Yocto —— Linux Kernel 配置和修改
文章目录
- 一、为什么用 Yocto 修改内核
- 1. 内核是如何被构建的
- 2. 内核源码从哪里来
- 二、Linux Kernel 配置编译
- 三、修改 Linux Kernel 内核源代码
- 四、制作 Linux Kernel 内核驱动
一、为什么用 Yocto 修改内核
在嵌入式 Linux 开发中,Linux 内核是系统的核心。不同的硬件平台需要不同的内核配置(如启用特定驱动、关闭不需要的模块、优化性能)。
Yocto Project 提供了一套强大而灵活的机制,让你可以在不修改原始内核源码的前提下,安全、可维护地定制内核。
1. 内核是如何被构建的
在 Yocto 中,内核由一个 .bb 配方文件构建,通常位于:
meta/recipes-kernel/linux/
├── linux-yocto_5.15.bb
├── linux-raspberrypi_5.10.bb
└── linux-stable_6.1.bb
这些配方使用 kernel.bbclass 来定义通用的构建逻辑。
2. 内核源码从哪里来
- 可以是 上游 Linux(
linux-stable) - 可以是 厂商维护的内核(如
linux-ti) - 也可以是 自定义 Git 仓库
Yocto 使用 SRC_URI 指定源码位置,支持 Git、HTTP、本地文件等。
二、Linux Kernel 配置编译
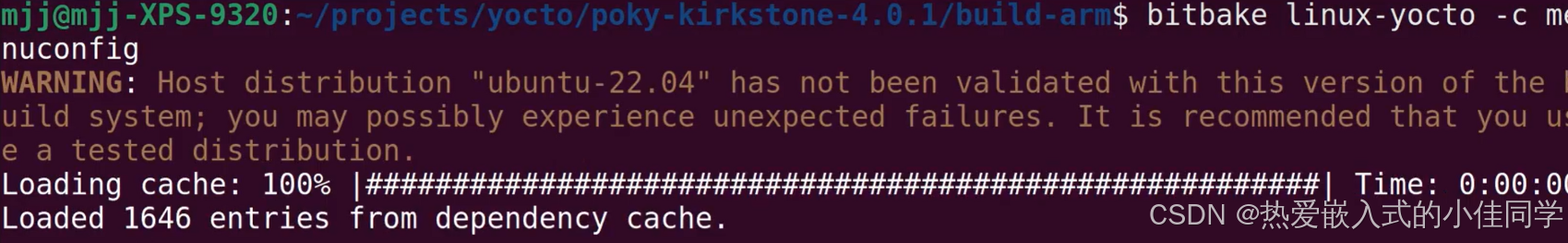
配置内核:
bitbake linux-yocto -c menuconfig
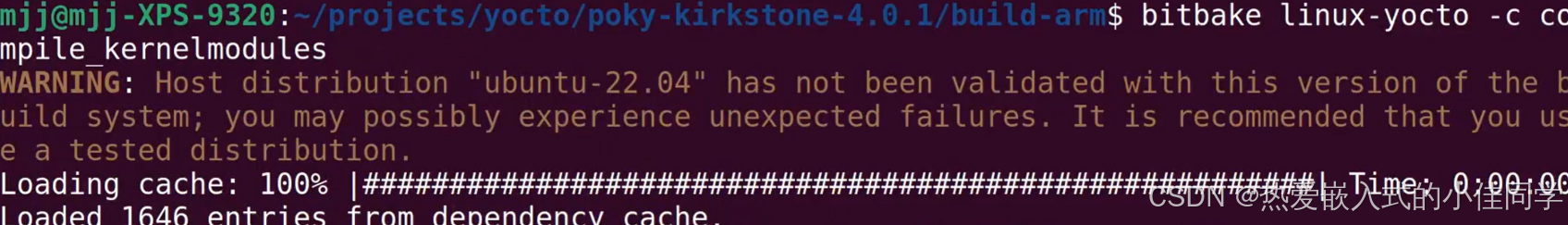
编译内核模块:
bitbake linux-yocto -c compile kernelmodules
查看方法:
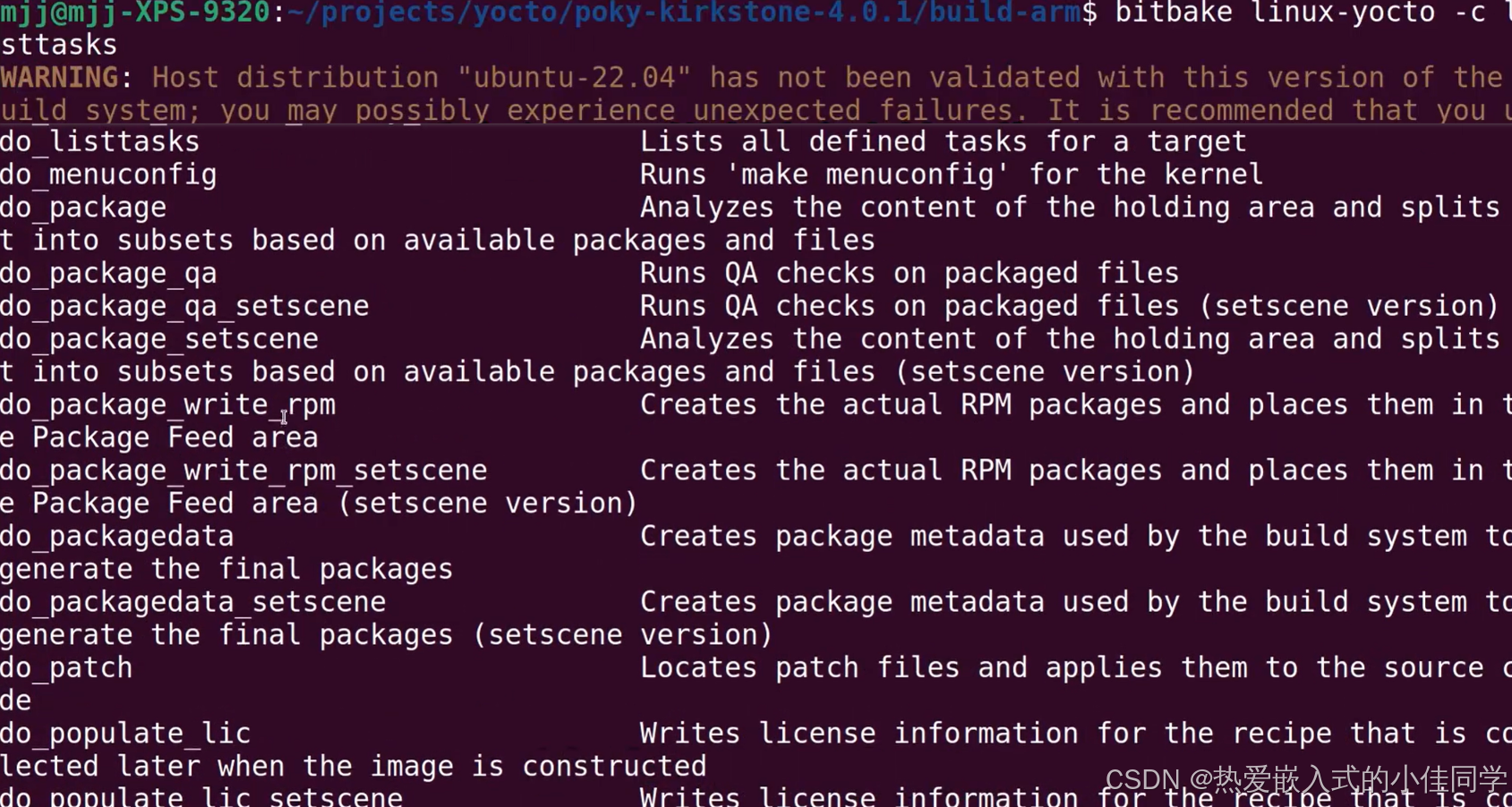
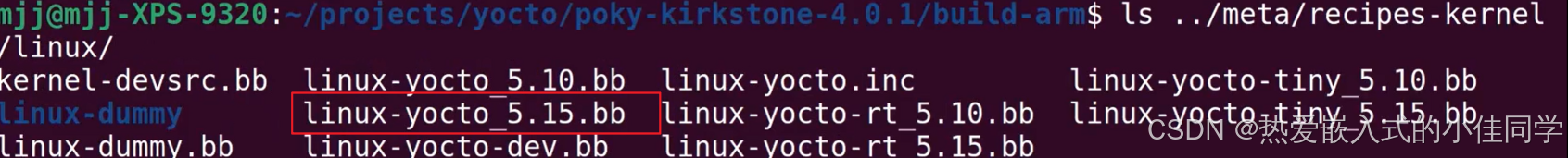
知道内核位置,不确定版本:
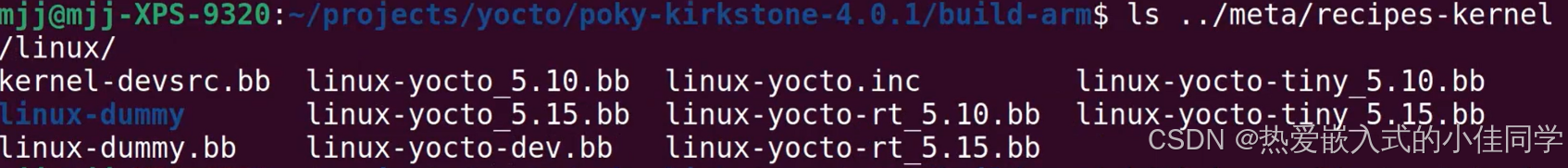
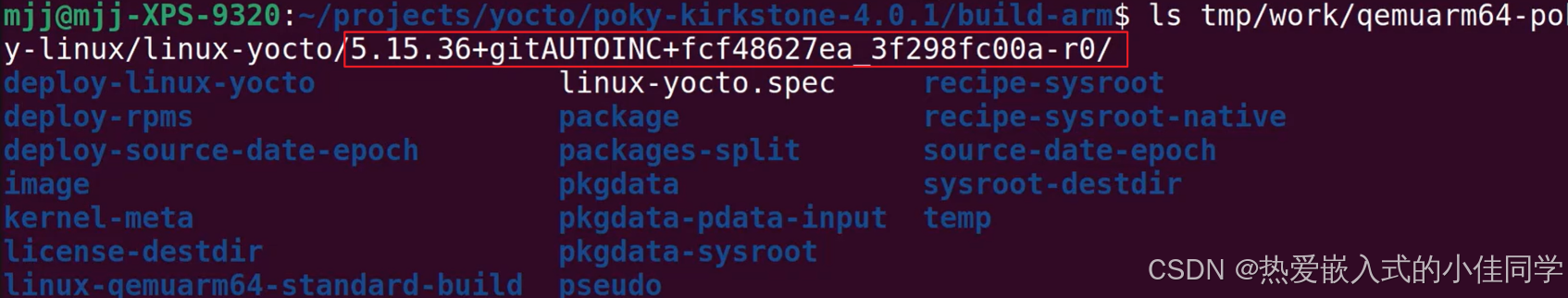
查看编译出的路径:
bitbake -e linux-yocto | grep ^S=

进入目录 git log 查看版本信息:
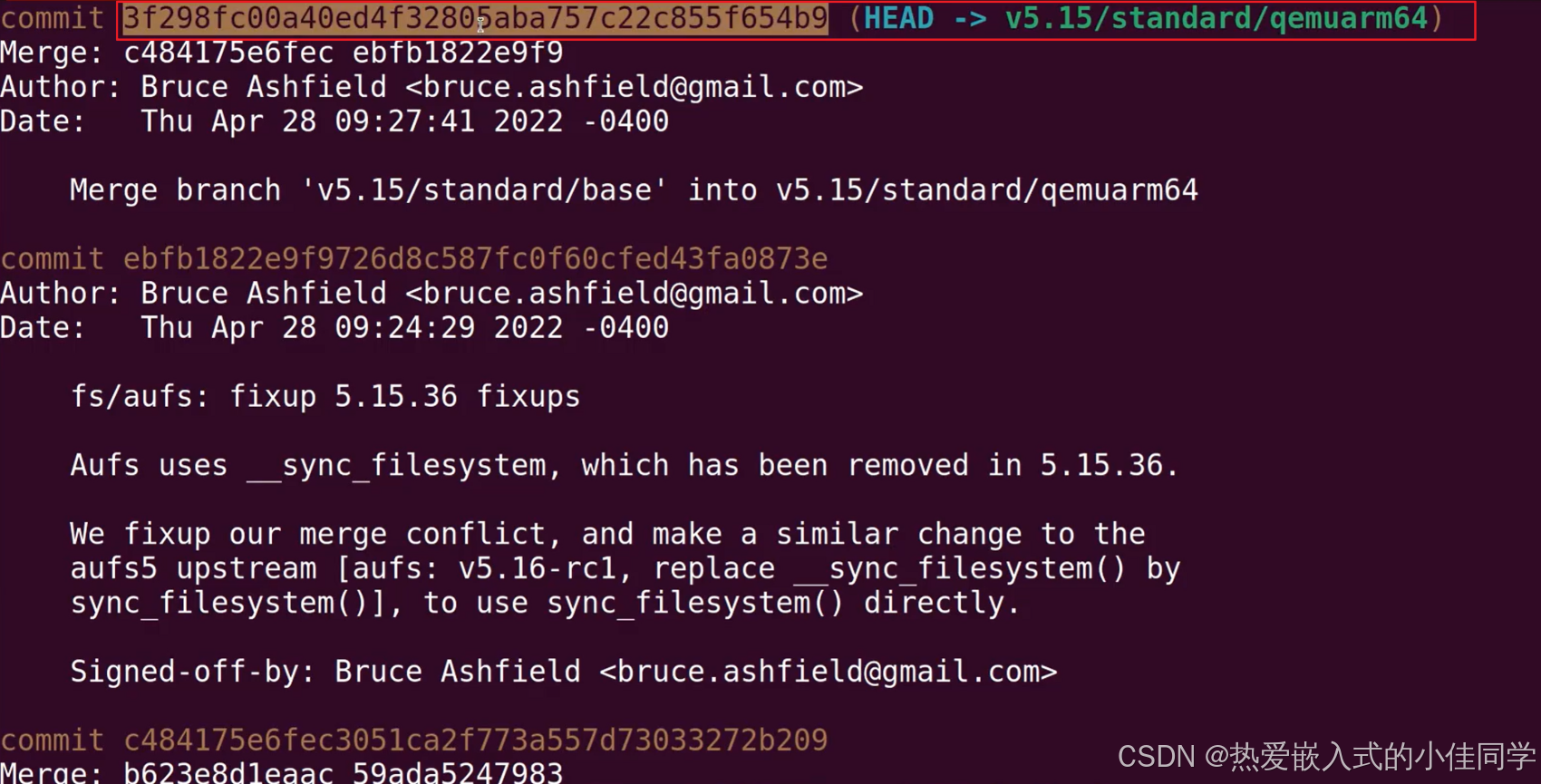
查看编译的架构:
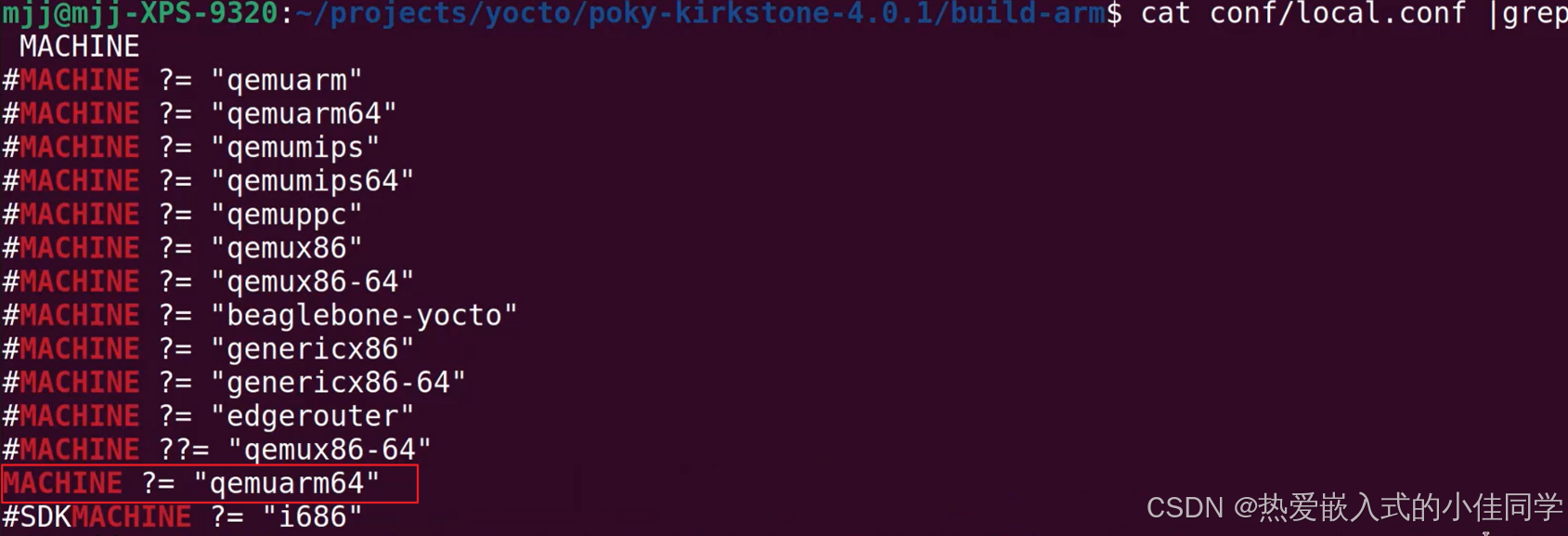
查看编译需要的配置文件:
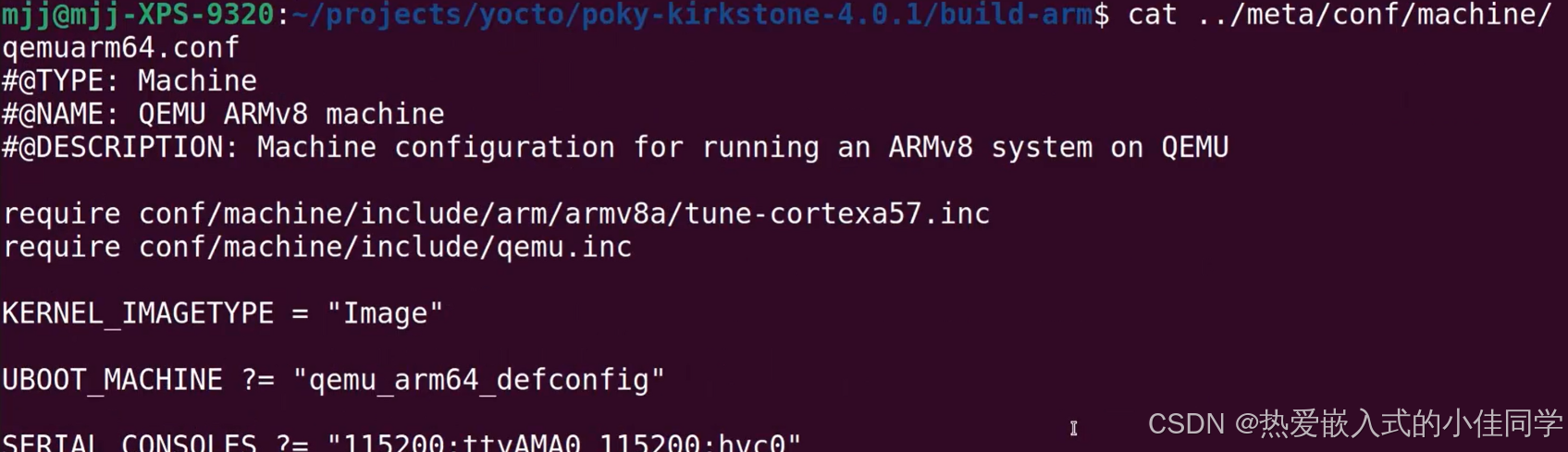
cat ../meta/conf/machine/qemuarm64.conf
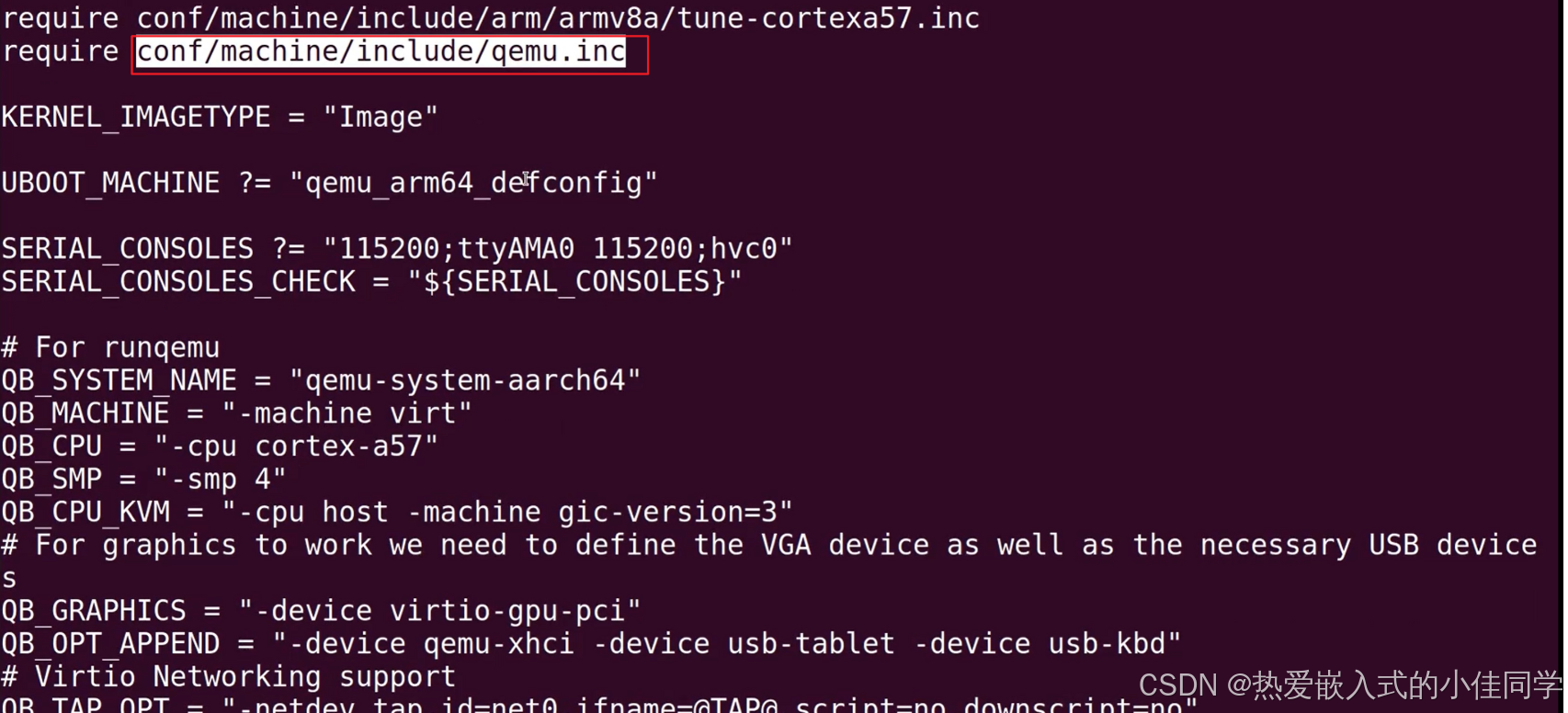
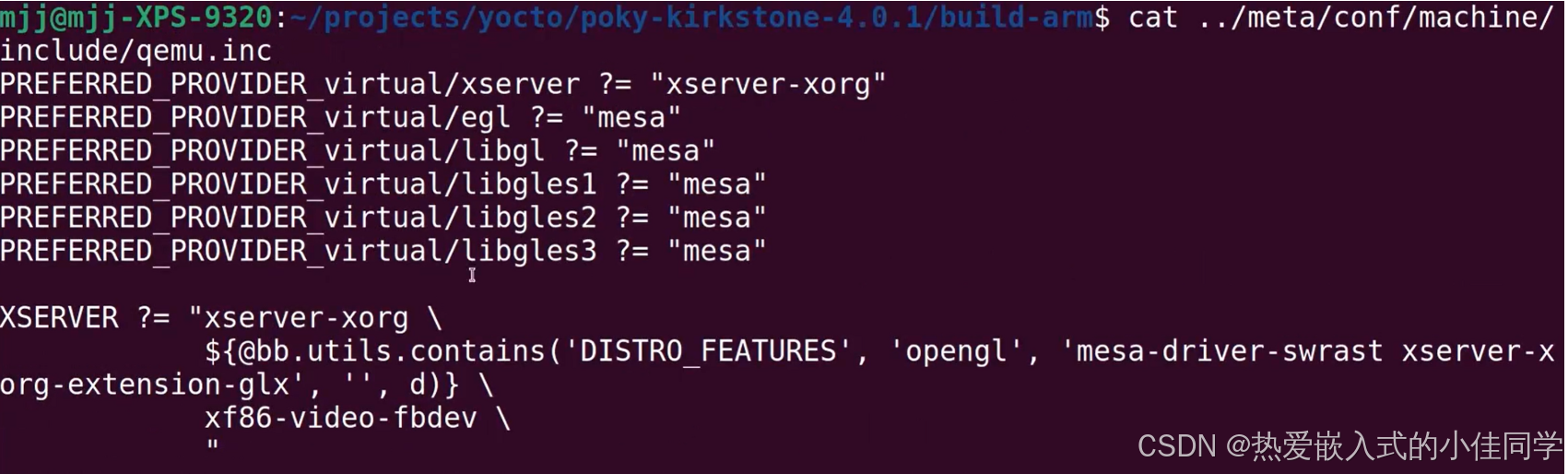
cat ../meta/conf/machine/include/qemu.inc
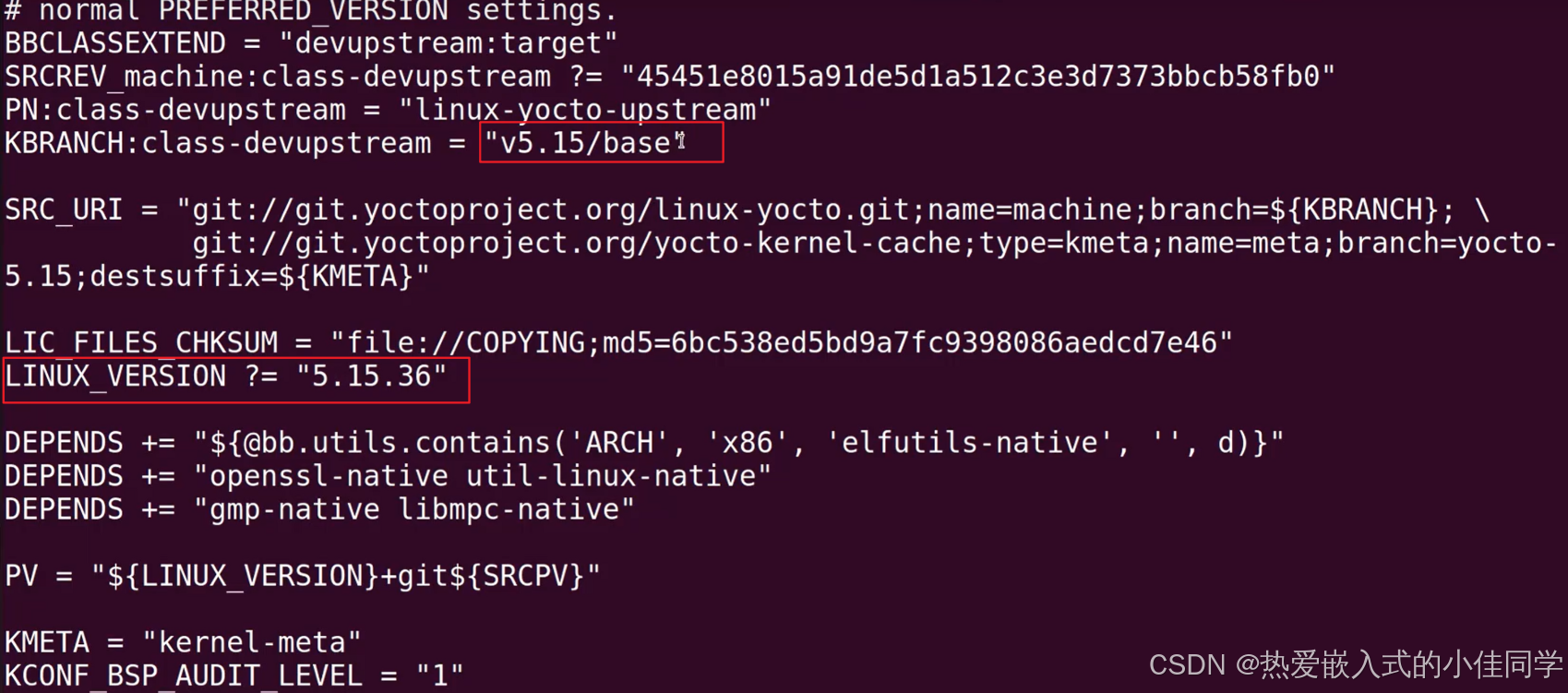
查看内核 bb :
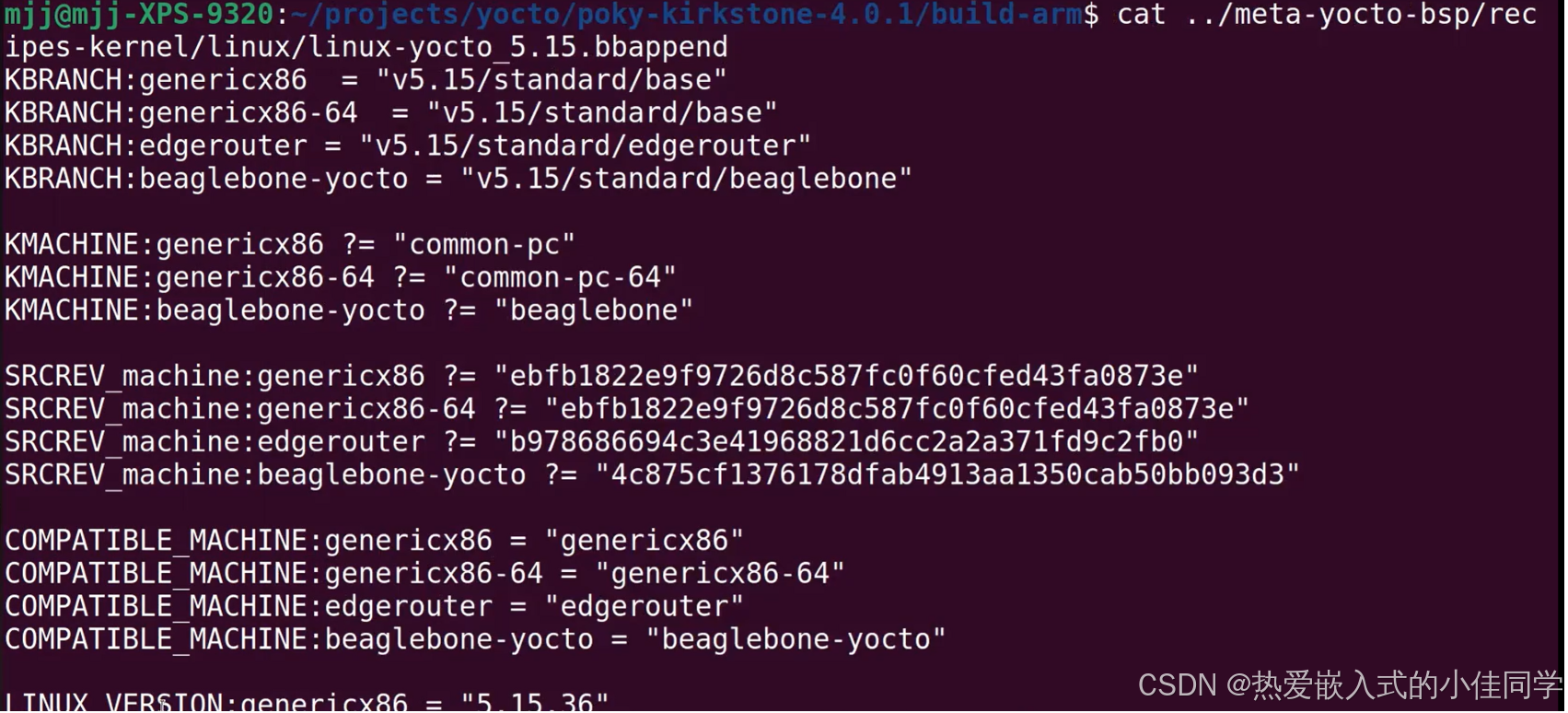
查看内核镜像类型:

查看设备树文件:

三、修改 Linux Kernel 内核源代码
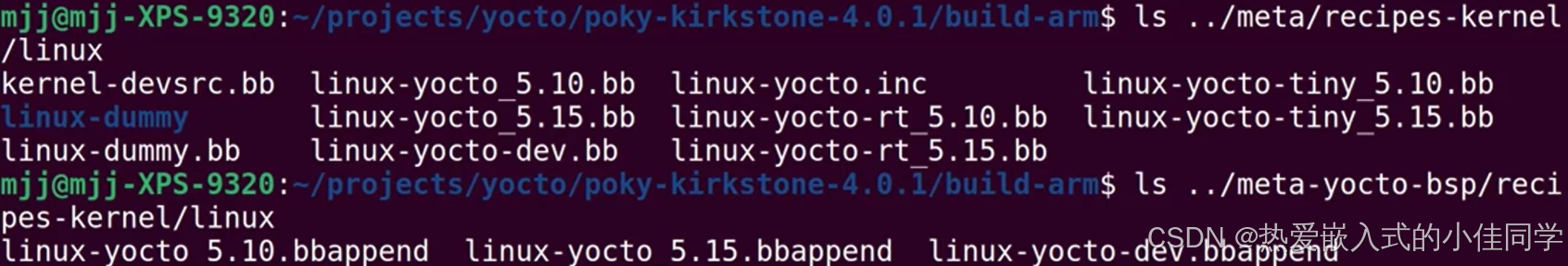
查看内核目录:
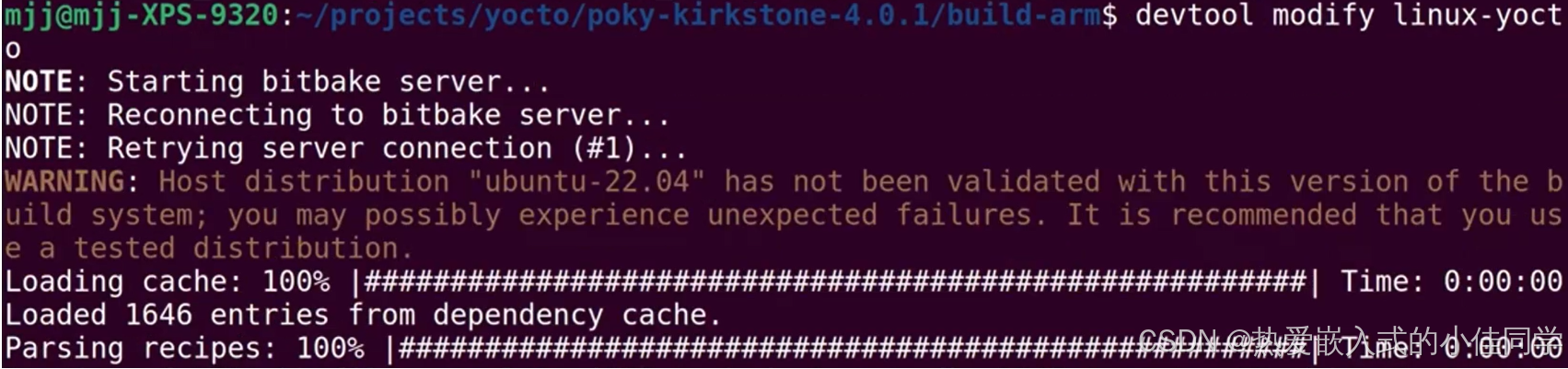
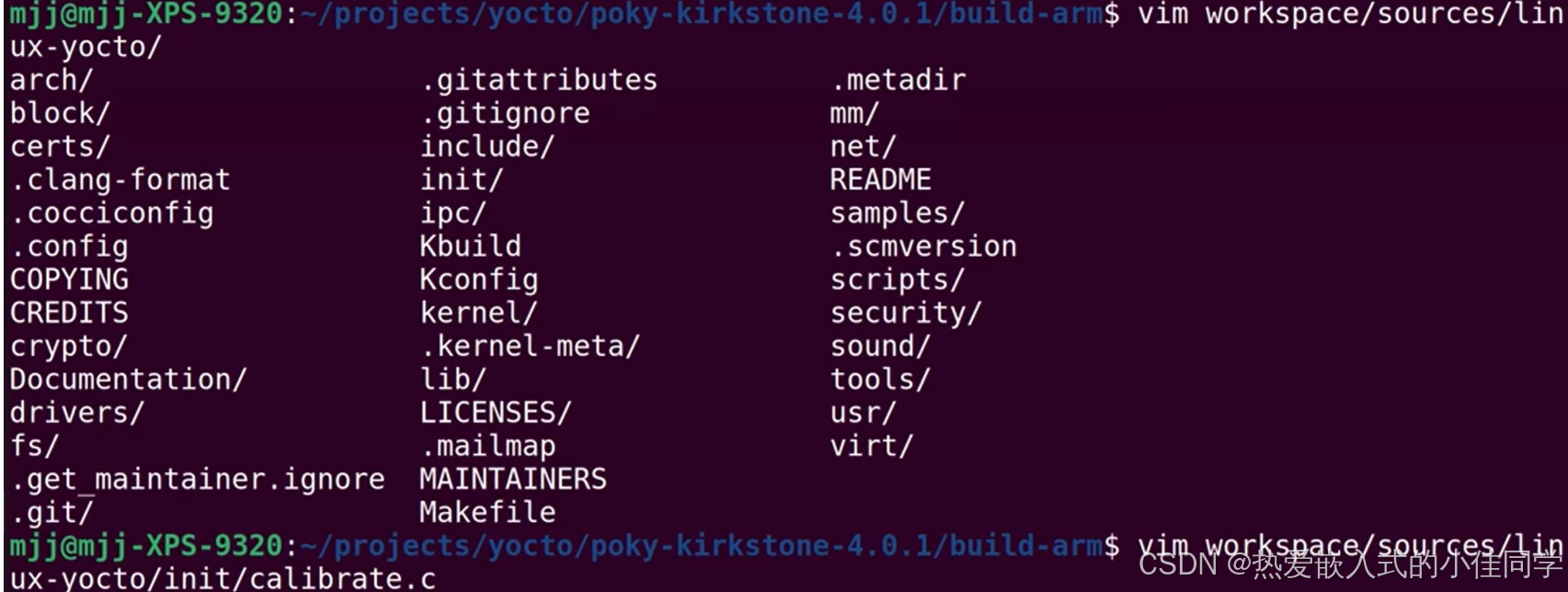
在工作区生成内核源码:
修改内核源码:
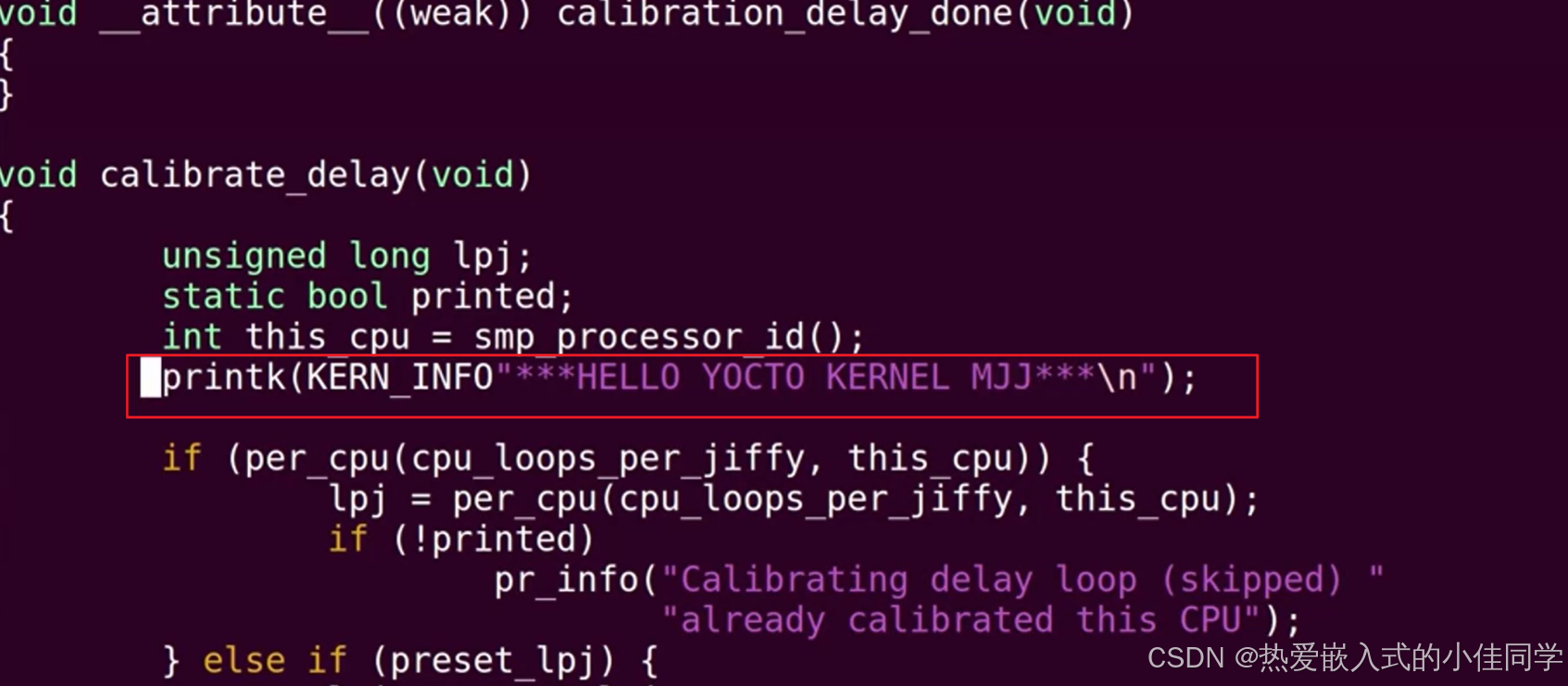
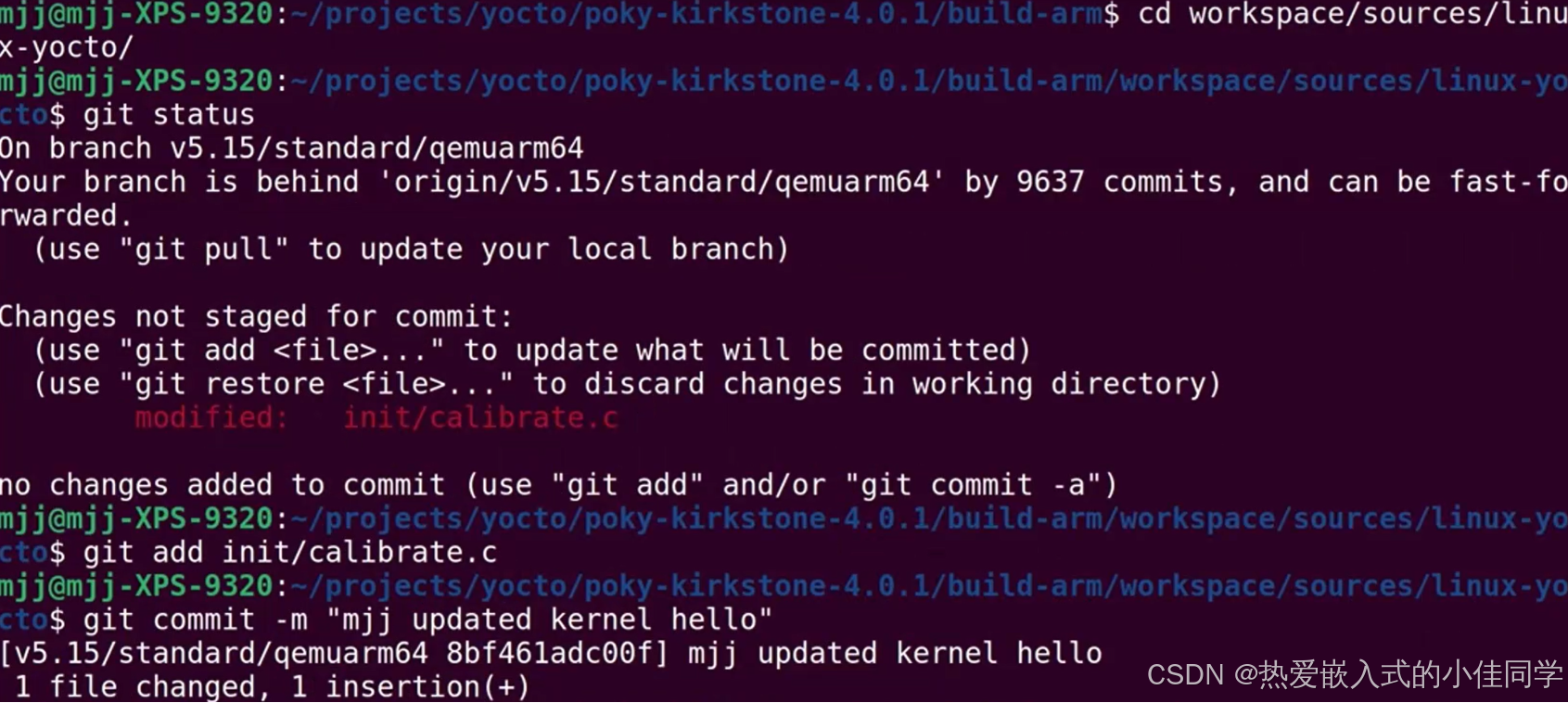
然后 commit 提交:
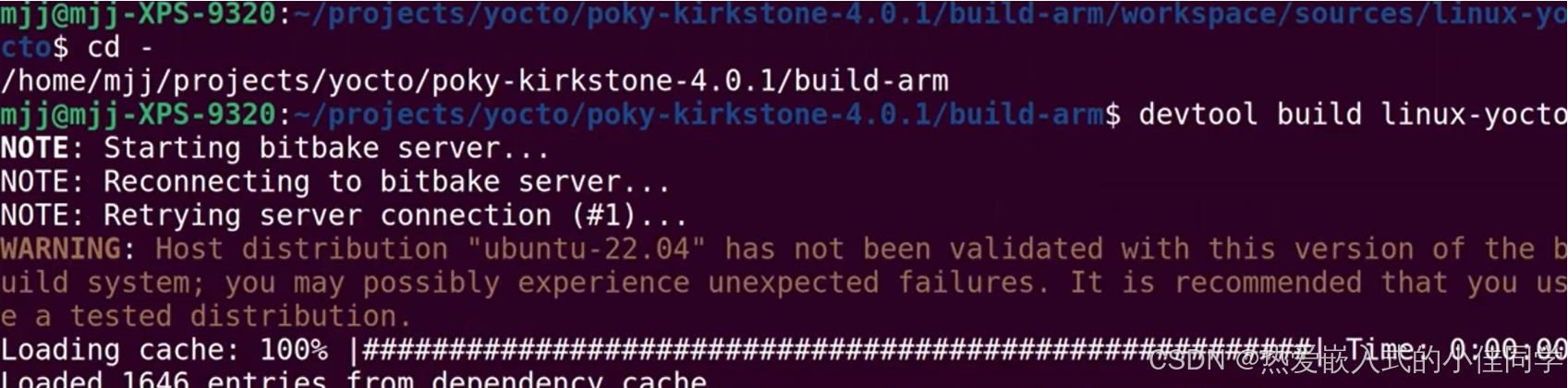
编译内核:
devtool build linux-yocto
构建镜像:
# devtool build-image core-image-sato 应该也可以,还未测试
bitbake core-image-sato
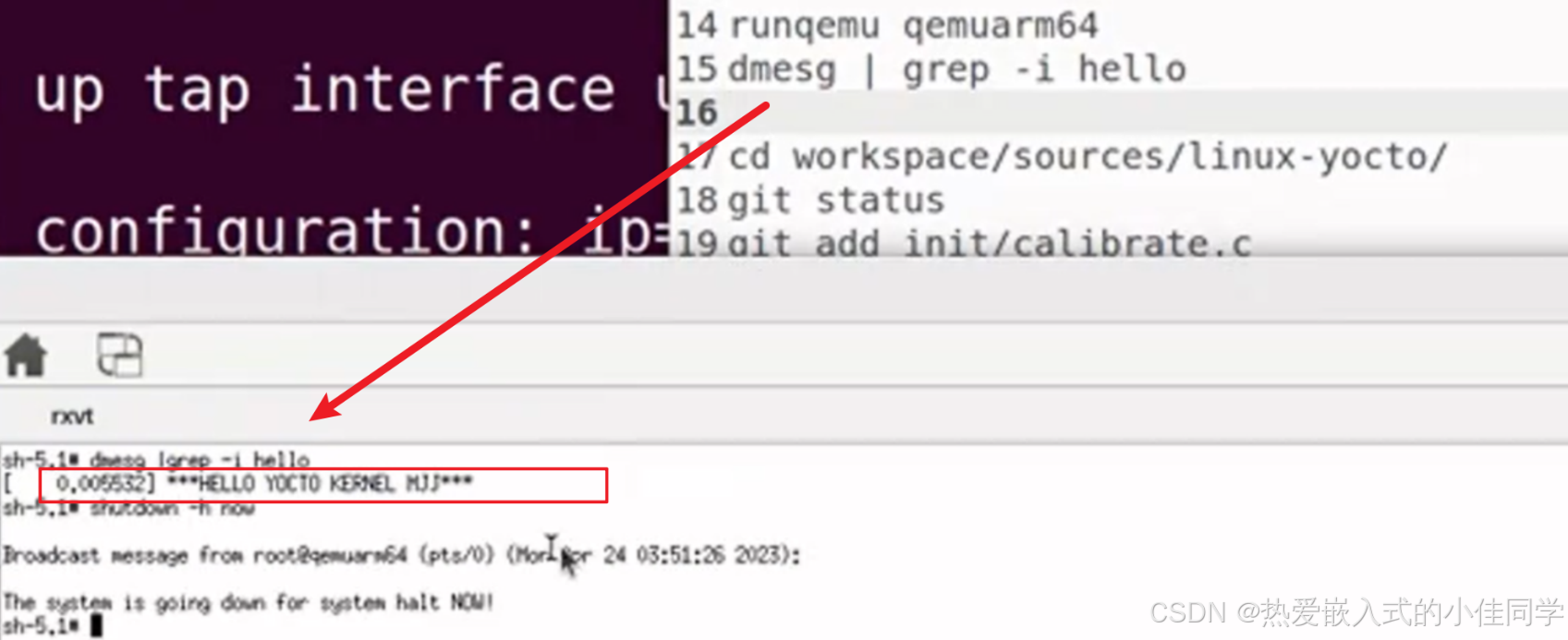
测试:
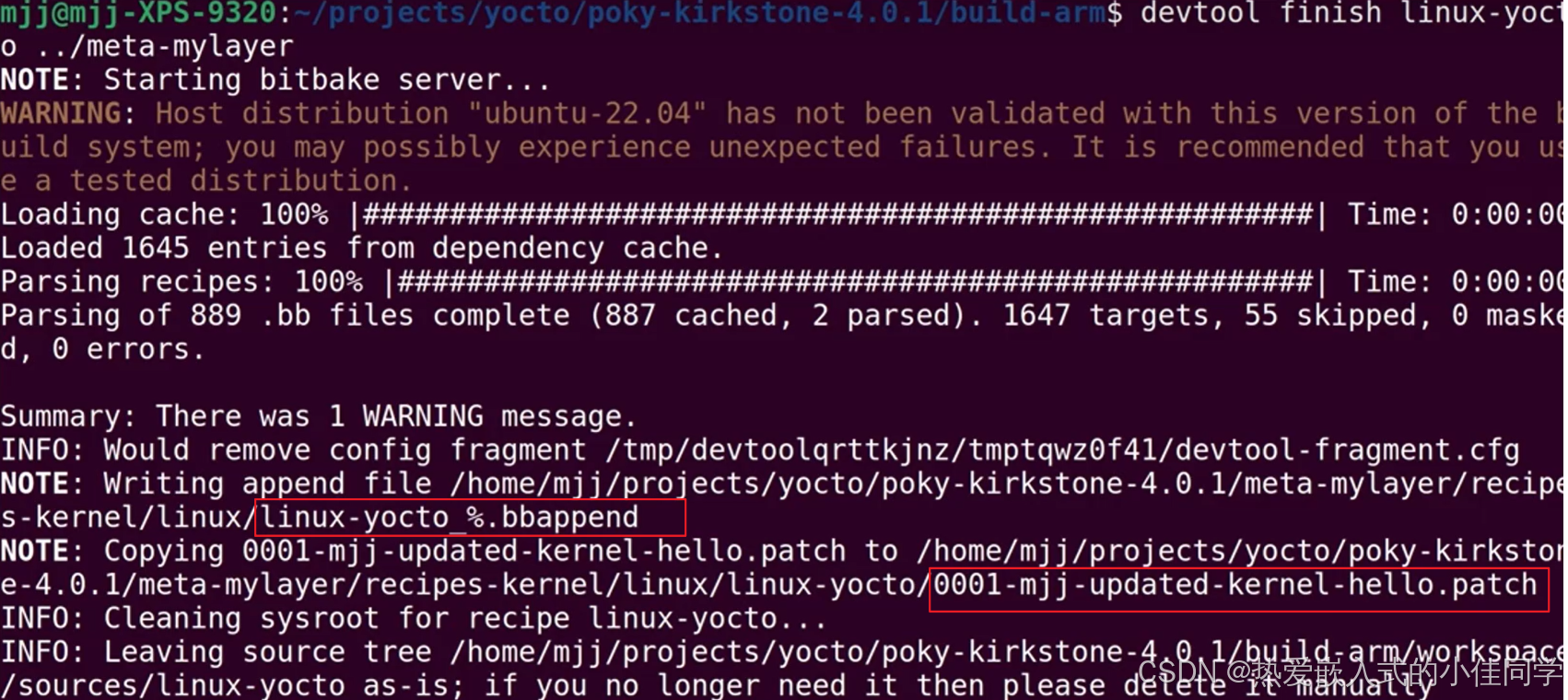
验证成功后打包回去,多了 bbappend 和 patch 文件:
devtool finish linux-yocto ../meta-mylayer
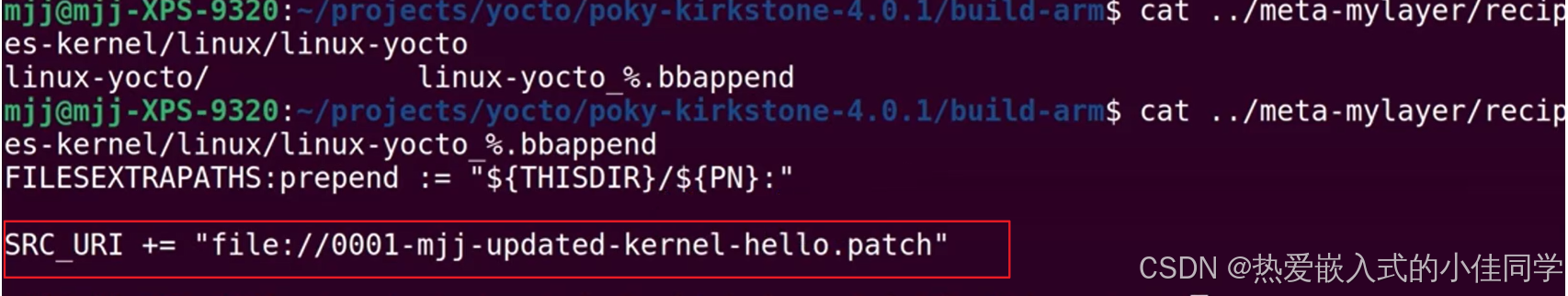
可以查看 bbappend 和 patch:
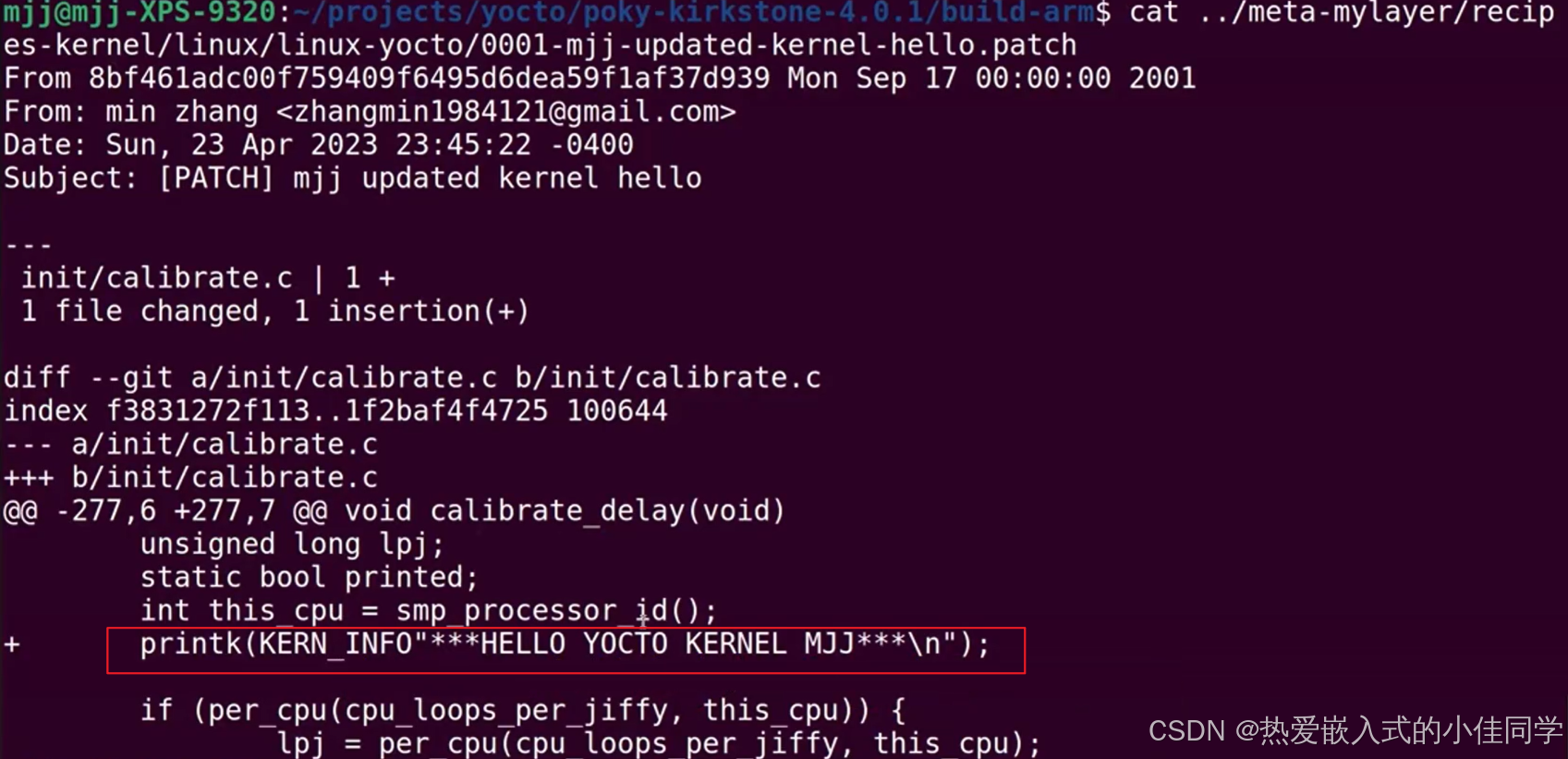
最后记得清理一下工作区和删除源码:

四、制作 Linux Kernel 内核驱动
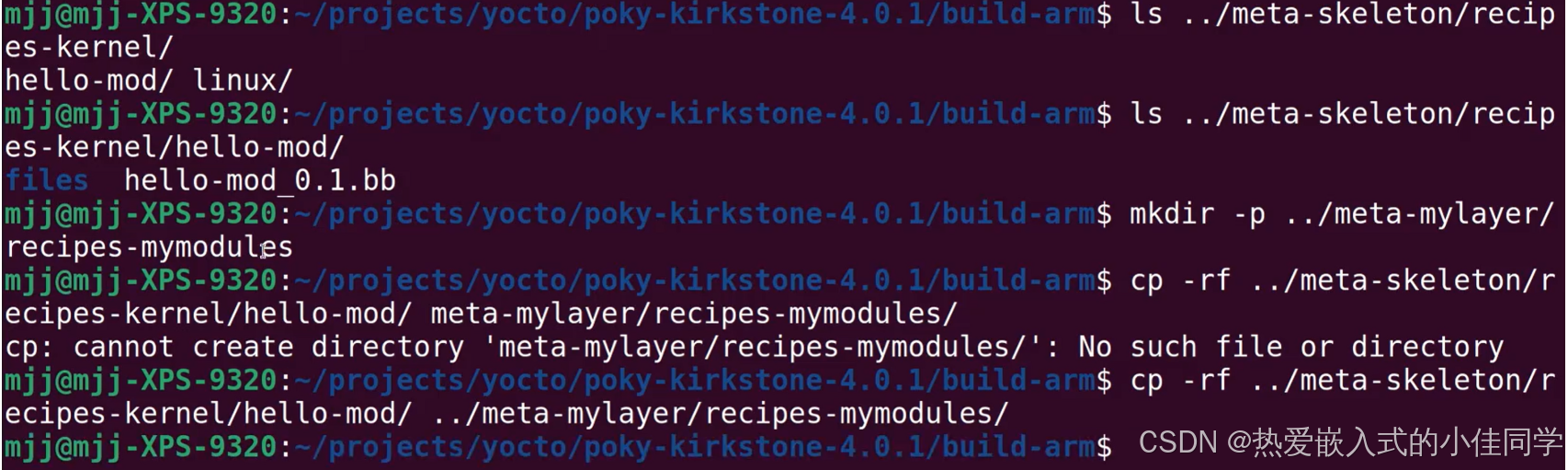
将示例模板复制到自己的 layer:
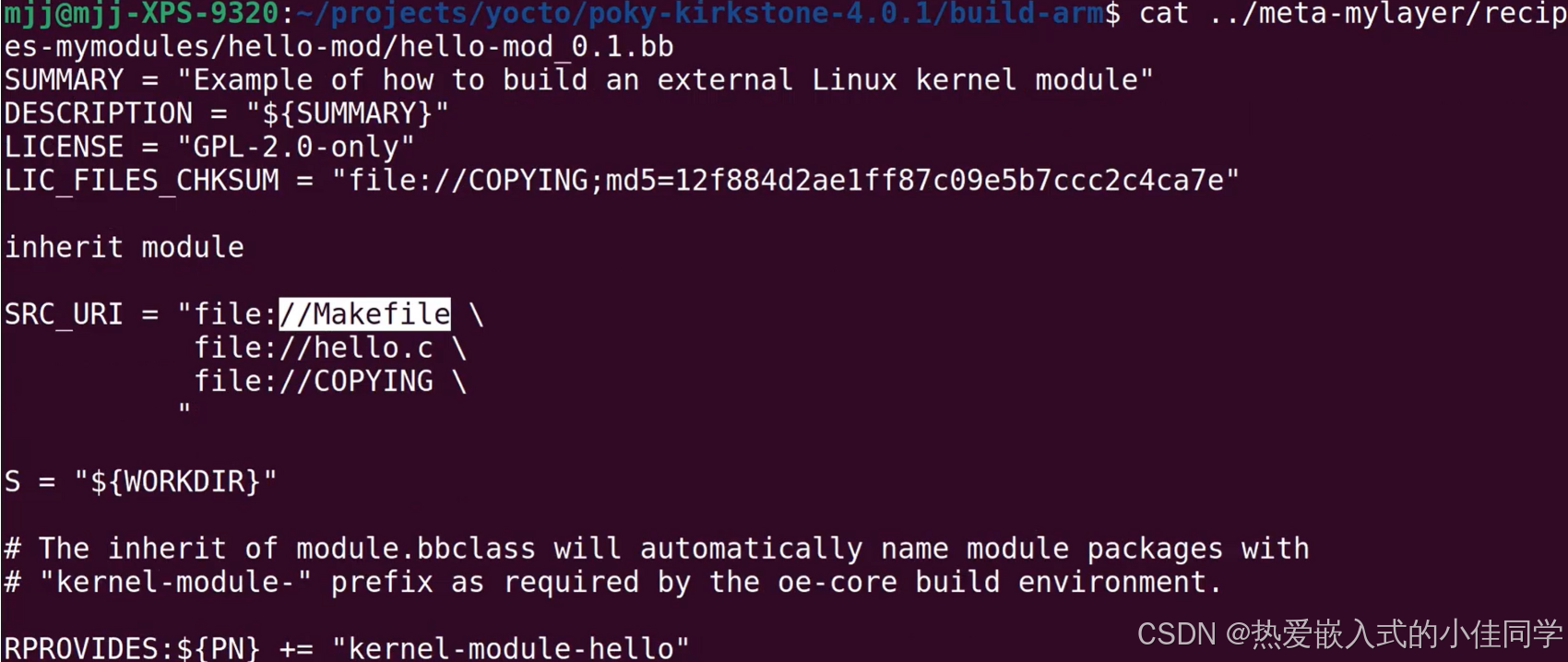
查看 bb 文件:
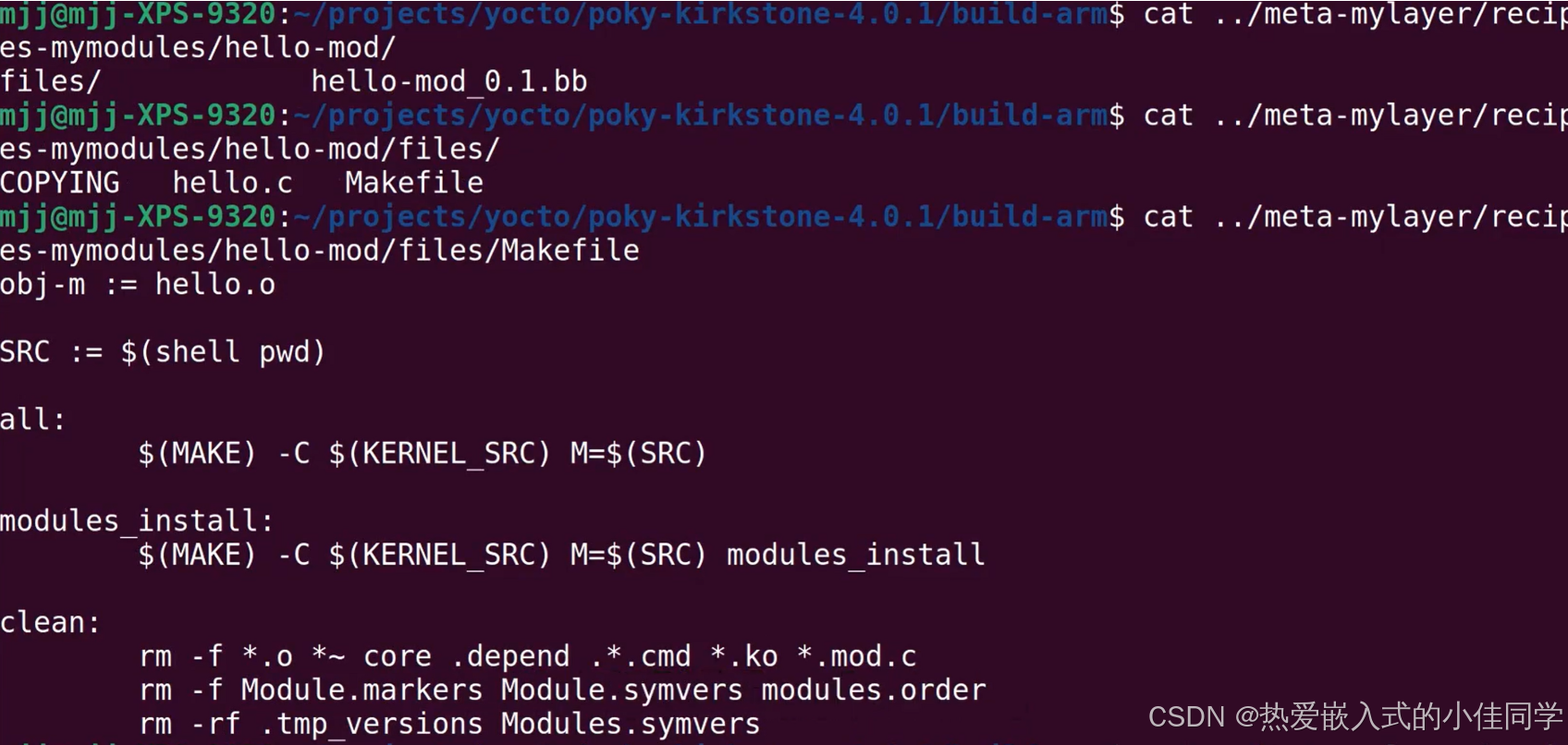
查看 Makefile 和 .c 文件:
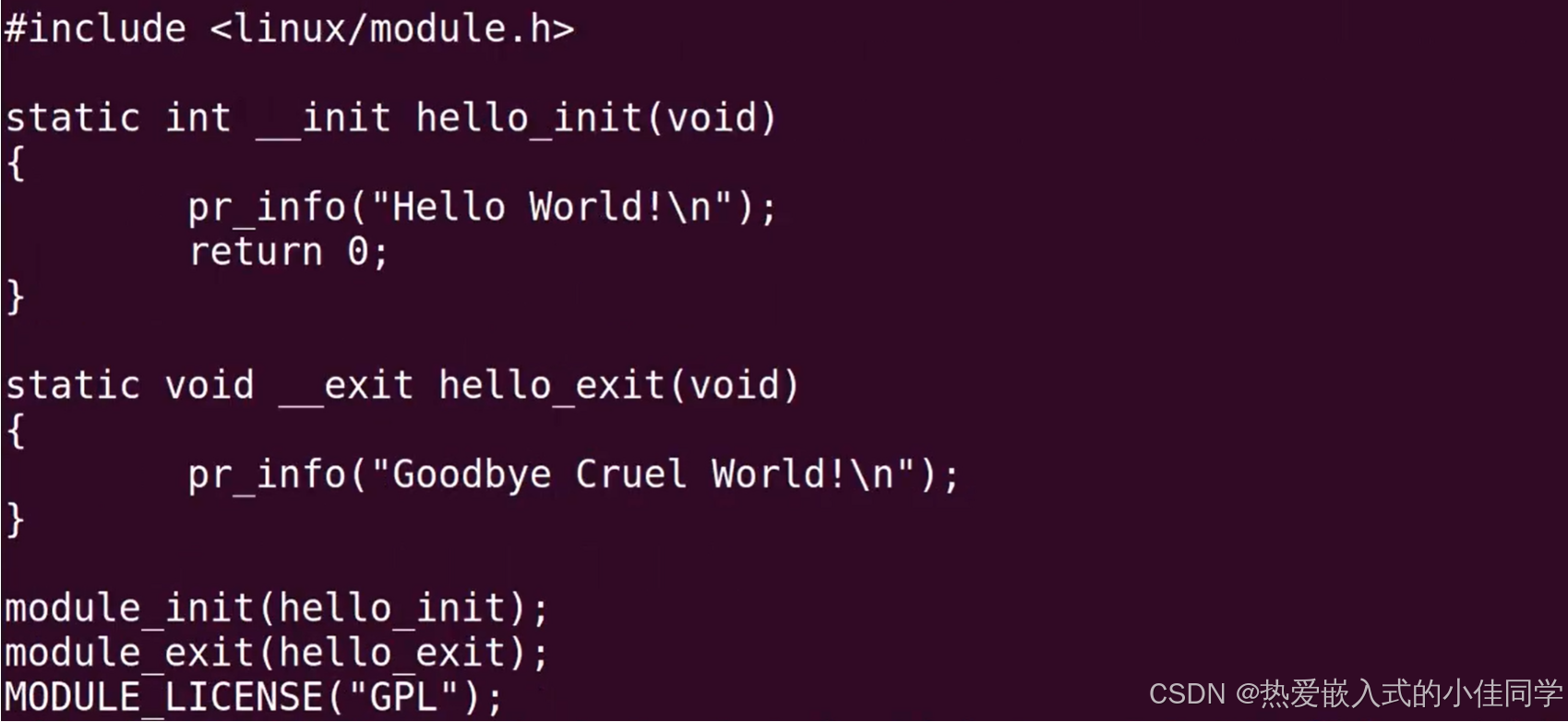
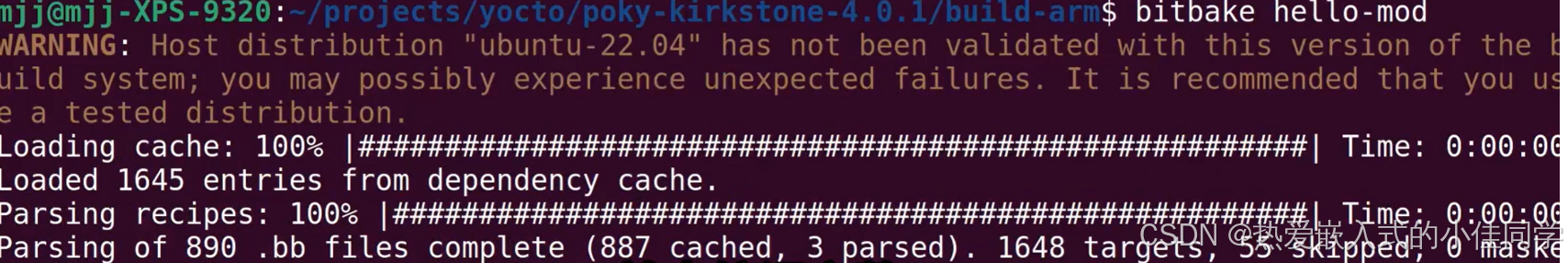
编译驱动代码:
bitbake hello-mod
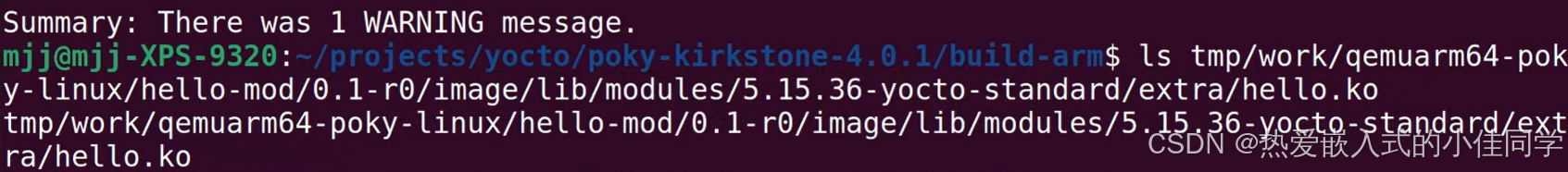
查看驱动是否编译成功:
修改配置文件,添加:

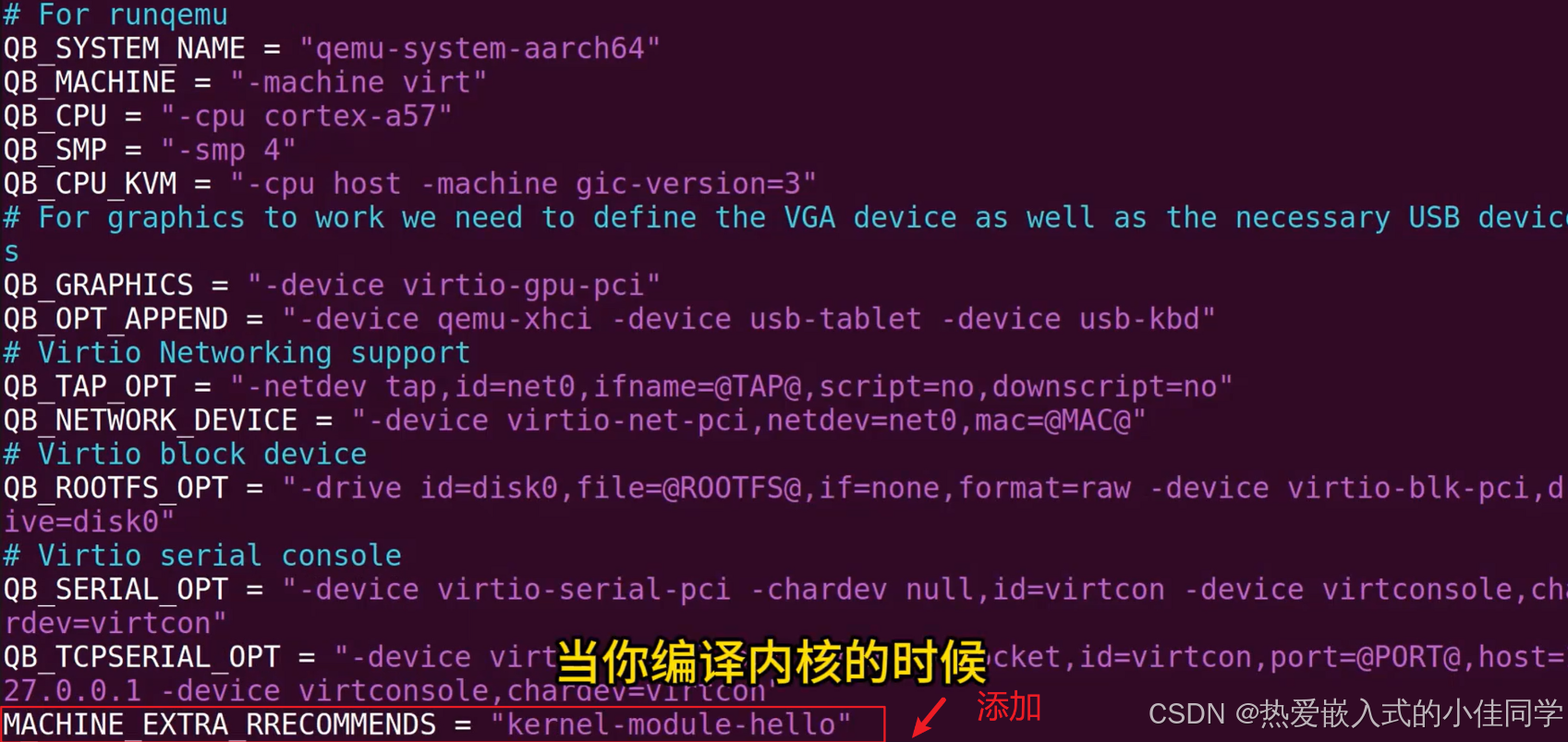
重新配置一下环境和编译驱动,构建镜像:
source oe-init-build-env build-arm
bitbake hello-mod
bitbake core-image-sato
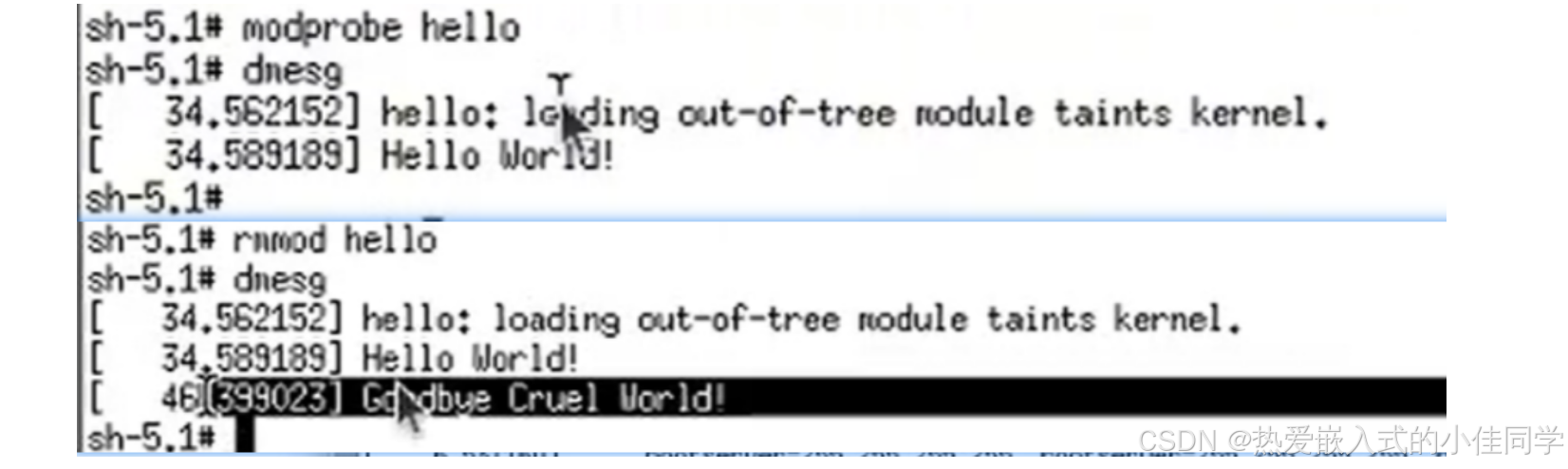
验证:
# 把内核日志打印出来,然后清空缓冲区
dmesg -c modprobe hello
dmesgrmmod hello
dmesg