Kafka Queue: 如何严格控制消息数量
KIP:
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/KIP-1206%3A+Strict+max+fetch+records+in+share+fetch
PR:
https://github.com/apache/kafka/pull/20246
Motivation: why strict limit needed
Queue 有超时概念
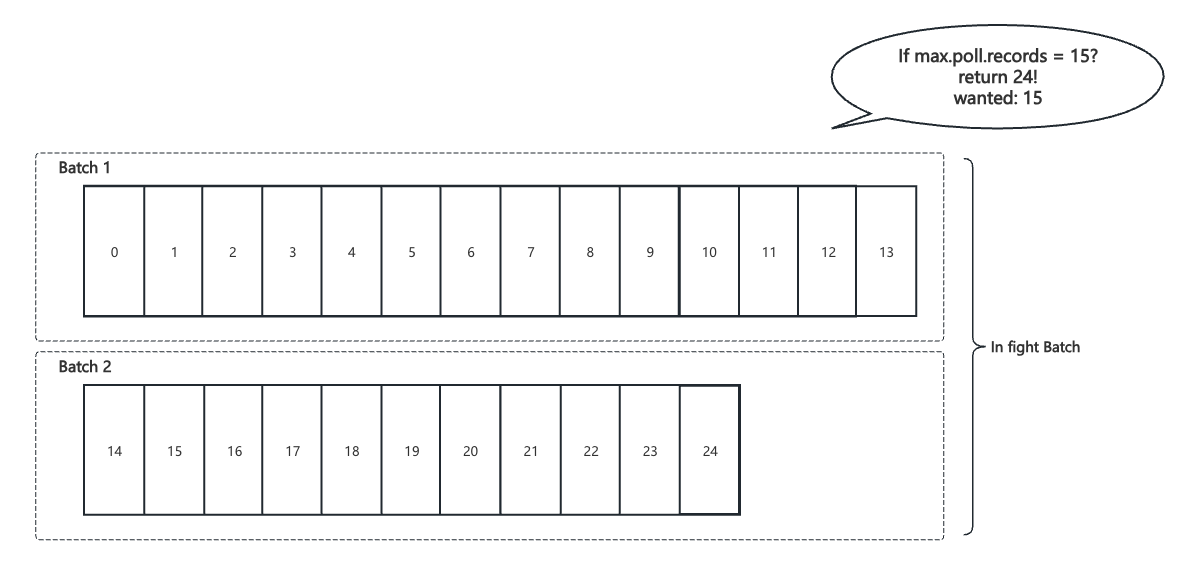
在shareFetch请求中,maxFetchRecords(max.poll.records)当前是软限制, 最终返回给客户端的消息数量需要与record batch对齐的,因此可能会超过限制。
FileRecord -> ShareAcquireRecord
public class ShareAcquiredRecords {private static final ShareAcquiredRecords EMPTY_SHARE_ACQUIRED_RECORDS = new ShareAcquiredRecords();/*** The list of acquired records. (size = 1)*/private final List<AcquiredRecords> acquiredRecords;
}
优点
- 没有额外开销(broker side + client side), 当前share-fetch的最小粒度是batch, 不会存在比如一个batch 里有1000条record只返回一条的情况
- 实现简单, 利用producer batch
缺点
- 语义不清晰,shareFetch 里有一个参数maxRecords, 目前取的是客户端设置的max.poll.recors. 即使设置成1, 还是有可能一次性拉到N >> 1 条消息,依赖生产者batch.size与linear.ms参数控制;
- 单条消息处理很慢的场景,需要控制消息数量(even down to 1)
- Posion records handing:假设一批消息里,某一条处理不了或者很慢,那么这一批消息都会超时重投。
There are two situations in which the delivery count handling needs to be more intelligent.
First, for records which are automatically released as a result of closing a share session normally, the delivery count should not be incremented. These records were fetched but they were not actually delivered to the client since the disposition of the delivery records is carried in the ShareAcknowledge which closes the share session. Any remaining records were not delivered, only fetched.
Second, for records which have a delivery count which is more than 1 or 2, there is a suspicion that the records are not being delivered due to a problem rather than just natural retrying. The batching of these records should be reduced, even down to a single record as a time so we do not have the failure to deliver a poisoned record actually causing adjacent records to be considered unsuccessful and potentially reach the delivery count limit without proper reason.
问题
Q1:最主要解决什么问题
最主要解决一次性拉太多record,又处理不完重新回到队列,然后deliveryCount增加;deliveryCount达到maxDeliveryCount限制后会停止投递
Q2:能不能从log端控制数量
之前知道有一个maxBytes参数在控制从log-segement中读取的日志数量
val readInfo: LogReadInfo = partition.fetchRecords(fetchParams = params,fetchPartitionData = fetchInfo,fetchTimeMs = fetchTimeMs,maxBytes = adjustedMaxBytes,minOneMessage = minOneMessage,updateFetchState = !readFromPurgatory)
最后追到FileRecord的slice方法,size可以理解为就是maxBytes
public FetchDataInfo read(long startOffset, int maxSize, Optional<Long> maxPositionOpt, boolean minOneMessage) throws IOException {if (maxSize < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid max size " + maxSize + " for log read from segment " + log);LogOffsetPosition startOffsetAndSize = translateOffset(startOffset);// if the start position is already off the end of the log, return nullif (startOffsetAndSize == null)return null;int startPosition = startOffsetAndSize.position;LogOffsetMetadata offsetMetadata = new LogOffsetMetadata(startOffsetAndSize.offset, this.baseOffset, startPosition);int adjustedMaxSize = maxSize;if (minOneMessage)adjustedMaxSize = Math.max(maxSize, startOffsetAndSize.size);// return empty records in the fetch-data-info when:// 1. adjustedMaxSize is 0 (or)// 2. maxPosition to read is unavailableif (adjustedMaxSize == 0 || maxPositionOpt.isEmpty())return new FetchDataInfo(offsetMetadata, MemoryRecords.EMPTY);// calculate the length of the message set to read based on whether or not they gave us a maxOffsetint fetchSize = Math.min((int) (maxPositionOpt.get() - startPosition), adjustedMaxSize);return new FetchDataInfo(offsetMetadata, log.slice(startPosition, fetchSize),adjustedMaxSize < startOffsetAndSize.size, Optional.empty());}
在minOneMessage = true情况下,adjustedMaxSize最小会是一个batch的大小,也就是至少会load一个batch出来
结论: 即使配置了maxBytes,还是有可能超过限制,因此设置成1可以控制读尽量少的record.
Q3:classic consumer group 拉消息的时候可以控制record数量吗
- 消费端的参数 **max.poll.records **仅是控制 客户端调用poll() 返回的请求数量,而没有控制fetch请求 从broker size 返回的请求数量
- KIP-1199 提出要在FetchRequest 里也引入这个参数,但是这个KIP里也提到:
Due to batching and compression, exact counts may not be achievable without decompressing entire batches. As such, this implementation will adopt a best-effort approach
设计
AcquireMode
public enum ShareAcquireMode {STRICT("STRICT"),BATCH_OPTIMIZED("BATCH_OPTIMIZED");public final String name;ShareAcquireMode(final String name) {this.name = name;}/*** Case-insensitive acquire mode lookup by string name.*/public static ShareAcquireMode of(final String name) {return ShareAcquireMode.valueOf(name.toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT));}
}
Share consumer changes
| Configuration | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
| share.acquire.mode | Controls how a shared consumer obtains records. If set to ‘strict’, the number of records actually sent back to the consumer will never exceed the value set in ‘share.max.fetch.records’. | Type: String default: BATCH_OPTIMIZED optional values: “STRICT” or “BATCH_OPTIMIZED” |
Batching
在 ShareAcquireMode.Strict 模式下, ShareFetchResponse的响应体里只包含单个batch
public class ShareAcquiredRecords {private static final ShareAcquiredRecords EMPTY_SHARE_ACQUIRED_RECORDS = new ShareAcquiredRecords();/*** The list of acquired records. (size = 1)*/private final List<AcquiredRecords> acquiredRecords;
}
How to implement
batch_optimized:
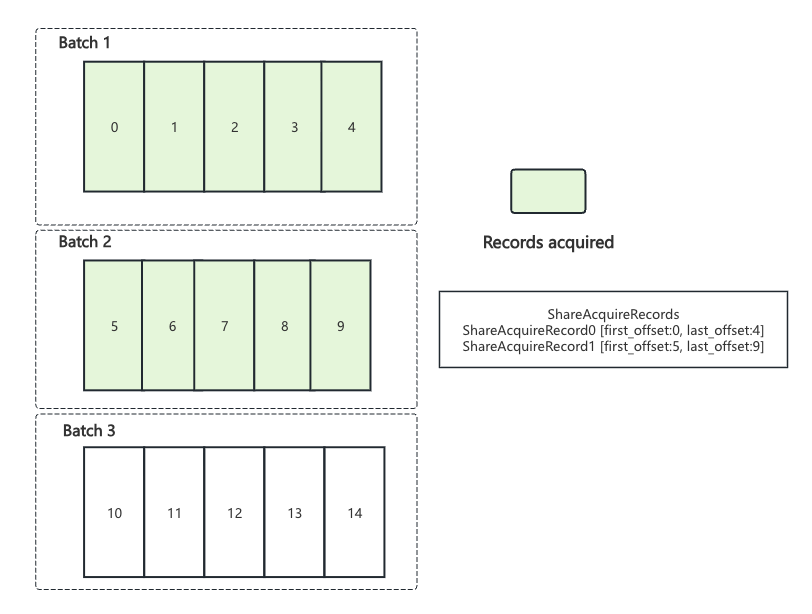
record_limit:
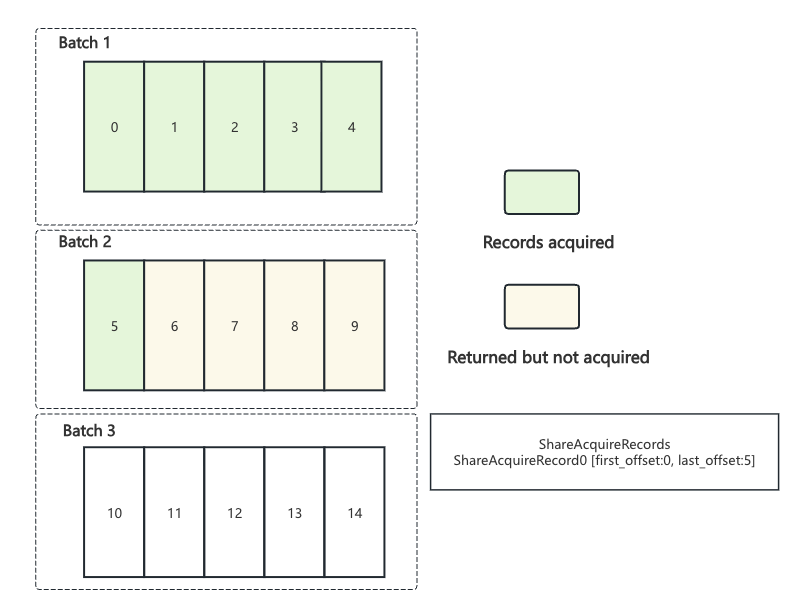
offset level timeout / batch level timeout :
默认为batch level timeout,当存在offset level timeout时,取消batch级别,改为每个offset独立超时
public void maybeInitializeOffsetStateUpdate() {if (offsetState == null) {offsetState = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>();// The offset state map is not initialized hence initialize the state of the offsets// from the first offset to the last offset. Mark the batch inflightState to null as// the state of the records is maintained in the offset state map now.for (long offset = this.firstOffset; offset <= this.lastOffset; offset++) {if (batchState.acquisitionLockTimeoutTask() != null) {// The acquisition lock timeout task is already scheduled for the batch, hence we need to schedule// the acquisition lock timeout task for the offset as well.long delayMs = batchState.acquisitionLockTimeoutTask().expirationMs() - time.hiResClockMs();AcquisitionLockTimerTask timerTask = acquisitionLockTimerTask(batchState.memberId(), offset, offset, delayMs);offsetState.put(offset, new InFlightState(batchState.state(), batchState.deliveryCount(), batchState.memberId(), timerTask));timer.add(timerTask);} else {offsetState.put(offset, new InFlightState(batchState.state(), batchState.deliveryCount(), batchState.memberId()));}}// Cancel the acquisition lock timeout task for the batch as the offset state is maintained.if (batchState.acquisitionLockTimeoutTask() != null) {batchState.cancelAndClearAcquisitionLockTimeoutTask();}batchState = null;}
}
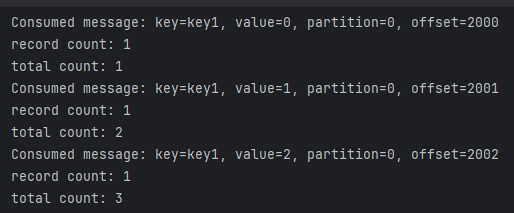
Test Result
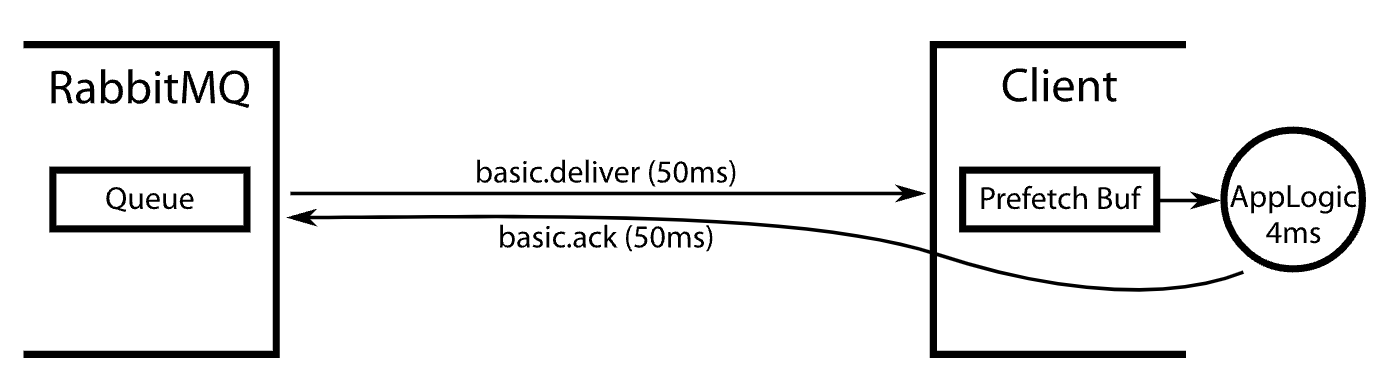
Compared to RabbitMQ Qos/Prefetch
- Pull vs Push : RabbitMQ 是push模型, 服务端主动向consumer推送消息
- 相同的设计想法:
- 避免所有消息被一个消费者拉走
- 控制消息拉取条数避免超时
- 控制吞吐量
Discussion
- 单个share-consumer,目前只支持拉取一批消息, 接着必须ack完这一批后才能再发下一次share-fetch. 是否可以支持同时发送多个Share-fetch请求. 比如说, 一个消费者poll() 下来10条消息, 处理了2条, 是不是可以支持不ack, 再拉2条.
- Classic Queue Feature:
- Dead letter Queue
- 定时消息
- Queue level / Message level ttl
- …
