IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2025年论文整理2(中英文摘要)
2025.05.27 最近需要看一些最新的论文,根据论文速览模块选出几篇与“信道建模、AI、通感一体化”等内容相关的论文,建立论文摘要泛读模块,大家可以快速找到自己感兴趣的论文并在IEEE上搜索进一步阅读。ps:很多方面我了解的不够深入,因此翻译可能不一定准确,请见谅。

【论文泛读2】IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2025年论文整理2(摘要)
- 1:Sensing-Enhanced Channel Estimation for Near-Field XL-MIMO Systems(近场通信)
- 1.1知识补充:近场通信
- 1.1.1 近场通信的物理背景
- 1.1.2 近场信道建模的复杂性
- 2 Channel Deduction: A New Learning Framework to Acquire Channel From Outdated Samples and Coarse Estimate
- 3 Edge Information Hub: Orchestrating Satellites, UAVs, MEC, Sensing and Communications for 6G Closed-Loop Controls
- 4 LEOEdge: A Satellite-Ground Cooperation Platform for the AI Inference in Large LEO Constellation
- 5 Joint User Identification, Channel Estimation, and Data Detection for Grant-Free NOMA in LEO Satellite Communications
- 6 Rate-Splitting for Joint Unicast and Multicast Transmission in LEO Satellite Networks With Non-Uniform Traffic Demand
- 6.1 补充:速率分割多址接入(RSMA)解析
- 6.1.1 核心思想
- 6.1.2 信号模型
- 6.1.2.1 接收信号与SINR
1:Sensing-Enhanced Channel Estimation for Near-Field XL-MIMO Systems(近场通信)
Keywords: Channel estimation, compressive sensing, discrete prolate spheroidal sequence, near-field localization, sensing-enhanced communication.
Abstract:
Future sixth-generation (6G) systems are expected to leverage extremely large-scale multiple-input multiple-output (XL-MIMO) technology, which significantly expands the range of the near-field region. The spherical wavefront characteristics in the near field introduce additional degrees of freedom (DoFs), namely distance and angle, into the channel model, which leads to unique challenges in channel estimation (CE). In this paper, we propose a new sensing-enhanced uplink CE scheme for near-field XL-MIMO, which notably reduces the required quantity of baseband samples and the dictionary size. In particular, we first propose a sensing method that can be accomplished in a single time slot. It employs power sensors embedded within the antenna elements to measure the received power pattern rather than baseband samples. A time inversion algorithm is then proposed to precisely estimate the locations of users and scatterers, which offers a substantially lower computational complexity. Based on the estimated locations from sensing, a novel dictionary is then proposed by considering the eigen-problem based on the near-field transmission model, which facilitates efficient near-field CE with less baseband sampling and a more lightweight dictionary. Moreover, we derive the general form of the eigenvectors associated with the near-field channel matrix, revealing their noteworthy connection to the discrete prolate spheroidal sequence (DPSS). Simulation results unveil that the proposed time inversion algorithm achieves accurate localization with power measurements only, and remarkably outperforms various widely-adopted algorithms in terms of computational complexity. Furthermore, the proposed eigen-dictionary considerably improves the accuracy in CE with a compact dictionary size and a drastic reduction in baseband samples by up to 66%.
摘要:
背景:未来的第六代(6G)系统预计将采用超大规模多输入多输出(extremely large-scale multiple-input multiple-output: XL-MIMO)技术,这显著扩展了近场区域的范围。近场中的球面波前特性在信道模型中引入了额外的自由度(DoFs),即距离和角度,这对信道估计(CE)提出了独特挑战。本文内容:
本文提出了一种面向近场XL-MIMO的感知增强上行链路信道估计方案,显著减少了所需的基带样本量和字典规模。细节:具体而言,我们首先提出了一种可在单个时隙内完成的感知方法,该方法利用嵌入在天线单元中的功率传感器测量接收功率模式而非基带样本。随后,提出了一种时间反转算法以精确估计用户和散射体的位置,其计算复杂度大幅降低。基于感知得到的定位结果,通过考虑近场传输模型的本征问题,提出了一种新型字典,从而以更少的基带采样和更轻量的字典实现高效近场信道估计。此外,我们推导了与近场信道矩阵相关的特征向量的一般形式,揭示了其与离散扁球面序列(DPSS)的重要联系。性能分析:仿真结果表明,所提出的时间反转算法仅通过功率测量即可实现高精度定位,并且在计算复杂度上显著优于多种广泛采用的算法。进一步,所提出的本征字典在紧凑的字典规模和高达66%的基带样本量削减下,显著提升了信道估计的精度。
1.1知识补充:近场通信
1.1.1 近场通信的物理背景
在传统无线通信中,通常假设收发端处于远场(Far-Field)区域,此时电磁波以平面波(Planar Wavefront)传播,信道模型仅需考虑角度(AoA/AoD)自由度。然而,当系统采用极大规模天线阵列(XL-MIMO)时,其物理孔径极大扩展,导致近场(Near-Field)区域范围显著增大(例如,毫米波频段下,XL-MIMO的近场区域可达数十米)。在近场区域,电磁波表现为球面波(Spherical Wavefront),信道模型中需同时考虑**距离(Distance)和角度(Angle)**两个自由度,这为信道估计(Channel Estimation, CE)带来了新的挑战。
1.1.2 近场信道建模的复杂性
近场信道矩阵的维度与天线数量平方成正比((N_{BS} \times N_{UE})),而传统远场压缩感知(CS)方法(如基于DFT的稀疏表示)无法直接适用。近场信道的关键特性包括:
- 空间非平稳性(Spatial Non-Stationarity):不同天线对同一目标的信道响应可能显著不同。
- 高秩特性(High-Rank Channel Matrix):近场信道矩阵的秩高于远场场景,导致稀疏性降低。
- 字典设计复杂度:需同时采样距离和角度维度,传统球面波字典(Spherical Wave Dictionary)需存储(O(N_{BS}^2))个码字,计算和存储开销巨大。
2 Channel Deduction: A New Learning Framework to Acquire Channel From Outdated Samples and Coarse Estimate
Keywords: Channel estimation; Estimation; OFDM; Correlation; Accuracy; Hands; Costs; Resistance; Mathematical models; Long short term memory; Channel acquisition; channel estimation; channel deduction; deep learning; massive MIMO; OFDM
Abstract:
How to reduce the pilot overhead required for channel estimation? How to deal with the channel dynamic changes and error propagation in channel prediction? To jointly address these two critical issues in next-generation transceiver design, in this paper, we propose a novel framework named channel deduction for high-dimensional channel acquisition in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO)-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) systems. Specifically, it makes use of the outdated channel information of past time slots, performs coarse estimation for the current channel with a relatively small number of pilots, and then fuses these two information to obtain a complete representation of the present channel. The rationale is to align the current channel representation to both the latent channel features within the past samples and the coarse estimate of current channel at the pilots, which, in a sense, behaves as a complementary combination of estimation and prediction and thus reduces the overall overhead. To fully exploit the highly nonlinear correlations in time, space, and frequency domains, we resort to learning-based implementation approaches. By using the highly efficient complex-domain multilayer perceptron (MLP)-mixer for across-space-frequency-domain representation and the recurrence-based or attention-based mechanisms for the past-present interaction, we respectively design two different channel deduction neural networks (CDNets). We provide a general procedure of data collection, training, and deployment to standardize the application of CDNets. Comprehensive experimental evaluations in accuracy, robustness, and efficiency demonstrate the superiority of the proposed approach, which reduces the pilot overhead by up to 88.9% compared to state-of-the-art estimation approaches and enables continuous operating even under unknown user movement and error propagation.
摘要:
背景:如何减少信道估计所需的导频开销?如何应对信道动态变化和信道预测中的误差传播?为共同解决下一代收发器设计中的这两个关键问题,本文内容:本文提出了一种名为“信道推演”的新型框架,用于多输入多输出(MIMO)-正交频分复用(OFDM)系统中的高维信道获取。细节:具体而言,该框架利用过去时隙的过时信道信息,以较少的导频对当前信道进行粗估计,并融合这两类信息以获取当前信道的完整表征。 其核心思想是将当前信道表征与过去样本中的潜在信道特征以及导频处的当前信道粗估计对齐,从而在某种意义上表现为估计与预测的互补结合,进而降低总体开销。为充分挖掘时域、空域和频域的高度非线性相关性,我们采用基于学习的实现方法。通过使用高效的复杂域多层感知器(MLP)-混合器进行跨空频域表征,并利用基于递归或注意力机制的过去-现在交互,分别设计了两种不同的信道演绎神经网络(CDNet)。性能分析:我们提供了数据收集、训练和部署的通用流程以标准化CDNet的应用。综合实验在准确性、鲁棒性和效率上的评估验证了所提方法的优越性:与最先进的估计方法相比,导频开销降低高达88.9%,并能在未知用户移动和误差传播下持续运行。
3 Edge Information Hub: Orchestrating Satellites, UAVs, MEC, Sensing and Communications for 6G Closed-Loop Controls
Keywords: Closed-loop control, edge information hub (EIH), linear quadratic regulator (LQR), satellite, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV).
Abstract:
An increasing number of field robots would be used for mission-critical tasks in remote or post-disaster areas. Due to the limited individual abilities, these robots usually require an edge information hub (EIH), with not only communication but also sensing and computing functions. Such EIH could be deployed on a flexibly-dispatched unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). Different from traditional aerial base stations or mobile edge computing (MEC), the EIH would direct the operations of robots via sensing-communication-computing-control closed-loop, which imposes stricter requirements on real-time capability, reliability, and resource efficiency. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a linear quadratic regulator (LQR)-based closed-loop control framework that unifies the heterogeneous resources (e.g., bandwidth, computing, energy) of EIH as a dynamic system and designs closed-loop optimization strategies to minimize end-to-end task execution cost. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed framework significantly outperforms traditional open-loop schemes in terms of latency, packet loss rate, and resource cost, while exhibiting strong robustness against sudden disturbances.
摘要 :
背景:越来越多的现场机器人将用于偏远或灾后区域的关键任务。由于个体能力有限,这些机器人通常需要一个兼具通信、感知和计算功能的边缘信息枢纽(EIH)。此类EIH可部署于灵活调度的无人飞行器(UAV)上。与传统空中基站或移动边缘计算(MEC)不同,EIH通过感知-通信-计算-控制闭环引导机器人操作,这对实时性、可靠性和资源效率提出了更高要求。本文内容:为应对这些挑战,本文提出一种基于线性二次调节器(LQR)的闭环控制框架,将EIH的异构资源(如带宽、计算、能源)统一建模为动态系统,并设计闭环优化策略以最小化端到端任务执行成本。性能分析:仿真结果表明,所提框架在时延、丢包率和资源成本方面显著优于传统开环方案,并展现出对突发干扰的强鲁棒性。
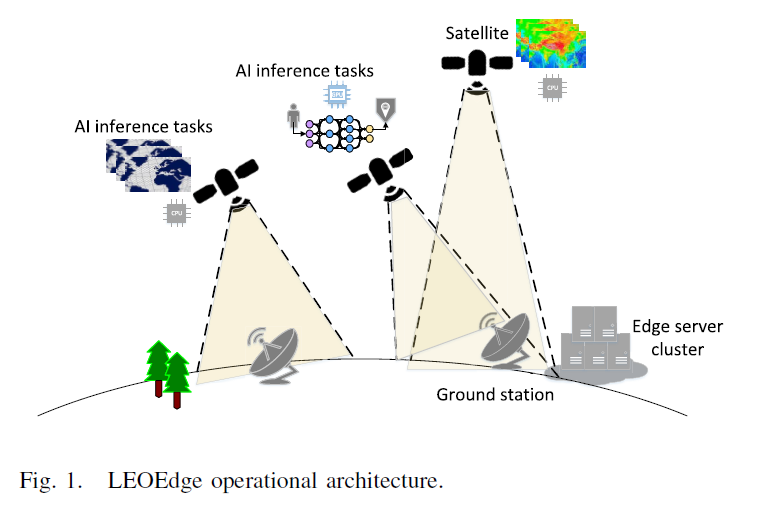
4 LEOEdge: A Satellite-Ground Cooperation Platform for the AI Inference in Large LEO Constellation
Keywords: Cloud-edge-device computing, task offloading, multi-layer optimization, LEO satellite.
Abstract:
With the rapid growth of low earth orbit (LEO) satellites, enabling LEO AI inference becomes a fast-increasing trend. However, due to resource heterogeneity, scheduling complexity, and fast movement, how to decide the place of executing each AI inference task is nontrivial in LEO systems. In this paper, we propose LEOEdge, an edge-assisted AI inference system for LEO satellites. We first introduce the adaptive modeling technologies that automatically generate the model for each satellite according to its computation resources. We then propose a layered scheduling optimization scheme to schedule the AI inference task in a distributed manner. LEOEdge also designs a seamless data transmission scheme to avoid transmission failure due to the LEO satellite movement. We conduct a series of simulation tests to validate the performance of the proposed LEOEdge, in terms of the neural network searching efficiency, average time execution latency, and delivery latency.
摘要:
背景:随着低地球轨道(LEO)卫星的快速增长,支持LEO卫星的AI推理成为新兴趋势。然而,由于资源异构性、调度复杂性和快速移动性,如何在LEO系统中确定每个AI推理任务的执行位置具有挑战性。本文内容:本文提出LEOEdge——一种面向LEO卫星的边缘辅助AI推理系统。首先引入自适应建模技术,根据卫星计算资源自动生成各卫星的模型。随后提出分层调度优化方案,以分布式方式调度AI推理任务。LEOEdge还设计了无缝数据传输方案,避免因LEO卫星移动导致的传输中断。通过一系列仿真实验验证了LEOEdge的性能:在神经网络搜索效率、平均执行时延和传输时延方面均表现出色。
5 Joint User Identification, Channel Estimation, and Data Detection for Grant-Free NOMA in LEO Satellite Communications
Keywords: Grant-free non-orthogonal multi access (GF-NOMA), low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite communications, message passing, sparse Bayesian learning (SBL).
Abstract:
Satellite Internet of things (S-IoT) aims to provide globally covered network services. In this paper, we conceive an uplink grant-free random access scheme for S-IoT network, where ground devices transmit data packets to the low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite, reducing signaling cost and making efficient use of spectrum resources by employing the non-orthogonal multiple access scheme. The impact of high operational speed of the LEO satellite is also taken into account. We further propose an iterative Gaussian approximated message passing-aided sparse Bayesian learning (GAMP-SBL) algorithm to address the joint channel estimation (CE), active user identification (UID) and data detection (DD) problem, where the three steps interacts with each other during the iterative process. Simulation results have demonstrated that our proposed joint receiver design outperforms the existing AMP-based schemes in terms of bit error rate (BER), convergence speed, as well as false alarm rate (FAR).
摘要:
背景:卫星物联网(S-IoT)旨在提供全球覆盖的网络服务。本文内容:本文为S-IoT网络设计了一种上行免调度随机接入方案,其中地面设备通过非正交多址(NOMA)技术向低地球轨道(LEO)卫星传输数据包,以降低信令开销并提升频谱效率。同时考虑了LEO卫星高速运行的影响。进一步提出一种迭代高斯近似消息传递辅助的稀疏贝叶斯学习(GAMP-SBL)算法,以解决联合信道估计(CE)、活跃用户识别(UID)和数据检测(DD)问题。性能分析:仿真结果表明,所提出的联合接收机设计在误码率(BER)、收敛速度和虚警率(FAR)上均优于现有基于近似消息传递(AMP)的方案。
6 Rate-Splitting for Joint Unicast and Multicast Transmission in LEO Satellite Networks With Non-Uniform Traffic Demand
Keywords: NOUM transmission, LEO SATCOM, ratematching, RSMA, heterogeneous traffic demands.
Abstract:
Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite communications (SATCOM) with ubiquitous global connectivity is deemed a pivotal catalyst in advancing wireless communication systems for 5G and beyond. LEO SATCOM excels in delivering versatile information services across expansive areas, facilitating both unicast and multicast transmissions via high-speed broadband capability. Nonetheless, given the broadband coverage of LEO SATCOM, traffic demand distribution within the service area is non-uniform, and the time/frequency/power resources available at LEO satellites remain significantly limited. Motivated by these challenges, we propose a rate-matching framework for non-orthogonal unicast and multicast (NOUM) transmission. Our approach aims to minimize the difference between offered rates and traffic demands for both unicast and multicast messages. By multiplexing unicast and multicast transmissions over the same radio resource, rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) is employed to manage interference between unicast and multicast streams, as well as inter-user interference under imperfect channel state information at the LEO satellite. To address the formulated problem’s non-smoothness and non-convexity, the common rate is approximated using the LogSumExp technique. Thereafter, we represent the common rate portion as the ratio of the approximated function, converting the problem into an unconstrained form. A generalized power iterat
