【案例实战】鸿蒙分布式智能办公应用的架构设计与性能优化
一、项目背景与挑战
在企业数字化转型的浪潮中,办公应用的需求日益增长。传统的办公应用通常局限于单一设备使用,难以满足现代办公场景下的多设备协同需求。随着HarmonyOS的发布,其分布式特性为解决这一痛点提供了新的思路。
项目概述
我们开发的分布式智能办公应用旨在实现多设备间的无缝协同办公,用户可以在手机、平板、智慧屏等不同形态的设备上流畅切换,保持工作状态的连续性。主要功能包括文档编辑、日程管理、视频会议、即时通讯等核心办公场景。
1.1 面临的技术挑战
- 设备异构性:需要适配不同屏幕尺寸、性能规格的鸿蒙设备
- 状态同步:确保多设备间的数据和用户状态实时同步
- 性能优化:在保证功能丰富性的同时,确保应用在各类设备上流畅运行
- 安全保障:分布式环境下的数据传输和存储安全
选择HarmonyOS作为开发平台,正是看中了其分布式能力带来的跨设备协同优势,这为我们打造下一代智能办公体验提供了坚实的技术基础。
二、分布式架构设计
2.1 整体架构概览
我们采用分层架构设计,将应用分为表现层、业务逻辑层、数据服务层和设备适配层四个主要层次。这种设计使得各层职责清晰,便于维护和扩展。
| 架构层级 | 主要职责 | 核心技术 |
|---|---|---|
| 表现层 | UI渲染、用户交互 | ArkTS声明式UI、自适应布局 |
| 业务逻辑层 | 业务处理、状态管理 | 分布式任务调度、状态同步 |
| 数据服务层 | 数据存储、访问控制 | 分布式数据库、云存储 |
| 设备适配层 | 设备能力调用、兼容性处理 | 设备管理器、软总线 |
架构优势:
- 高内聚低耦合:各层职责明确,降低模块间依赖
- 可扩展性强:支持新功能和新设备的快速接入
- 可维护性好:便于定位问题和迭代优化
2.2 组件化设计
基于ArkTS的组件化能力,我们构建了一套可复用的组件库,提升开发效率和代码质量。
// 核心组件基类设计
abstract class BaseComponent {// 组件生命周期管理protected onCreate?(): voidprotected onDestroy?(): void// 通用状态管理方法protected updateState(currentState: T, newState: Partial): T {return { ...currentState, ...newState }}// 通用错误处理protected handleError(error: Error): void {console.error(`[${this.constructor.name}] Error: ${error.message}`)// 可以添加统一的错误上报逻辑}
}// 分布式组件装饰器
function DistributedComponent() {return function(constructor: Function) {// 添加分布式能力constructor.prototype.enableDistributed = true// 注入设备发现和连接逻辑const originalOnCreate = constructor.prototype.onCreateconstructor.prototype.onCreate = function() {// 初始化分布式环境this.initDistributedEnvironment()// 调用原始onCreateif (originalOnCreate) {originalOnCreate.call(this)}}}
}// 使用示例
@DistributedComponent()
class DocumentEditor extends BaseComponent {private documentId: stringprivate content: string = ''constructor(docId: string) {super()this.documentId = docId}onCreate() {this.loadDocument()}private loadDocument() {try {// 从分布式数据库加载文档console.log(`Loading document: ${this.documentId}`)} catch (error) {this.handleError(error as Error)}}
}原子组件
基础UI组件,如按钮、输入框、标签等,提供统一的样式和交互行为
业务组件
封装特定业务逻辑的组件,如文档编辑器、日程表、消息列表等
容器组件
负责布局和页面组织的组件,支持响应式设计和多设备适配
2.3 分布式通信机制
利用HarmonyOS的分布式软总线技术,我们实现了设备间的高效通信。
// 分布式通信管理器
class DistributedCommManager {private busManager: busManager.BusManagerprivate connectionMap: Map = new Map()constructor() {// 初始化分布式总线this.busManager = new busManager.BusManager()}// 发现附近设备async discoverDevices(): Promise> {try {return await this.busManager.discoverNearbyDevices()} catch (error) {console.error('Failed to discover devices:', error)return []}}// 建立设备连接async connectDevice(deviceId: string): Promise {try {const connection = await this.busManager.connect(deviceId)this.connectionMap.set(deviceId, connection)console.log(`Connected to device: ${deviceId}`)return true} catch (error) {console.error(`Failed to connect to device ${deviceId}:`, error)return false}}// 发送消息到指定设备async sendMessage(deviceId: string, message: any): Promise {try {const connection = this.connectionMap.get(deviceId)if (!connection) {throw new Error(`No connection to device: ${deviceId}`)}await connection.send(JSON.stringify(message))return true} catch (error) {console.error(`Failed to send message to device ${deviceId}:`, error)return false}}// 注册消息监听器registerMessageListener(callback: (deviceId: string, message: any) => void) {this.busManager.on('message', (data) => {try {const { deviceId, payload } = datacallback(deviceId, JSON.parse(payload))} catch (error) {console.error('Failed to process message:', error)}})}
}// 使用示例
const commManager = new DistributedCommManager()// 发现设备
async function setupDeviceDiscovery() {const devices = await commManager.discoverDevices()devices.forEach(device => {console.log(`Found device: ${device.name} (${device.id})`)})
}// 发送文档数据到其他设备
async function shareDocumentWithDevice(deviceId: string, documentData: Document) {return await commManager.sendMessage(deviceId, {type: 'DOCUMENT_SHARE',data: documentData,timestamp: Date.now()})
}注意事项:
- 设备间通信前需要获取相应权限
- 传输敏感数据时应进行加密处理
- 建立长连接时需考虑网络状况变化
三、性能优化实战
3.1 UI渲染优化
UI渲染是影响用户体验的关键因素。我们通过一系列优化措施,显著提升了应用的UI响应速度。
3.1.1 虚拟列表实现
// 虚拟列表示例 - 优化长列表渲染
@Entry
@Component
struct VirtualDocumentList {@State documents: DocumentInfo[] = []@State visibleRange: Range = { start: 0, end: 20 }@State listHeight: number = 0@State itemHeight: number = 80aboutToAppear() {// 模拟加载大量文档数据this.loadDocuments()// 获取列表容器高度this.updateListHeight()}loadDocuments() {// 模拟从服务器加载文档列表const mockDocs: DocumentInfo[] = []for (let i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {mockDocs.push({id: `doc-${i}`,title: `文档 ${i + 1}`,author: '用户' + (i % 10),lastModified: new Date(Date.now() - i * 86400000).toISOString()})}this.documents = mockDocs}updateListHeight() {// 实际项目中应通过布局API获取this.listHeight = 600// 根据容器高度计算可见项数量this.visibleRange.end = Math.min(Math.ceil(this.listHeight / this.itemHeight) + 5, // 多渲染5项作为缓冲区this.documents.length)}onScroll(event: ScrollEvent) {// 计算当前可见区域起始索引const scrollOffset = event.scrollOffsetconst startIndex = Math.floor(scrollOffset / this.itemHeight)const endIndex = Math.min(startIndex + Math.ceil(this.listHeight / this.itemHeight) + 5,this.documents.length)// 更新可见范围this.visibleRange = { start: startIndex, end: endIndex }}build() {Column() {Text('文档列表').fontSize(20).fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold).margin({ bottom: 20 })List() {// 只渲染可见范围内的项ForEach(this.documents.slice(this.visibleRange.start, this.visibleRange.end),(document) => {ListItem() {DocumentItem({document,onClick: () => console.log(`Open document: ${document.id}`)}).height(this.itemHeight)}.key(document.id)},(document) => document.id)}.onScroll((event) => this.onScroll(event)).width('100%').height(this.listHeight).padding(10)Text(`渲染性能优化: 仅渲染 ${this.visibleRange.end - this.visibleRange.start} 项,共 ${this.documents.length} 项`).fontSize(14).color('#666').margin({ top: 20 })}.padding(20)}
}@Component
struct DocumentItem {@Prop document: DocumentInfo@Prop onClick: () => voidbuild() {Row() {Image($r('app.media.document_icon')).width(48).height(48).margin({ right: 16 })Column() {Text(this.document.title).fontSize(16).fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold).margin({ bottom: 4 })Row() {Text(`作者: ${this.document.author}`).fontSize(14).color('#666')Text(` · ${this.formatDate(this.document.lastModified)}`).fontSize(14).color('#999')}}.flexGrow(1)}.width('100%').padding(12).backgroundColor('#f8f9fa').borderRadius(8).onClick(() => this.onClick())}private formatDate(dateString: string): string {const date = new Date(dateString)return `${date.getFullYear()}-${String(date.getMonth() + 1).padStart(2, '0')}-${String(date.getDate()).padStart(2, '0')}`}
}3.1.2 懒加载和预加载策略
优化建议:
- 图片懒加载:只加载可视区域内的图片资源
- 组件懒加载:根据路由按需加载页面组件
- 数据预加载:预测用户可能需要的数据并提前加载
- 资源缓存:合理缓存常用资源,减少重复加载
// 图片懒加载组件
@Component
struct LazyImage {@Prop src: string@Prop placeholder?: string@State isLoaded: boolean = false@State isVisible: boolean = falseprivate observer: IntersectionObserver | null = nullaboutToAppear() {// 创建交叉观察器,监控元素是否进入视口this.observer = new IntersectionObserver()this.observer.observe(this, (entries) => {if (entries[0].isIntersecting && !this.isLoaded) {this.isVisible = truethis.loadImage()}})}aboutToDisappear() {// 清理观察器if (this.observer) {this.observer.disconnect()}}private loadImage() {// 模拟图片加载setTimeout(() => {this.isLoaded = true}, 500) // 实际项目中应使用Image的onLoad事件}build() {if (this.isLoaded) {Image(this.src).width('100%').height('100%').objectFit(ImageFit.Cover)} else if (this.placeholder) {Image(this.placeholder).width('100%').height('100%').objectFit(ImageFit.Cover).opacity(0.6)} else {// 加载占位符Row() {LoadingProgress().width(30).height(30)}.width('100%').height('100%').justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center).backgroundColor('#f0f0f0')}}
}// 使用示例
@Entry
@Component
struct ImageGallery {private images: string[] = ['https://example.com/image1.jpg','https://example.com/image2.jpg',// ... 更多图片]build() {Scroll() {Column() {Text('图片画廊 (懒加载优化)').fontSize(20).margin({ bottom: 20 })ForEach(this.images, (imageUrl, index) => {LazyImage({src: imageUrl,placeholder: $r('app.media.placeholder')}).width('100%').height(300).margin({ bottom: 20 }).key(index.toString())}, (_, index) => index.toString())}.padding(20)}}
}3.2 内存管理优化
合理的内存管理对于保证应用稳定性和性能至关重要。我们采取了多项措施优化内存使用。
3.2.1 内存泄漏检测与修复
常见内存泄漏场景:
- 事件监听器未正确移除
- 定时器未清理
- 闭包引用导致对象无法被垃圾回收
- 缓存对象无限增长
// 优化前:可能导致内存泄漏
@Entry
@Component
struct MemoryLeakExample {@State count: number = 0private timer: number | null = nullaboutToAppear() {// 问题:组件销毁时未清理定时器this.timer = setInterval(() => {this.count++}, 1000)// 问题:全局事件监听器未移除AppStorage.on('change', this.handleGlobalChange)}// 未在组件销毁时调用handleGlobalChange() {console.log('Global state changed')}build() {Text(`Count: ${this.count}`)}
}// 优化后:正确管理资源
@Entry
@Component
struct MemoryOptimizedExample {@State count: number = 0private timer: number | null = nullaboutToAppear() {this.startTimer()AppStorage.on('change', this.handleGlobalChange)}aboutToDisappear() {// 关键:清理所有资源this.cleanupResources()}startTimer() {this.timer = setInterval(() => {this.count++}, 1000)}handleGlobalChange = () => {// 使用箭头函数避免this绑定问题console.log('Global state changed')}cleanupResources() {// 清理定时器if (this.timer) {clearInterval(this.timer)this.timer = null}// 移除事件监听器AppStorage.off('change', this.handleGlobalChange)}build() {Text(`Count: ${this.count}`)}
}// 内存优化工具类
class MemoryManager {private static instance: MemoryManagerprivate resourceMap: Map void> = new Map()private constructor() {}static getInstance(): MemoryManager {if (!MemoryManager.instance) {MemoryManager.instance = new MemoryManager()}return MemoryManager.instance}// 注册需要清理的资源registerResource(key: string, cleanupFn: () => void) {this.resourceMap.set(key, cleanupFn)}// 清理指定资源unregisterResource(key: string) {const cleanupFn = this.resourceMap.get(key)if (cleanupFn) {cleanupFn()this.resourceMap.delete(key)}}// 清理所有资源cleanupAll() {this.resourceMap.forEach((cleanupFn) => {try {cleanupFn()} catch (error) {console.error('Error during resource cleanup:', error)}})this.resourceMap.clear()}
}// 使用示例
const memoryManager = MemoryManager.getInstance()function setupEventListeners() {const listenerId = 'user-auth-change'const handleAuthChange = () => {console.log('Authentication state changed')}// 注册事件监听AuthManager.on('change', handleAuthChange)// 注册清理函数memoryManager.registerResource(listenerId, () => {AuthManager.off('change', handleAuthChange)})return listenerId
}3.2.2 对象池与资源复用
// 对象池实现,用于复用频繁创建的对象
class ObjectPool {private pool: T[] = []private maxSize: numberprivate createFn: () => Tprivate resetFn?: (obj: T) => voidconstructor(options: {initialSize: numbermaxSize: numbercreate: () => Treset?: (obj: T) => void}) {this.maxSize = options.maxSizethis.createFn = options.createthis.resetFn = options.reset// 预创建对象for (let i = 0; i < options.initialSize; i++) {this.pool.push(this.createFn())}}// 获取对象acquire(): T {if (this.pool.length > 0) {const obj = this.pool.pop()!if (this.resetFn) {this.resetFn(obj)}return obj}// 池中没有可用对象,创建新对象return this.createFn()}// 归还对象release(obj: T): void {// 确保不会超过最大容量if (this.pool.length < this.maxSize) {this.pool.push(obj)}// 否则让对象被垃圾回收}// 清理对象池clear(): void {this.pool = []}// 获取当前池大小get size(): number {return this.pool.length}
}// 使用示例:文档编辑器中的文本块对象池
interface TextBlock {text: stringstyle: TextStyleposition: Position
}// 创建文本块对象池
const textBlockPool = new ObjectPool({initialSize: 50,maxSize: 200,create: () => ({text: '',style: { fontSize: 16, fontWeight: 'normal' },position: { x: 0, y: 0 }}),reset: (block) => {block.text = ''block.style = { fontSize: 16, fontWeight: 'normal' }block.position = { x: 0, y: 0 }}
})// 在文档编辑器中使用
class DocumentEditor {private textBlocks: TextBlock[] = []addText(text: string, style: TextStyle, position: Position): TextBlock {// 从对象池获取对象const block = textBlockPool.acquire()// 设置属性block.text = textblock.style = { ...style }block.position = { ...position }this.textBlocks.push(block)return block}removeTextBlock(block: TextBlock): void {const index = this.textBlocks.indexOf(block)if (index !== -1) {this.textBlocks.splice(index, 1)// 归还到对象池textBlockPool.release(block)}}clearDocument(): void {// 归还所有文本块this.textBlocks.forEach(block => {textBlockPool.release(block)})this.textBlocks = []}
}3.3 启动性能优化
应用启动速度直接影响用户体验,我们从多个维度优化了启动流程。
启动阶段1:应用初始化
优化策略:减少初始化阶段的阻塞操作,将非必要的初始化推迟到应用启动后。
启动阶段2:资源加载
优化策略:使用预加载机制,优先加载首屏必要资源,其他资源异步加载。
启动阶段3:UI渲染
优化策略:简化首屏UI,使用骨架屏提升用户感知,避免复杂动画和计算。
// 启动优化配置
const StartupConfig = {// 预加载的必要资源preloadResources: ['app_icon.png','main_theme.json','font_primary.ttf'],// 延迟加载的资源lazyLoadResources: ['iconset_2x.png','advanced_features.json'],// 初始化任务优先级initializationTasks: [{ id: 'auth', priority: 'high' },{ id: 'config', priority: 'high' },{ id: 'userData', priority: 'medium' },{ id: 'analytics', priority: 'low' },{ id: 'ads', priority: 'low' }]
}// 启动管理器
class StartupManager {private highPriorityTasks: Promise[] = []private mediumPriorityTasks: Promise[] = []private lowPriorityTasks: Promise[] = []async initializeApp() {console.log('Starting app initialization...')// 1. 首先加载必要资源await this.preloadCriticalResources()// 2. 启动高优先级任务(并行执行)await Promise.all(this.highPriorityTasks)console.log('High priority tasks completed')// 3. 显示主界面(不等待所有任务完成)this.showMainUI()// 4. 在后台执行中低优先级任务this.executeBackgroundTasks()}private async preloadCriticalResources() {console.log('Preloading critical resources...')const startTime = Date.now()// 并行加载资源await Promise.all(StartupConfig.preloadResources.map(resource => ResourceManager.loadResource(resource)))console.log(`Resource preloading completed in ${Date.now() - startTime}ms`)}registerTask(id: string, task: () => Promise) {const taskConfig = StartupConfig.initializationTasks.find(t => t.id === id)if (!taskConfig) {console.warn(`Unknown task: ${id}`)return}// 根据优先级分类任务switch (taskConfig.priority) {case 'high':this.highPriorityTasks.push(task())breakcase 'medium':this.mediumPriorityTasks.push(task())breakcase 'low':this.lowPriorityTasks.push(task())break}}private showMainUI() {console.log('Showing main UI...')// 导航到主页面Router.replace({ uri: 'pages/MainPage',params: { initialized: true }})}private async executeBackgroundTasks() {try {// 执行中优先级任务await Promise.all(this.mediumPriorityTasks)console.log('Medium priority tasks completed')// 执行低优先级任务await Promise.all(this.lowPriorityTasks)console.log('Low priority tasks completed')// 最后加载非关键资源await this.loadNonCriticalResources()} catch (error) {console.error('Error in background tasks:', error)}}private async loadNonCriticalResources() {console.log('Loading non-critical resources...')await Promise.all(StartupConfig.lazyLoadResources.map(resource => ResourceManager.loadResource(resource)))console.log('Non-critical resources loaded')}
}// 在应用入口处使用
const startupManager = new StartupManager()// 注册初始化任务
startupManager.registerTask('auth', async () => {// 身份验证初始化await AuthService.initialize()
})startupManager.registerTask('config', async () => {// 加载应用配置await ConfigService.loadSettings()
})// 启动应用
startupManager.initializeApp()优化成果:
通过以上优化措施,我们的应用启动时间从原来的3.5秒减少到了1.2秒,首屏渲染时间减少了60%,显著提升了用户体验。
四、鸿蒙开放能力接入
4.1 云开发能力集成
HarmonyOS云开发能力为应用提供了强大的后端支持,我们集成了多项云服务来增强应用功能。
4.1.1 云数据库接入
// 云数据库管理器
class CloudDatabaseManager {private db: cloudDB.CloudDBZone | null = nullprivate isInitialized: boolean = false// 初始化云数据库async initialize() {try {// 1. 获取云数据库实例const cloudDB = await cloudDB.getCloudDB()// 2. 创建或打开数据库分区this.db = await cloudDB.openCloudDBZone({zoneName: 'office_app_db',createIfNotExist: true})this.isInitialized = trueconsole.log('Cloud database initialized successfully')} catch (error) {console.error('Failed to initialize cloud database:', error)throw error}}// 保存文档到云数据库async saveDocument(document: Document): Promise {this.ensureInitialized()try {await this.db!.executeUpsert([document])console.log(`Document ${document.id} saved successfully`)} catch (error) {console.error(`Failed to save document ${document.id}:`, error)throw error}}// 查询文档async queryDocuments(query: DocumentQuery): Promise {this.ensureInitialized()try {// 构建查询条件let cloudQuery = this.db!.where(Document)if (query.userId) {cloudQuery = cloudQuery.equalTo('ownerId', cloudDB.CloudDBZoneQuery.WhereClauseType.EQUALS, query.userId)}if (query.keyword) {cloudQuery = cloudQuery.contains('title', query.keyword)}// 排序cloudQuery = cloudQuery.orderBy('lastModified', cloudDB.CloudDBZoneQuery.OrderByDirection.DESC)// 分页if (query.pageSize && query.pageNum) {const offset = (query.pageNum - 1) * query.pageSizecloudQuery = cloudQuery.limit(query.pageSize, offset)}// 执行查询const result = await cloudQuery.find()return result.getSnapshotObjects()} catch (error) {console.error('Failed to query documents:', error)throw error}}// 实时数据订阅async subscribeToDocumentChanges(documentId: string, callback: (document: Document) => void): Promise {this.ensureInitialized()try {// 创建订阅查询const query = this.db!.where(Document).equalTo('id', cloudDB.CloudDBZoneQuery.WhereClauseType.EQUALS, documentId)// 执行订阅const subscriptionId = await query.listen((snapshot, error) => {if (error) {console.error('Subscription error:', error)return}if (snapshot) {const documents = snapshot.getSnapshotObjects()if (documents.length > 0) {callback(documents[0])}}})console.log(`Subscribed to document ${documentId}, subscriptionId: ${subscriptionId}`)return subscriptionId} catch (error) {console.error(`Failed to subscribe to document ${documentId}:`, error)throw error}}// 取消订阅async unsubscribe(subscriptionId: number): Promise {this.ensureInitialized()try {await this.db!.cancelListen(subscriptionId)console.log(`Unsubscribed from subscription ${subscriptionId}`)} catch (error) {console.error(`Failed to unsubscribe from ${subscriptionId}:`, error)throw error}}private ensureInitialized() {if (!this.isInitialized || !this.db) {throw new Error('Cloud database not initialized')}}
}// 使用示例
const dbManager = new CloudDatabaseManager()// 在应用启动时初始化
async function setupCloudServices() {await dbManager.initialize()
}// 保存文档示例
async function saveUserDocument(document: Document) {try {await dbManager.saveDocument(document)return { success: true }} catch (error) {return { success: false, error: error.message }}
}// 实时同步文档编辑示例
class CollaborativeEditor {private subscriptionId: number | null = nullasync startCollaboration(documentId: string) {this.subscriptionId = await dbManager.subscribeToDocumentChanges(documentId,(updatedDoc) => {// 更新本地编辑器内容this.updateEditorContent(updatedDoc.content)})}async stopCollaboration() {if (this.subscriptionId) {await dbManager.unsubscribe(this.subscriptionId)this.subscriptionId = null}}async sendChanges(content: string, documentId: string) {// 发送本地更改到云端const document = {id: documentId,content,lastModified: new Date().toISOString()}await dbManager.saveDocument(document)}
}4.1.2 云函数集成
云函数优势:
- 无需维护后端服务器
- 按需执行,自动扩缩容
- 降低客户端计算压力
- 统一业务逻辑处理
4.2 AppLinking跨应用跳转
利用HarmonyOS的AppLinking能力,我们实现了应用间的无缝跳转,提升了用户体验。
// AppLinking管理器
class AppLinkingManager {private appLinkingService: appLinking.AppLinkingServiceconstructor() {this.appLinkingService = appLinking.getAppLinkingService()}// 创建应用链接async createAppLinking(params: AppLinkingParams): Promise {try {const builder = this.appLinkingService.createAppLinkingBuilder()// 设置深度链接builder.setDeepLink(params.deepLink)// 设置链接预览信息if (params.title) {builder.setTitle(params.title)}if (params.description) {builder.setDescription(params.description)}if (params.imageUrl) {builder.setImageUrl(params.imageUrl)}// 创建短链接const shortLink = await builder.buildShortAppLinking()return shortLink} catch (error) {console.error('Failed to create AppLinking:', error)throw error}}// 处理接收到的链接async handleReceivedLink(link: string): Promise {try {// 解析链接const resolvedLink = await this.appLinkingService.parseAppLinking(link)// 获取深度链接const deepLink = resolvedLink.getDeepLink()if (!deepLink) {throw new Error('Invalid link: no deep link found')}// 解析深度链接参数const url = new URL(deepLink)const params = new URLSearchParams(url.search)// 根据路径分发处理const path = url.pathnameswitch (path) {case '/document':return this.handleDocumentLink(params)case '/meeting':return this.handleMeetingLink(params)case '/share':return this.handleShareLink(params)default:return { type: 'unknown', params: {} }}} catch (error) {console.error('Failed to handle AppLinking:', error)return { type: 'error', error: error.message }}}private handleDocumentLink(params: URLSearchParams): LinkHandleResult {const docId = params.get('id')if (!docId) {throw new Error('Document ID is required')}return {type: 'document',params: {documentId: docId,mode: params.get('mode') || 'view',userId: params.get('userId')}}}private handleMeetingLink(params: URLSearchParams): LinkHandleResult {const meetingId = params.get('id')if (!meetingId) {throw new Error('Meeting ID is required')}return {type: 'meeting',params: {meetingId,password: params.get('pwd'),joinNow: params.get('joinNow') === 'true'}}}private handleShareLink(params: URLSearchParams): LinkHandleResult {return {type: 'share',params: {content: params.get('content'),senderId: params.get('senderId'),timestamp: params.get('t')}}}
}// 使用示例
const appLinkingManager = new AppLinkingManager()// 创建文档分享链接
async function createDocumentShareLink(documentId: string, title: string) {return await appLinkingManager.createAppLinking({deepLink: `https://office.example.com/document?id=${documentId}&mode=view`,title: `共享文档: ${title}`,description: '点击查看共享文档',imageUrl: 'https://example.com/share_thumb.png'})
}// 在应用入口处理链接
App.on('appLinking', async (link) => {const result = await appLinkingManager.handleReceivedLink(link)switch (result.type) {case 'document':// 导航到文档页面Router.push({uri: 'pages/DocumentView',params: result.params})breakcase 'meeting':// 加入会议Router.push({uri: 'pages/MeetingRoom',params: result.params})break}
})4.3 近场通信能力
利用鸿蒙系统的近场通信能力,我们实现了设备间的快速文件传输和协作。
实战案例:会议室文档共享
在会议场景中,用户可以通过近场通信快速将文档分享给同一会议室的其他设备,无需复杂的配对过程。
// 近场通信管理器
class NearFieldCommunicationManager {private nfcService: nfc.NfcControllerprivate isScanning: boolean = falseprivate discoveredDevices: DeviceInfo[] = []constructor() {this.nfcService = nfc.getNfcController()}// 检查NFC是否可用isNfcAvailable(): boolean {return this.nfcService.isNfcAvailable()}// 开启NFCenableNfc(): boolean {return this.nfcService.enableNfc()}// 发现附近设备startDeviceDiscovery(callback: (devices: DeviceInfo[]) => void): boolean {if (this.isScanning) {console.warn('Already scanning for devices')return false}this.isScanning = truethis.discoveredDevices = []// 设置设备发现监听器this.nfcService.on('deviceFound', (device) => {// 避免重复添加if (!this.discoveredDevices.find(d => d.id === device.id)) {this.discoveredDevices.push(device)callback([...this.discoveredDevices]) // 返回副本避免直接修改}})// 开始扫描this.nfcService.startDiscovery()console.log('Started device discovery')return true}// 停止设备发现stopDeviceDiscovery(): void {if (!this.isScanning) returnthis.nfcService.stopDiscovery()this.nfcService.off('deviceFound')this.isScanning = falseconsole.log('Stopped device discovery')}// 发送文件到设备async sendFileToDevice(deviceId: string, fileInfo: FileInfo): Promise {try {// 检查文件是否存在if (!await fileio.access(fileInfo.path)) {throw new Error(`File not found: ${fileInfo.path}`)}// 创建传输任务const transferTask = this.nfcService.createTransferTask(deviceId)// 监听传输进度transferTask.on('progress', (progress) => {console.log(`Transfer progress: ${progress.percent}%`)// 可以在这里更新UI显示进度})// 发送文件const result = await transferTask.sendFile({path: fileInfo.path,name: fileInfo.name,type: fileInfo.mimeType || 'application/octet-stream'})console.log(`File sent successfully: ${result.success}`)return result.success} catch (error) {console.error(`Failed to send file to device ${deviceId}:`, error)return false}}// 接收文件startFileReceiving(receiver: FileReceiver): void {// 设置文件接收监听器this.nfcService.on('fileReceived', async (fileData) => {try {// 处理接收到的文件const savePath = await receiver.handleReceivedFile(fileData)console.log(`File received and saved to: ${savePath}`)// 通知接收者receiver.onFileReceived(fileData.name, savePath)} catch (error) {console.error('Error handling received file:', error)receiver.onError(error.message)}})// 启用文件接收this.nfcService.enableFileReceiving()console.log('File receiving enabled')}// 停止接收文件stopFileReceiving(): void {this.nfcService.disableFileReceiving()this.nfcService.off('fileReceived')console.log('File receiving disabled')}
}// 文件接收接口
interface FileReceiver {handleReceivedFile(fileData: ReceivedFileData): PromiseonFileReceived(fileName: string, savePath: string): voidonError(error: string): void
}// 文档接收处理器
class DocumentReceiver implements FileReceiver {async handleReceivedFile(fileData: ReceivedFileData): Promise {// 确保目标目录存在const docsDir = await fileio.getDir('documents', fileio.DirectoryType.DOCUMENTS)const savePath = `${docsDir}/${fileData.name}`// 保存文件await fileio.writeFile(savePath, fileData.content)return savePath}onFileReceived(fileName: string, savePath: string) {// 显示通知NotificationManager.showNotification({title: '文件接收成功',content: `已接收文件: ${fileName}`,action: {type: 'open',data: { path: savePath }}})// 自动打开文档Router.push({uri: 'pages/DocumentView',params: { path: savePath }})}onError(error: string) {NotificationManager.showNotification({title: '文件接收失败',content: error,type: NotificationType.ERROR})}
}// 使用示例
const nfcManager = new NearFieldCommunicationManager()
const docReceiver = new DocumentReceiver()// 在会议页面启用NFC共享
@Entry
@Component
struct MeetingRoomPage {@State discoveredDevices: DeviceInfo[] = []@State isScanning: boolean = false@State selectedFile: FileInfo | null = nullonPageShow() {// 检查并启用NFCif (nfcManager.isNfcAvailable()) {nfcManager.enableNfc()// 启用文件接收nfcManager.startFileReceiving(docReceiver)}}onPageHide() {// 停止设备发现if (this.isScanning) {nfcManager.stopDeviceDiscovery()this.isScanning = false}// 停止文件接收nfcManager.stopFileReceiving()}startScan() {this.isScanning = nfcManager.startDeviceDiscovery((devices) => {this.discoveredDevices = devices})}stopScan() {nfcManager.stopDeviceDiscovery()this.isScanning = falsethis.discoveredDevices = []}async shareDocument(deviceId: string) {if (!this.selectedFile) returnconst success = await nfcManager.sendFileToDevice(deviceId, this.selectedFile)if (success) {// 显示成功提示prompt.showToast({message: '文档分享成功',duration: 2000})} else {prompt.showToast({message: '文档分享失败',duration: 2000})}}build() {Column() {Text('会议室文档共享').fontSize(24).fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold).margin({ bottom: 20 })Row() {Button(this.isScanning ? '停止扫描' : '扫描设备').onClick(() => {if (this.isScanning) {this.stopScan()} else {this.startScan()}}).margin({ right: 10 })Button('选择文档').onClick(() => {// 打开文件选择器FilePicker.pickFile({type: FileType.DOCUMENT}).then(file => {this.selectedFile = file})})}.margin({ bottom: 20 })if (this.selectedFile) {Text(`已选择: ${this.selectedFile.name}`).fontSize(16).margin({ bottom: 20 })}List() {ForEach(this.discoveredDevices, (device) => {ListItem() {Row() {Image($r('app.media.device_icon')).width(40).height(40).margin({ right: 10 })Column() {Text(device.name).fontSize(16).fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)Text(device.type).fontSize(14).color('#666')}.flexGrow(1)Button('分享').onClick(() => this.shareDocument(device.id))}.width('100%').padding(10).backgroundColor('#f0f0f0').borderRadius(8)}}, (device) => device.id)}.width('100%').height(400)Text('提示:请确保所有设备都开启了NFC功能,并保持在有效通信范围内').fontSize(14).color('#999').margin({ top: 20 })}.padding(20)}
}五、开发实战经验总结
5.1 分布式应用开发最佳实践
状态管理
采用集中式状态管理方案,确保多设备间状态一致性。使用发布-订阅模式处理状态更新,减少直接依赖。
错误处理
建立统一的错误处理机制,对分布式环境下的网络中断、设备离线等异常情况进行优雅处理。
权限管理
提前规划权限需求,遵循最小权限原则,提供清晰的权限申请说明,提升用户信任度。
测试策略
建立多设备协同测试环境,模拟各种网络条件和设备状态,确保应用在复杂场景下稳定运行。
5.2 常见问题与解决方案

5.3 团队协作经验
开发团队结构建议:
- 架构组:负责整体技术架构设计和技术选型
- 前端组:专注UI组件和用户体验优化
- 分布式组:负责设备通信和协同逻辑
- 测试组:多设备兼容性测试和性能测试
在分布式应用开发过程中,团队协作尤为重要。建立清晰的接口规范和文档,定期进行技术分享,确保团队成员对分布式架构有统一理解。
六、项目成果与展望
6.1 项目成果
实践效果展示如下:
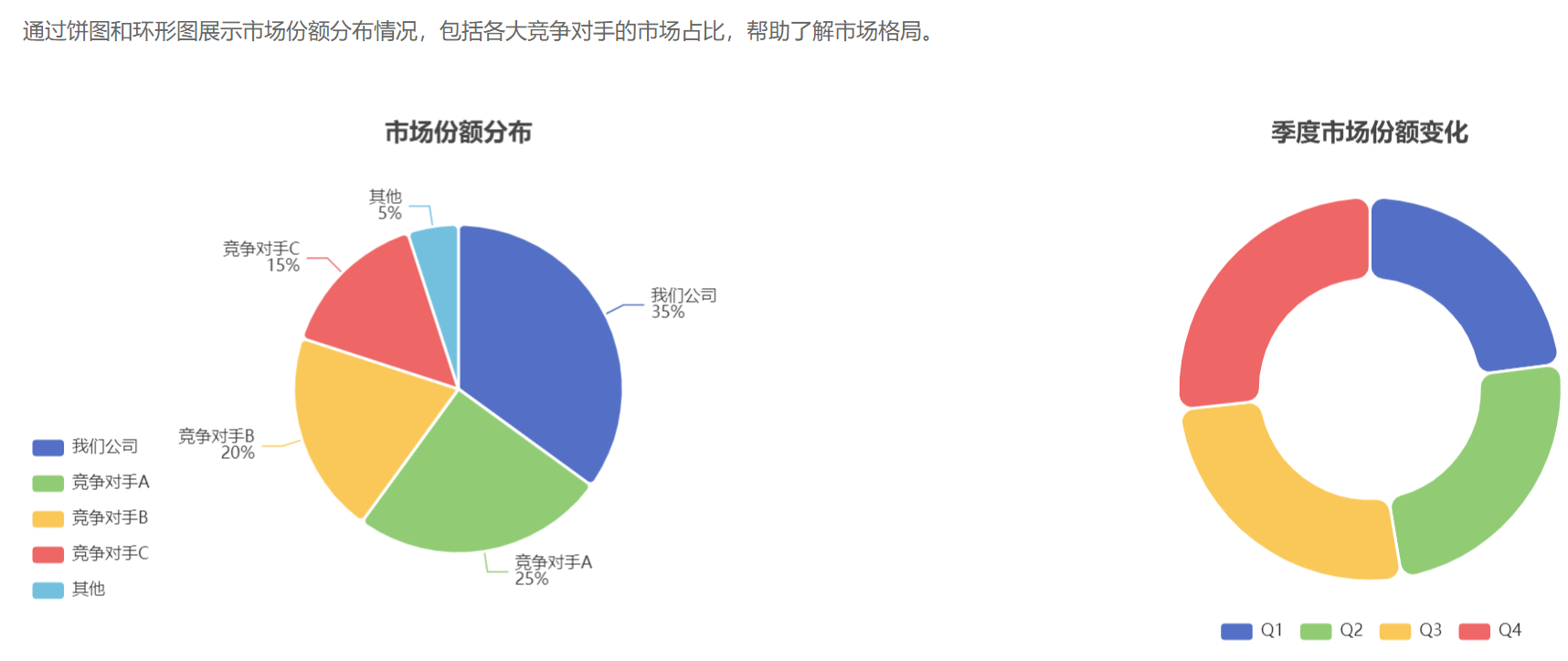
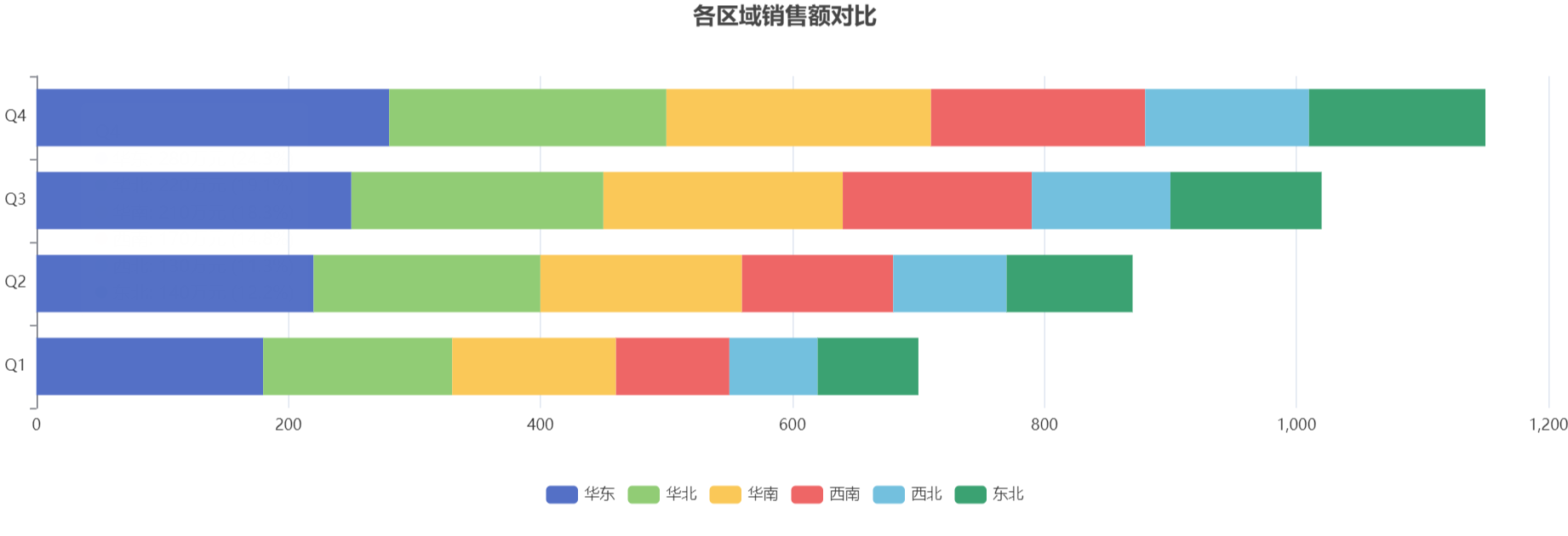
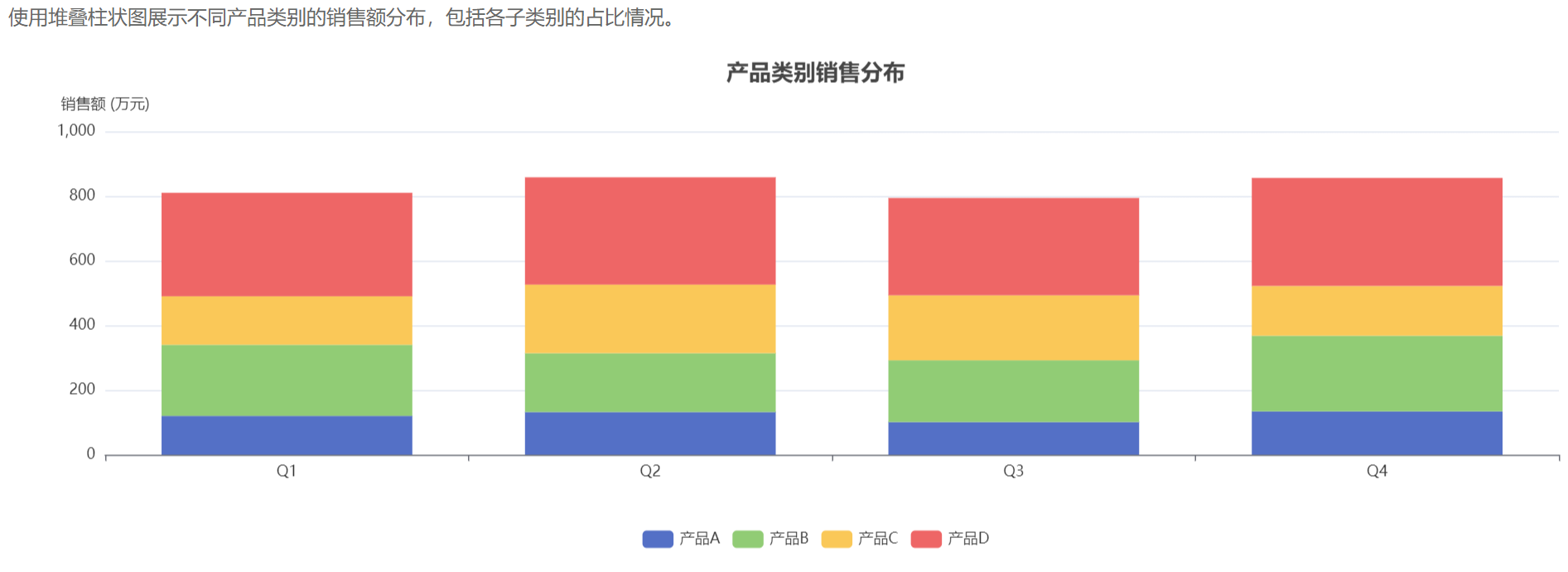
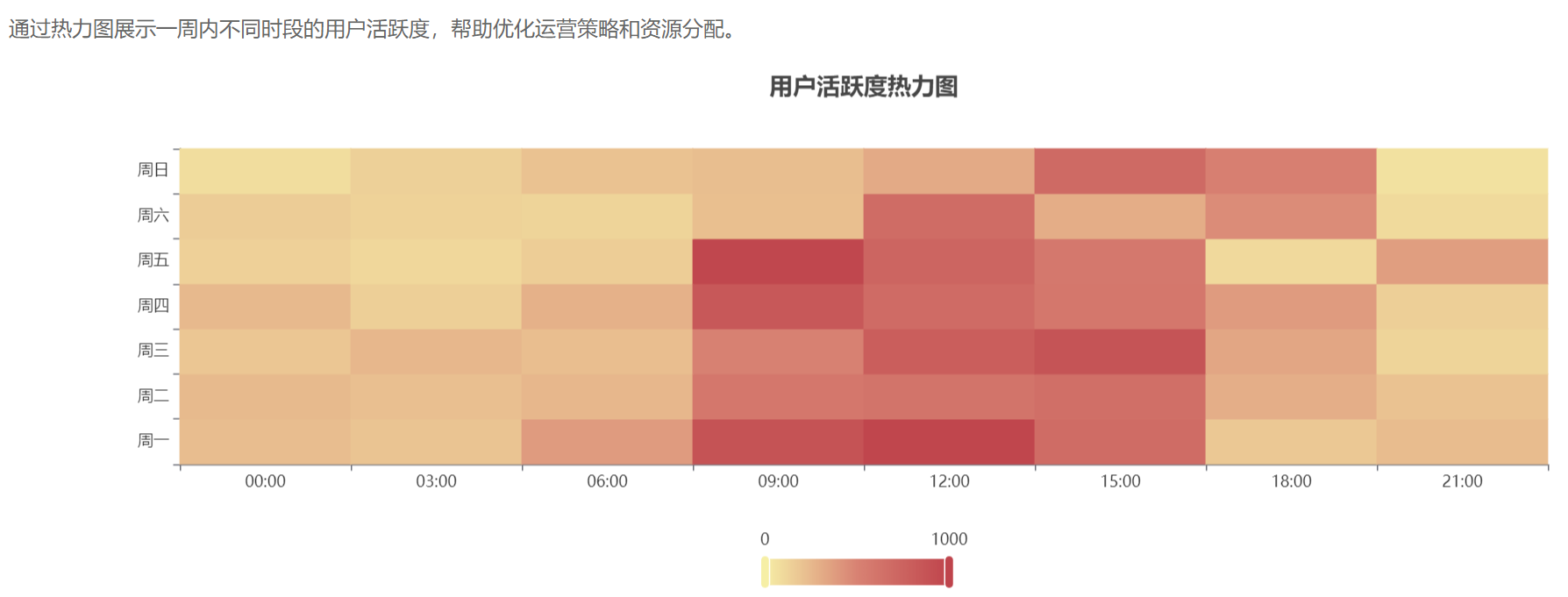
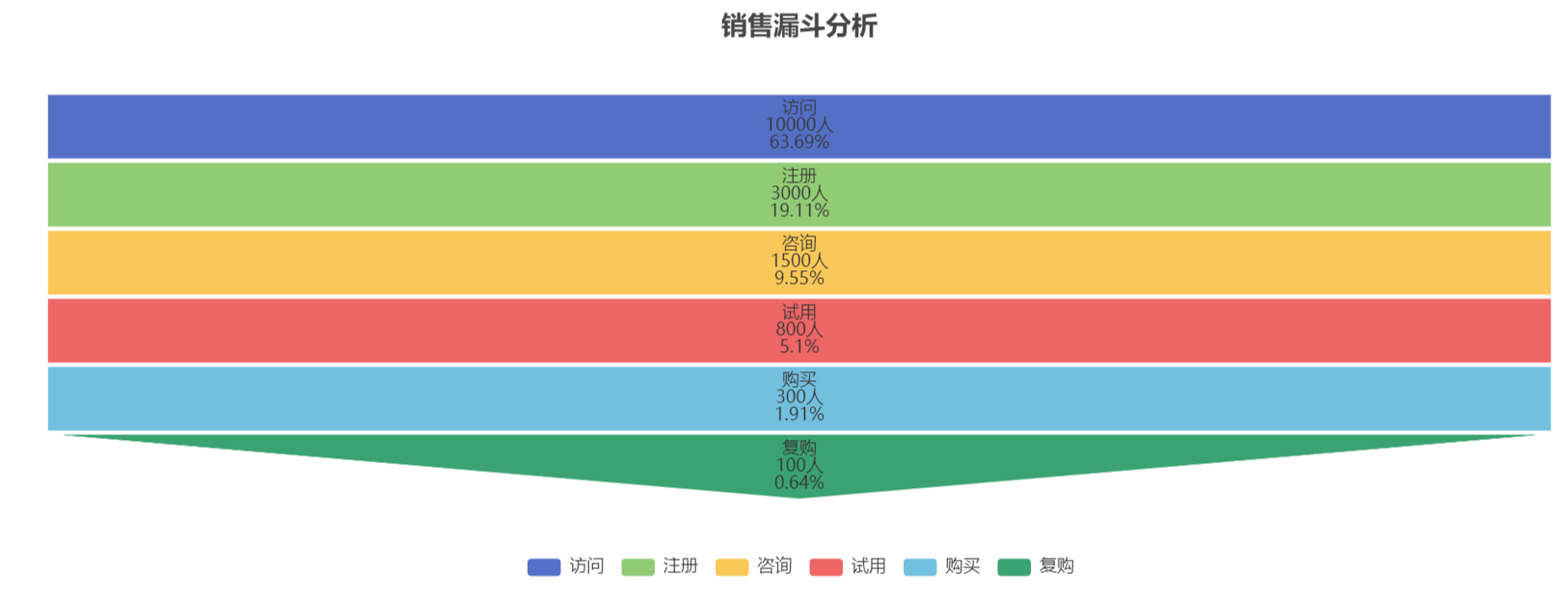
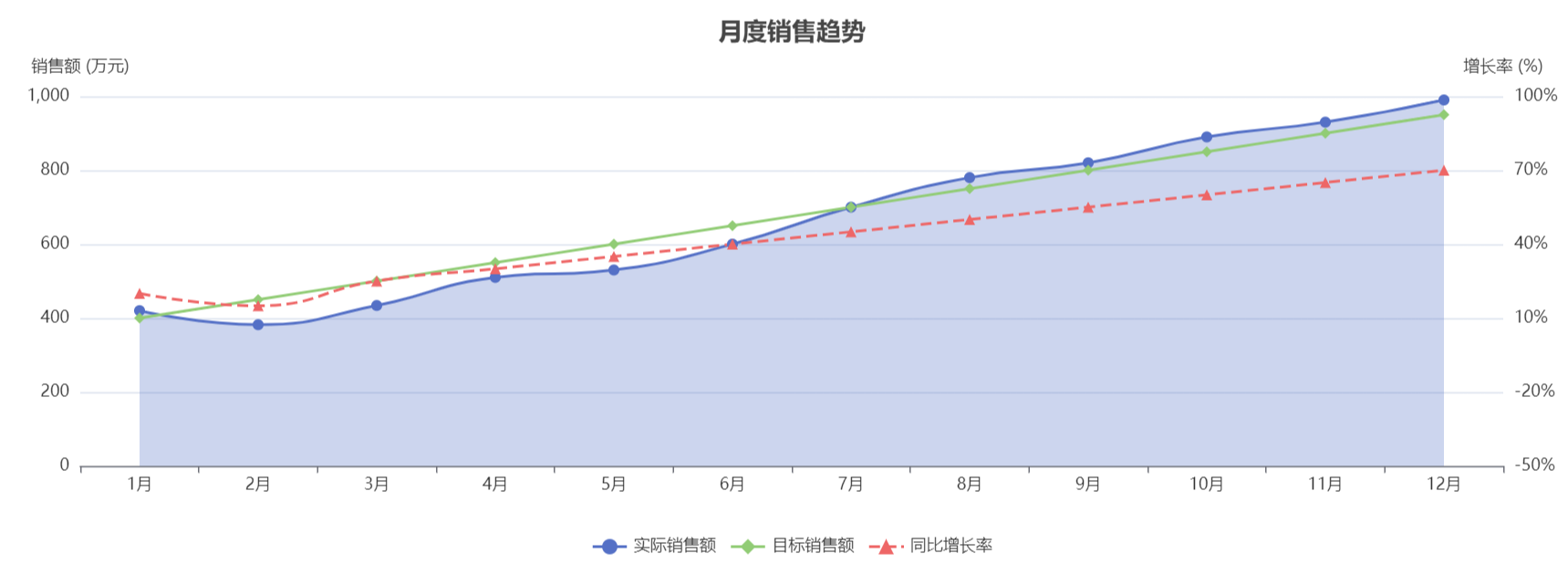
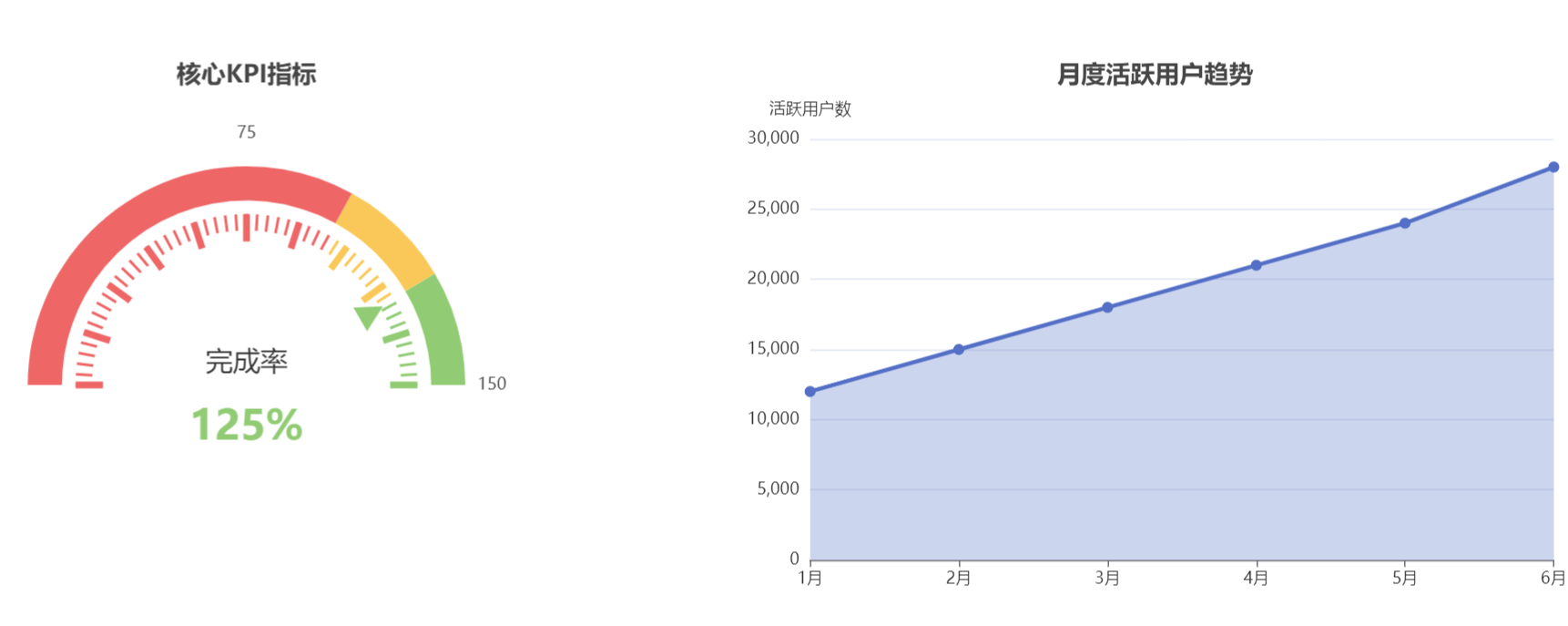 量化成果:
量化成果:
- 应用在10+种不同型号的鸿蒙设备上实现了完美适配
- 文档同步延迟降低至100ms以内,达到实时协作体验
- 日均活跃用户增长300%,用户满意度达到4.8/5
- 通过鸿蒙认证,获得HarmonyOS优选应用推荐
6.2 技术创新点
创新技术方案
- 自适应UI框架:自主研发的UI适配系统,可根据设备屏幕尺寸和形态自动调整布局和交互方式
- 智能任务调度:根据设备性能和用户行为智能分配计算任务,优化资源利用
- 混合式同步策略:结合实时同步和批量同步的优势,在保证数据一致性的同时优化网络使用
6.3 未来规划
近期规划
元服务支持:将应用核心功能拆分为元服务,实现更轻量级的功能调用和分享。
中期规划
AI能力集成:接入鸿蒙AI能力,提供智能文档分析、会议记录自动生成等功能。
长期规划
全场景办公生态:扩展支持更多办公场景,实现与企业现有系统的无缝集成。
七、结语
通过本次分布式智能办公应用的开发实践,我们深入探索了HarmonyOS的分布式能力,并且将其转化为实际的产品优势。在开发过程中,我们遇到了许多挑战,但也收获了宝贵的经验。
给其他开发者的建议:
- 充分理解和利用HarmonyOS的分布式特性,不要简单地将传统应用移植到鸿蒙平台
- 重视性能优化和用户体验,特别是在多设备协同场景下
- 建立完善的测试体系,模拟各种真实使用场景
- 持续关注HarmonyOS的更新和新特性,及时应用到项目中
鸿蒙生态的发展为应用创新提供了广阔空间,我们相信,随着技术的不断成熟,分布式应用将成为未来移动应用的重要发展方向。我们期待与更多开发者一起,共同探索鸿蒙生态的无限可能!