【深入浅出PyTorch】--上采样+下采样
我们来系统地介绍 上采样(Upsampling) 和 下采样(Downsampling) 的概念、作用,以及在 PyTorch 中的实现方式。
目录
1.下采样
1.1.nn.MaxPool2d
1.2.nn.AvgPool2d
1.3.nn.Conv2d
2.上采样
2.1.nn.Upsample
2.2.nn.ConvTranspose2d
1.下采样
🔹 定义
下采样 是指 降低特征图的空间尺寸(高度和宽度),通常用于减少计算量、扩大感受野、提取高层语义信息。
🔹 作用
-
减少特征图大小,降低内存消耗
-
扩大感受野(每个神经元“看到”的区域更大)
-
提取更抽象的语义特征(如物体类别)
-
常用于编码器(Encoder)中
🔹 常见方法
-
最大池化(Max Pooling)
-
平均池化(Average Pooling)
-
带步长的卷积(Strided Convolution)
1.1.nn.MaxPool2d
原理请看:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_58602552/article/details/148617896?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
# 最大池化,窗口大小2x2,步长2
pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
x = pool(x) # 输出尺寸减半print(x.shape)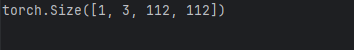
1.2.nn.AvgPool2d
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
# 最大池化,窗口大小2x2,步长2x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)pool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
x = pool(x)print(x.shape)1.3.nn.Conv2d
# 使用步长为2的卷积实现下采样
conv_down = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
x = conv_down(x) # 尺寸减半,同时提取特征2.上采样
🔹 定义:
上采样 是指 增大特征图的空间尺寸(高度和宽度),用于恢复空间分辨率,常用于解码器(Decoder)或分割任务中。
🔹 作用:
-
恢复图像尺寸(如从 32×32 → 64×64)
-
与跳跃连接(skip connection)结合,融合细节信息
-
生成高分辨率输出(如语义分割图)
🔹 常见方法:
-
插值法(Interpolation):双线性、双三次等
-
转置卷积(Transposed Convolution):也叫反卷积(Deconvolution)
2.1.nn.Upsample
torch.nn.Upsample(size=None,scale_factor=None,mode='nearest',align_corners=None,recompute_scale_factor=None
)| 参数名 | 默认值 | 说明 | 可选值示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
size | None | 指定输出特征图的目标空间尺寸。可与 scale_factor 二选一或共用。 | 64, (128, 128), (32, 64, 64)(3D) |
scale_factor | None | 指定每个空间维度的放大倍数。例如 2 表示放大 2 倍。 | 2, 1.5, (2, 2), (2, 1.5) |
mode | 'nearest' | 插值方法,决定如何“填补”放大后的像素值。不同模式影响输出平滑度。 | 'nearest', 'bilinear', 'bicubic', 'trilinear' |
align_corners | None(等价于 False) | 是否对齐输入和输出的角点像素。在分割任务中建议设为 True。 | True, False |
recompute_scale_factor | None | 是否重新计算 scale_factor(避免插值误差)。如果 size 未指定且 scale_factor 为浮点数,建议设为 True。 | True, False |
| 模式 | 维度 | 平滑性 | 速度 | 适用场景 | 推荐指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
'nearest'(临近插值) | 1D/2D/3D | ❌ 粗糙,有锯齿 | ⚡️ 极快 | 快速原型、分类任务 | ⭐⭐☆ |
'bilinear'(线性插值) | 2D | ✅ 平滑 | 快 | 图像分割、重建、U-Net | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
'bicubic'() | 2D | ✅✅ 非常平滑 | 较慢 | 高质量图像放大 | ⭐⭐⭐ |
'trilinear' | 3D | ✅ 平滑 | 快 | 3D 医学图像分割(如 MRI) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
✅ 推荐:在语义分割任务中,使用 'bilinear' + align_corners=True
>>> input = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float32).view(1, 1, 2, 2)
>>> input
tensor([[[[ 1., 2.],[ 3., 4.]]]])>>> m = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
>>> m(input)
tensor([[[[ 1., 1., 2., 2.],[ 1., 1., 2., 2.],[ 3., 3., 4., 4.],[ 3., 3., 4., 4.]]]])>>> m = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear') # align_corners=False
>>> m(input)
tensor([[[[ 1.0000, 1.2500, 1.7500, 2.0000],[ 1.5000, 1.7500, 2.2500, 2.5000],[ 2.5000, 2.7500, 3.2500, 3.5000],[ 3.0000, 3.2500, 3.7500, 4.0000]]]])>>> m = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
>>> m(input)
tensor([[[[ 1.0000, 1.3333, 1.6667, 2.0000],[ 1.6667, 2.0000, 2.3333, 2.6667],[ 2.3333, 2.6667, 3.0000, 3.3333],[ 3.0000, 3.3333, 3.6667, 4.0000]]]])>>> # Try scaling the same data in a larger tensor
>>>
>>> input_3x3 = torch.zeros(3, 3).view(1, 1, 3, 3)
>>> input_3x3[:, :, :2, :2].copy_(input)
tensor([[[[ 1., 2.],[ 3., 4.]]]])
>>> input_3x3
tensor([[[[ 1., 2., 0.],[ 3., 4., 0.],[ 0., 0., 0.]]]])>>> m = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear') # align_corners=False
>>> # Notice that values in top left corner are the same with the small input (except at boundary)
>>> m(input_3x3)
tensor([[[[ 1.0000, 1.2500, 1.7500, 1.5000, 0.5000, 0.0000],[ 1.5000, 1.7500, 2.2500, 1.8750, 0.6250, 0.0000],[ 2.5000, 2.7500, 3.2500, 2.6250, 0.8750, 0.0000],[ 2.2500, 2.4375, 2.8125, 2.2500, 0.7500, 0.0000],[ 0.7500, 0.8125, 0.9375, 0.7500, 0.2500, 0.0000],[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]]]])>>> m = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
>>> # Notice that values in top left corner are now changed
>>> m(input_3x3)
tensor([[[[ 1.0000, 1.4000, 1.8000, 1.6000, 0.8000, 0.0000],[ 1.8000, 2.2000, 2.6000, 2.2400, 1.1200, 0.0000],[ 2.6000, 3.0000, 3.4000, 2.8800, 1.4400, 0.0000],[ 2.4000, 2.7200, 3.0400, 2.5600, 1.2800, 0.0000],[ 1.2000, 1.3600, 1.5200, 1.2800, 0.6400, 0.0000],[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]]]])
2.2.nn.ConvTranspose2d
具体原理:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_58602552/article/details/152280344?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
(转置卷积)
| 转置卷积 | ✅ 是 | 可学习上采样模式 | 可能出现棋盘伪影 | 精确分割、生成任务 |
# 转置卷积:将特征图放大2倍,同时学习上采样方式
upconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
x = upconv(x) # 输出尺寸 ×2kernel_size=2,stride=2:完美放大2倍- 可学习参数,比插值更灵活
- 但可能产生“棋盘效应”(checkerboard artifacts)
