10.1 快速排序(排序(下))
快速排序
文章目录
- 快速排序
- 10.1 基础概念
- 10.2 代码实现
- 10.3 内容补充
10.1 基础概念
算法过程:
- 在数据中挑选主元
- 将数据分成两个子列,小于主元的数据位于左子列,大于主元的数据位于右子列
- 再对左子列和右子列分别递归调用,直至仅剩一个数据
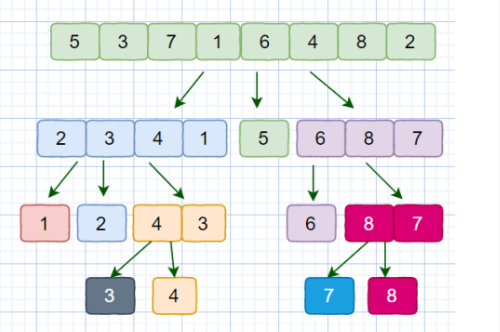
伪代码描述:
void quick_sort(element_type A[], int N)
{if (N < 2) return; //如果只有一个元素,returnpivot = 从A[]中选一个主元;将s = {A[[] \ pivot}分成2个独立子集:A1 = {a ∈ s| a <= pivot} 和A2 = {a ∈ s| a >= pivot};A[] = quick_sort(A1, N1) ∪{pivot}∪quick_sort(A2, N2);
}
注意:对于较小的数组(N <= 20)排序,快速排序不如插入排序好,因此我们通常会设定一个值cutoff,来检查数组中元素个数,如果元素个数过少,我们使用插入排序
10.2 代码实现
/*
**作用:对当前数组首元素,尾元素和中间元素进行比较。将最小值放至数组首位,** 最大值放置数组末尾,中间值放至数组末尾前一个位置。将中间值作为主元** 并返回
*/
element_type median3(element_type A[], int left, int right)
{int center = (left + right) / 2;if (A[left] > A[center])swap(&A[left], &A[center]);if (A[left] > A[right])swap(&A[left], &A[right]);if (A[center] > A[right])swap(&A[center], &A[right]);//此时A[left] <= A[center] <= A[right]swap(&A[center], &A[right-1]); //将基准pivot放到数组末尾前一个为止//如此剩余的数组只需要考虑A[left+1]...A[right-2]return A[right-1]; //返回基准pivot
}/*
**作用:使用递归算法实现快速排序
*/
void QSort(element_type A[], int left, int right)
{int cutoff, low, high;element_type pivot;cutoff = 100; //设定数据量下限if (right - left >= cutoff){ //如果数据量够大,使用快速排序pivot = median3(A, left, right); //选基准low = left; high = right - 1;while (1){ //将序列中比基准小的元素移至左边,大的移至右边while (A[++low] < pivot);while (A[--high] > pivot);if (low < high) swap(&A[low], &A[high]);else break;}swap(&A[low], &A[right-1]); //此时A[low]即位pivot正确位置QSort(A, left, low-1); //递归解决左子列QSort(A, low+1, right); //递归解决右子列}else insertion_sort(&A[left], right-left+1); //数据量过小,使用插入排序
}/*
**作用:快速排序的对外接口
*/
void quick_sort(element_type A[], int N)
{QSort(A, 0, N-1);
}
10.3 内容补充
1. CSDN:快速排序算法—图文详解,一篇就够了!
2. 菜鸟教程:快速排序
