用红黑数封装实现map,set
引言
可以先了解一下红黑树的底层原理和接口
C++:模拟实现红黑树-CSDN博客
一、介绍set,map
在 C++ 中,map 和 set 是标准模板库(STL)提供的关联容器,它们基于红黑树(一种自平衡二叉搜索树)实现,具有自动排序和快速查找的特性。以下是它们的详细介绍:
1. set(集合)
set 是一种有序、不允许重复元素的容器,元素会按照默认(升序)或自定义的规则自动排序。
核心特性
- 元素唯一:插入重复元素时会被忽略。
- 自动排序:默认按
<运算符升序排列,可通过自定义比较器修改排序规则(如降序)。 - 查找高效:红黑树结构支持
O(log n)时间复杂度的插入、删除和查找操作。
#include <set>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {set<int> s; // 定义一个存放 int 类型的 set(默认升序)// 插入元素s.insert(3);s.insert(1);s.insert(2);s.insert(2); // 重复元素,会被忽略// 遍历(自动排序为 1, 2, 3)for (auto it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it) {cout << *it << " "; // 输出:1 2 3}// 查找元素auto it = s.find(2);if (it != s.end()) {cout << "\n找到元素:" << *it; // 输出:找到元素:2}// 删除元素s.erase(2); // 删除值为 2 的元素return 0;
}变种:multiset
multiset 与 set 类似,但允许重复元素,其他特性一致。
2. map(映射)
map是一种键值对(key-value) 容器,其中 key 唯一且有序,value 可重复。map 会根据 key 自动排序(默认升序)。
核心特性
- 键唯一:每个
key只能对应一个value,插入重复key会覆盖旧值。 - 自动排序:按
key的默认(或自定义)规则排序。 - 高效操作:插入、删除、查找(通过
key)的时间复杂度为O(log n)。
#include <map>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {map<string, int> m; // 键为 string,值为 int(默认按 key 升序)// 插入键值对m["apple"] = 5;m.insert({"banana", 3});m["apple"] = 10; // 重复 key,覆盖旧值(变为 10)// 遍历(按 key 升序:apple, banana)for (auto& pair : m) { // pair 是 pair<string, int> 类型cout << pair.first << ": " << pair.second << endl;}// 输出:// apple: 10// banana: 3// 查找 keyauto it = m.find("banana");if (it != m.end()) {cout << "找到:" << it->first << " = " << it->second; // 输出:找到:banana = 3}// 删除 keym.erase("apple");return 0;
}变种:multimap
multimap 允许重复的 key,即一个 key 可对应多个 value,其他特性与 map 一致。
unordered_set和unordered_map(基于哈希表,查找时间接近O(1),但不排序)。
二、模拟实现
1.了解源码中是如何实现的
SGI-STL30版本源代码,map和set的源代码在 map/set/stl_map.h/stl_set.h/stl_tree.h等几个头文件中。
下面截取的源码中的部分代码
// set
#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_TREE_H
#include <stl_tree.h>
#endif
#include <stl_set.h>
#include <stl_multiset.h>
// map
#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_TREE_H
#include <stl_tree.h>
#endif
#include <stl_map.h>
#include <stl_multimap.h>
// stl_set.h
template <class Key, class Compare = less<Key>, class Alloc = alloc>
class set {
public:// typedefs:typedef Key key_type;typedef Key value_type;
private:typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type,identity<value_type>, key_compare, Alloc> rep_type;rep_type t; // red-black tree representing set
};
// stl_map.h
template <class Key, class T, class Compare = less<Key>, class Alloc = alloc>
class map {
public:// typedefs:typedef Key key_type;typedef T mapped_type;typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;
private:typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type,select1st<value_type>, key_compare, Alloc> rep_type;rep_type t; // red-black tree representing map
};
// stl_tree.h
struct __rb_tree_node_base
{typedef __rb_tree_color_type color_type;typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr;color_type color;base_ptr parent;base_ptr left;base_ptr right;
};// stl_tree.h
template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc= alloc>
class rb_tree {
protected:typedef void* void_pointer;typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr;typedef __rb_tree_node<Value> rb_tree_node;typedef rb_tree_node* link_type;typedef Key key_type;typedef Value value_type;
public:// insert⽤的是第⼆个模板参数左形参pair<iterator, bool> insert_unique(const value_type& x);// erase和find⽤第⼀个模板参数做形参size_type erase(const key_type& x);iterator find(const key_type& x);
protected:size_type node_count; // keeps track of size of treelink_type header;
};
template <class Value>
struct __rb_tree_node : public __rb_tree_node_base
{typedef __rb_tree_node<Value>* link_type;Value value_field;
};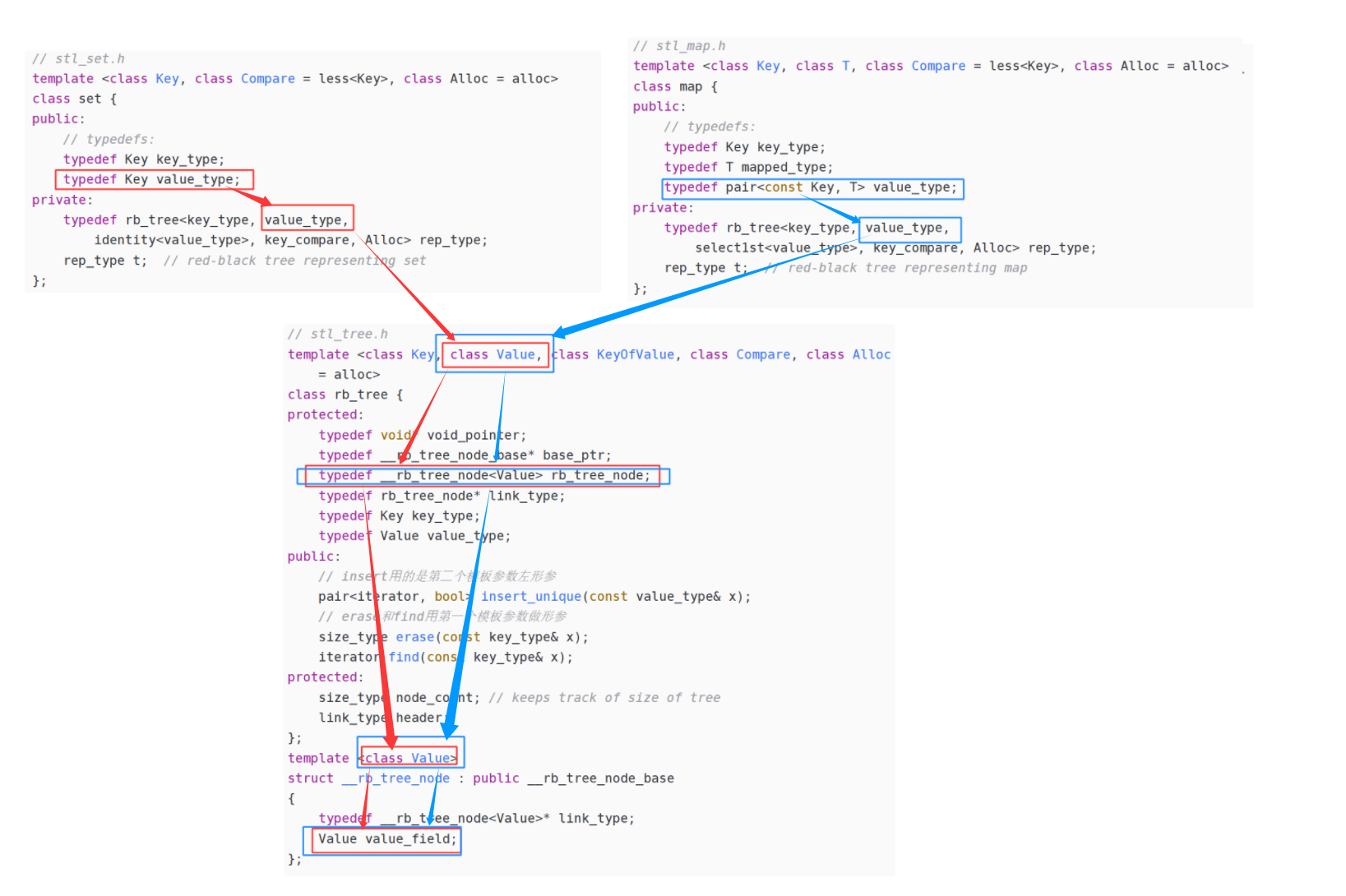
可以看到源码中rb_tree用了一个巧妙的泛型思想实现,rb_tree是实现key的搜索场景,还是 key/value 的搜索场景不是直接写死的,而是由第二个模板参数Value决定_rb_tree_node中存储的数据类型。
set实例化rb_tree时第二个模板参数给的是key,map实例化rb_tree时第二个模板参数给的是 pair,这样一颗红黑树既可以实现key搜索场景的set,也可以实现key/value搜索场景的map。
源码里面模板参数是用T代表value,而内部写的value_type不是我们我们日常 key/value场景中说的value,源码中的value_type反而是红黑树结点中存储的真实的数据的类型。
rb_tree第二个模板参数Value已经控制了红黑树结点中存储的数据类型,为什么还要传第一个模板参数Key呢?尤其是set,两个模板参数是一样的,why?
答:对于 map和set,find/erase时的函数参数都是Key,所以第一个模板参数是传给find/erase等函数做形参的类型的。对于set 而言两个参数是一样的,但是对于map而言就完全不一样了,map insert的是pair对象,但是find和ease的是Key对象。(看下面的代码实现)
2.搭建基本框架
// map.h#pragma once#include"RBTree.h"namespace mystl
{template<class K, class V>class map{public:bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _t.Insert(kv);}private:RBTree<K, pair<K, V>> _t;};}// set.h#pragma oncenamespace mystl
{template<class K>class set{public:bool insert(const K& k){return _t.Insert(k);}private:RBTree<K, K> _t;};
}发现了第一个问题,下面红黑谁的比较实现是按照pair的比较来实现的,当data是key的时候这里的比较大小,当data是pair的时候,这里的比较大小就不符合了,这里怎么改成更高维度的比较呢??
// RBTree.h#pragma onceenum Colour
{RED,BLACK
};//template<class K, class V>
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{//pair<K, V> _kv;//RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;//RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;//需要记录一下父节点,用于更新平衡//RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;T _data;RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;Colour _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_data(data),_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr){ }/*RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V> & kv):_kv(kv),_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr){}*/
};template<class K, class T>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public://......bool Insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(kv);cur->_col = RED;if (parent->_kv.first < kv.first){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (grandfather->_left == parent){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;// 叔叔存在且为红->变色if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = BLACK;uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续往上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else // 叔叔不存在,或者叔叔存在且为黑->旋转+变色{if (cur == parent->_left){// g// p u//c // 右单旋RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{// g// p u// c // 左右单旋RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}else // grandfather->_right == parent{// g// u pNode* uncle = grandfather->_left;// 叔叔存在且为红,-》变色即可if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续往上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else // 叔叔不存在,或者存在且为黑{// 情况二:叔叔不存在或者存在且为黑// 旋转+变色// g// u p// cif (cur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{ // g// u p// cRotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}解决:在红黑数中通过仿函数来控制比较(参考的源码)
// map.h
template<class K, class V>
class map
{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};
public:bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _t.Insert(kv);}
private:RBTree<K, pair<K, V, MapKeyOfT>> _t;
};// set.h
template<class K>
class set
{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){// 看上去多此一举,但是可以更好的复用底层的RBTreereturn key;}};
public:bool insert(const K& k){return _t.Insert(k);}
private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public://......bool Insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}KeyOfT kot;Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (kot(cur->data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}//......3.迭代器的实现
3.1节点的实现
iterator实现的大框架跟list的iterator思路是一致的,用一个类型封装结点的指针,再通过重载运算符实现,迭代器像指针一样访问的行为。
这里的难点是operator++和operator--的实现。之前使用部分,分析了map和set的迭代器走的是中序遍历,左子树->根结点->右子树,那么begin()会返回中序第一个结点的iterator迭代器。
迭代器++的核心逻辑就是不看全局,只看局部,只考虑当前中序局部要访问的下一个结点:
开始时候在树的最左侧节点
当前节点右不为空,下一个是右子树中序的第一个(最左节点)
当前节点右为空,下一个是孩子是父亲左的那个父节点
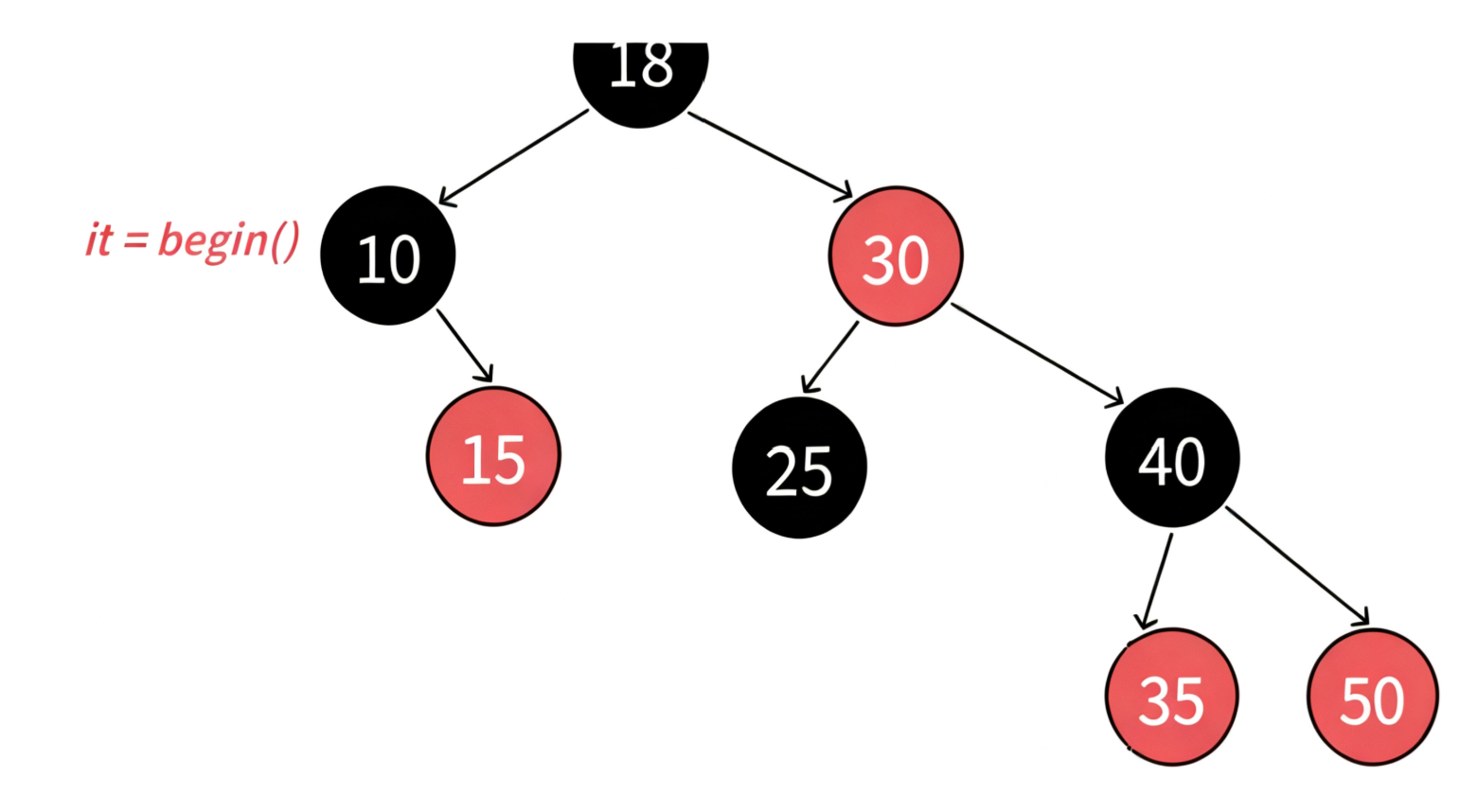
节点是实现:
template<class T>
struct TreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef TreeIterator<T> Self;Node* _node;TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){ }T operator*(){return _node->_data;}T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator!=(const Self& s) const{return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s) const{return _node == s._node;}Self& operator++(){//开始时候在树的最左侧// 当前节点右不为空,下一个是右子树中序的第一个(最左节点)// 当前节点右为空,下一个孩子是父亲左的那个父节点if (_node->_right){Node* min = _node->_right;while (min->_left){min = min->_left;}_node = min;}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}};
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:typedef TreeIterator<T> Iterator;Iterator Begin(){Node* min = _root;while (min && min->_left){min = min->_left;}return Iterator(min);}Iterator End(){return Iterator(nullptr);}
//......3.2[]的实现,const迭代器的实现
// RBTree.h
#pragma onceenum Colour
{RED,BLACK
};//template<class K, class V>
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{//pair<K, V> _kv;//RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;//RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;//需要记录一下父节点,用于更新平衡//RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;T _data;RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;Colour _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_data(data),_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr){ }/*RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V> & kv):_kv(kv),_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr){}*/
};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct TreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){ }Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator!=(const Self& s) const{return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s) const{return _node == s._node;}Self& operator++(){//开始时候在树的最左侧// 当前节点右不为空,下一个是右子树中序的第一个(最左节点)// 当前节点右为空,下一个孩子是父亲左的那个父节点if (_node->_right){Node* min = _node->_right;while (min->_left){min = min->_left;}_node = min;}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:typedef TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;typedef TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> Const_Iterator;Iterator Begin(){Node* min = _root;while (min && min->_left){min = min->_left;}return Iterator(min);}Iterator End(){return Iterator(nullptr);}pair<Iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return { Iterator(_root), true };}KeyOfT kot;Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return {Iterator(cur), false};}}cur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = cur;cur->_col = RED;if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (grandfather->_left == parent){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;// 叔叔存在且为红->变色if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = BLACK;uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续往上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else // 叔叔不存在,或者叔叔存在且为黑->旋转+变色{if (cur == parent->_left){// g// p u//c // 右单旋RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{// g// p u// c // 左右单旋RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}else // grandfather->_right == parent{// g// u pNode* uncle = grandfather->_left;// 叔叔存在且为红,-》变色即可if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续往上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else // 叔叔不存在,或者存在且为黑{// 情况二:叔叔不存在或者存在且为黑// 旋转+变色// g// u p// cif (cur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{ // g// u p// cRotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK;return {Iterator(newnode), true};}Node* Find(const K& key){KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}
private:void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (parent == _root){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subL;}else{parentParent->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = parentParent;}}void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;subR->_left = parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (parent == _root){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subR;}else{parentParent->_right = subR;}subR->_parent = parentParent;}}
private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};三、所有代码
//set.h#pragma oncenamespace mystl
{template<class K>class set{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){// 看上去多此一举,但是可以更好的复用底层的RBTreereturn key;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.Begin();}iterator end(){return _t.End();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& k){return _t.Insert(k);}private:RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;};
}
// map.h#pragma once#include"RBTree.h"namespace mystl
{template<class K, class V>class map{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.Begin();}iterator end(){return _t.End();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _t.Insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert({ key, V() });return ret.first->second;}private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT > _t;};
}
// RBTree.h#pragma onceenum Colour
{RED,BLACK
};//template<class K, class V>
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{//pair<K, V> _kv;//RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;//RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;//需要记录一下父节点,用于更新平衡//RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;T _data;RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;Colour _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_data(data),_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr){ }/*RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V> & kv):_kv(kv),_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr){}*/
};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct TreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){ }Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator!=(const Self& s) const{return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s) const{return _node == s._node;}Self& operator++(){//开始时候在树的最左侧// 当前节点右不为空,下一个是右子树中序的第一个(最左节点)// 当前节点右为空,下一个孩子是父亲左的那个父节点if (_node->_right){Node* min = _node->_right;while (min->_left){min = min->_left;}_node = min;}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:typedef TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;typedef TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> Const_Iterator;Iterator Begin(){Node* min = _root;while (min && min->_left){min = min->_left;}return Iterator(min);}Iterator End(){return Iterator(nullptr);}pair<Iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return { Iterator(_root), true };}KeyOfT kot;Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return {Iterator(cur), false};}}cur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = cur;cur->_col = RED;if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (grandfather->_left == parent){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;// 叔叔存在且为红->变色if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = BLACK;uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续往上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else // 叔叔不存在,或者叔叔存在且为黑->旋转+变色{if (cur == parent->_left){// g// p u//c // 右单旋RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{// g// p u// c // 左右单旋RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}else // grandfather->_right == parent{// g// u pNode* uncle = grandfather->_left;// 叔叔存在且为红,-》变色即可if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续往上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else // 叔叔不存在,或者存在且为黑{// 情况二:叔叔不存在或者存在且为黑// 旋转+变色// g// u p// cif (cur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{ // g// u p// cRotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK;return {Iterator(newnode), true};}Node* Find(const K& key){KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}
private:void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (parent == _root){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subL;}else{parentParent->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = parentParent;}}void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;subR->_left = parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (parent == _root){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subR;}else{parentParent->_right = subR;}subR->_parent = parentParent;}}
private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};