博弈dp|凸包|math分类
lc464
博弈dp
(DFS)+ memo
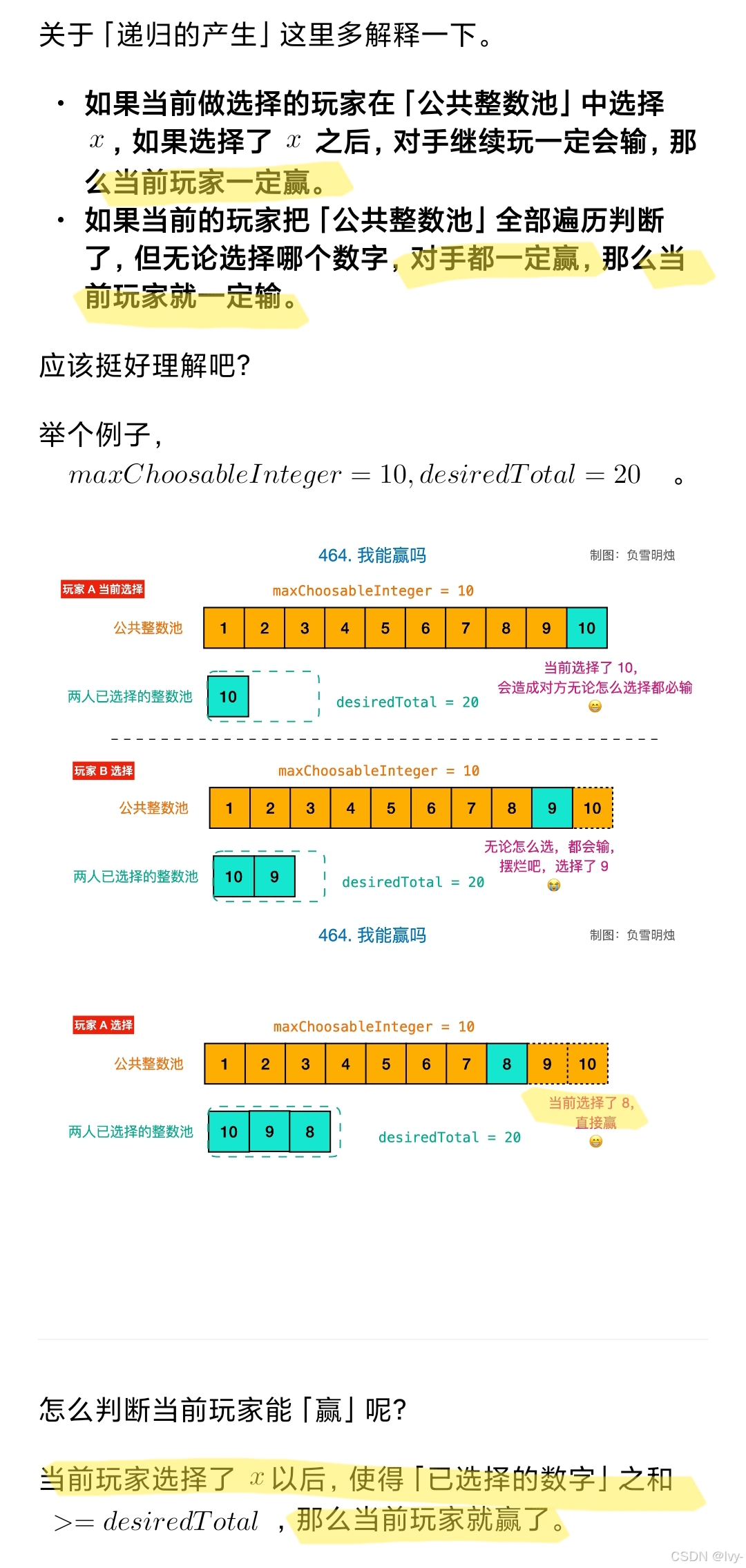
判断在“从1到maxChoosableInteger中选数,累加先到desiredTotal者胜”的游戏里,先手是否能必胜
if (!dfs((1 << x) | state, sum + x, maxChoosableInteger, desiredTotal)) {
visited[state] = 1;
return true;
}



class Solution {
private:
int visited[1 << 21];
public:
bool canIWin(int maxChoosableInteger, int desiredTotal) {
if (maxChoosableInteger >= desiredTotal)
return true;
if (maxChoosableInteger * (maxChoosableInteger + 1) / 2 < desiredTotal)
return false;
return dfs(0, 0, maxChoosableInteger, desiredTotal);
}
bool dfs(int state, int sum, int maxChoosableInteger, int desiredTotal) {
if (visited[state] == 1) return true;
if (visited[state] == 2) return false;
for (int x = 1; x <= maxChoosableInteger; ++x) {
if ((1 << x) & state) continue;
if (sum + x >= desiredTotal) {
visited[state] = 1;
return true;
}
if (!dfs((1 << x) | state, sum + x, maxChoosableInteger, desiredTotal)) {
visited[state] = 1;
return true;
}
}
visited[state] = 2;
return false;
}
};

原来不太优雅的代码
class Solution {
public:
bool canIWin(int maxChoosableInteger, int desiredTotal) {
if(maxChoosableInteger>=desiredTotal)
return true;
int sum=(1+maxChoosableInteger)*maxChoosableInteger/2;
if(sum<desiredTotal)return false;
int n=desiredTotal;
unordered_map<long long,bool> memo;
auto dfs=[&](auto&&dfs,int s,int mask)->bool{
if(s<=0)return false;
long long ma=s<<31|mask;
if(memo.count(ma))return memo[ma];
bool res=false;
for(int i=1;i<=maxChoosableInteger;++i){
if((mask>>i)&1==1)continue;
if(!dfs(dfs,s-i,mask|1<<i)){
res=true;
break;
}
}
return memo[ma]=res;
};
return dfs(dfs,n,0);
}
};
lc335
- 单次线性扫描,按 i 与 i-3/i-4/i-5 的三类局部判据检测交叉即可。
概述
- 从原点开始按“北-西-南-东”循环方向移动,每次移动长度由数组给出,判断整条路径是否出现任意两条线段相交(含端点相交)
思路(O(n) 常数空间)
- 题为 LeetCode 335(路径交叉),存在三种局部相交模式,判断是否在移动到第 i 段时与前面至多 5 段产生相交即可:
1) 第 i 段与 i-3 段“简单环绕”相交:
d[i] >= d[i-2] 且 d[i-1] <= d[i-3]
2) 第 i 段与 i-4 段“贴边重叠”相交
d[i-1] == d[i-3] 且 d[i]+d[i-4] >= d[i-2]
3) 第 i 段与 i-5 段“复杂回绕”相交
d[i-2] >= d[i-4] 且 d[i-1] <= d[i-3] 且 d[i-1]+d[i-5] >= d[i-3] 且 d[i]+d[i-4] >= d[i-2]
- 证明要点:路径每步只可能与最近的若干条边发生交叉,超过 5 段之外的交叉会被上述局部交叉先捕获;因此线性一次扫描即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool isSelfCrossing(vector<int>& d) {
int n = d.size();
bool ret = false;
for (int i = 3; i < n; ++i) {
// case 1: i 与 i-3 相交
if (d[i] >= d[i-2] && d[i-1] <= d[i-3]) ret = true;
// case 2: i 与 i-4 贴边
if (i >= 4 && d[i-1] == d[i-3] && d[i] + d[i-4] >= d[i-2]) ret = true;
// case 3: i 与 i-5 复杂回绕
if (i >= 5 &&
d[i-2] >= d[i-4] &&
d[i-1] <= d[i-3] &&
d[i-1] + d[i-5] >= d[i-3] &&
d[i] + d[i-4] >= d[i-2]) ret = true;
if (ret) break;
}
return ret;
}
};
lc587
凸包
先排序,再用单调链按“右拐弹出、共线保留”的规则构造上下凸壳并合并去重得到边界所有点Andrew’s Monotone Chain 算法
概述
- 给定若干棵树的坐标点,要求用最短的绳子把花园围起来,即求包含所有点的最小周长凸包。
- 返回恰好在围栏周边的点坐标,边上的共线点也需包含在结果中。
思路
- 经典“围栏”/凸包问题(LeetCode 587: Erect the Fence)。
- 采用 Andrew’s Monotone Chain 算法:
- 按 x 再 y 排序,线性扫描构造下凸壳和上凸壳。
- 对方向,用叉积 cross(o,a,b) = (a-o) × (b-o):当 cross < 0 表示出现右拐则弹出,cross == 0(共线)时保留边界上的点以包含所有共线点。
- 最后合并上下壳并去重。
- 算法稳定、实现简洁,时间复杂度 O(n log n)(排序为主),空间 O(n),可轻松满足 n ≤ 3000
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> outerTrees(vector<vector<int>>& pts) {
int n = pts.size();
if(n <= 1) return pts;
sort(pts.begin(), pts.end());
auto cross = [&](const vector<int>& o, const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b){
long long x1 = a[0]-o[0], y1 = a[1]-o[1];
long long x2 = b[0]-o[0], y2 = b[1]-o[1];
return x1*y2 - x2*y1;
};
vector<vector<int>> st;
// lower hull
for(auto &p: pts)
{
while(st.size() >= 2 && cross(st[st.size()-2], st.back(), p) < 0) st.pop_back();
st.push_back(p);
}
// upper hull
size_t k = st.size();
for(int i = n-2; i >= 0; --i){
auto &p = pts[i];
while(st.size() > k && cross(st[st.size()-2], st.back(), p) < 0)
st.pop_back();
st.push_back(p);
}
// 去掉首尾重复点
if(!st.empty()) st.pop_back();
// 去重(因为要包含边上所有共线点,上下链可能重复)
sort(st.begin(), st.end());
st.erase(unique(st.begin(), st.end()), st.end());
vector<vector<int>> ret = st;
return ret;
}
};
// 补充说明
// - 关键点在于弹栈条件只对“右拐”(cross < 0)弹出,cross == 0 时保留从而包含边界上的所有共线点,符合题意要求。
// - 时间复杂度 O(n log n),空间 O(n),不会超时。
