Linux系统编程——exec函数族
Linux系统编程——exec函数族
execl
int execl(const char* path, const char* arg,...);
功能:创建一个运行path指定可执行文件的进程
path:指定文件路径
arg:参数列表第一个必须是该命令的名称,其余为选项和参数,也可以没有。
返回值:失败返回-1并设置errno
实例
代码:
#include <cstdio>
#include <unistd.h>int main()
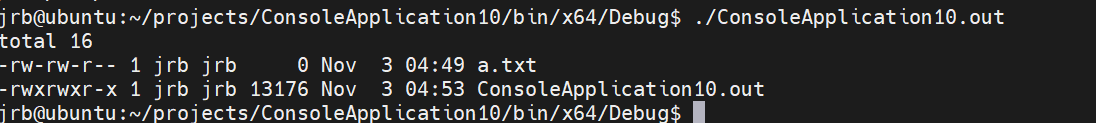
{execl("/bin/ls", "ls","-l", NULL);return 0;
}
执行结果:
execle
int execle(const char* path, const char* arg, ..., char* const envp[]);
功能:创建一个运行path指定可执行文件的进程
path:路径名
arg:参数列表包含执行文件名称,结尾以NULL结束
envp:指定的环境变量,结尾以NULL结束。
返回值:失败返回-1并设置errno
实例
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main()
{char* envp[] = { "PATH=hello", NULL };execle("/usr/bin/env", "env", NULL, envp);return 0;
}
执行结果:

execlp
int execlp(const char* file, const char* arg, ...);
功能:启动一个进程,运行file指定的文件,不需要指定路径,会自动搜索
file:文件名
argv:参数列表包含执行文件名称,结尾以NULL结束
返回值:失败返回-1并设置errno
实例
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main()
{execlp("ls", "ls", "-l", NULL);return 0;
}
执行结果:

execv
int execv(const char* path, char* const argv[]);
功能:创建一个运行path指定可执行文件的进程
argv:参数列表包含执行文件名称,结尾以NULL结束
返回值:失败返回-1并设置errno
实例
代码:
#include <cstdio>
#include <unistd.h>int main()
{char* arg[] = { "ls","-l", NULL };execv("/bin/ls",arg);return 0;
}
执行结果:

execvpe
int execvpe(const char* file, char* const arg[], char* const envp[]);
功能:启动一个进程,运行file指定的文件,不需要指定路径,会自动搜索,可以指定环境变量
file:文件名
arg:执行的命令参数,包括命令名,选项等末尾以NULL结尾
envp:指定的环境变量,以NULL结尾。
返回值:失败返回-1并设置errno
实例
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main()
{char* arg[] = { "env", NULL };char* envp[] = { "PATH=hello", NULL };execvpe("env", arg, envp);return 0;
}
执行结果:

execvp
int execvp(const char* file, char* const argv[]);
功能:启动一个进程,运行file指定的文件,不需要指定路径,会自动搜索
file:文件名
argv[]:参数列表包含执行文件名称,结尾以NULL结束。
返回值:失败返回-1并设置errno
实例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main()
{char* arg[] = { "ls","-l", NULL };execvp("ls", arg);return 0;
}运行结果:
后缀总结
l:以列表形式列出要执行的操作
v:将要执行的操作放到数组中
p:只指定文件名、不需要指定路径,会自动搜索
e:指定环境变量
