1.平均汇聚
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
#需要拟合预测的函数:
def f(x):return 2 * torch.sin(x) + x**0.8
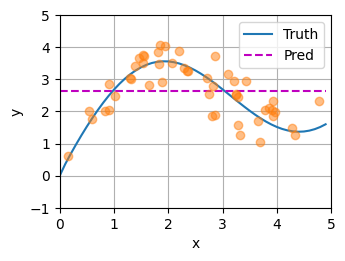
def plot_kernel_reg(y_hat):d2l.plot(x_test, [y_truth, y_hat], 'x', 'y', legend=['Truth', 'Pred'],xlim=[0, 5], ylim=[-1, 5])d2l.plt.plot(x_train, y_train, 'o', alpha=0.5)
n_train = 50
x_train, _ = torch.sort(torch.rand(n_train) * 5)
y_train = f(x_train) + torch.normal(0.0, 0.5, (n_train,))
x_test = torch.arange(0, 5, 0.1)
y_truth = f(x_test)#真实的输出
n_test = len(x_test)
y_hat = torch.repeat_interleave(y_train.mean(), n_test)
plot_kernel_reg(y_hat)
2.非参数注意力汇聚
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
#需要拟合预测的函数:
def f(x):return 2 * torch.sin(x) + x**0.8
def plot_kernel_reg(y_hat):d2l.plot(x_test, [y_truth, y_hat], 'x', 'y', legend=['Truth', 'Pred'],xlim=[0, 5], ylim=[-1, 5])d2l.plt.plot(x_train, y_train, 'o', alpha=0.5)
n_train = 50
x_train, _ = torch.sort(torch.rand(n_train) * 5)
y_train = f(x_train) + torch.normal(0.0, 0.5, (n_train,))
x_test = torch.arange(0, 5, 0.1)
y_truth = f(x_test)#真实的输出
n_test = len(x_test)
#相当于做Q
X_repeat = x_test.repeat_interleave(n_train).reshape((-1, n_train))
attention_weights=nn.functional.softmax(-(X_repeat-x_train)**2/2,dim=1)
y_hat=torch.matmul(attention_weights,y_train)
plot_kernel_reg(y_hat)
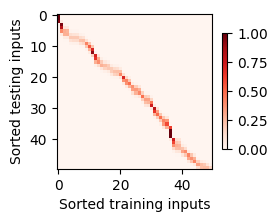
d2l.show_heatmaps(attention_weights.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0),xlabel='Sorted training inputs',ylabel='Sorted testing inputs')
3.带参数注意力汇聚
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
#需要拟合预测的函数:
def f(x):return 2 * torch.sin(x) + x**0.8
def plot_kernel_reg(y_hat):d2l.plot(x_test, [y_truth, y_hat], 'x', 'y', legend=['Truth', 'Pred'],xlim=[0, 5], ylim=[-1, 5])d2l.plt.plot(x_train, y_train, 'o', alpha=0.5)
class NWKernelRegression(nn.Module):def __init__(self, **kwargs):super().__init__(**kwargs)self.w = nn.Parameter(torch.rand((1,), requires_grad=True))def forward(self, queries, keys, values):# queries和attention_weights的形状为(查询个数,“键-值”对个数)queries = queries.repeat_interleave(keys.shape[1]).reshape((-1, keys.shape[1]))self.attention_weights = nn.functional.softmax(-((queries - keys) * self.w)**2 / 2, dim=1)# values的形状为(查询个数,“键-值”对个数)return torch.bmm(self.attention_weights.unsqueeze(1),values.unsqueeze(-1)).reshape(-1)n_train = 50
x_train, _ = torch.sort(torch.rand(n_train) * 5)
y_train = f(x_train) + torch.normal(0.0, 0.5, (n_train,))
x_test = torch.arange(0, 5, 0.1)
y_truth = f(x_test)#真实的输出
n_test = len(x_test)# X_tile的形状:(n_train,n_train),每一行都包含着相同的训练输入
X_tile = x_train.repeat((n_train, 1))
# Y_tile的形状:(n_train,n_train),每一行都包含着相同的训练输出
Y_tile = y_train.repeat((n_train, 1))
# keys的形状:('n_train','n_train'-1)
keys = X_tile[(1 - torch.eye(n_train)).type(torch.bool)].reshape((n_train, -1))
# values的形状:('n_train','n_train'-1)
values = Y_tile[(1 - torch.eye(n_train)).type(torch.bool)].reshape((n_train, -1))net = NWKernelRegression()
loss = nn.MSELoss(reduction='none')
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.5)
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='loss', xlim=[1, 5])
#训练:
for epoch in range(5):trainer.zero_grad()l = loss(net(x_train, keys, values), y_train)l.sum().backward()trainer.step()print(f'epoch {epoch + 1}, loss {float(l.sum()):.6f}')animator.add(epoch + 1, float(l.sum()))
# keys的形状:(n_test,n_train),每一行包含着相同的训练输入(例如,相同的键)
keys = x_train.repeat((n_test, 1))
# value的形状:(n_test,n_train)
values = y_train.repeat((n_test, 1))
y_hat = net(x_test, keys, values).unsqueeze(1).detach()
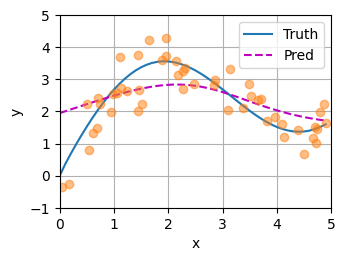
plot_kernel_reg(y_hat)
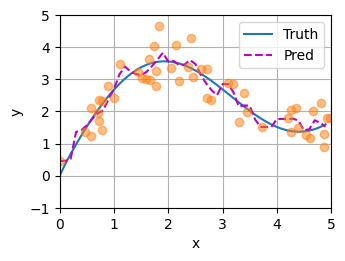
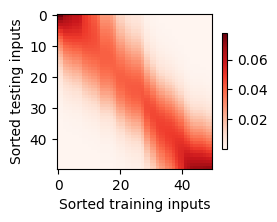
d2l.show_heatmaps(net.attention_weights.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0),xlabel='Sorted training inputs',ylabel='Sorted testing inputs')