java-网络编程-UDP,TCP通信
基本通信架构
- CS架构(Client客户端/Server服务端)
- BS架构(Browser浏览器/Server服务端)
网络通信三要素
IP地址
常用命令:
ipconfig:查看本机IP地址
ping IP地址:检查网络是否连通
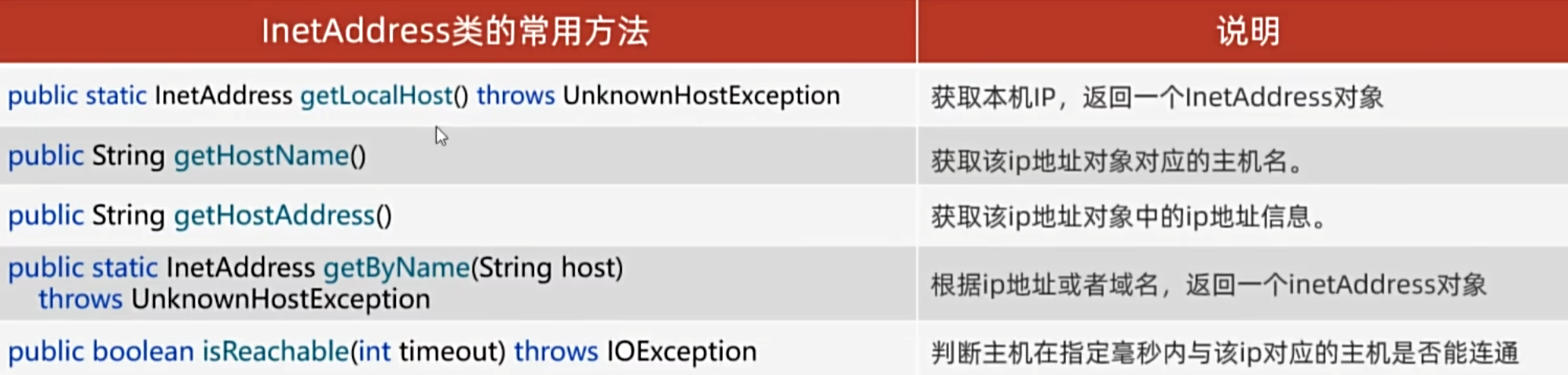
InetAddress
代表IP地址
常用方法
public class InetAddressDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//InetAddress获取本机IP对象和对方IP对象try {//1、获取本机IP对象InetAddress local = InetAddress.getLocalHost();System.out.println(local);System.out.println(local.getHostName());System.out.println(local.getHostAddress());//2、获取对方IP对象InetAddress remote = InetAddress.getByName("www.mihoyo.com");System.out.println(remote.getHostName());System.out.println(remote.getHostAddress());//3、判断IP地址是否可达boolean reachable = remote.isReachable(5000);System.out.println(reachable);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
端口
计算机内部标记应用程序的序号,范围0-65535
- 分类
周知端口:0-1023,被预定义的知名应用占用
注册端口:1024-49151,分配给应用程序和用户进程
动态端口:49152-65535,动态分配
协议
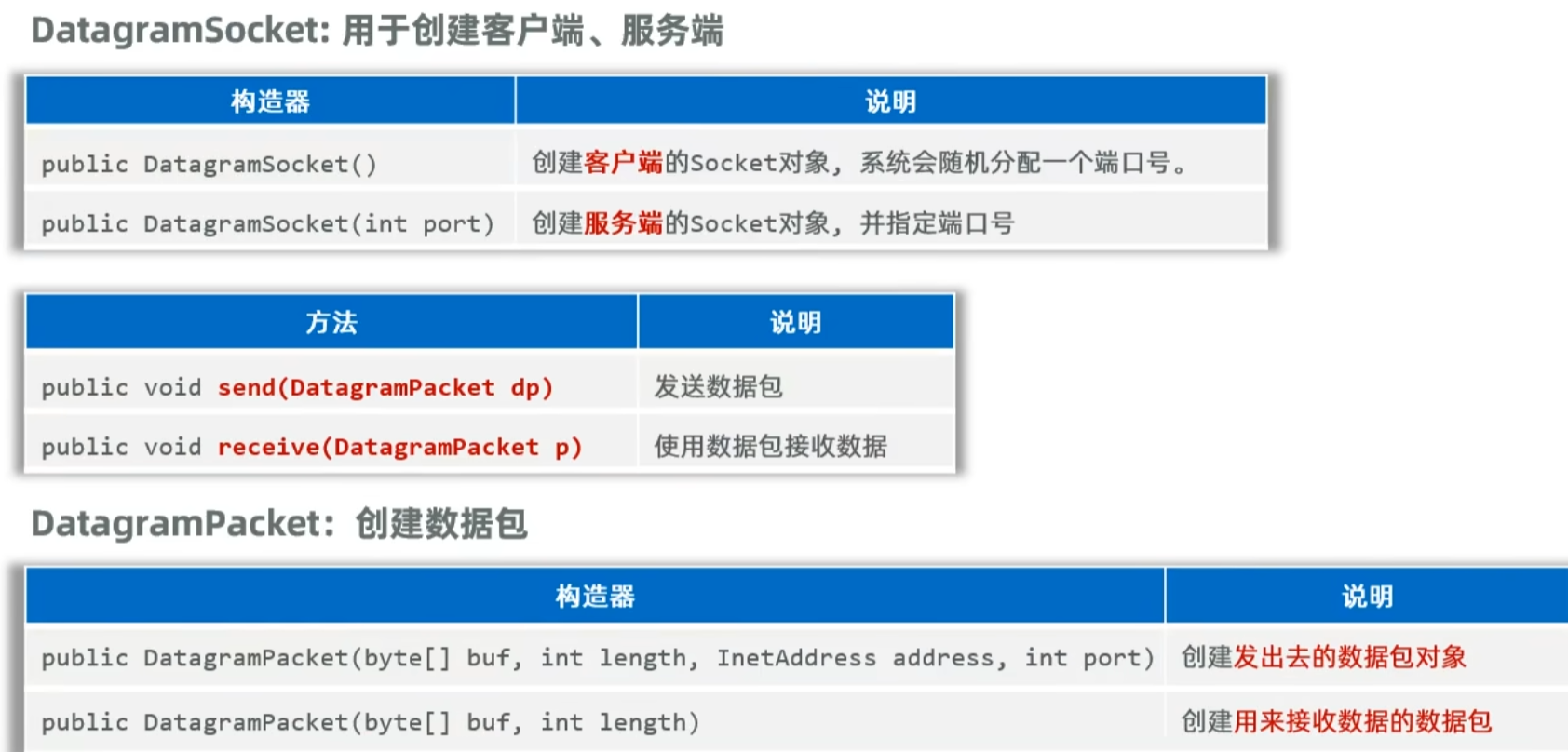
UDP(用户数据报协议):无连接,不可靠
数据按照包发
java提供了java.net.DatagramSocket类实现UDP通信
- 一发一收
public class UPDClientDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {System.out.println("客户端启动了...");//UPD通信一发一收:客户端//1、创建发送端对象DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket();//2、创建数据包对象,封装数据byte[] data = "UPD通信一发一收".getBytes();/*** public DatagramPacket(byte[] buf, int length, InetAddress address, int port)* 参数一:数据,字节数组* 参数二:数据长度* 参数三:指定接收端的IP地址* 参数四:指定接收端的端口号*/DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(data, data.length, InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 10086);//3、发送端对象发送数据包的数据socket.send(packet);}
}
public class UPDServerDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {System.out.println("服务端启动了...");//UPD通信一发一收:服务端//1、创建接收端对象,注册端口DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(10086);//2、创建数据包对象,接收数据byte[] buf = new byte[1024 * 64];DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length);//3、接收数据socket.receive(packet);//4、解析数据//获取当前接收到的数据长度int length = packet.getLength();String data = new String(buf, 0, length);System.out.println("服务端收到数据:" + data);//获取对方IP对象和程序端口String ip = packet.getAddress().getHostAddress();int port = packet.getPort();System.out.println("对方IP:" + ip + ",端口:" + port);}
}
- 多发多收
public class UPDServerDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {System.out.println("服务端启动了...");//UPD通信多发多收:服务端//1、创建接收端对象,注册端口DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(10086);//2、创建数据包对象,接收数据byte[] buf = new byte[1024 * 64];DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length);while (true) {//3、接收数据socket.receive(packet);//阻塞式接收数据//4、解析数据//获取当前接收到的数据长度int length = packet.getLength();String data = new String(buf, 0, length);System.out.println("服务端收到数据:" + data);//获取对方IP对象和程序端口String ip = packet.getAddress().getHostAddress();int port = packet.getPort();System.out.println("对方IP:" + ip + ",端口:" + port);System.out.println("----------------");}}
}
public class UPDClientDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {System.out.println("客户端启动了...");//UPD通信多发多收:客户端//1、创建发送端对象DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket();DatagramPacket packet = null;Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);while (true) {System.out.println("请输入要发送的数据:");String data = sc.nextLine();//若输入exit则退出if ("exit".equals(data)) {System.out.println("客户端退出了...");socket.close();break;}//2、创建数据包对象,封装数据byte[] bytes = data.getBytes();packet = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 10086);//3、发送端对象发送数据包的数据socket.send(packet);}}
}
TCP(传输控制协议):面向连接,可靠通信
java提供了java.net.Socket类实现TCP通信

- 一发一收
客户端
public class ClientDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//TCP通信下一发一收:客户端//1、创建socket管道对象,请求与服务端的socket链接,可靠连接Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10086);//2、从socket通信管道中得到字节输出流OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();//3、特殊数据流DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);dos.writeInt(1);dos.writeUTF("嗨,想我了吗?");//4、关闭管道socket.close();}
}服务端
服务端是通过java.net包下的ServerSocket类实现的

public class ServerDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {System.out.println("服务端启动了...");//TCP通信一发一收:服务端//1、创建服务端ServerSocket对象,注册端口ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(10086);//2、调用accept方法,阻塞等待客户端连接,一旦有客户端连接,返回Socket对象Socket socket = server.accept();//3、获取输入流,读取数据InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();//4、把字节输入流包装成特殊数据输入流DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);//5、读取数据int id = dis.readInt();String msg = dis.readUTF();System.out.println("id:" + id + ",收到消息:" + msg);//6、客户端ip和端口System.out.println("客户端IP:" + socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress());System.out.println("客户端端口:" + socket.getPort());}
}
- 多发多收
public class ClientDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {System.out.println("客户端启动了...");//TCP通信下多发多收:客户端//1、创建socket管道对象,请求与服务端的socket链接,可靠连接Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10086);//2、从socket通信管道中得到字节输出流OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();//3、特殊数据流DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);while (true) {System.out.println("请输入:");String msg = sc.nextLine();if ("exit".equals(msg)) {System.out.println("886,程序退出...");socket.close();break;}dos.writeUTF(msg);dos.flush();}}
}
public class ServerDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {System.out.println("服务端启动了...");//TCP通信多发多收:服务端//1、创建服务端ServerSocket对象,注册端口ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(10086);//2、调用accept方法,阻塞等待客户端连接,一旦有客户端连接,返回Socket对象Socket socket = server.accept();//3、获取输入流,读取数据InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();//4、把字节输入流包装成特殊数据输入流DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);while (true) {//5、读取数据String msg = dis.readUTF();System.out.println("收到消息:" + msg);//6、客户端ip和端口System.out.println("客户端IP:" + socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress());System.out.println("客户端端口:" + socket.getPort());System.out.println("-------------------------");}}
}
服务端支持多个客户端同时连接
public class ServerDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {System.out.println("服务端启动了...");//TCP通信多发多收:服务端,支持多个客户端连接//1、创建服务端ServerSocket对象,注册端口ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(10086);while (true) {//2、调用accept方法,阻塞等待客户端连接,一旦有客户端连接,返回Socket对象Socket socket = server.accept();//3、把这个客户端管道交给一个独立的子线程专门负责接收这个管道的消息new ServerReader(socket).start();}}
}
public class ServerReader extends Thread{private Socket socket;public ServerReader(Socket socket) {this.socket = socket;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);while (true) {String msg = dis.readUTF();System.out.println("客户端:" + msg);//客户端ip和端口System.out.println("客户端ip:" + socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress());System.out.println("客户端端口:" + socket.getPort());}} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("客户端下线了" + socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress());}}
}
线程池处理网页请求
public class ServerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {System.out.println("服务端启动了...");//B/S架构原理//1、创建服务端ServerSocket对象,注册端口ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8080);//创建线程池对象使用ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 10,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(100),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy());while (true) {//2、调用accept方法,阻塞等待客户端连接,一旦有客户端连接,返回Socket对象Socket socket = server.accept();System.out.println("一个客户端连接了," + socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress());//3、把这个客户端管道包装成一个任务交给线程池处理pool.execute(new ServerReader(socket));}}
}
public class ServerReader extends Thread{private Socket socket;public ServerReader(Socket socket) {this.socket = socket;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {//给当前对应的浏览器管道响应一个网页数据回去OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();//通过字节输出流包装写出去的数据给浏览器//把字节输出流包装成打印流PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(os);//写响应的网页数据回去ps.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");ps.println("Content-Type:text/html;charset=utf-8");ps.println();//必须换行ps.println("<html>");ps.println("<head><title>技术宅拯救世界</title></head>");ps.println("<body>");ps.println("<h1 style='color:pink;font-size=20px'>嗨,想我了吗?</h1>");ps.println("</body>");ps.println("</html>");ps.close();socket.close();} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("客户端下线了" + socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress());}}
}
