STM32 重定向 printf 到串口的 GCC 方法与 Keil 方法对比
前言
我在查看他人的项目源码时,发现了一个名为 syscalls.c 的文件。查阅资料后了解到,这个文件是 STM32CubeMX 针对 arm-none-eabi-gcc(即嵌入式版的 GCC)的底层实现。平时在网上搜索重定向 printf 到串口的方法时,大多数教程都是针对 ARM 环境的。本文将介绍 GCC 环境下如何重定向 printf 到串口,以及两者的实现细节差异。
不同开发环境使用的编译器和 C 标准库对比如下:
| IDE/工具链 | 编译器 | C 标准库 |
|---|---|---|
| Keil MDK (AC5) | ARMCC | ARM C Library / MicroLib |
| Keil MDK (AC6) | ARMCLANG | ARM C Library / MicroLib |
| STM32CubeIDE | GCC (arm-none-eabi-gcc) | Newlib |
| System Workbench | GCC (arm-none-eabi-gcc) | Newlib |
| IAR EWARM | ICCARM | DLIB / CLIB |
printf 重定向的原理
在上位机(自己的电脑)编写 C 语言程序时,会使用很多标准库函数:
printf("Hello"); // 打印
malloc(100); // 分配内存
strcpy(a, b); // 字符串复制
不同编译器对标准库都有各自的底层实现,但实现效果相同,因为它们遵循同一套标准。
各编译器使用的 C 标准库如下:
| 编译器 | 使用的 C 标准库 |
|---|---|
| Keil AC5 | ARM C Library 或 MicroLib |
| GCC | Newlib |
| 电脑上的 GCC | glibc(太大,嵌入式不适用) |
调用 printf 时的执行流程如下:
用户代码:printf("Hello %d", 123)↓
【标准库层】处理格式化字符串 → "Hello 123"↓
【底层接口】逐字符输出↓
【硬件层】UART 发送数据
不同的标准库在"底层接口"这一层使用不同的函数名和机制,这就是问题的根源。两者的主要区别如下:
- Keil (ARMCC):实现
fputc()函数 - GCC (Newlib):实现
_write()或__io_putchar()函数
Keil MDK 实现方法
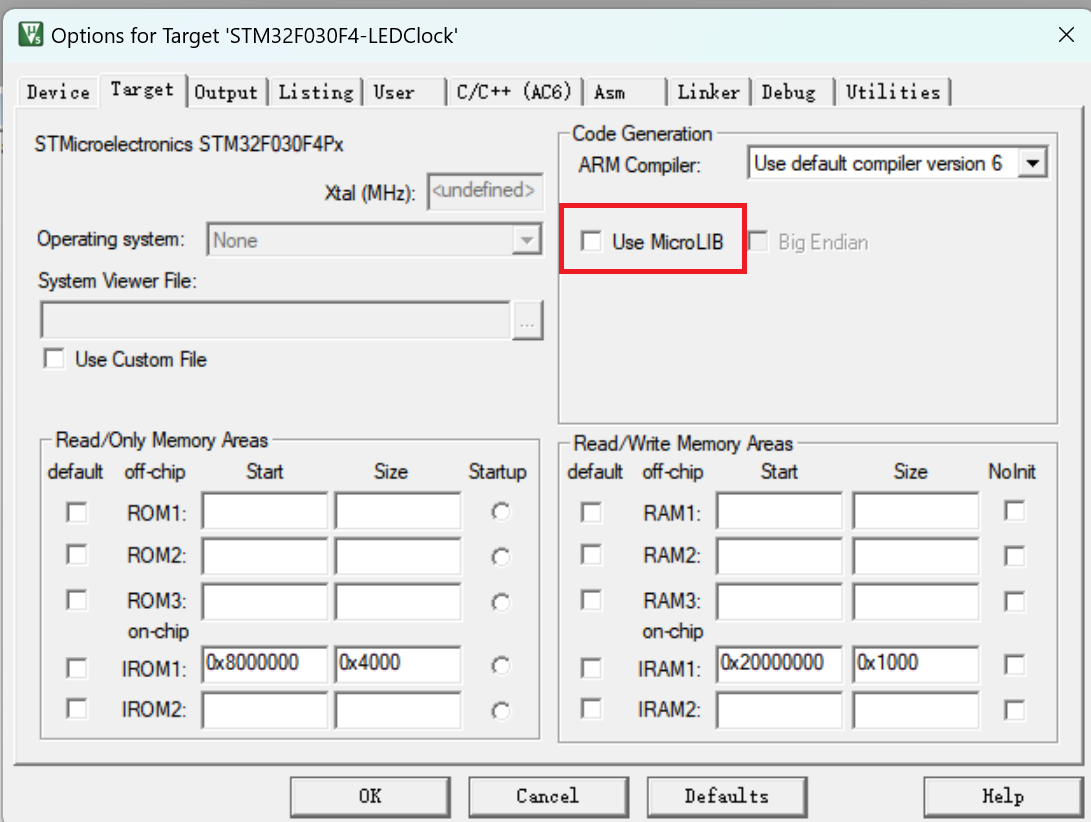
使用 MicroLib(最简单)
MicroLib 是 ARM C Library 的精简版本,去除了文件操作等复杂功能。可以在 Keil 中直接启用,只需勾选相应选项即可。
启用 MicroLib 后,只需实现相应的底层接口即可,这里是 fputc 函数(串口可自行更改):
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stm32xxx_hal.h"extern UART_HandleTypeDef huart1;int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
{HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, (uint8_t *)&ch, 1, HAL_MAX_DELAY);return ch;
}
使用标准库
使用标准库需要定义的内容较多,但都是固定的。可以参考正点原子的教程:
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stm32f0xx_hal.h" // 假设已定义 UART 句柄
extern UART_HandleTypeDef huart1;/*** @brief 重定向 fputc 函数,实现 printf 到 UART* @param ch 要输出的字符* @param f 文件指针(这里用不到)* @retval 输出的字符*/
int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
{HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, (uint8_t *)&ch, 1, HAL_MAX_DELAY);return ch;
}/*** @brief 重定向 fgetc 函数,实现 scanf 从 UART 接收* @param f 文件指针* @retval 接收到的字符*/
int fgetc(FILE *f)
{uint8_t ch;HAL_UART_Receive(&huart1, &ch, 1, HAL_MAX_DELAY);return ch;
}// 避免使用半主机模式(semihosting)
#pragma import(__use_no_semihosting)// 标准库需要的支持函数
struct __FILE
{ int handle;
};FILE __stdout;
FILE __stdin;void _sys_exit(int x)
{ x = x;
}
GCC (Newlib) 实现方法
GCC 的实现流程如下:printf() → 格式化 → _write() → __io_putchar() → UART 硬件。通过 _write() 系统调用实现输出。
直接实现 _write
#include <unistd.h>
#include "stm32xxx_hal.h"extern UART_HandleTypeDef huart1;int _write(int file, char *ptr, int len)
{HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, (uint8_t *)ptr, len, HAL_MAX_DELAY);return len;
}
使用 syscalls.c
这是 STM32CubeIDE 和 System Workbench 的标准做法。由于这个文件是自动生成的,这里不再赘述。
/*** File : syscalls.c** Abstract : System Workbench Minimal System calls file** For more information about which c-functions* need which of these lowlevel functions* please consult the Newlib libc-manual** Environment : System Workbench for MCU** Distribution: The file is distributed "as is," without any warranty* of any kind.*//* Includes */
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/times.h>/* Variables */
extern int errno;
extern int __io_putchar(int ch) __attribute__((weak));
extern int __io_getchar(void) __attribute__((weak));register char * stack_ptr asm("sp");char *__env[1] = { 0 };
char **environ = __env;/* Functions */
void initialise_monitor_handles()
{
}int _getpid(void)
{return 1;
}int _kill(int pid, int sig)
{errno = EINVAL;return -1;
}void _exit (int status)
{_kill(status, -1);while (1) {} /* Make sure we hang here */
}__attribute__((weak)) int _read(int file, char *ptr, int len)
{int DataIdx;for (DataIdx = 0; DataIdx < len; DataIdx++){*ptr++ = __io_getchar();}return len;
}__attribute__((weak)) int _write(int file, char *ptr, int len)
{int DataIdx;for (DataIdx = 0; DataIdx < len; DataIdx++){__io_putchar(*ptr++);}return len;
}caddr_t _sbrk(int incr)
{extern char end asm("end");static char *heap_end;char *prev_heap_end;if (heap_end == 0)heap_end = &end;prev_heap_end = heap_end;if (heap_end + incr > stack_ptr){errno = ENOMEM;return (caddr_t) -1;}heap_end += incr;return (caddr_t) prev_heap_end;
}int _close(int file)
{return -1;
}int _fstat(int file, struct stat *st)
{st->st_mode = S_IFCHR;return 0;
}int _isatty(int file)
{return 1;
}int _lseek(int file, int ptr, int dir)
{return 0;
}int _open(char *path, int flags, ...)
{/* Pretend like we always fail */return -1;
}int _wait(int *status)
{errno = ECHILD;return -1;
}int _unlink(char *name)
{errno = ENOENT;return -1;
}int _times(struct tms *buf)
{return -1;
}int _stat(char *file, struct stat *st)
{st->st_mode = S_IFCHR;return 0;
}int _link(char *old, char *new)
{errno = EMLINK;return -1;
}int _fork(void)
{errno = EAGAIN;return -1;
}int _execve(char *name, char **argv, char **env)
{errno = ENOMEM;return -1;
}
附录
名词解释
本文涉及的一些专业术语解释如下。
半主机模式(Semihosting)
半主机模式是让单片机通过调试器(比如 ST-Link、J-Link)借用电脑的功能(比如在电脑屏幕上打印信息、读写电脑的文件)。当程序需要脱离调试器独立运行时(比如烧录后拔掉调试器),必须禁用半主机模式,否则在运行 printf 时,程序会一直等待调试器,导致卡死。
arm-none-eabi-gcc
这是嵌入式 ARM 版本的 GCC。none 表示没有操作系统(裸机运行),eabi 是 Embedded Application Binary Interface(嵌入式应用程序二进制接口)的缩写。
Newlib
一个专为嵌入式系统设计的 C 标准库,适用于 GCC 工具链(STM32CubeIDE、PlatformIO 等)。syscalls.c 就是为 Newlib 准备的底层接口文件。
AC5 和 AC6
Keil MDK 使用的两代编译器:
| 项目 | AC5 | AC6 |
|---|---|---|
| 全名 | ARM Compiler 5 | ARM Compiler 6 |
| 核心 | ARMCC | ARMCLANG(基于 LLVM) |
| 年代 | 老版本(已停止更新) | 新版本(推荐使用) |
| C 库 | ARM C Library | ARM C Library |
两者都不使用 Newlib,所以都不需要 syscalls.c。
glibc
Linux 电脑上使用的标准 C 库(体积较大,嵌入式系统不适用)。
总结对比
| 项目 | Keil | GCC |
|---|---|---|
| 函数名 | fputc() | _write() / __io_putchar() |
| syscalls.c | 不需要 | 推荐使用 |
| 半主机模式处理 | #pragma 禁用 | syscalls.c 已处理 |
