Java中文件操作和IO
文件操作和IO
- 文件的基本概念
- File
- 属性
- 构造方法
- 方法
- 文件读写-数据流(stream)
- InputStream
- Scanner对字符读取
- OutputStream
- PrintWriter
- Reader和Writer
- 实例练习
- 示例一
- 示例二
- 示例三
文件的基本概念
狭义上问文件,针对硬盘这种I/O设备的存储
随着文件变多,为了更好的管理,就按照层级结构对文件进行组织(也就是树形结构这种),这样就有了文件夹或者目录这种概念
一个文件夹中可以有多个文件,并且文件夹中也可以有文件夹,就这样不断层层嵌套,这样的层级结构
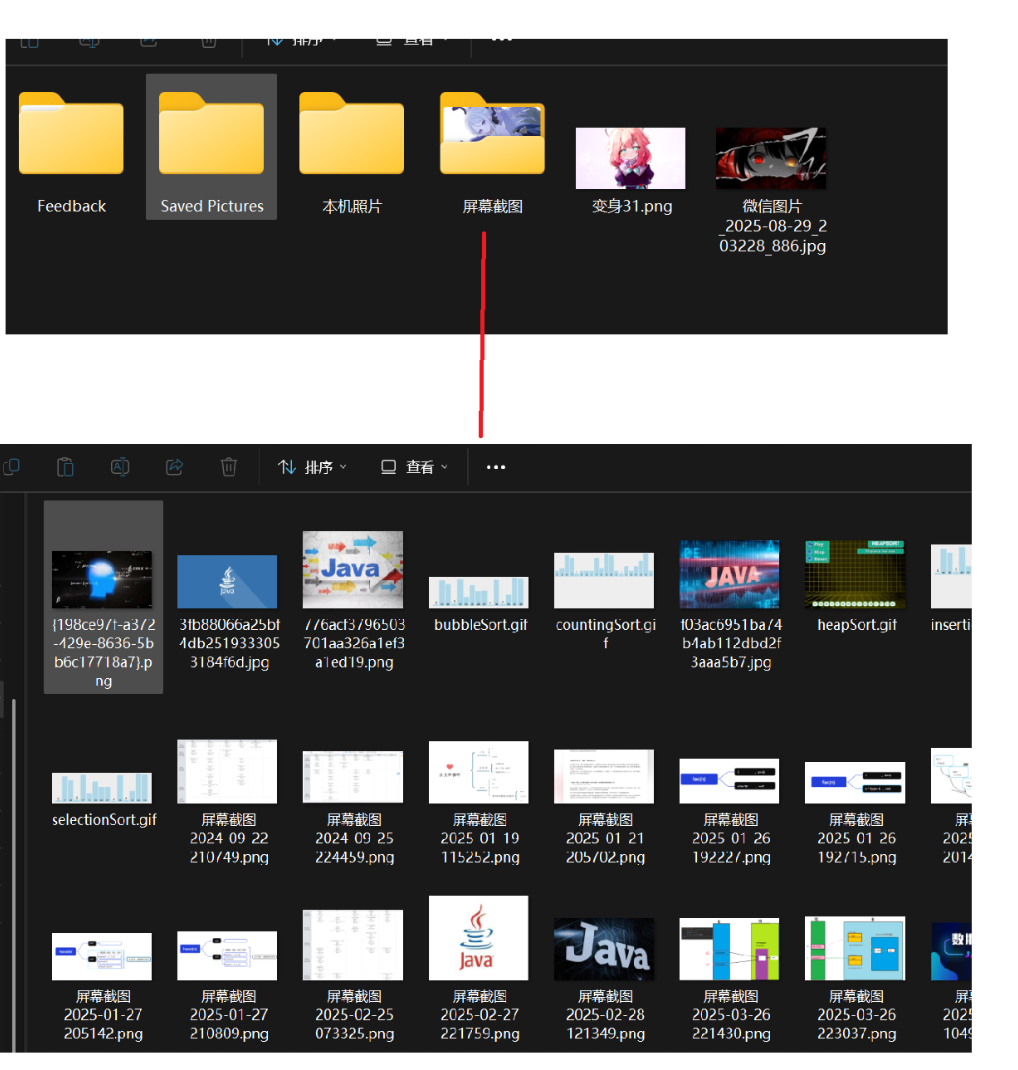
文件路径(Path)
分为绝对路径和相对路径
绝对路径:从树型结构的⻆度来看,树中的每个结点都可以被⼀条从根开始,到达文件终点
相对路径:可以从任意节点,进行路径描述

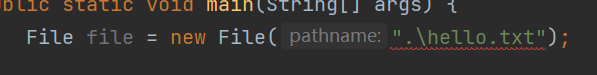
这里再Windows中使用 \ 反斜杠进行分割,其也可以使用 / 斜杠进行分割,但反斜杠 \ 这种方式在代码中需要进行字符进行转义才可以使用,因此使用 / 斜杠最好
文件类型
文本文件和二进制文件
文本文件:内部存储的内容是"字符串",每一个部分都是一个"字符"(字符集/字符编码)
二进制文件:没有限制,可以是任何数据
简单方法看文件是什么编码
直接使用记事本打开,如果是乱码,就是二进制文件,不乱码就是文本文件
File
属性
| 类型 | 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| static String | pathSeparator | 依赖于系统的路径分隔符,String类型的表⽰ |
| staticchar | pathSeparator | 依赖于系统的路径分隔符,char类型的表⽰ |
构造方法
| 签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
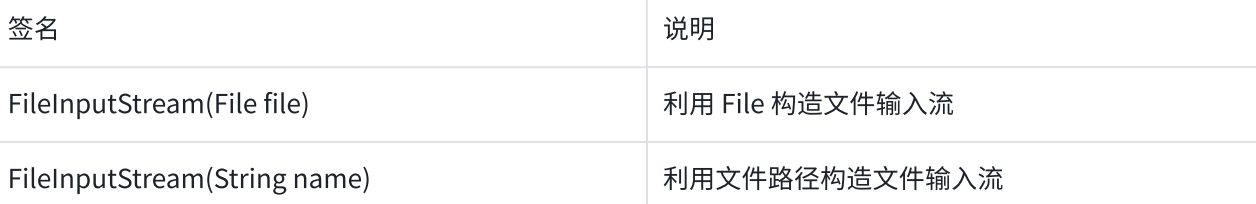
| File(File parent, String child) | 根据父目录和子目录,创建一个File实例 |
| File(String pathname) | 根据⽂件路径创建⼀个新的File实例,路径可以是绝对路径或者相对路径 |
| File(String parent,String child) | 根据⽗⽬录+孩⼦⽂件路径,创建⼀个新的File实例,⽗⽬录⽤路径表⽰ |
此时这里的File(String pathname)根据当前目录,其如果是相对目录的话 就是想对当前idea打开文件的路径
方法
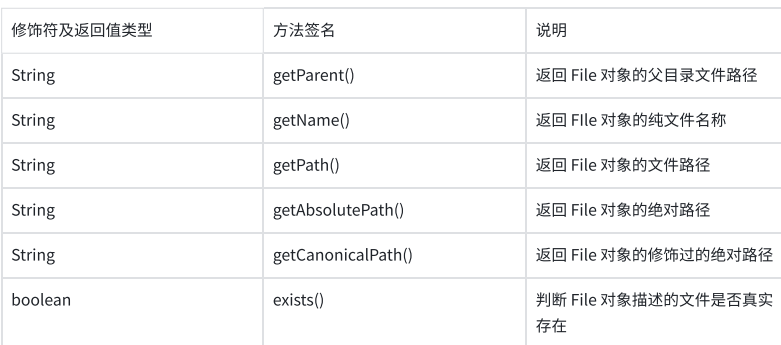

public class demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {File file = new File("d:/JAVA/Test/test.txt");// File file = new File("./hello.txt");//这样就会在java当前文件中找是否有这个文件System.out.println(file.getParent());//父目录System.out.println(file.getName());//文件名System.out.println(file.getPath());//文件位置System.out.println(file.getAbsoluteFile());System.out.println(file.getCanonicalFile());}
}
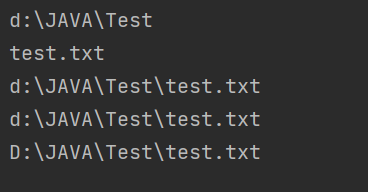
此时getAbsoluteFile()和getCanonicalFile()这个方法好像差不多,实则不然
这里getCanonicalFile()获取信息更标准,并且会把中间一些不必要的删除
public class demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) {File file = new File("d:/JAVA/Test/hello.txt");System.out.println(file.exists());//是否存在System.out.println(file.isFile());//是否是一个普通文件System.out.println(file.isDirectory());//是否是一个目录}
}
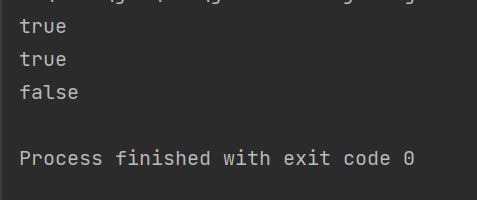
此时这个文件是一个普通文件,不是目录,文件存在
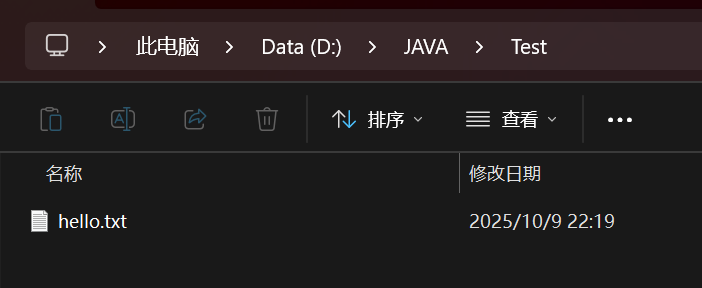
file.delete();//删除文件,直接从硬盘上删除
public class demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) {File file = new File("d:/JAVA/Test/hello.txt");System.out.println(file.exists());//删除文件file.delete();System.out.println(file.exists());}
}
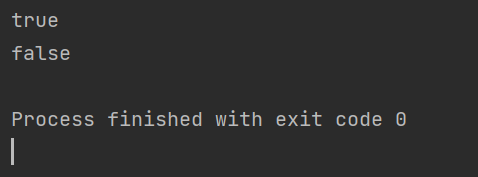
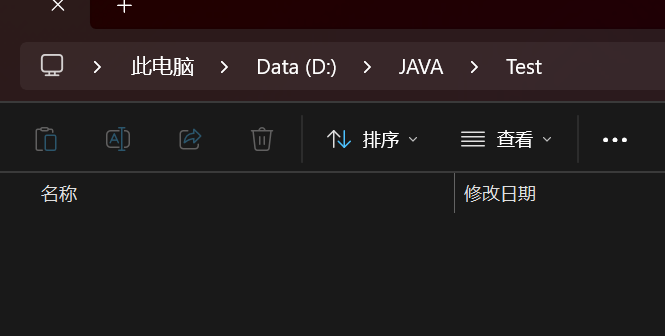
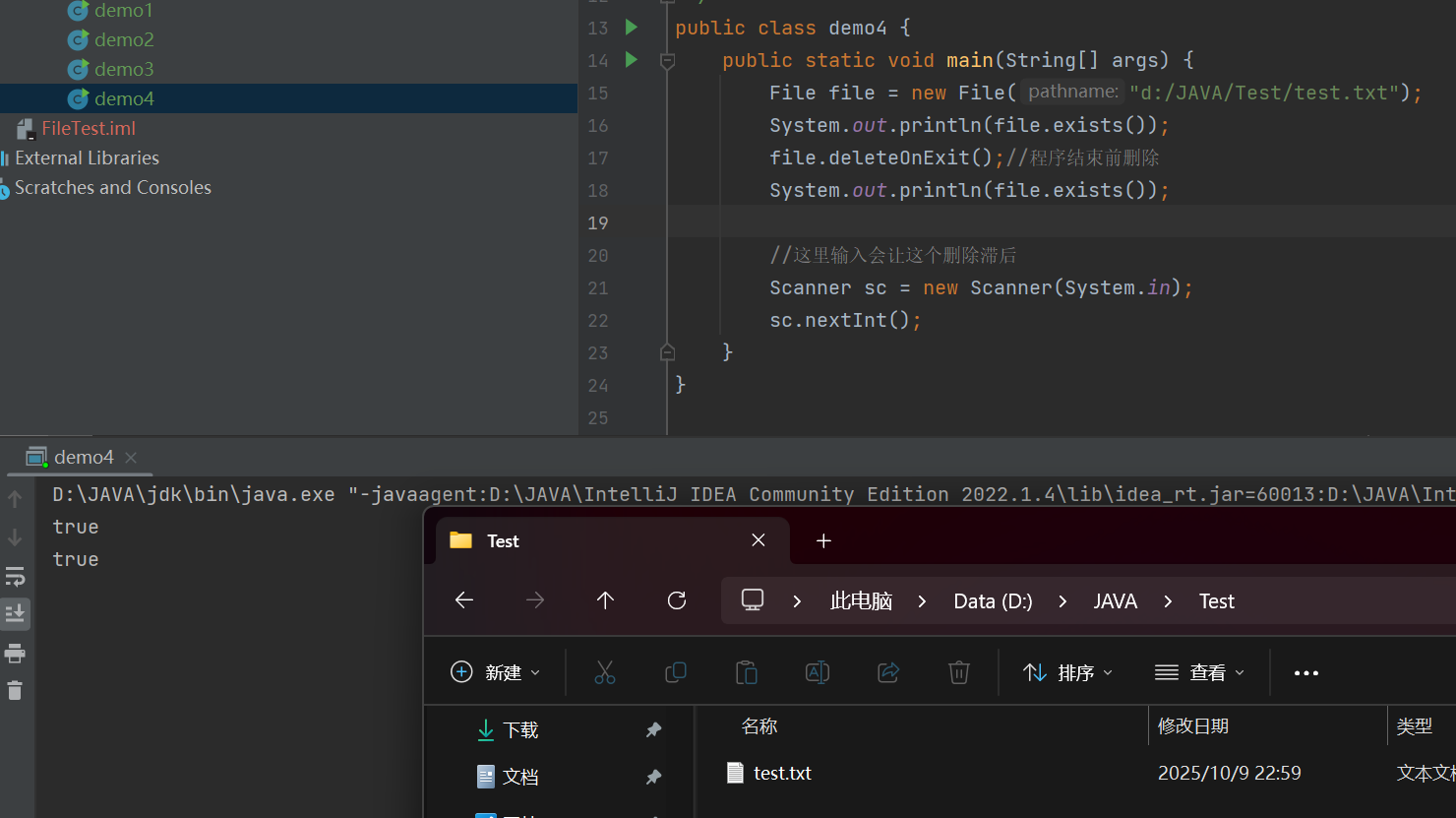
file.deleteOnExit();//也是删除,JVM退出之前才进行删除
public class demo4 {public static void main(String[] args) {File file = new File("d:/JAVA/Test/test.txt");System.out.println(file.exists());file.deleteOnExit();//程序结束前删除System.out.println(file.exists());//这里输入会让这个删除滞后Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);sc.nextInt();}
}这里输入会阻塞主线程,所以当我输入输入未完成的时候,其文件还处于未删除状态,当输入完成,后面没有什么逻辑,其就会开始删除了
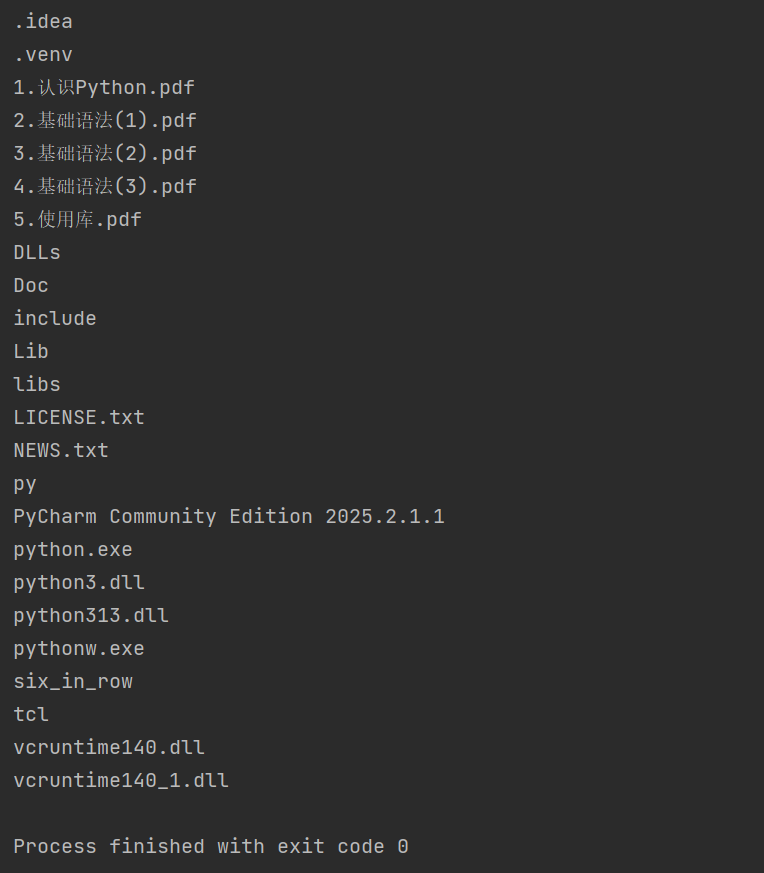
String[] fileNames = file.list();//返回file目录下所以文件名并用String[]接收返回值
public class demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {File file = new File("d:/Java/python");String[] fileNames = file.list();if(fileNames == null){System.out.println("空目录");return;}for(String fileName : fileNames){System.out.println(fileName);}}
}
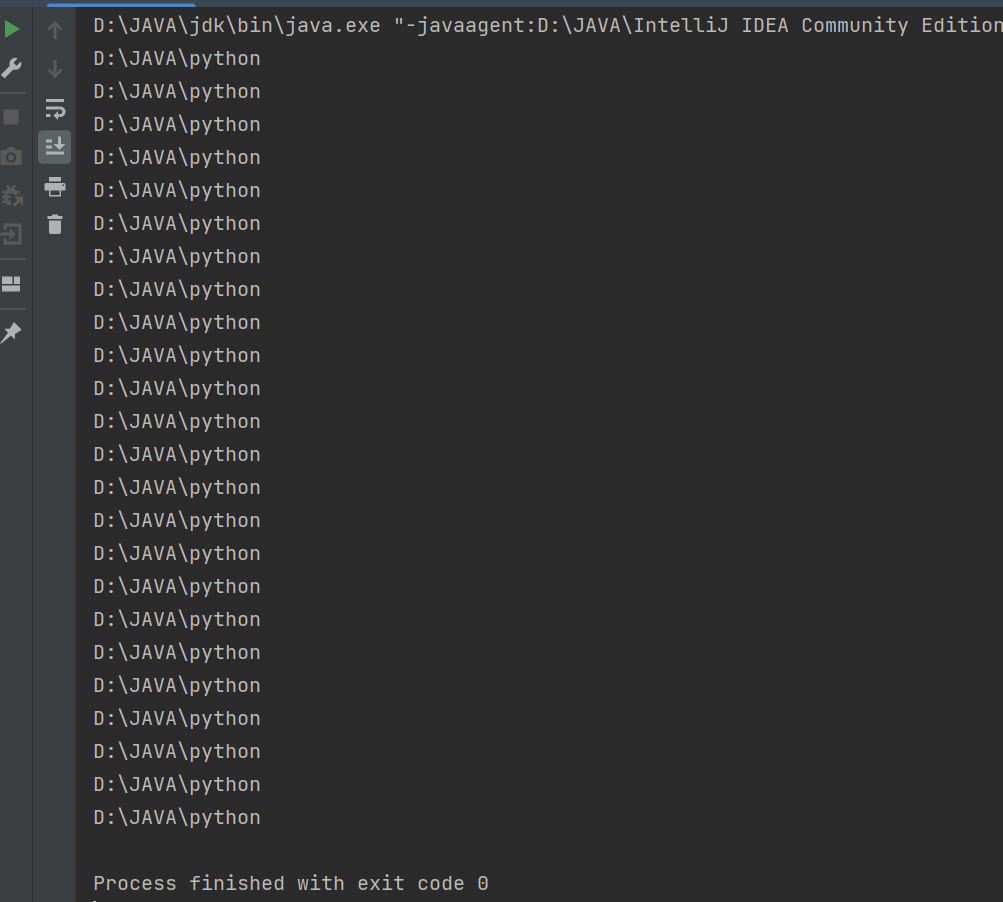
File[] files = file.listFiles();
//此时返回file目录下所有文件,每一个文件用File表示
public class demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {File file = new File("d:/Java/python");File[] files = file.listFiles();if(files == null){System.out.println("空目录");return;}for (File f : files){System.out.println(file.getCanonicalFile());}}
}
file.mkdirs();//只可以创建一个当前目录
file.mkdirs();//如果创建过程中需要中间目录也会进行创建
返回值都是boolean
public class demo6 {public static void main(String[] args) {File file = new File("d:/Java/Test/aaa");System.out.println(file.isDirectory());//判断这个目录是否存在file.mkdir();//创建file对象的目录System.out.println(file.isDirectory());}
}
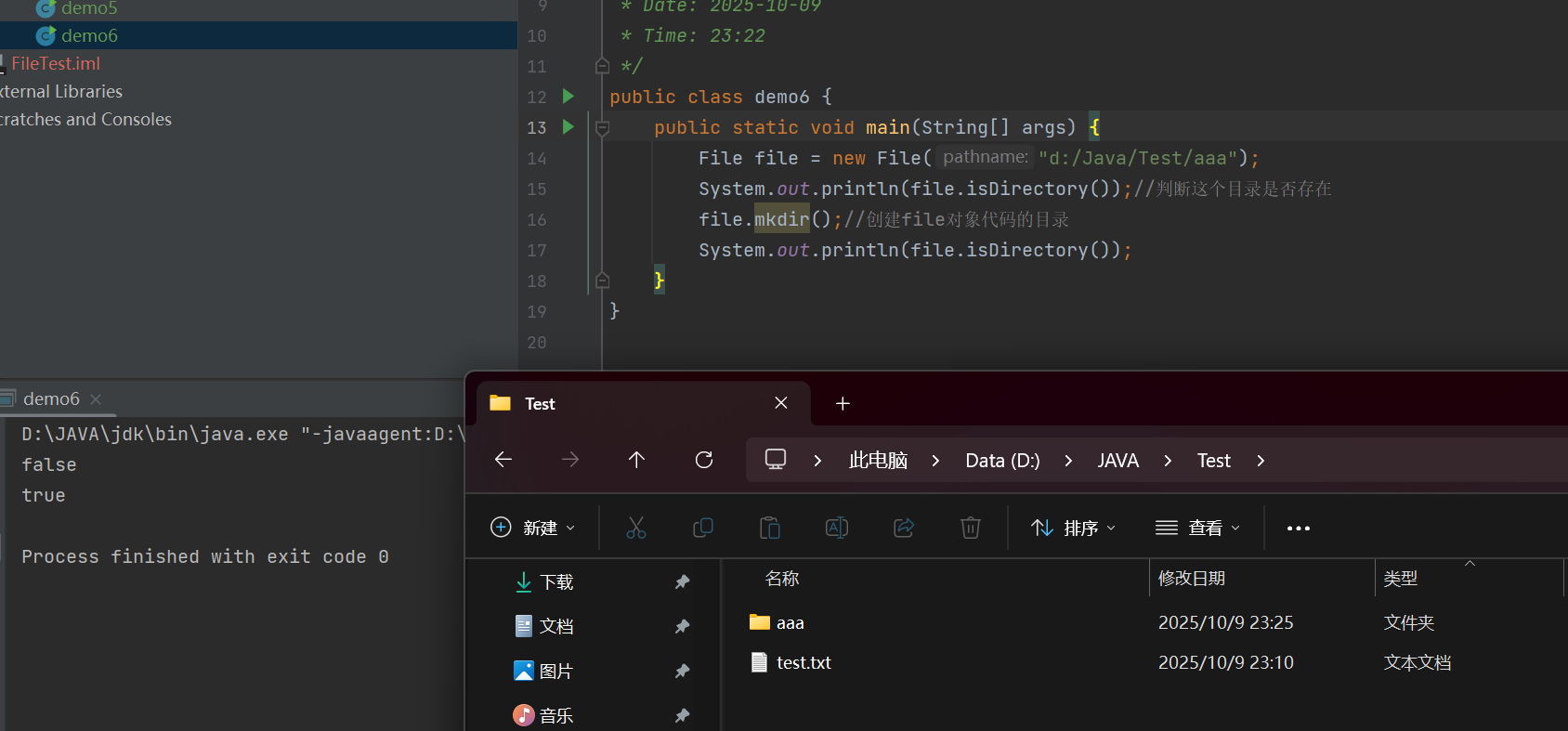
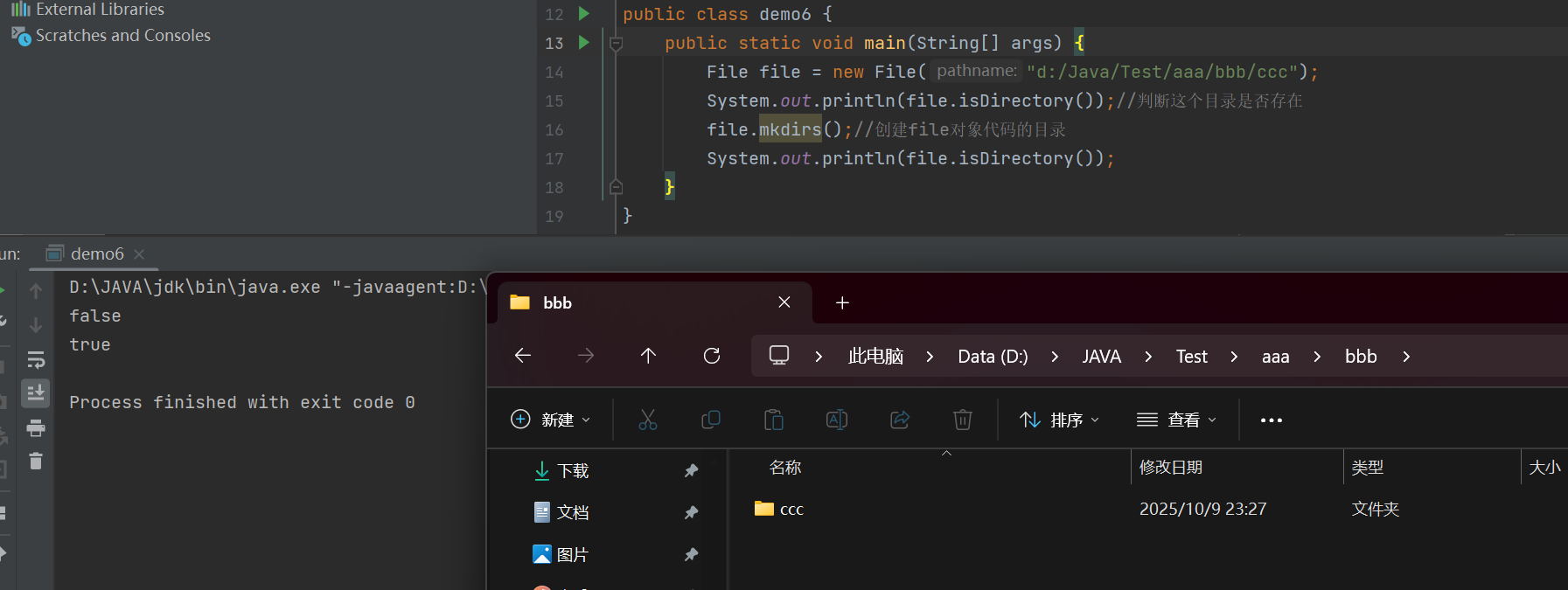
public class demo6 {public static void main(String[] args) {File file = new File("d:/Java/Test/aaa/bbb/ccc");System.out.println(file.isDirectory());//判断这个目录是否存在file.mkdirs();//创建file对象的目录,如果需要创建中间目录,也会创建System.out.println(file.isDirectory());}
}
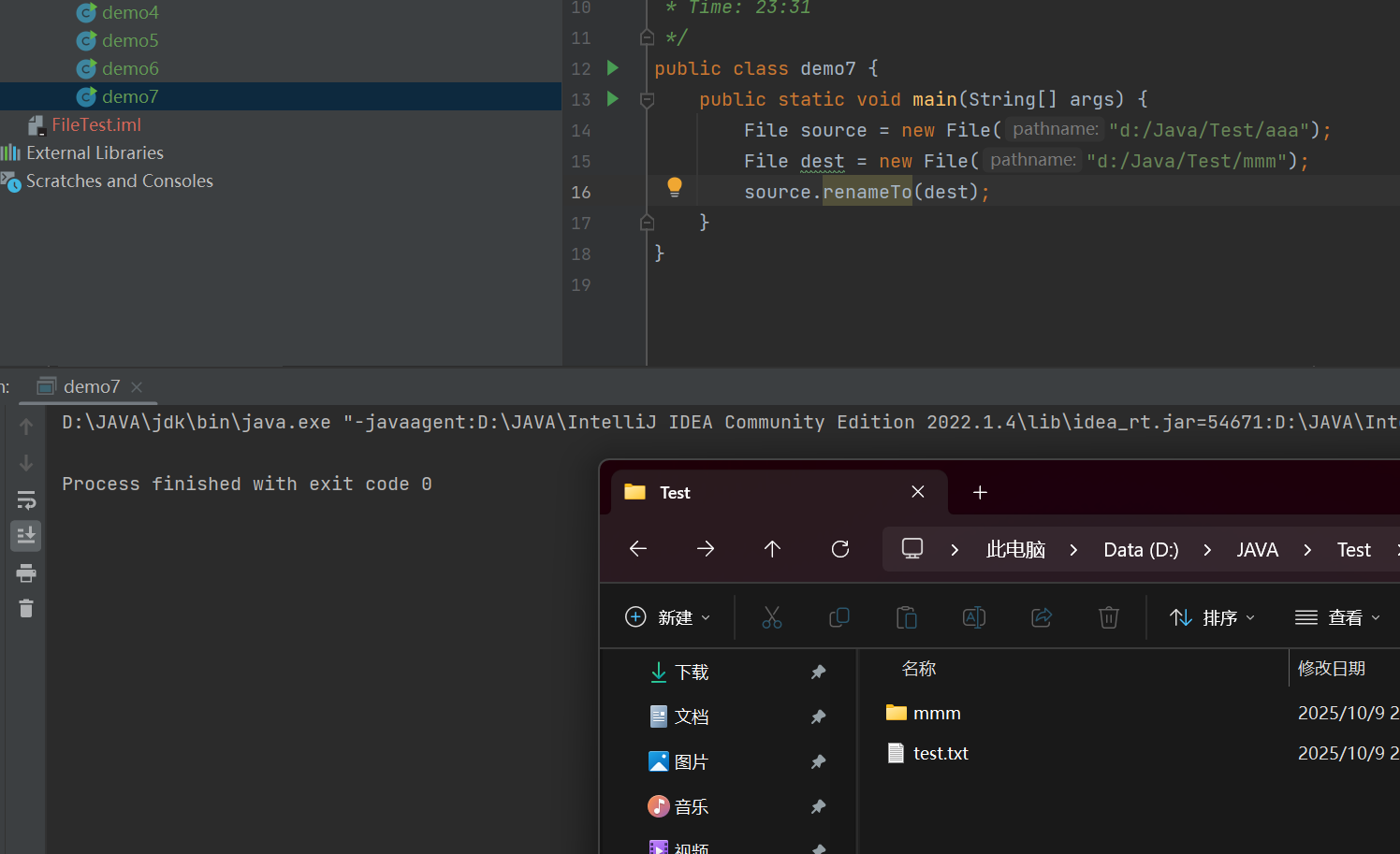
renameTo(File dest);
//对文件进行改名,相当于文件的剪切和粘贴操作
//如果此时的目录是./aaa/bbb/ccc,这里对aaa文件夹进行改名是修改不了
public class demo7 {public static void main(String[] args) {File source = new File("d:/Java/Test/aaa");File dest = new File("d:/Java/Test/mmm");source.renameTo(dest);}
}
文件读写-数据流(stream)
读:就是把文件内容数据读取出来
写:就是向文件夹中写数据
分为两个大类
1.字节流:读写以字节为单位,像这里InputStream输入,OutputStream输出
2.字符流:读写以字符为单位,像这里Reader输入,Writer输出
InputStream
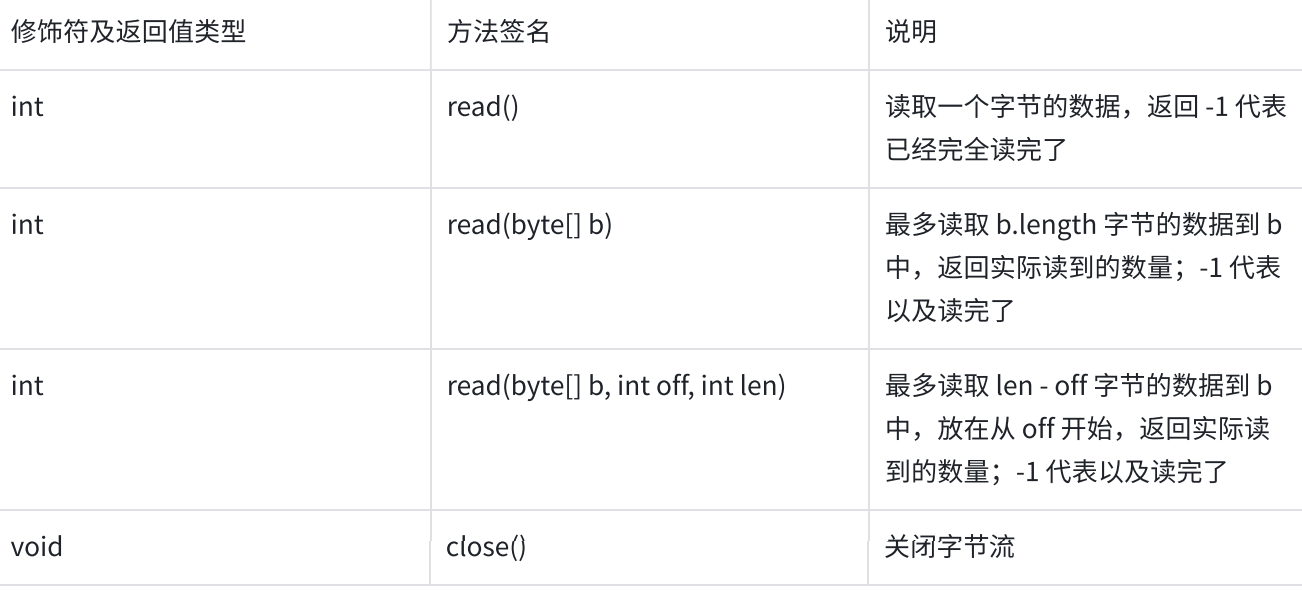
read()读取一个字节的数据,返回-1表示读完了
read(byte[] b),b是"输出型参数"
read(byte[] b,int off, int len)//从off偏移量开始读取,读len个字节
-1表示的是读到了文件末尾
注意:这里返回值都是int,因为"字节对齐"的概念,因为计算机读取4/8个字节
的效率大于读取1/2个字节
InputStream是一个抽象类,因此不可以直接实例化对象,可以实例化FileInputStream对象
这里可能有FileNotFoundException异常,这个异常是IOException的子类
public class demo8 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("D:/JAVA/Test/test.txt");while (true){int n = inputStream.read();if(n == -1){break;//文件读取完毕}System.out.printf("%x",n);System.out.println();}}
}
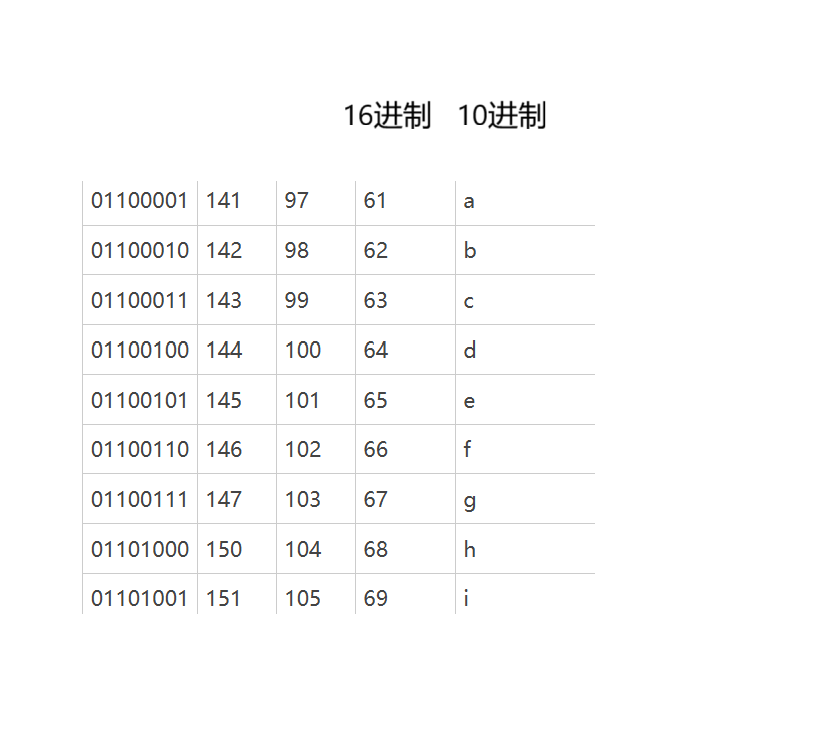
上面这个是会不断的读取硬盘,每一个字节都会触发一次read()读取,并且读取硬盘也比较慢,因此我们需要对其进行优化,并且还没有使用close进行文件关闭
关闭文件close()
在操作系统中有进程,进程中有个PCB里面有文件描述符表,每次打开文件,都会在这里进行记录,但是这个文件描述附表是不能自动扩容,因此如果打开文件过多,就放不下了,必须关闭文件其才会将其资源释放出来
public class demo8 {public static void main(String[] args){InputStream inputStream = null;try {inputStream = new FileInputStream("D:/JAVA/Test/test.txt");while (true){//将这些数据放入1024数组中,可能超出//因此这里采用存储,一次可以读这么多的数据byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int n = 0;n = inputStream.read(bytes);if(n == -1){break;}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {System.out.printf("%x\n",bytes[i]);}}} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}finally {//进行资源释放if(inputStream != null){try{inputStream.close();} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}}
}
上面这个代码中try catch中又嵌套try catch,这样的代码十分的丑陋,因此
try with resources
public class demo8 {public static void main(String[] args){//上面还是try with resources语法解决上面问题try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("D:/JAVA/Test/test.txt");){while (true){byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int n = inputStream.read(bytes);if(n == -1){break;}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {System.out.printf("%x\n",bytes[i]);}}} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
并且这里会自动调用close
Scanner对字符读取
上面读取字符还是以byte单位进行读取,因此可以使用Scanner
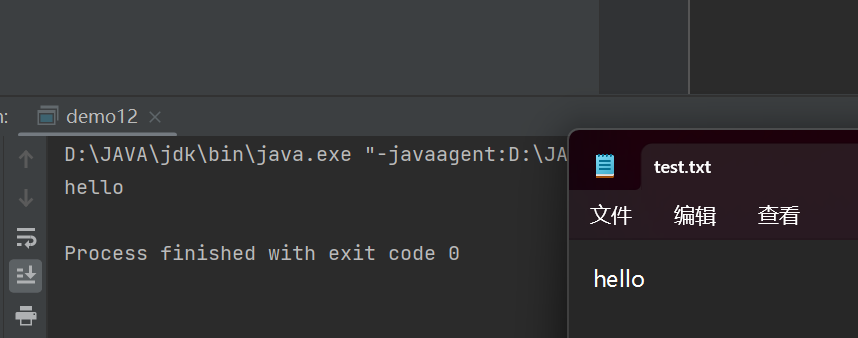
public class demo12 {public static void main(String[] args) {try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("d:/Java/Test/test.txt")) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(inputStream,"UTF-8");String s = scanner.next();System.out.println(s);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
OutputStream

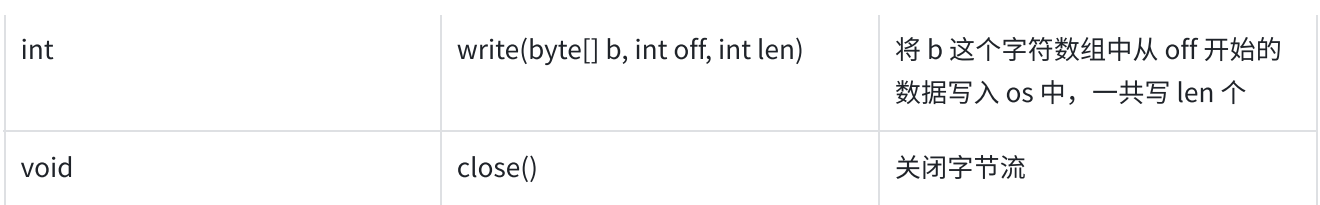
这里的OutputStream 仍然是一个抽象类,因此需要实例化FileOutputStream对象
public class demo9 {public static void main(String[] args) {try (OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:/Java/Test/test.txt")){outputStream.write(65);outputStream.write(66);outputStream.write(67);outputStream.write(68);}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}此时对这个文件进行写入
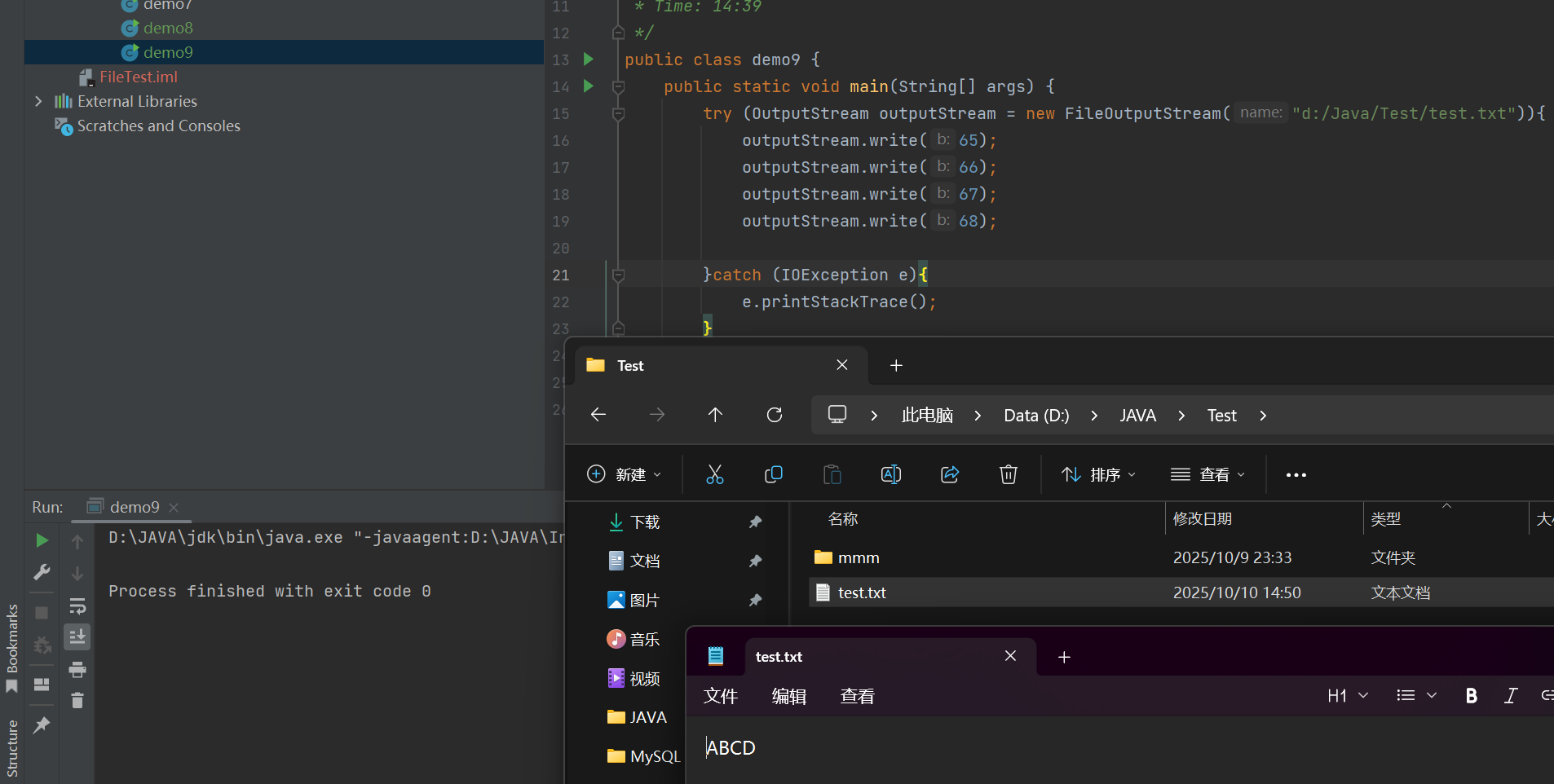
使用byte[]数组写入
public class demo9 {public static void main(String[] args) {try (OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:/Java/Test/test.txt")){
// outputStream.write(65);
// outputStream.write(66);
// outputStream.write(67);
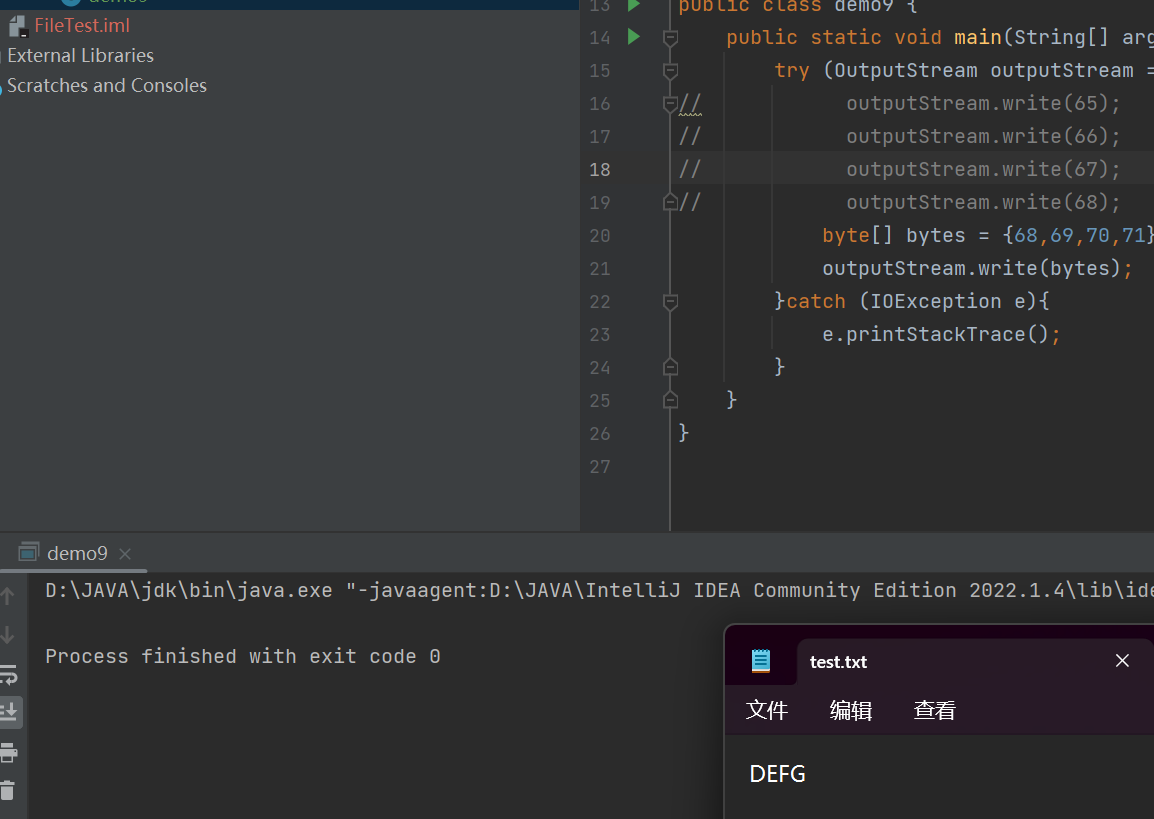
// outputStream.write(68);byte[] bytes = {68,69,70,71};outputStream.write(bytes);}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
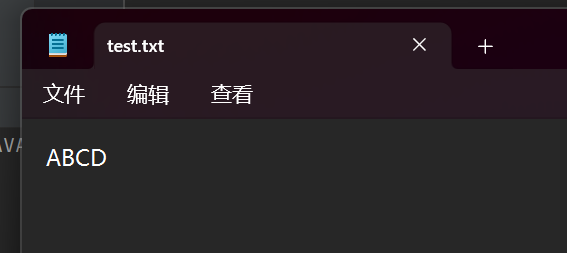
}此时法现一个问题,就是前面写的ABCD好像被这次写的覆盖了
这里默认是覆盖写
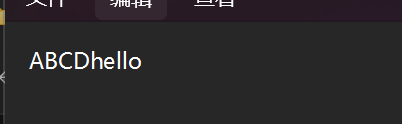
//将这个写入变成追加写
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:/Java/Test/test.txt",true)
//将这个参数设置成true其就会变成追加写
public class demo9 {public static void main(String[] args) {try (OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:/Java/Test/test.txt",true)){byte[] bytes = {'h','e','l','l','o'};outputStream.write(bytes);}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}
写之前
写之后
PrintWriter
这个类提供了print/println/printf进行文件的写入操作
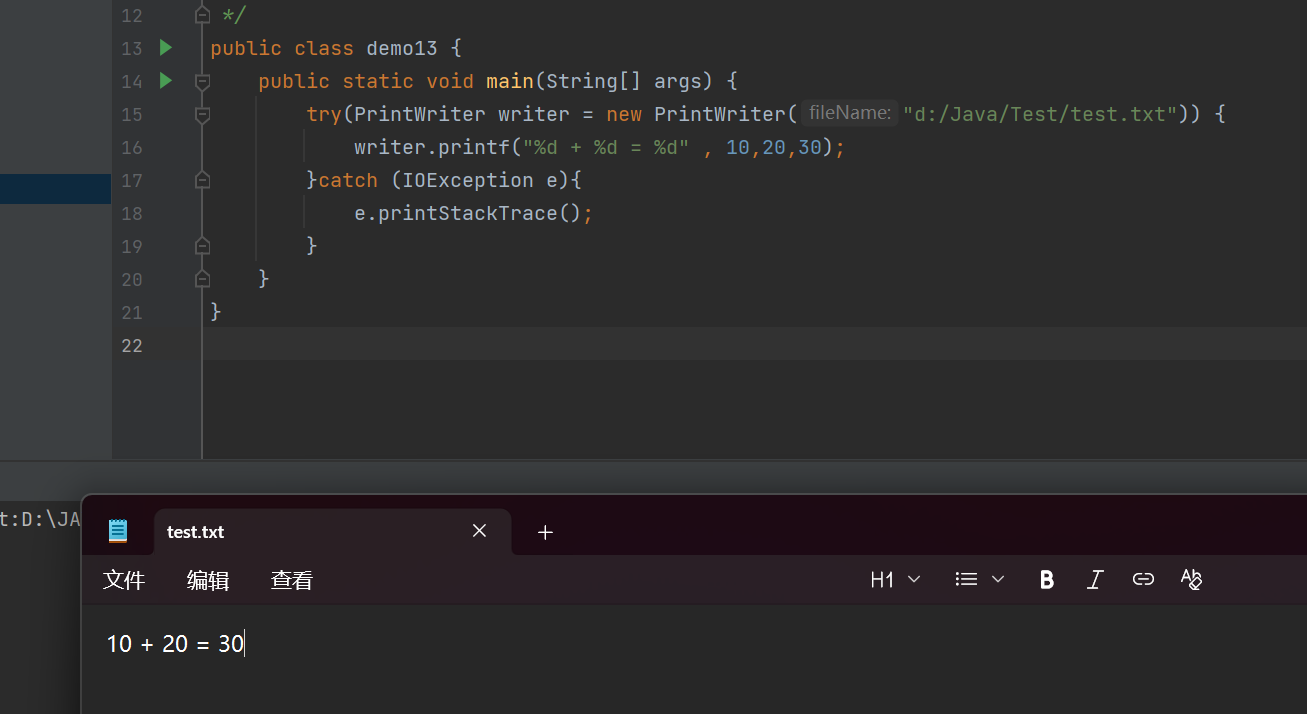
public class demo13 {public static void main(String[] args) {try(PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter("d:/Java/Test/test.txt")) {writer.printf("%d + %d = %d" , 10,20,30);}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}
Reader和Writer
Reader是一个抽象类,因此不可以直接实例化对象,但是可以实例化FileReader对象
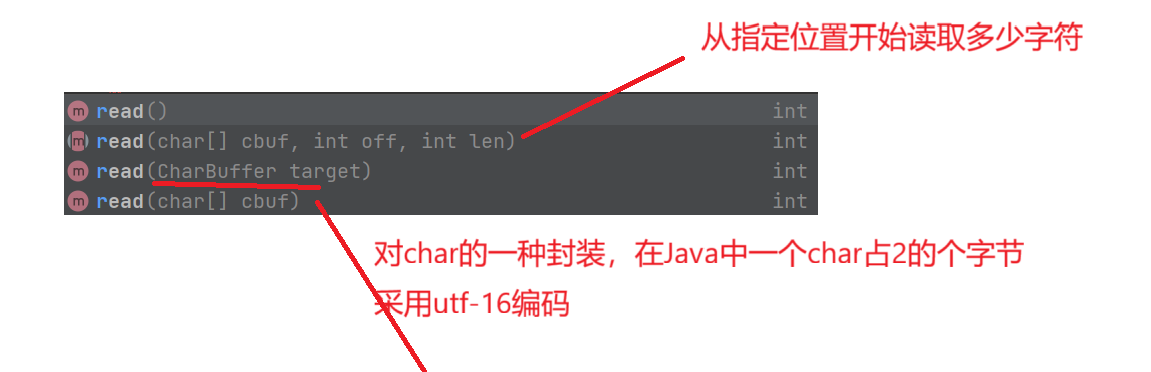
public class demo10 {public static void main(String[] args) {try(Reader reader = new FileReader("d:/Java/Test/test.txt")) {while (true){int n = reader.read();if(n == -1){break;}// System.out.print(n);System.out.println((char) n);}}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}
上面这样重复读取,一次读取一个字符有些浪费时间,因此这里可以每次使用一个char[]进行接收1024个字符,就这样,循环读取,直到读取完
public class demo10 {public static void main(String[] args) {try(Reader reader = new FileReader("d:/Java/Test/test.txt")) {//上面这样会重复读取,因此我们可以使用一个char[]数组一次接收1024个字符while (true){char[] chars = new char[1024];int n = reader.read(chars);//将读取到的信息放入chars数组中if(n == -1){break;}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {System.out.println(chars[i]);}}}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}
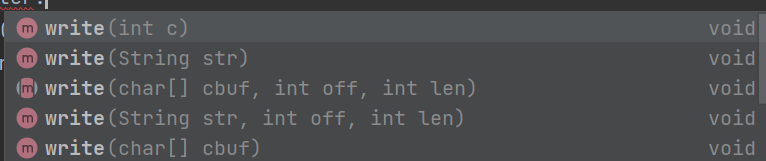
//Writer是一个抽象类
Writer writer = new FileWriter()
public class demo11 {public static void main(String[] args) {try(Writer writer = new FileWriter("d:/Java/Test/test.txt")){writer.write("hello world");}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}
实例练习
示例一
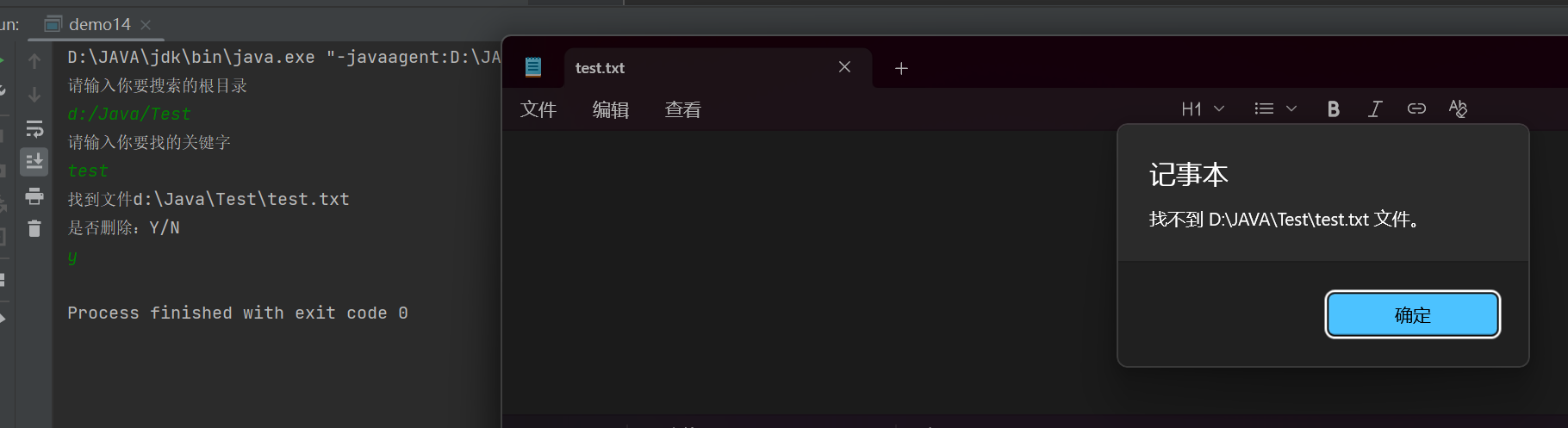
扫描指定⽬录,并找到名称中包含指定字符的所有普通⽂件(不包含⽬录),并且后续询问⽤⼾是否要删除该⽂件
1.先输入目录和关键字
2.读取内容,获取路径,并进行删除
//根据关键字,当前目录下找出所有相关的文件
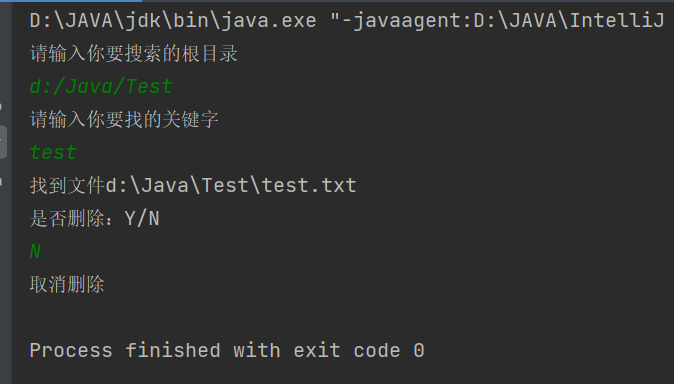
public class demo14 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入你要搜索的根目录");String rootPath = sc.next();File rootfile = new File(rootPath);if(!rootfile.isDirectory()){System.out.println("输入目录不存在或者不是目录");return;}System.out.println("请输入你要找的关键字");String key = sc.next();reserch(rootfile,key);}//找文件private static void reserch(File rootfile, String key) {//列出文件所有内容File[] files = rootfile.listFiles();if(files == null){System.out.println("文件目录下为空");return;}for(File file : files){//判断是否是文件if(file.isFile()){//判断是否包含关键字Delete(file,key);}else if(file.isDirectory()){//是目录文件,需要继续搜索reserch(file,key);}else{}}}//删除操作private static void Delete(File file, String key) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);//判断是否包含关键字if(file.getName().contains(key)){System.out.println("找到文件"+file.getAbsolutePath());System.out.println("是否删除:Y/N");String choice = sc.next();//进行删除if(choice.equals("Y")||choice.equals("y")){file.delete();}else{System.out.println("取消删除");}}}
}
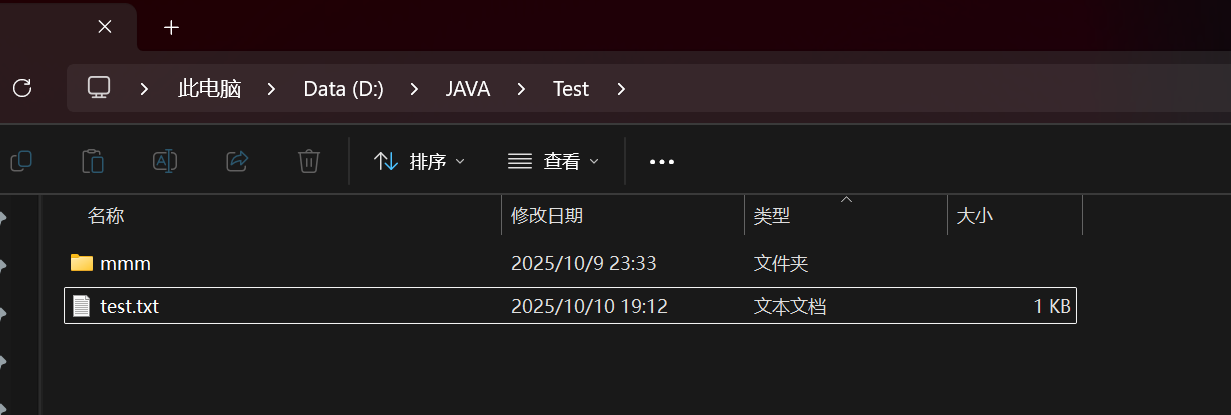
删除成功
示例二
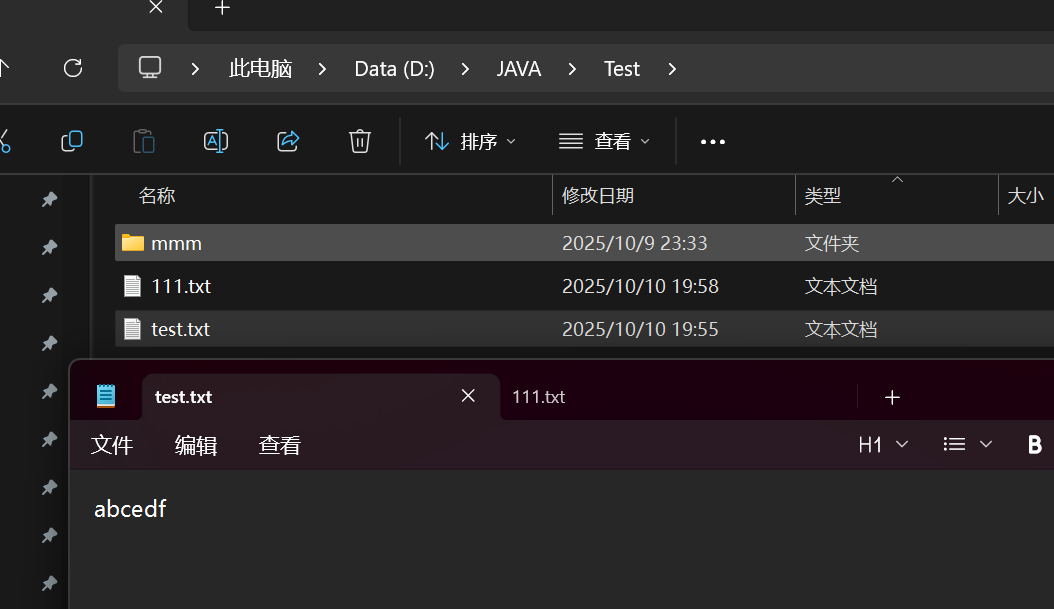
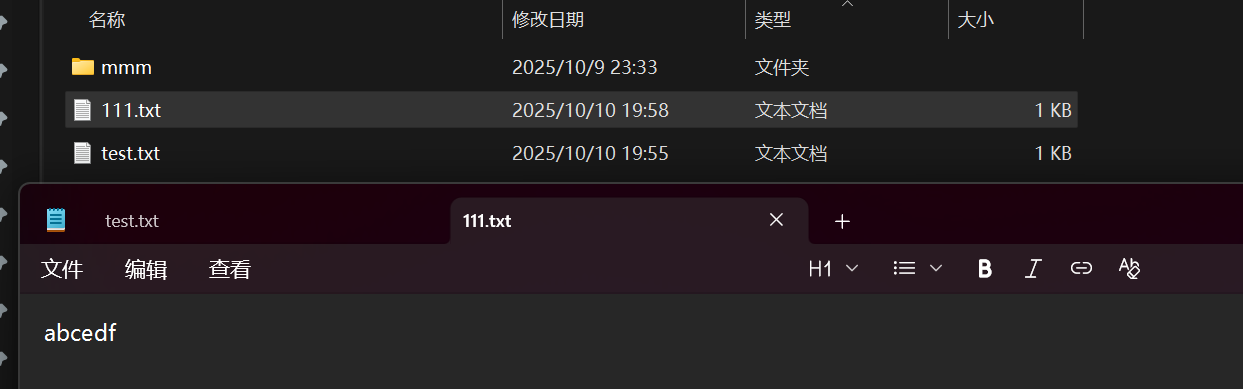
进⾏普通⽂件的复制
1.输入源文件路径和目标目录(判断是否存在)
2.进行源文件读和目标文件的写(目标文件会自动创建,因此目标文件只要父目录存在即可)
//将一个文件的内容复制到另一个文件中
public class demo15 {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.输入复制和被复制的文件目录Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入源文件路径");String src = sc.next();System.out.println("输入目标文件路径");String dest = sc.next();//判断sc这个路径是否合法File srcFile = new File(src);if(!srcFile.isFile()){System.out.println("源文件路径不合法");return;}//判断目标文件的parent是否存在File destFile = new File(dest);if(!destFile.getParentFile().isDirectory()){System.out.println("目标文件不合法");return;}//打开src和dest文件,对dest进行写入try(InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(srcFile);OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(destFile)) {while (true) {byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int n = inputStream.read(bytes);if (n == -1) {break;}outputStream.write(bytes, 0, n);}}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}
示例三
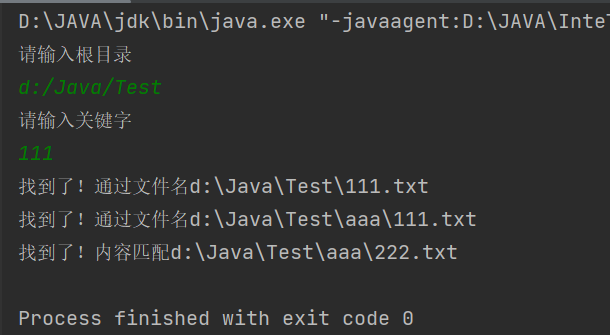
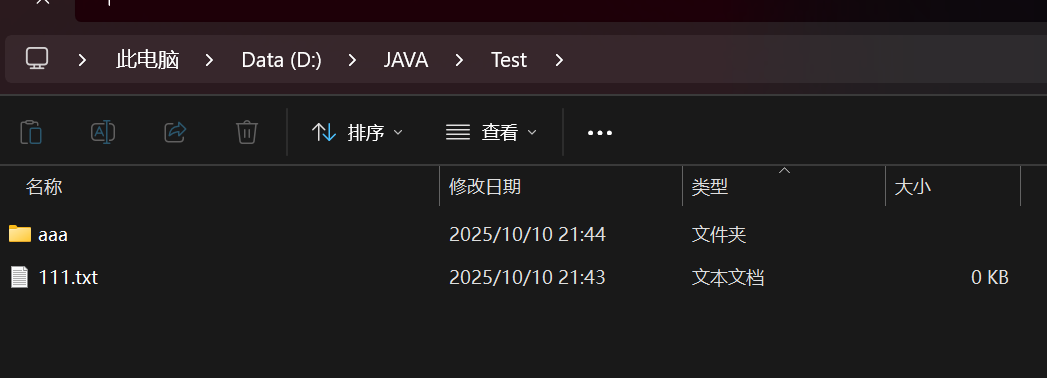
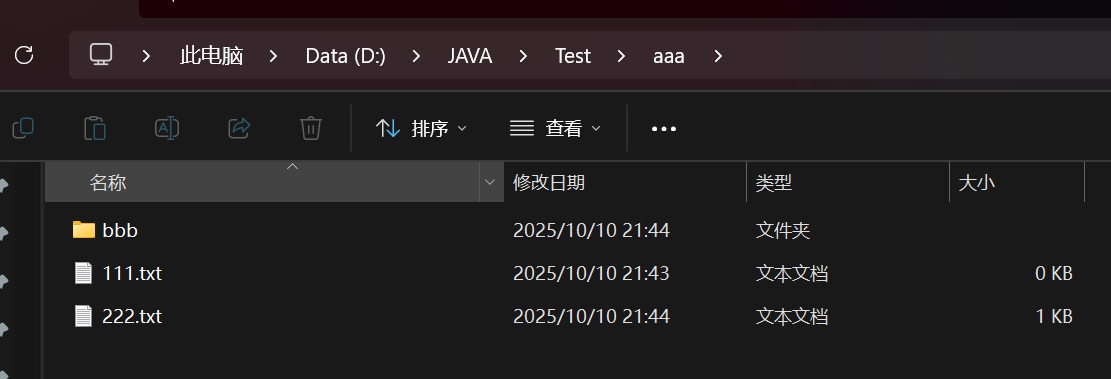
扫描指定⽬录,并找到名称或者内容中包含指定字符的所有普通⽂件(不包含⽬录)
这里和示例一区别就是也需要对文件内容进行判断是否包含关键字
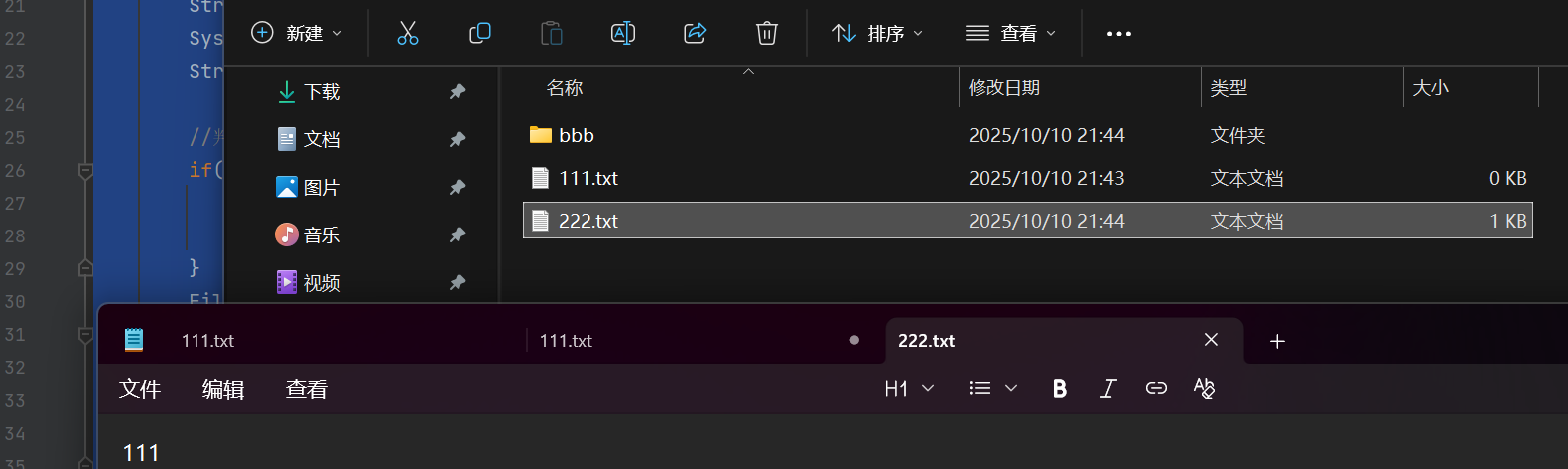
public class demo16 {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.输入根目录和关键字Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入根目录");String rootPath = sc.next();System.out.println("请输入关键字");String key = sc.next();//判断key关键字是否合法if(key.isEmpty()){System.out.println("关键字不合法");return;}File rootFile = new File(rootPath);if(!rootFile.isDirectory()){//不是路径System.out.println("根目录有误");return;}search(rootFile,key);}public static void search(File rootFile,String key){//列出所有File[] files = rootFile.listFiles();if(files == null){System.out.println("没有文件");return;}for(File file : files){if(file.isFile()){//进行文件名及其内容进行判断是否有关key关键字trySearch(file,key);}else if(file.isDirectory()){//如果是路径,需要继续进行找search(file,key);}}}private static void trySearch(File file, String key) {//1.先看文件名是否包含if(file.getName().contains(key)){System.out.println("找到了!通过文件名"+file.getAbsolutePath());}//这里判断内容中是否有关于关键字的,此时文件内容放一起进行判断内容是否有关于这个关键字//使用Reader这样可以一个字符,一个字符的读取try(Reader reader = new FileReader(file)) {StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();while (true){char[] chars = new char[1024];int n = reader.read(chars);if(n == -1){break;}//将真实字符数量拼接一起result.append(chars,0,n);}if(result.indexOf(key) >= 0){//找到了System.out.println("找到了!内容匹配" + file.getAbsolutePath());}else {return;}}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}