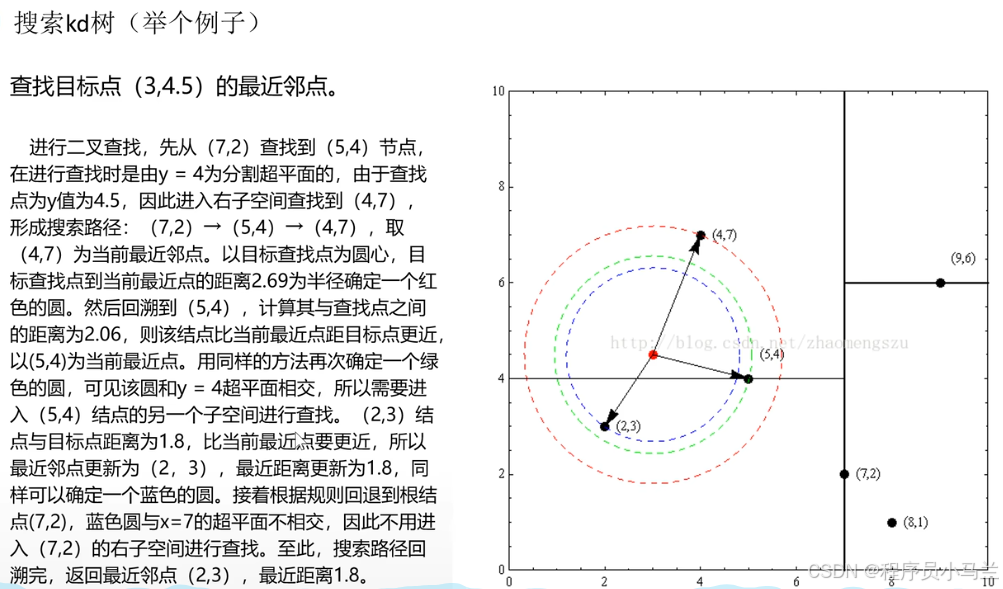
5、构建时间复杂度O(n log n),查询平均时间复杂度O(log n)。
二、实例代码:
用Qt C++实现,对于struct {double a; double b; double c;}类型的元素,输入键a和键b,想要查找最接近键a和键b对应的c。
//kdtree.h
#ifndef KDTREE_H
#define KDTREE_H#include <QVector>
#include <memory>struct DataPoint {double a;double b;double c;
};class KDNode {
public:DataPoint point;std::unique_ptr<KDNode> left;std::unique_ptr<KDNode> right;int axis;KDNode(const DataPoint& p, int ax) : point(p), axis(ax) {}
};class KDTree {
public:void build(const QVector<DataPoint>& points);double findNearestValue(double targetA, double targetB);void clear(); bool isEmpty() const;private:std::unique_ptr<KDNode> root;std::unique_ptr<KDNode> buildRecursive(QVector<DataPoint>::iterator begin,QVector<DataPoint>::iterator end,int depth);void nearestSearch(KDNode* node, const DataPoint& target,DataPoint& best, double& bestDist) const;double distance(const DataPoint& p1, const DataPoint& p2) const;
};
#endif // KDTREE_H//kdtree.cpp
#include "kdtree.h"
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <limits>void KDTree::build(const QVector<DataPoint>& points) {auto copy = points;root = buildRecursive(copy.begin(), copy.end(), 0);
}std::unique_ptr<KDNode> KDTree::buildRecursive(QVector<DataPoint>::iterator begin,QVector<DataPoint>::iterator end,int depth) {if (begin == end) return nullptr;int axis = depth % 2;int len = std::distance(begin, end);auto mid = begin + len / 2;std::nth_element(begin, mid, end, [axis](const DataPoint& p1, const DataPoint& p2) {return axis == 0 ? p1.a < p2.a : p1.b < p2.b;});auto node = std::make_unique<KDNode>(*mid, axis);node->left = buildRecursive(begin, mid, depth + 1);node->right = buildRecursive(mid + 1, end, depth + 1);return node;
}double KDTree::findNearestValue(double targetA, double targetB) {DataPoint target{targetA, targetB, 0};DataPoint best;double bestDist = std::numeric_limits<double>::max();nearestSearch(root.get(), target, best, bestDist);return best.c;
}void KDTree::clear() {root.reset();
}bool KDTree::isEmpty() const {return root == nullptr;
}void KDTree::nearestSearch(KDNode* node, const DataPoint& target,DataPoint& best, double& bestDist) const {if (!node) return;double dist = distance(node->point, target);if (dist < bestDist) {bestDist = dist;best = node->point;}double diff = node->axis == 0 ? target.a - node->point.a : target.b - node->point.b;KDNode* near = diff <= 0 ? node->left.get() : node->right.get();KDNode* far = diff <= 0 ? node->right.get() : node->left.get();nearestSearch(near, target, best, bestDist);if (fabs(diff) < bestDist) {nearestSearch(far, target, best, bestDist);}
}double KDTree::distance(const DataPoint& p1, const DataPoint& p2) const {return std::hypot(p1.a - p2.a, p1.b - p2.b);
}
