Android 内存优化
文章目录
- 1、内存泄漏 VS 内存溢出
- 1-1、内存泄漏: (Memory Leak)
- 1-2、内存溢出OOM(Out Of Memory)
- 2、内存泄漏的几种情况
- 2-1、单例造成的内存泄漏
- 2-2、外部类持有非静态内部类的静态对象
- 2-2-1、示例
- 2-2-2、LeakCanary分析
- 2-2-3、解决方法
- 解决方法1:使用静态内部类
- 解决方法2:不要写内部类,放在外面
- 2-3、多线程导致的内存泄漏
- 2-3-1、代码例子
- 2-3-2、原因
- 2-3-3、解决方法
- 2-4、匿名内部类持有外部类对象
- 2-4-1、模拟代码
- 2-4-2、原因
- 2-4-3、LeakCanary分析
- 2-4-5、解决方法
- 3、内存泄漏工具LeakCanary
- 3-1、导入
- 3-2、LeakCanary原理
- 3-3、LeakCanary的使用方式
1、内存泄漏 VS 内存溢出
1-1、内存泄漏: (Memory Leak)
- 内存泄漏的定义:用资源的时候为他开辟了一段空间,当你用完时忘记释放资源了,这时内存还被占用着,一次没关系,但是内存泄漏次数多了就会导致内存溢出
- 例子:你向系统申请分配内存进行使用(new),可是使用完了以后却不归还(delete),结果你申请到的那块内存你自己也不能再访问(也许你把它的地址给弄丢了),而系统也不能再次将它分配给需要的程序。就相当于你租了个带钥匙的柜子,你存完东西之后把柜子锁上之后,把钥匙丢了或者没有将钥匙还回去,那么结果就是这个柜子将无法供给任何人使用,也无法被垃圾回收器回收,因为找不到他的任何信息。
- 内存泄漏的几种情况
- 单例造成的内存泄漏
- 非静态内部类造成的内存泄漏
- 匿名内部类造成的内存泄漏
- 线程
- 资源未关闭造成的内存泄漏
1-2、内存溢出OOM(Out Of Memory)
- 系统已经不能再分配出你所需要的空间,比如系统现在只有1G的空间,但是你偏偏要2个G空间,这就叫内存溢出
2、内存泄漏的几种情况
2-1、单例造成的内存泄漏
2-1-1、示例1:Activity正常回收
- MainActivity
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {private static final String TAG = "MainActivity";@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);findViewById(R.id.textview).setOnClickListener(this);}@Overridepublic void onClick(View v) {Intent intent = new Intent(this, MemoryActivity.class);startActivity(intent);}
}
- MemoryActivity
public class MemoryActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private static final String TAG = "MemoryActivity";@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_memory);// AppManager.getInstance(this);}@Overrideprotected void finalize() throws Throwable {super.finalize();Log.e(TAG, "finalize: ");}
}
- MainActivity跳转MemoryActivity后,按返回,置为后台,过会MemoryActivity会回调finalize方法,证明被垃圾回收了,正常现象。日志如下
MemoryActivity com...ur.androiddemo E finalize:
2-1-2、示例2:单例导致Activity无法回收
- AppManager单例的静态特性使得单例的生命周期和应用的生命周期一样长,这就说明了如果一个对象已经不需要使用了,而单例对象还持有该对象的引用,那么这个对象将不能被正常回收,这就导致了内存泄漏。
public class AppManager {private static AppManager instance;private Context context;private AppManager(Context context) {this.context = context;}public static AppManager getInstance(Context context) {if (instance != null) {instance = new AppManager(context);}return instance;}
}
- 修改代码如下:MemoryActivity的onCreate方法添加AppManager.getInstance(this),就会导致单例对象持有Activity的引用,当Activity返回后应该被销毁,但是因为单例持有该Activity的引用,导致无法回收,造成内存泄漏
public class MemoryActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private static final String TAG = "MemoryActivity";@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_memory);AppManager.getInstance(this);}@Overrideprotected void finalize() throws Throwable {super.finalize();Log.e(TAG, "finalize: ");}
}
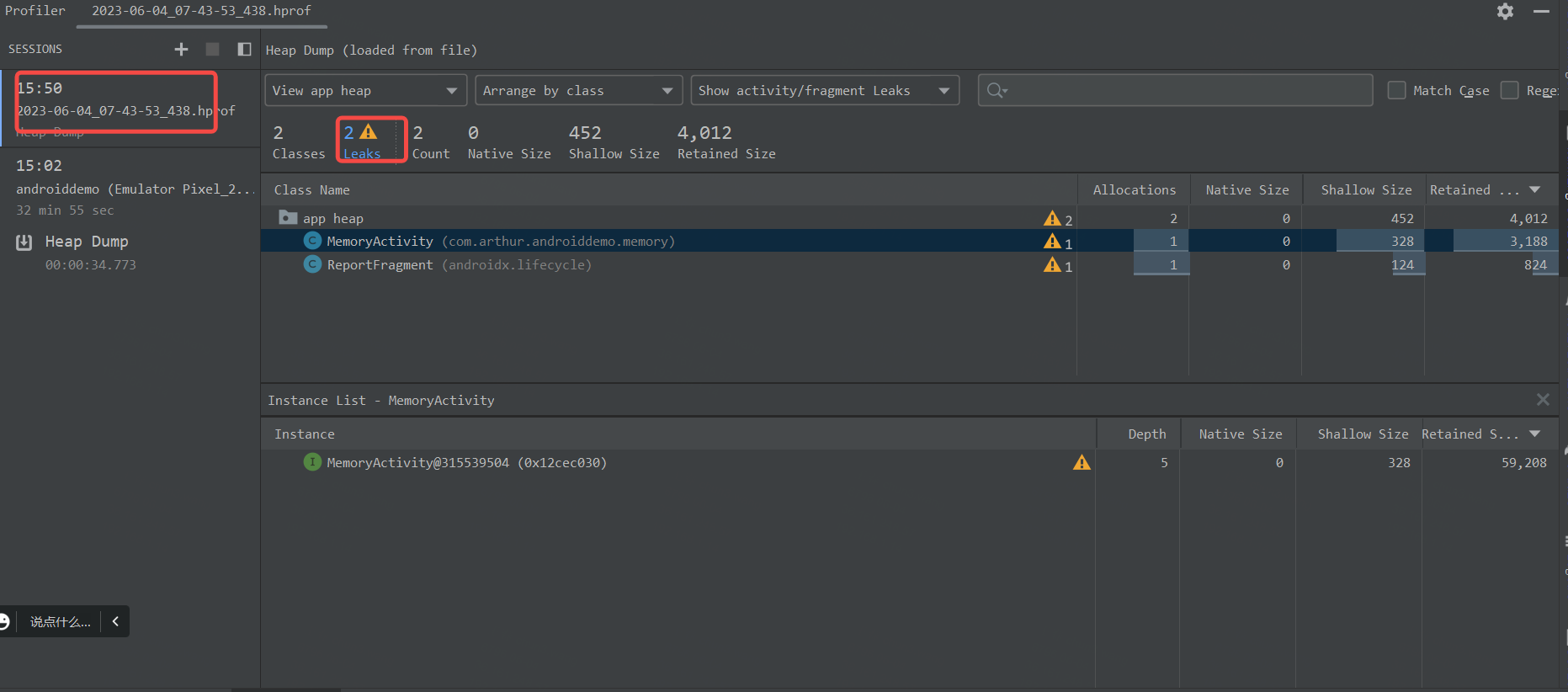
2-1-3、排查方法
Heap Dump 堆内存
- 可以查看某一时刻的内存情况,可以导出为hprof文件
- 各名词解释
- Allocations:某个类的实例数量
- Native Size:类对象所引用的 Native 对象 (蓝色节点) 所消耗的内存大小(以字节为单位)

- Shallow Size:这列数据其实非常简单,就是对象本身消耗的内存大小,在上图中,即为红色节点自身所占内存(以字节为单位)。
- Retained Size:稍复杂些,它是下图中所有橙色节点的大小(以字节为单位),由于一旦删除红色节点,其余的橙色节点都将无法被访问,这时候它们就会被 GC 回收掉。Retained Size值:每个对象的Retained Size除了包括自己的大小,还包括引用对象的大小,整个类的Retained Size大小累加起来就大了很多,Retained Size可以用来大概反应哪种类占的内存比较多。

LeakCanary分析
- 日志要点
-
====================================
HEAP ANALYSIS RESULT
====================================
1 APPLICATION LEAKS
References underlined with "~~~" are likely causes.
Learn more at https://squ.re/leaks.
59208 bytes retained by leaking objects
Signature: 00d3afc56cbd3786b0905130c8c53c28fbbf6c07
┬───
│ GC Root: Thread object
│
├─ android.os.HandlerThread instance
│ Leaking: NO (PathClassLoader↓ is not leaking)
│ Thread name: 'LeakCanary-Heap-Dump'
│ ↓ Thread.contextClassLoader
├─ dalvik.system.PathClassLoader instance
│ Leaking: NO (AppManager↓ is not leaking and A ClassLoader is never leaking)
│ ↓ ClassLoader.runtimeInternalObjects
├─ java.lang.Object[] array
│ Leaking: NO (AppManager↓ is not leaking)
│ ↓ Object[980]
├─ com.arthur.androiddemo.memory.AppManager class
│ Leaking: NO (a class is never leaking)
│ ↓ static AppManager.instance
│ ~~~~~~~~
├─ com.arthur.androiddemo.memory.AppManager instance
│ Leaking: UNKNOWN
│ Retaining 59.2 kB in 899 objects
│ context instance of com.arthur.androiddemo.memory.MemoryActivity with mDestroyed = true
│ ↓ AppManager.context
│ ~~~~~~~
╰→ com.arthur.androiddemo.memory.MemoryActivity instance
Leaking: YES (ObjectWatcher was watching this because com.arthur.androiddemo.memory.MemoryActivity received
Activity#onDestroy() callback and Activity#mDestroyed is true)
Retaining 59.2 kB in 898 objects
key = 6af4fa83-f707-45d7-8271-c5c96b47fd91
watchDurationMillis = 70636
retainedDurationMillis = 65630
mApplication instance of android.app.Application
mBase instance of androidx.appcompat.view.ContextThemeWrapper
====================================
0 LIBRARY LEAKS
A Library Leak is a leak caused by a known bug in 3rd party code that you do not have control over.
See https://square.github.io/leakcanary/fundamentals-how-leakcanary-works/#4-categorizing-leaks
====================================
0 UNREACHABLE OBJECTS
An unreachable object is still in memory but LeakCanary could not find a strong reference path
from GC roots.
====================================
METADATA
Please include this in bug reports and Stack Overflow questions.
Build.VERSION.SDK_INT: 29
Build.MANUFACTURER: unknown
LeakCanary version: 2.8.1
App process name: com.arthur.androiddemo
Stats: LruCache[maxSize=3000,hits=27701,misses=51422,hitRate=35%]
RandomAccess[bytes=2591138,reads=51422,travel=11095045388,range=12376690,size=16587684]
Heap dump reason: 4 retained objects, app is not visible
Analysis duration: 2102 ms
Heap dump file path: /data/user/0/com.arthur.androiddemo/cache/leakcanary/2023-06-04_07-43-53_438.hprof
Heap dump timestamp: 1685864636526
Heap dump duration: 473 ms
====================================
2-1-4、解决方法
- 这是一个普通的单例模式,当创建这个单例的时候,由于需要传入一个Context,所以这个Context的生命周期的长短至关重要:
- 传入的是Application的Context:这将没有任何问题,因为单例的生命周期和Application的一样
- 传入的是Activity的Context:当这个Context所对应的Activity退出时,由于该Context和Activity的生命周期一样长(Activity间接继承于Context),所以当前Activity退出时它的内存并不会被回收,因为单例对象持有该Activity的引用。
- 措施:不管传入什么Context最终将使用Application的Context,而单例的生命周期和应用的一样长,这样就防止了内存泄漏
public class AppManager {private static AppManager instance;private Context context;private AppManager(Context context) {this.context = context.getApplicationContext();}public static AppManager getInstance(Context context) {if (instance == null) {instance = new AppManager(context);}return instance;}
}
2-2、外部类持有非静态内部类的静态对象
2-2-1、示例
public class InnerActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private static final String TAG = "InnerActivity";// 非静态内部类 的 静态实例private static InnerClass innerClass = null;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);if (innerClass == null){innerClass = new InnerClass();}}// 非静态内部类public class InnerClass{}@Overrideprotected void finalize() throws Throwable {super.finalize();Log.e(TAG, "finalize: " );}
}
- 原因
- 非静态内部类的静态实例默认持有外部类的引用;
- 外部类MainActivity持有非静态内部类的静态对象InnerClass,而非静态内部类的静态对象innerClass的生命周期等于应用程序的生命周期
- MainActivity销毁的时候,非静态内部类的静态对象innerClass持有外部类SecondActivity的引用,导致无法被回收,造成内存泄漏
2-2-2、LeakCanary分析
- 日志要点:~~~ 标记的大概率就是内存泄漏的原因
====================================
HEAP ANALYSIS RESULT
====================================
1 APPLICATION LEAKS
References underlined with "~~~" are likely causes.
Learn more at https://squ.re/leaks.
66270 bytes retained by leaking objects
Signature: ad751665dd7d6494c990ce847d195451452d9df7
┬───
│ GC Root: System class
│
├─ android.os.StrictMode$InstanceTracker class
│ Leaking: NO (InnerActivity↓ is not leaking and a class is never leaking)
│ ↓ static StrictMode$InstanceTracker.sInstanceCounts
├─ java.util.HashMap instance
│ Leaking: NO (InnerActivity↓ is not leaking)
│ ↓ HashMap[key()]
├─ com.arthur.androiddemo.memory.InnerActivity class
│ Leaking: NO (a class is never leaking)
│ ↓ static InnerActivity.innerClass
│ ~~~~~~~~~~
├─ com.arthur.androiddemo.memory.InnerActivity$InnerClass instance
│ Leaking: UNKNOWN
│ Retaining 66.3 kB in 1038 objects
│ this$0 instance of com.arthur.androiddemo.memory.InnerActivity with mDestroyed = true
│ ↓ InnerActivity$InnerClass.this$0
│ ~~~~~~
╰→ com.arthur.androiddemo.memory.InnerActivity instance
Leaking: YES (ObjectWatcher was watching this because com.arthur.androiddemo.memory.InnerActivity received
Activity#onDestroy() callback and Activity#mDestroyed is true)
Retaining 66.3 kB in 1037 objects
key = ff8d9e31-4d08-4e25-8142-a33daf20364b
watchDurationMillis = 30682
retainedDurationMillis = 25676
mApplication instance of android.app.Application
mBase instance of androidx.appcompat.view.ContextThemeWrapper
====================================
0 LIBRARY LEAKS
A Library Leak is a leak caused by a known bug in 3rd party code that you do not have control over.
See https://square.github.io/leakcanary/fundamentals-how-leakcanary-works/#4-categorizing-leaks
====================================
0 UNREACHABLE OBJECTS
An unreachable object is still in memory but LeakCanary could not find a strong reference path
from GC roots.
====================================
METADATA
Please include this in bug reports and Stack Overflow questions.
Build.VERSION.SDK_INT: 29
Build.MANUFACTURER: unknown
LeakCanary version: 2.8.1
App process name: com.arthur.androiddemo
Stats: LruCache[maxSize=3000,hits=27756,misses=51552,hitRate=34%]
RandomAccess[bytes=2597888,reads=51552,travel=11157018019,range=12385431,size=16596365]
Heap dump reason: 4 retained objects, app is not visible
Analysis duration: 2106 ms
Heap dump file path: /data/user/0/com.arthur.androiddemo/cache/leakcanary/2023-06-04_08-12-56_118.hprof
Heap dump timestamp: 1685866379300
Heap dump duration: 531 ms
====================================
2-2-3、解决方法
解决方法1:使用静态内部类
- 退出界面后过会就会执行finalize
public class InnerActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private static final String TAG = "InnerActivity";// 非静态内部类 的 静态实例private static InnerClass innerClass = null;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);if (innerClass == null){innerClass = new InnerClass();}}// 非静态内部类public static class InnerClass{}@Overrideprotected void finalize() throws Throwable {super.finalize();Log.e(TAG, "finalize: " );}
}
解决方法2:不要写内部类,放在外面
- InnerActivity
public class InnerActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private static final String TAG = "InnerActivity";// 非静态内部类 的 静态实例private static InnerClass innerClass = null;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);if (innerClass == null){innerClass = new InnerClass();}}@Overrideprotected void finalize() throws Throwable {super.finalize();Log.e(TAG, "finalize: " );}
}
- InnerClass单独放在一个文件里面
public class InnerClass {
}
2-3、多线程导致的内存泄漏
2-3-1、代码例子
- 下例只是在线程运行期间的50s后销毁Activity则不影响回收;50s内销毁Activity无法被回收,但是过了50s之后,下次GC就能正常回收
public class ThreadActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private static final String TAG = "ThreadActivity";@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_memory);new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Thread.sleep(50000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}).start();}@Overrideprotected void finalize() throws Throwable {super.finalize();Log.e(TAG, "finalize: ");}
}
2-3-2、原因
- 原理:工作线程实例在工作时间内持有外部类引用,使得外部类无法被垃圾回收器GC回收,从而导致内存泄漏
- 两个必要条件
- 工作线程实例持有外部类引用
- 工作线程的生命周期>外部类的生命周期,即工作线程仍在运行时而外部类需销毁
- AsyncTask、实现Runnable接口、继承Thread类都有上述问题
2-3-3、解决方法
- 使用静态内部类
public class ThreadActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private static final String TAG = "ThreadActivity";@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_memory);new MyThread().start();}@Overrideprotected void finalize() throws Throwable {super.finalize();Log.e(TAG, "finalize: ");}private static class MyThread extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();try {Thread.sleep(5* 60*000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}2-4、匿名内部类持有外部类对象
2-4-1、模拟代码
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private static final String TAG = "MainActivity";// 匿名内部类默认持有外部类MainActivity对象实例private Handler mUIHandler = new Handler() {@Overridepublic void handleMessage(Message msg) {super.handleMessage(msg);Log.e(TAG, "handleMessage: "+msg );}};@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);// 1、在50秒内退出MainActivity,此时MessageQueue还有消息,持有Handler对象,// 匿名内部类Handler持有MainActivity对象的引用,导致内存泄漏// 2、在50秒后退出MainActivity,则不会导致内存泄漏mUIHandler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(1,50 * 1000);}
}
2-4-2、原因
- 由于Handler匿名内部类默认持有外部类MainActivity的引用,假如MainActivity已经不再被使用了,但是由于MessageQueue仍然有消息要处理,那么就会导致MainActivity对象被Handler一直持有,从而导致HandlerActivity对象无法被GC正常回收,进而造成内存泄漏。
- Looper > MessagQueue > Message > Handler > Activity
- 详细原因参考:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000019532971
- 优化:将Handler类独立出来,或者使用静态内部类,因为静态内部类不持有外部类的引用。如果使用持有外部类MainActivity对象,可以使用弱引用实现。
2-4-3、LeakCanary分析
2022-04-17 22:54:30.469 10417-10512/com.arthur.leakcanary D/LeakCanary: ====================================HEAP ANALYSIS RESULT====================================1 APPLICATION LEAKSReferences underlined with "~~~" are likely causes.Learn more at https://squ.re/leaks.110763 bytes retained by leaking objectsSignature: dca112f2558c9868d2758a5e63f2a4db56cdf4a4┬───│ GC Root: Input or output parameters in native code│├─ android.os.MessageQueue instance│ Leaking: NO (MessageQueue#mQuitting is false)│ HandlerThread: "main"│ ↓ MessageQueue[0]│ ~~~├─ android.os.Message instance│ Leaking: UNKNOWN│ Retaining 110.9 kB in 1269 objects│ Message.what = 1│ Message.when = 60449259 (40171 ms after heap dump)│ Message.obj = null│ Message.callback = null│ Message.target = instance @315500656 of com.arthur.leakcanary.MainActivity$1│ ↓ Message.target│ ~~~~~~├─ com.arthur.leakcanary.MainActivity$1 instance│ Leaking: UNKNOWN│ Retaining 110.8 kB in 1268 objects│ Anonymous subclass of android.os.Handler│ this$0 instance of com.arthur.leakcanary.MainActivity with mDestroyed = true│ ↓ MainActivity$1.this$0│ ~~~~~~╰→ com.arthur.leakcanary.MainActivity instance Leaking: YES (ObjectWatcher was watching this because com.arthur.leakcanary.MainActivity received Activity#onDestroy() callback and Activity#mDestroyed is true) Retaining 110.8 kB in 1267 objects key = f862522b-3d28-46c7-b9d9-9af326045f1c watchDurationMillis = 5137 retainedDurationMillis = 131 mApplication instance of com.arthur.leakcanary.MyApp mBase instance of android.app.ContextImpl====================================0 LIBRARY LEAKSA Library Leak is a leak caused by a known bug in 3rd party code that you do not have control over.See https://square.github.io/leakcanary/fundamentals-how-leakcanary-works/#4-categorizing-leaks====================================0 UNREACHABLE OBJECTSAn unreachable object is still in memory but LeakCanary could not find a strong reference pathfrom GC roots.====================================METADATAPlease include this in bug reports and Stack Overflow questions.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT: 27Build.MANUFACTURER: GoogleLeakCanary version: 2.8.1App process name: com.arthur.leakcanaryStats: LruCache[maxSize=3000,hits=17013,misses=30442,hitRate=35%]RandomAccess[bytes=1532541,reads=30442,travel=6832412172,range=8829641,size=11484945]Heap dump reason: 2 retained objects, app is not visibleAnalysis duration: 2346 msHeap dump file path: /storage/emulated/0/Download/leakcanary-com.arthur.leakcanary/2022-04-17_22-54-26_679.hprofHeap dump timestamp: 1650207270389Heap dump duration: 753 ms====================================
2-4-5、解决方法
- 使用静态匿名内部类
package com.arthur.leakcanary;import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.util.Log;public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private static final String TAG = "MainActivity";private static Handler mUIHandler = new Handler() {@Overridepublic void handleMessage(Message msg) {super.handleMessage(msg);Log.e(TAG, "handleMessage: "+msg );}};@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);mUIHandler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(1,50000);}
}
- Activity销毁时 将Handler手动置为null,此时Message对象的target对象为null,自然将上面的引用链条断开了,GCroot无法访问Activity对象,这样Activity就可以被回收了。但是会泄露Message对象。
- 在Activity的onDestroy方法中调用Handler对象的removeCallbacksAndMessages(null) 将messagequeue 清空。
- 将Handler设置为静态内部类。然后内部通过若引用持有Activity对象。因为静态内部类不持有外部类的引用。所以就不会引起内存泄露。但是会泄露Handler对象。
- 或者使用静态内部类 + WeakReference:
private static class SafeHandler extends Handler {private final WeakReference<Activity> mActivityRef;public SafeHandler(Activity activity) {mActivityRef = new WeakReference<>(activity);}@Overridepublic void handleMessage(Message msg) {Activity activity = mActivityRef.get();if (activity != null) {// 处理消息}}
}
3、内存泄漏工具LeakCanary
3-1、导入
- 官网:https://github.com/square/leakcanary
- 导包
debugImplementation 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android:2.8.1'
- 导包后无须进行任何初始化操作,就可以在监听到内存泄漏
3-2、LeakCanary原理
- LeakCanary可以hook到Android生命周期中,从而自动检测Activity、Fragment、ViewModel何时destroy,并进行垃圾收集。ObjectWatcher持有这些被destroy的对象的弱引用,如果运行垃圾回收,并等待5秒钟后ObjectWatcher仍未清除 ,则认定可能发生内存泄漏。
3-3、LeakCanary的使用方式
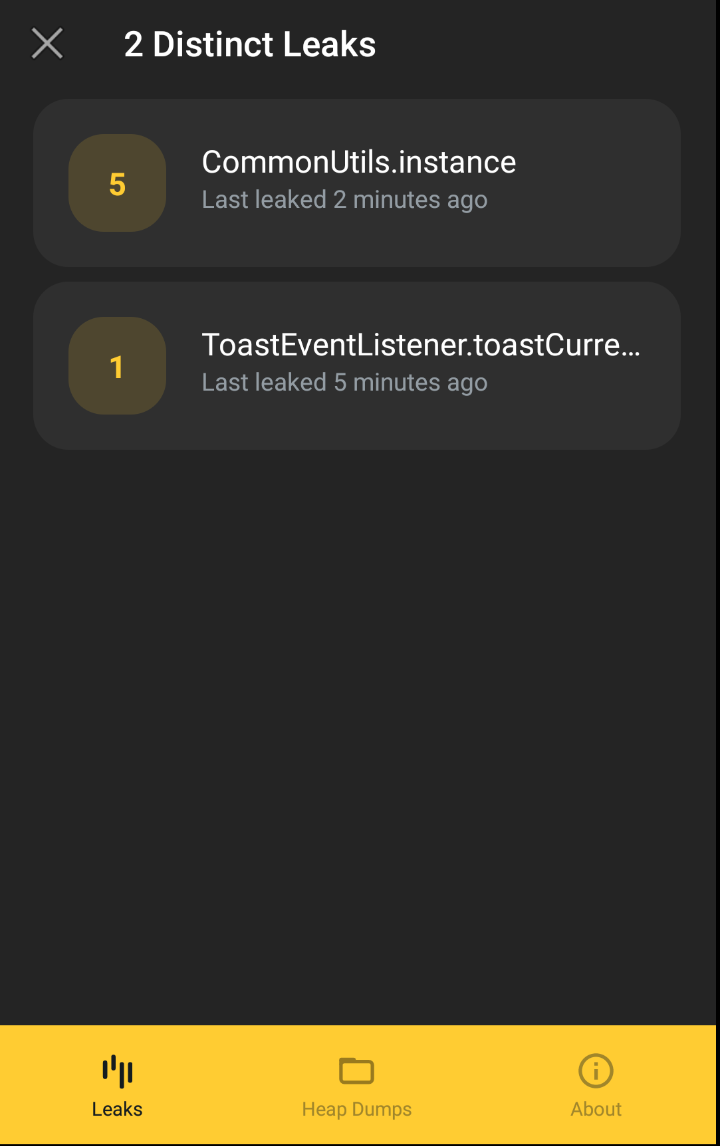
- 内存泄漏之后,可以通过多种方式分析。有以下几种方式。
1、LeakCanary将显示带有摘要的通知,
2、Logcat中显示结果
3、详细可以在默认安装的APP Leaks中查看,

4、最后也可以查看hprof文件(/data/data/package/cache/leakcanary/2022-04-17_15-30-15_516.hprof)