格式化输入/输出函数
格式化输出函数
格式化输入函数
int scanf(const char* format, ...);
int fscanf(FILE* fp, const char* format, ...);
int sscanf(char* buf, const char* format, ...);
功能:将format中的格式化输入到对应的参数中
format:输入的格式
fp:文件指针
buf:作为输入的缓冲区
返回值:成功返回字符数(sscanf返回存入数组中的字符数),失败返回EOF
格式化输出函数
int printf(const char* format, ...);
int fprintf(FILE* stream, const char* format, ...);
int sprintf(char* buf, const char* format, ...);
功能:将format中的格式化输出到对应的参数
format:输出的格式
fp:文件指针
buf:作为输出的缓冲区
返回值:成功返回字符数(sprintf返回存入数组中的字符数),失败返回EOF
实现文件读写
写文件
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>typedef struct student
{int id;char name[50];float marks;
}student_t;int main(int argc, char** argv)
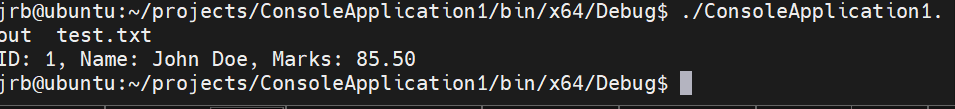
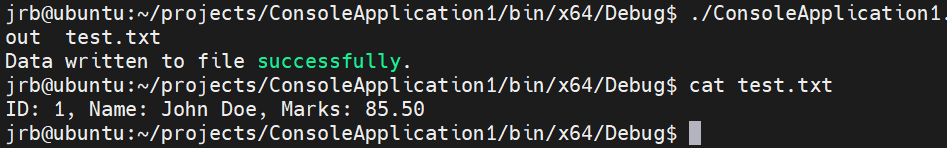
{FILE* fp;char fp_filename[128];char buffer[256];int ret;student_t stu = {1, "John Doe", 85.50};if (argc != 2) {printf("Usage: %s <filename>\n", argv[0]);return -1;}strcpy(fp_filename, argv[1]);// Open file for writingif (NULL == (fp = fopen(fp_filename, "w"))) {perror("fopen");return -1;}//writesprintf(buffer, "ID: %d, Name: %s, Marks: %.2f\n", stu.id, stu.name, stu.marks);fprintf(fp, "%s", buffer);printf("Data written to file successfully.\n");fclose(fp);return 0;
}执行结果:
文件读操作
#include <cstdio>
#include <string.h>typedef struct student
{int id;char name[50];float marks;
}student_t;int main(int argc, char** argv)
{FILE* fp;char fp_filename[128];char buffer[256];int ret;student_t stu = {1, "John Doe", 85.50};if (argc != 2) {printf("Usage: %s <filename>\n", argv[0]);return -1;}strcpy(fp_filename, argv[1]);// Open file for writingif (NULL == (fp = fopen(fp_filename, "r"))) {perror("fopen");return -1;}// readfscanf(fp, "%s", buffer);sscanf(buffer, "ID: %d, Name: %s, Marks: %f", &stu.id, stu.name, &stu.marks);printf("ID: %d, Name: %s, Marks: %.2f\n", stu.id, stu.name, stu.marks);fclose(fp);return 0;
}
执行结果: