2.c++面向对象(三)
一.赋值运算符重载
1.运算符重载

(.*) (::) (sizeof) (?:) (.)这五个运算符都是不能进行重载的

.*运算符的解释
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class OB
{
public:void func() {cout << "void func()" << endl;}
};typedef void(OB::*PtrFunc)() ;//成员函数指针类型int main()
{// 函数指针// void (*ptr)();// 成员函数要加&才能取到函数指针PtrFunc fp = &OB::func;//定义成员函数指针p指向函数func//普通函数,函数名就是这个函数的地址,如果是类内的函数,那么规定要加一个&OB temp;//定义ob类对象temp(temp.*fp)();return 0;
}就像是类中通过.来取出函数的地址的地址,在通过*进行解引用
== 运算符重载:
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}int GetYear(){return _year;}//private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};// 重载成全局,无法访问私有成员
// 1、提供这些成员get和set
// 2、友元 后面会讲
// 3、重载为成员函数(一般使用这种)bool operator==(const Date& d1, const Date& d2)
{return d1._year == d2._year&& d1._month == d2._month&& d1._day == d2._day;
}//d1-d2
//d1+d2 没有意义
//d1*d2 没有意义
//一个类要重载哪些运算符是看需求,看重载有没有价值和意义int main()
{Date d3(2024, 4, 14);Date d4(2024, 4, 15);// 显式调用operator==(d3, d4);// 直接写,装换调用,编译会转换成operator==(d3, d4);d3 == d4;return 0;
}d1-d2
d1+d2 没有意义
d1*d2 没有意义
一个类要重载哪些运算符是看需求,看重载有没有价值和意义
上面的代码,我们可以看到,成员变量如果是private的话,我们重载,无法直接使用成员变量,我们有以下三种方法:
重载成全局,无法访问私有成员
1、提供这些成员get和set
2、友元 后面会讲
3、重载为成员函数(一般使用这种)
以下是重载成成员函数:(非全局的重载)
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}//// d3.Func(d4);//bool Func(const Date& d)//{// return this->_year == d._year// && this->_month == d._month// && this->_day == d._day;//}// d3.operator==(d4);bool operator==(const Date& d){return this->_year == d._year&& this->_month == d._month&& this->_day == d._day;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d3(2024, 4, 14);Date d4(2024, 4, 15);// 显式调用d3.operator==(d4);// 转换调用 等价于d3.operator==(d4);d3 == d4;int i = 0, j = 1;bool ret = i == j;return 0;
}

![]()
如果全局的和类内的同时存在,那么我们会调用哪一个?
优先调用类内部的,全局的不会去调用
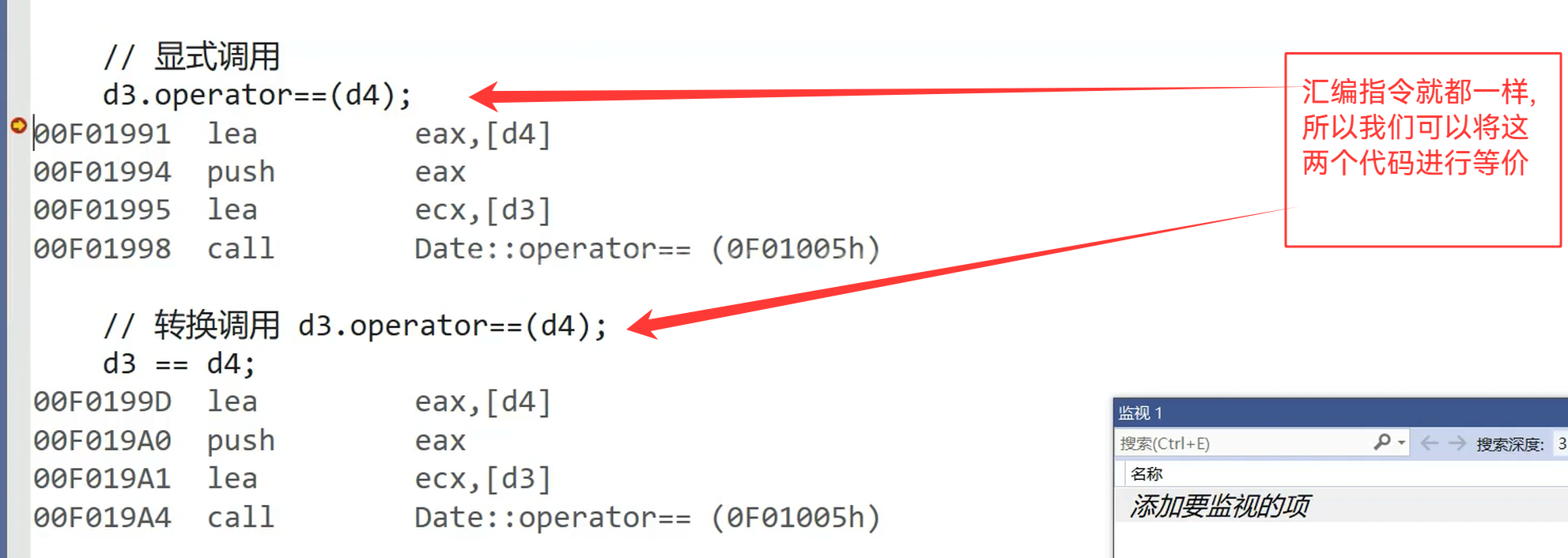
如果是d3.operator==(d4),那么this指针指向的就是d3
2.赋值运算符重载
1. 赋值运算符重载格式

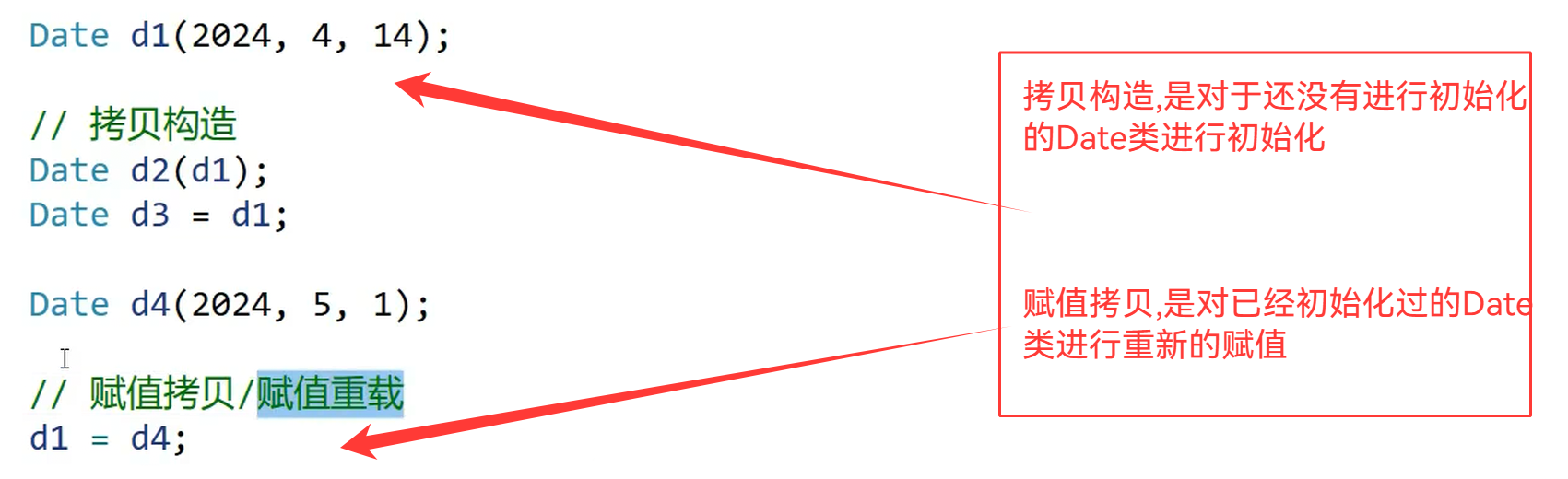
拷贝构造和赋值拷贝的区别:
![]()
void operator=(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}赋值重载这样写就行了吗?

像这种连续赋值就不行了
d4先赋值给d2 , d2作为返回值再赋值给d1( 赋值表达式的返回值是左操作数 ,所以我们要进行返回参数)
我们想拿到d2,d2作为前面的this指针,所以我们直接返回this指针
所以我们会有下面两种写法,一种是返回*this的拷贝,另一种是返回*this的引用(我们可以看看两者有什么差别)
Date operator=(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;return *this;}
Date& operator=(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;return *this;}为了更好的看到差别,我们将代码贴出来:
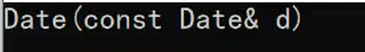
"拷贝构造"Date(const Date& d)
{cout << "Date(const Date& d)" << endl;_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;
}下面是引用和传值做返回值的案例:
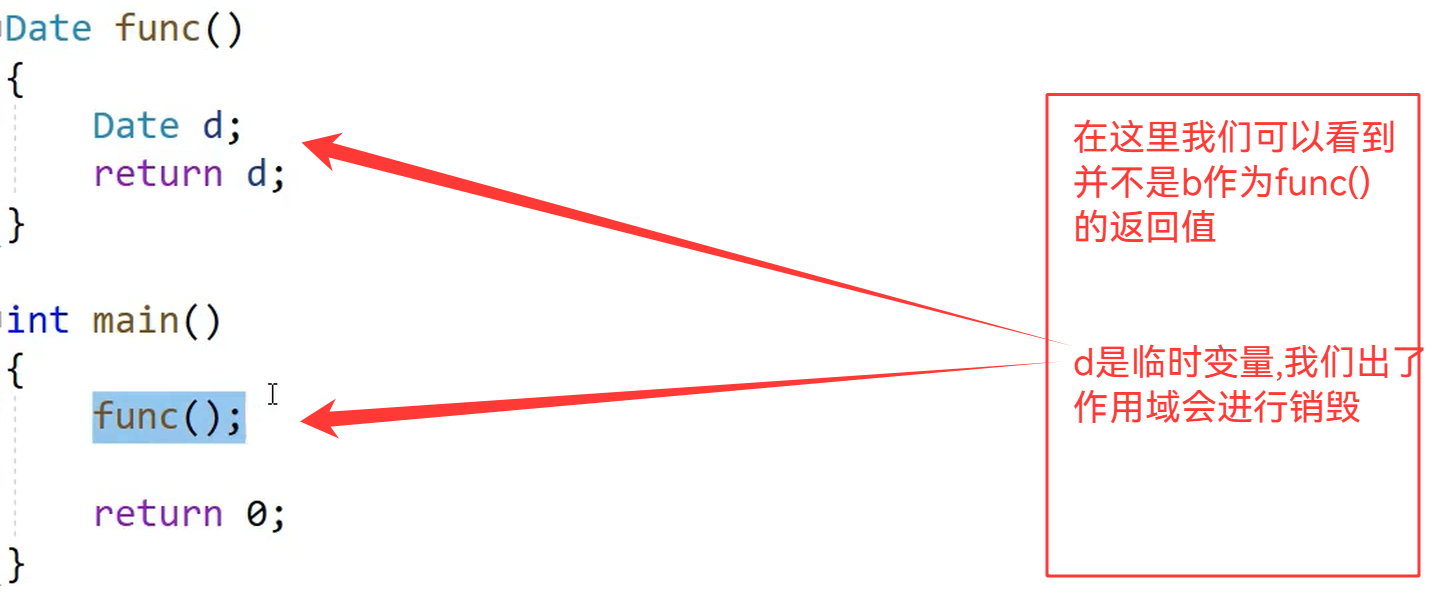
d的拷贝会作为返回值,传递给func()作为返回值,所以会进行拷贝
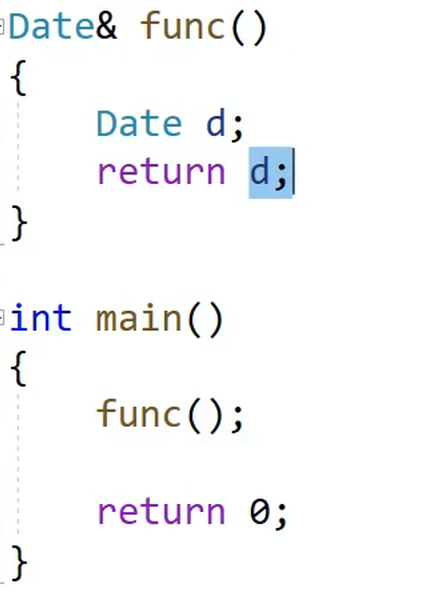
现在以Date&作为返回值,所以不会发生拷贝(但是会有一个问题,d是临时变量,出了作用域就析构了,所以返回的是一个异常的地址)
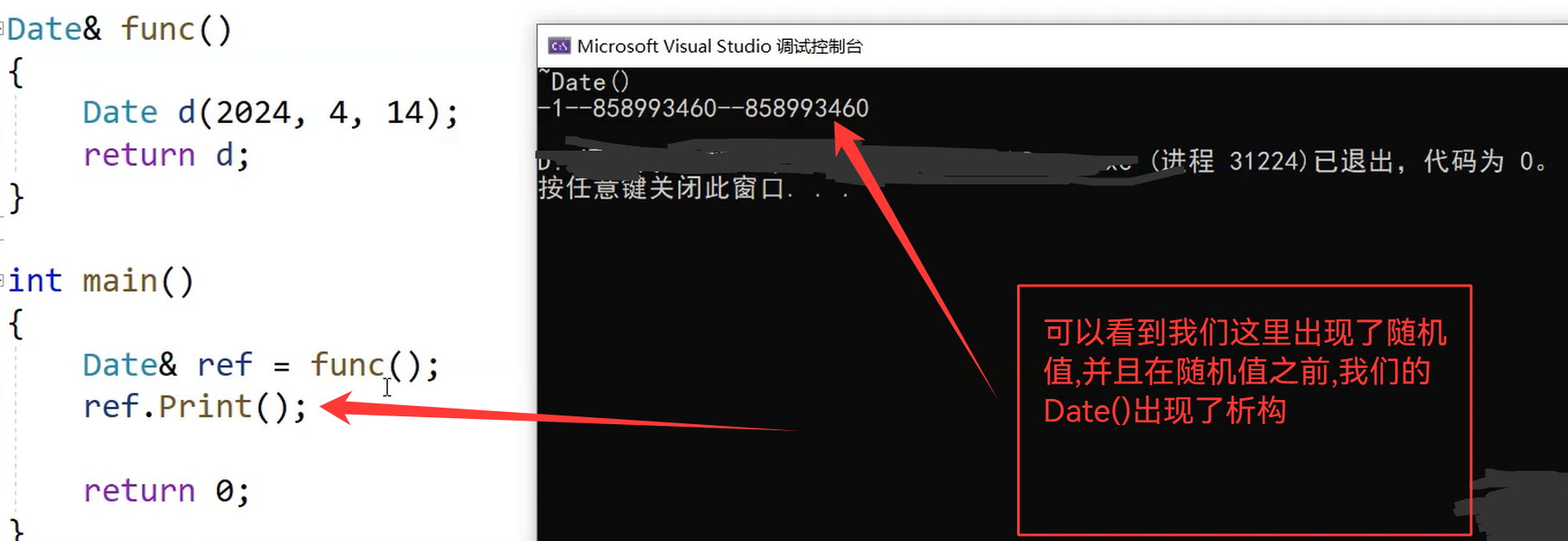

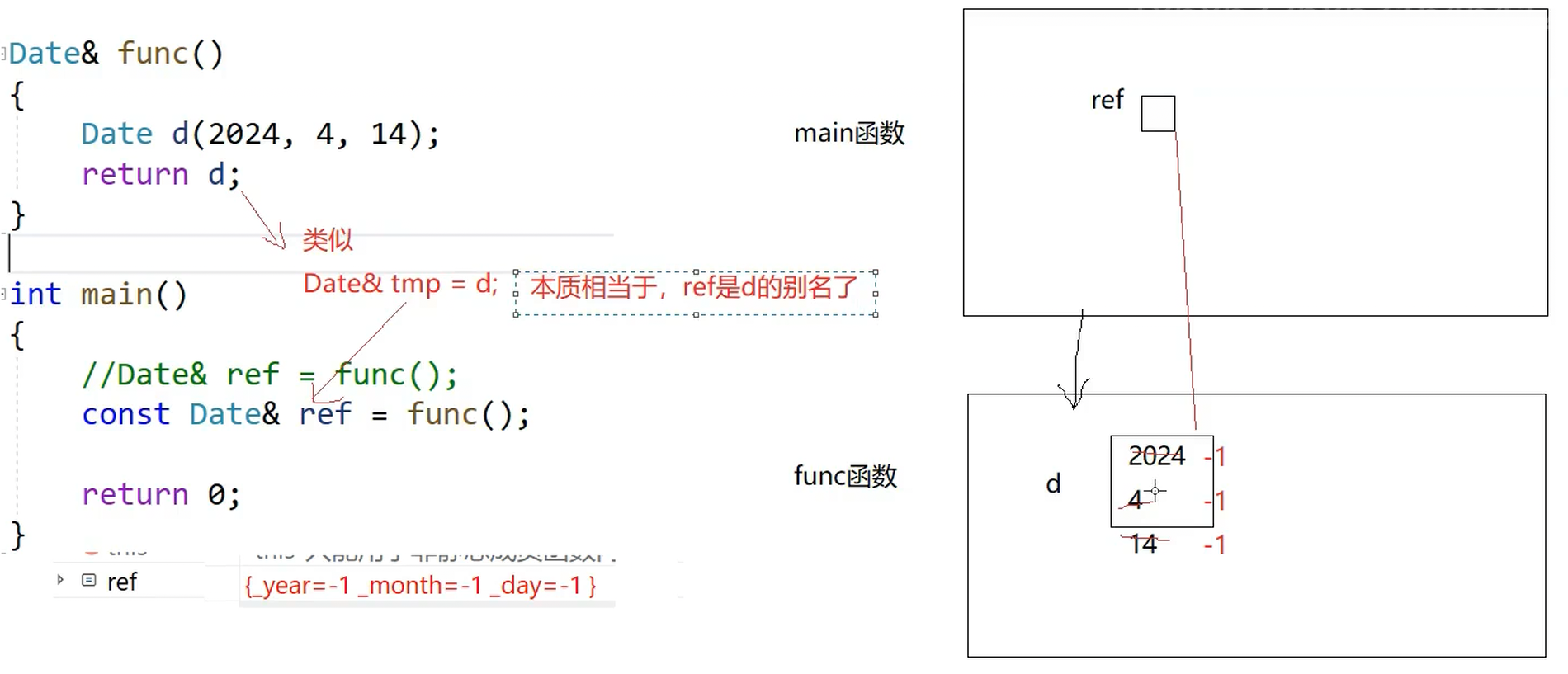
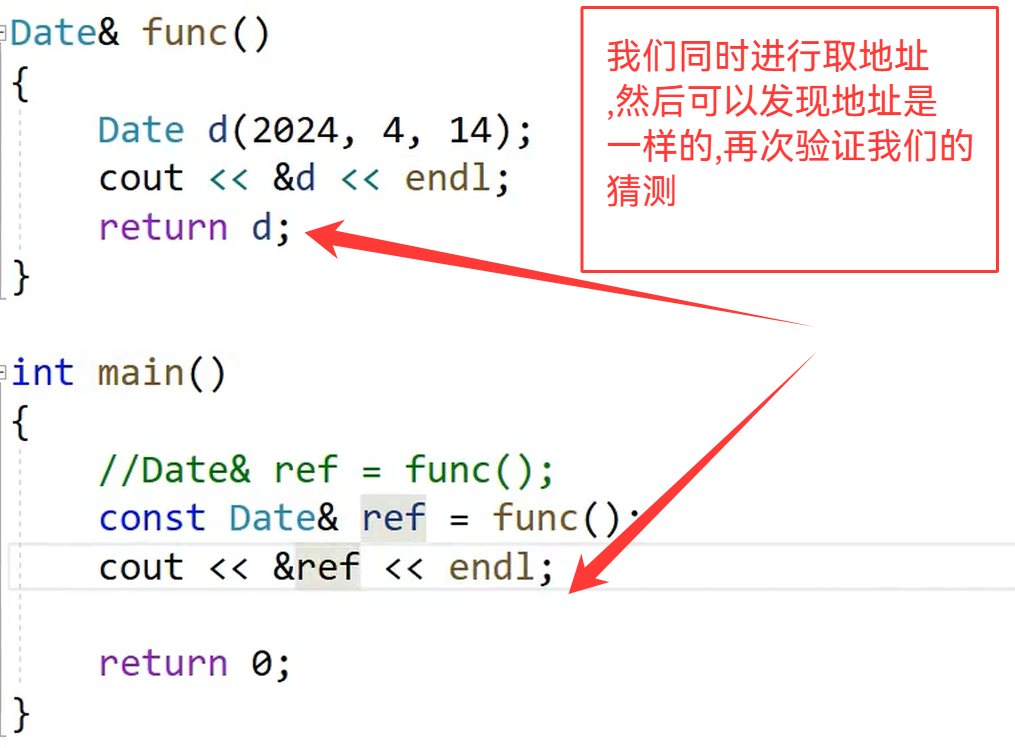
这样ref就相当于是野指针的东西了




回到刚刚的问题上面来:
所以我们是推荐传引用返回的,this出了作用域还是存在的,所以通过传引用来减少拷贝
Date& operator=(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;return *this;}但是我们思考一下,这个重载运算符代码写的对吗?
![]()
不排除有人会这样写代码(这样就会导致赋值的时候白赋值了)
所以我们为了防止这样,代码可以这么写:
Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;}2.赋值运算符只能重载成类的成员函数不能重载成全局函数

简单理解就是规定
3. 用户没有显式实现时,编译器会生成一个默认赋值运算符重载,以值的方式逐字节拷贝。注 意:内置类型成员变量是直接赋值的,而自定义类型成员变量需要调用对应类的赋值运算符 重载完成赋值。

插播补充知识:在类里面,不声明默认是内联函数,但是声明和定义分离就不是内联函数了
3.前置++和后置++重载
class Date
{
public:// 构造函数Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}// 前置++:返回+1之后的结果// 注意:this指向的对象函数结束后不会销毁,故以引用方式返回提高效率Date& operator++(){_day += 1;return *this;}// 后置++:// 前置++和后置++都是一元运算符,为了让前置++与后置++形成能正确重载// C++规定:后置++重载时多增加一个int类型的参数,但调用函数时该参数不用传递,编译器自动传递// 注意:后置++是先使用后+1,因此需要返回+1之前的旧值,故需在实现时需要先将this保存一份,然后给this+1// 而temp是临时对象,因此只能以值的方式返回,不能返回引用Date operator++(int){Date temp(*this);_day += 1;return temp;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d;Date d1(2022, 1, 13);d = d1++; // d: 2022,1,13 d1:2022,1,14d = ++d1; // d: 2022,1,15 d1:2022,1,15return 0;
}二.Date类的实现
"Date.cpp"#include"Date.h"Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;
}void Date::Print()
{cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}// d1 < d2
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{if (_year < d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year){if (_month < d._month){return true;}else if (_month == d._month){return _day < d._day;}}return false;
}// d1 <= d2
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d)
{return *this < d || *this == d;
}bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{return !(*this <= d);
}bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{return !(*this < d);
}bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;
}bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)
{return !(*this == d);
}// d1 += 50
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);++_month;if (_month == 13){++_year;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}// d1 + 50
//Date Date::operator+(int day)
//{
// Date tmp = *this;
// tmp._day += day;
// while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
// {
// tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
// ++tmp._month;
// if (tmp._month == 13)
// {
// ++tmp._year;
// tmp._month = 1;
// }
// }
//
// return tmp;
//}Date Date::operator+(int day)
{Date tmp = *this;tmp += day;return tmp;
}
"Date.h"#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;#include<assert.h>class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1);void Print();// 直接定义类里面,他默认是inline// 频繁调用int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){assert(month > 0 && month < 13);static int monthDayArray[13] = { -1, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };// 365天 5h +if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)){return 29;}else{return monthDayArray[month];}}bool operator<(const Date& d);bool operator<=(const Date& d);bool operator>(const Date& d);bool operator>=(const Date& d);bool operator==(const Date& d);bool operator!=(const Date& d);// d1 + 100Date& operator+=(int day);Date operator+(int day);Date& operator-=(int day);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
"test.cpp"#include"Date.h"int main()
{Date d1(2024, 4, 14);Date d2 = d1 + 50;d1.Print();d2.Print();return 0;
}