TypeScript 中的「类」:从语法到实战的完整指南
什么是类?类(Class)是面向对象编程(OOP)中的一个核心概念,用于描述具有相同属性和行为的 对象 的 模板或蓝图。类(class)是面向对象的基石头,通过类可以创建多个具有相同结构和功能的对象实例,在 TypeScript 中,它不仅保留了 ES6 Class 的全部能力,还额外增加了类型系统、访问修饰符、抽象类、接口实现等高级特性,让我们能够用更优雅、更安全、更可扩展的方式组织代码。
本文将带你由浅入深掌握 TypeScript 中类的所有核心知识点,并配套一个图书管理系统综合案例,真正做到「学完即可落地」
一、类的基础语法和实例化
类是对象的模板,用于描述具有相同属性和方法的对象集合。在 TypeScript 中,使用class关键字定义类,一个完整的类通常包含属性、构造函数、方法和访问器。
①类的创建:
class 类名称{
属性----类属性,对象属性
方法----构造方法,静态方法,普通方法,修饰符修饰方法,抽象方法
}
②实例化对象:
let 对象名 = new 类名(参数1,参数2,....)
③通过对象操作对应的属性和方法
代码示例:
class Product{// 私有属性(需要再外部访问和修改的话需要设置get或者set方法)和普通属性private name:stringprice:number// 构造函数:创建对象时调用,通常用于初始化属性constructor(name:string,price:number){this.name = namethis.price = price}// 参数属性:直接在构造函数中定义并初始化属性// constructor(public name: string, private price: number) {}// 方法show(){return `商品名称:${this.name},商品价格:${this.price}`}// 访问器(getter / setter)set Newname(name:string){this.name = name}get Name():string{return this.name}
}// 实例化对象
const p = new Product('手机',5000)
console.log(p.show())
p.Newname = "小米15pro";
console.log(p.Name)运行结果:

二. 基本特性
2.1 访问修饰符(public、private、protected)
TypeScript 提供三种访问修饰符,控制属性和方法的访问范围:
| 修饰符 | 类内部 | 子类 | 类外部 |
|---|---|---|---|
public | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
private | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
protected | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
代码示例:
class Person1 {// private 访问修饰符private:仅允许类内部访问该成员,子类和外部均无法访问。private id : number;// public 修饰的属性或方法是公有的,可以在子类和类的外部地方调用。public name : string;// protected:允许类内部和其子类访问该成员,但不允许类外部访问。protected age : number;// constructor构造函数----类似于Python的__init__方法constructor(id:number,name: string, age: number) {// 类的内部调用this.id = idthis.name = name;this.age = age;}sayHello(){console.log(`大家好,我是${this.name},我今年${this.age}岁了。`);}
}// 继承,创建子类power
class power extends Person1 {constructor(id:number,name: string, age: number) {// 表示调用父类的构造函数super(id,name, age);}// 子类访问父类的public属性show(){// 在子类不能访问private的属性// console.log(this.id)// 在子类能访问public的属性console.log(this.name);// 在子类能访问protected的属性console.log(this.age)}
}const teacher = new Person1(101,"李花猪", 18);
// 在类的外部不能访问private的属性
// console.log(teacher.id)// 在类的外部访问public的属性
console.log(teacher.name)// 在类的外部不能访问protected的属性
// console.log(teacher.age)
2.2 只读属性和可选属性、静态成员
①使用
readonly关键字定义只读属性,只能在声明时或构造函数中赋值,后续不可修改。②使用 属性名? 定义可选属性,可以传值也可以不传值。
③静态成员(
static)属于类本身,而非实例,通过类名.成员名访问,常用于工具函数或常量。
① 只读属性和可选属性
代码示例:
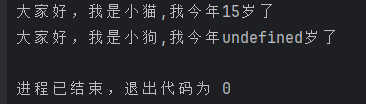
class Animal {readonly name: string; // 只读属性age?: number; // 可选属性constructor(theName: string,age?: number) {this.name = theName;this.age = age;}// 实例方法show(){console.log(`大家好,我是${this.name},我今年${this.age}岁了`);// this.name = '小猫'; // 报错只读属性不能修改}
}let cat = new Animal('小猫',15);
// cat.name = '喵喵喵'; // 报错只读属性不能修改
cat.show()// 可以选择不初始化age赋值
let dog = new Animal('小狗')
dog.show();运行结果:
②静态成员
代码示例:
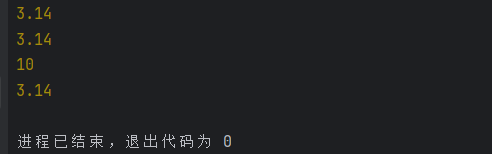
class Circle{// 静态属性static PI = 3.14;radius: number;constructor(radius: number) {this.radius = radius;}// 在静态方法this是指向的类本事,不是指向实例static class_show(){let num1 = this.PI; // 不会报错console.log(num1)let num2 = Circle.PI; // 不会报错console.log(num2)// let num3 = this.radius; // 报错 静态方法不能访问实例属性}// 在实例方法中this指向实例,不是指向类obj_show(){let num1 = this.radius;console.log(num1)let num2 = Circle.PI;console.log(num2)// let num3 = Circle.radius; // 报错,radius是实例属性,不能通过类访问// let num3 = this.PI; // 报错,PI是静态属性,在实例方法中this指向的是实例,不能this静态属性}
}const circle = new Circle(10);
// circle.class_show() // 报错,静态方法不能通过实例访问
Circle.class_show()
circle.obj_show()运行结果:
2.3 类的继承与多态
使用
extends继承;子类必须super()调用父类构造器。子类可 重写父类方法 实现 多态。
代码示例:
// 父类
class Vehicle {constructor(public brand: string) {}start(): void {console.log(`${this.brand} 启动`);}
}// 子类
class Car extends Vehicle {constructor(brand: string, public seats: number) {super(brand); // 必须先调用父类构造函数}// 重写父类方法start(): void {console.log(`${this.brand} 汽车启动,有${this.seats}个座位`);}
}const car = new Car("Tesla", 5);
car.start(); // 输出:Tesla 汽车启动,有5个座位运行结果:

2.4 抽象类
抽象类(abstract)是 不能直接实例化的基类,可包含抽象方法(无实现),子类必须实现抽象方法:
示例代码:
// 抽象类
abstract class Shape {constructor(public color: string) {}// 抽象方法:子类必须实现abstract calculateArea(): number;// 具体方法:子类可直接使用displayColor(): void {console.log(`Color: ${this.color}`);}
}// 子类实现抽象类
class Circle extends Shape {constructor(color: string, public radius: number) {super(color);}// 实现抽象方法calculateArea(): number {return Math.PI * this.radius **2;}
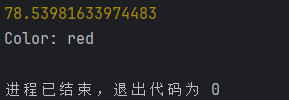
}const circle = new Circle("red", 5);
console.log(circle.calculateArea()); // 输出:78.5398...
circle.displayColor(); // 输出:Color: red
// const shape = new Shape("blue"); // 错误:抽象类不能实例化运行结果:
三、类与接口的结合
类与接口的配合使用,可实现代码解耦和行为规范约束。
3.1 类实现接口
使用implements关键字让类实现接口,类必须实现接口中定义的所有属性和方法:
// 定义接口
interface Movable {speed: number;move(): void;
}// 类实现接口
class Bicycle implements Movable {speed: number;constructor(speed: number) {this.speed = speed;}move(): void {console.log(`Bicycle moving at ${this.speed} km/h`);}
}const bike = new Bicycle(15);
bike.move(); // 输出:Bicycle moving at 15 km/h一个类可实现多个接口:
interface Resizable {resize(width: number, height: number): void;
}class ImageBox implements Movable, Resizable {speed: number;width: number;height: number;constructor(speed: number, width: number, height: number) {this.speed = speed;this.width = width;this.height = height;}move(): void { /* 实现move方法 */ }resize(width: number, height: number): void { /* 实现resize方法 */ }
}四、综合案例
🧩 需求
图书分 普通书 和 电子书
每本书都有:标题、价格、库存
电子书额外有:下载链接
提供一个 购物车,可以:
① 把书加入购物车
② 列出购物车里的书名
③ 计算总价(自动打 9 折)
示例代码:
// 1️⃣ 接口:描述所有书的公共形状
interface Book {title: string;price: number;inStock: boolean;
}// 2️⃣ 抽象类:实现公共逻辑
abstract class BaseBook implements Book {constructor(public title: string,public price: number,public inStock: boolean) {}
}// 3️⃣ 普通书
class PaperBook extends BaseBook {}// 4️⃣ 电子书
class EBook extends BaseBook {constructor(title: string,price: number,public downloadUrl: string) {super(title, price, true); // 电子书默认有库存}
}// 5️⃣ 购物车类
class Cart {private items: Book[] = [];add(book: Book) {this.items.push(book);}listTitles(): string[] {return this.items.map(b => b.title);}totalPrice(): number {const sum = this.items.reduce((s, b) => s + b.price, 0);return sum * 0.9; // 9 折}
}// 6️⃣ 使用示例
const cart = new Cart();
cart.add(new PaperBook('TypeScript 入门', 50, true));
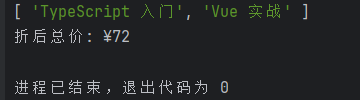
cart.add(new EBook('Vue 实战', 30, 'https://download.dev/vue'));console.log(cart.listTitles()); // [ 'TypeScript 入门', 'Vue 实战' ]
console.log('折后总价: ¥' + cart.totalPrice()); // ¥72.00运行结果: