手写MyBatis第99弹:MyBatis线程安全问题与连接池调优
多线程调试深度实战:揭秘MyBatis线程安全问题与连接池调优
「多线程调试终极指南:SqlSession线程安全验证 + 线程转储分析连接池泄漏」
多线程环境下的MyBatis行为剖析
在现代高并发应用中,理解框架在多线程环境下的行为至关重要。MyBatis作为Java生态中广泛使用的持久层框架,其线程安全特性和连接池行为直接影响着应用的稳定性和性能。掌握多线程调试技巧,是我们深入理解这些复杂问题的关键。
🥂(❁´◡`❁)您的点赞👍➕评论📝➕收藏⭐是作者创作的最大动力🤞
💖📕🎉🔥 支持我:点赞👍+收藏⭐️+留言📝欢迎留言讨论
🔥🔥🔥(源码 + 调试运行 + 问题答疑)
🔥🔥🔥 有兴趣可以联系我。文末有免费源码
免费获取源码。
更多内容敬请期待。如有需要可以联系作者免费送
更多源码定制,项目修改,项目二开可以联系作者
点击可以进行搜索(每人免费送一套代码):千套源码目录(点我)2025元旦源码免费送(点我)
我们常常在当下感到时间慢,觉得未来遥远,但一旦回头看,时间已经悄然流逝。对于未来,尽管如此,也应该保持一种从容的态度,相信未来仍有许多可能性等待着我们。
SqlSession线程不安全性的实证分析
SqlSession的生命周期与线程绑定
SqlSession是MyBatis的核心接口,但其设计初衷并非线程安全。通过多线程调试,我们可以直观验证这一特性:
public class SqlSessionThreadSafetyTest {@Testpublic void testSqlSessionThreadSafety() throws InterruptedException {SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();List<Thread> threads = new ArrayList<>();List<Exception> exceptions = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());// 创建多个线程同时使用同一个SqlSessionfor (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {try {// 在不同线程中执行查询操作UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);User user = mapper.findById(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100));System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " found: " + user);// 模拟并发更新操作if (user != null) {user.setName("UpdatedBy-" + Thread.currentThread().getName());mapper.updateUser(user);}} catch (Exception e) {exceptions.add(e);System.err.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " error: " + e.getMessage());}});threads.add(thread);thread.start();}// 等待所有线程完成for (Thread thread : threads) {thread.join();}// 分析收集到的异常assertFalse("Should have concurrency issues", exceptions.isEmpty());exceptions.forEach(e -> assertTrue(e instanceof PersistenceException || e instanceof SQLException));}}线程安全问题的调试观察点
在调试过程中,我们需要重点关注以下可能发生线程安全问题的位置:
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {private final Executor executor;// 观察点1:Executor的线程安全性@Overridepublic <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {try {MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);// 多个线程可能同时访问同一个MappedStatementreturn executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), RowBounds.DEFAULT, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);} catch (Exception e) {throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);} finally {ErrorContext.instance().reset();}}// 观察点2:脏标记的并发访问private boolean dirty = false;@Overridepublic void commit(boolean force) {try {executor.commit(isCommitOrRollbackRequired(force));dirty = false; // 竞态条件可能发生在这里} catch (Exception e) {throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error committing transaction. Cause: " + e, e);} finally {ErrorContext.instance().reset();}}}多线程调试的高级技巧
线程感知断点配置
IDEA提供了强大的线程感知调试功能,让我们能够精确控制调试行为:
public class ThreadAwareDebugger {public void debugConcurrentAccess() {// 条件断点:只在特定线程中触发// 条件表达式:Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("http-nio-8080-exec-1")// 观察线程局部变量的状态ThreadLocal<SqlSession> localSqlSession = new ThreadLocal<>();// 在多线程环境中观察ThreadLocal的行为ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {final int taskId = i;executor.submit(() -> {try {// 设置线程特定的SqlSessionif (localSqlSession.get() == null) {localSqlSession.set(sqlSessionFactory.openSession());}// 执行数据库操作UserMapper mapper = localSqlSession.get().getMapper(UserMapper.class);User user = mapper.findById(taskId);// 观察不同线程中SqlSession的独立性System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - Session: " + System.identityHashCode(localSqlSession.get()));} finally {// 清理线程局部资源SqlSession session = localSqlSession.get();if (session != null) {session.close();localSqlSession.remove();}}});}executor.shutdown();}}并发问题复现策略
系统性复现并发问题需要精心设计的测试场景:
public class ConcurrencyTestBuilder {public void buildRaceConditionTest() throws InterruptedException {CountDownLatch startLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);CountDownLatch endLatch = new CountDownLatch(3);SqlSession sharedSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();AtomicInteger successCount = new AtomicInteger(0);AtomicInteger failureCount = new AtomicInteger(0);for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {new Thread(() -> {try {startLatch.await(); // 等待同时开始UserMapper mapper = sharedSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);// 并发更新同一条记录User user = mapper.findById(1);if (user != null) {user.setVersion(user.getVersion() + 1);int updated = mapper.updateUser(user);if (updated > 0) {successCount.incrementAndGet();}}} catch (Exception e) {failureCount.incrementAndGet();System.err.println("Thread " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " failed: " + e.getMessage());} finally {endLatch.countDown();}}).start();}// 同时释放所有线程startLatch.countDown();endLatch.await();System.out.println("Success: " + successCount.get() + ", Failures: " + failureCount.get());sharedSession.close();}}线程转储在连接池问题排查中的实战应用
连接池泄漏的诊断与分析
数据库连接池泄漏是生产环境中常见的问题,线程转储是诊断这类问题的利器:
public class ConnectionPoolMonitor {// 模拟连接池泄漏场景public void simulateConnectionLeak() throws SQLException {DataSource dataSource = getDataSource();// 故意不关闭连接,模拟泄漏for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();// 使用连接但不关闭PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement("SELECT 1 FROM DUAL");ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery();// 故意不调用 conn.close()}// 此时生成线程转储分析连接状态generateThreadDump();}private void generateThreadDump() {// 生成线程转储的多种方式ThreadMXBean threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean();ThreadInfo[] threadInfos = threadMXBean.dumpAllThreads(true, true);for (ThreadInfo threadInfo : threadInfos) {// 分析持有数据库连接的线程if (isDatabaseConnectionThread(threadInfo)) {System.out.println("Potential connection holder: " + threadInfo.getThreadName());System.out.println("Stack trace:");for (StackTraceElement element : threadInfo.getStackTrace()) {System.out.println(" " + element);}}}}private boolean isDatabaseConnectionThread(ThreadInfo threadInfo) {// 根据堆栈信息判断是否与数据库连接相关return Arrays.stream(threadInfo.getStackTrace()).anyMatch(element -> element.getClassName().contains("Connection") ||element.getClassName().contains("PreparedStatement") ||element.getMethodName().contains("getConnection"));}}线程转储的深度解析技巧
理解线程转储中的关键信息对于诊断连接池问题至关重要:
分析线程状态:
-
RUNNABLE:正在执行数据库操作的线程
-
WAITING:等待获取连接的线程
-
BLOCKED:因连接池竞争而阻塞的线程
识别连接持有者:
// 在线程转储中查找连接持有线程的模式"http-nio-8080-exec-5" #32 daemon prio=5 os_prio=31 tid=0x00007fe36b0c5000 nid=0x6b03 runnable [0x0000700006e96000]java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLEat java.net.SocketInputStream.socketRead0(Native Method)at java.net.SocketInputStream.socketRead(SocketInputStream.java:116)at java.net.SocketInputStream.read(SocketInputStream.java:171)at java.net.SocketInputStream.read(SocketInputStream.java:141)at com.mysql.cj.protocol.ReadAheadInputStream.fill(ReadAheadInputStream.java:107)at com.mysql.cj.protocol.ReadAheadInputStream.readFromUnderlyingStreamIfNecessary(ReadAheadInputStream.java:150)- 持有 <0x0000000740a8b2b8> (a com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl) // 关键信息!连接池监控与调试实战
HikariCP连接池调试
HikariCP是常用的高性能连接池,其调试需要特殊关注点:
public class HikariCPDebugger {public void monitorHikariPool() {HikariDataSource dataSource = (HikariDataSource) getDataSource();HikariPoolMXBean poolMXBean = dataSource.getHikariPoolMXBean();// 实时监控连接池状态ScheduledExecutorService monitor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);monitor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {System.out.println("=== HikariCP Pool Status ===");System.out.println("Active connections: " + poolMXBean.getActiveConnections());System.out.println("Idle connections: " + poolMXBean.getIdleConnections());System.out.println("Total connections: " + poolMXBean.getTotalConnections());System.out.println("Threads awaiting connection: " + poolMXBean.getThreadsAwaitingConnection());System.out.println("=============================");// 生成线程转储分析等待连接的线程if (poolMXBean.getThreadsAwaitingConnection() > 5) {generateThreadDumpForWaiters();}}, 0, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);}private void generateThreadDumpForWaiters() {ThreadMXBean threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean();ThreadInfo[] allThreads = threadMXBean.dumpAllThreads(true, true);System.out.println("=== Threads waiting for database connections ===");for (ThreadInfo threadInfo : allThreads) {if (isWaitingForConnection(threadInfo)) {System.out.println("Waiting thread: " + threadInfo.getThreadName());System.out.println("State: " + threadInfo.getThreadState());System.out.println("Stack trace:");for (StackTraceElement element : threadInfo.getStackTrace()) {System.out.println(" at " + element);}System.out.println("---");}}}private boolean isWaitingForConnection(ThreadInfo threadInfo) {return threadInfo.getThreadState() == Thread.State.WAITING &&Arrays.stream(threadInfo.getStackTrace()).anyMatch(element -> element.getClassName().contains("HikariPool") &&element.getMethodName().contains("getConnection"));}}Druid连接池问题诊断
对于Druid连接池,我们可以利用其内置的监控功能:
public class DruidPoolDebugger {public void debugDruidPool() throws SQLException {DruidDataSource dataSource = (DruidDataSource) getDataSource();// 启用Druid的统计功能dataSource.setStatLogger(new StatLogger() {@Overridepublic void log(StatLoggerContext context) {// 记录连接池统计信息用于调试System.out.println("Druid Stats - Active: " + dataSource.getActiveCount() +", Pooling: " + dataSource.getPoolingCount() +", WaitThread: " + dataSource.getWaitThreadCount());}});// 模拟高并发场景ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20);for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {executor.submit(() -> {try (Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement("SELECT SLEEP(1)")) {stmt.execute();} catch (SQLException e) {System.err.println("Connection error: " + e.getMessage());}});}executor.shutdown();}}生产环境线程问题排查流程
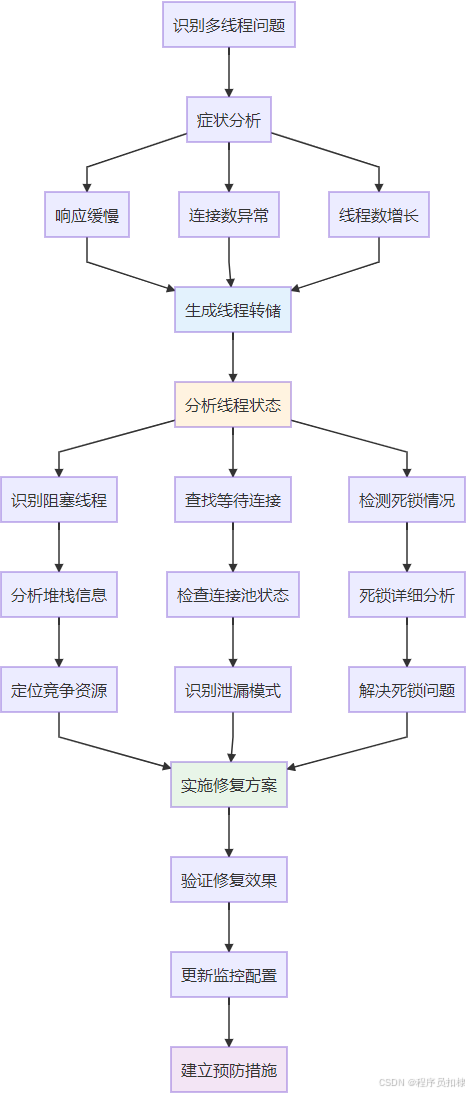
系统性诊断方法
建立完整的线程问题排查流程:
-
症状识别:
-
应用响应缓慢
-
数据库连接数异常增长
-
线程数持续增加
-
-
数据收集:
-
生成线程转储(jstack、IDEA)
-
收集连接池监控指标
-
记录系统资源使用情况
-
-
模式分析:
-
识别阻塞的线程
-
分析等待连接的线程堆栈
-
查找资源泄漏模式
-
-
解决方案:
-
修复资源泄漏代码
-
优化连接池配置
-
调整线程池参数
-
自动化监控与告警
建立自动化的线程监控体系:
public class ThreadMonitorService {@Scheduled(fixedRate = 30000) // 每30秒检查一次public void monitorThreadHealth() {ThreadMXBean threadBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean();// 检查线程数是否异常int threadCount = threadBean.getThreadCount();if (threadCount > 1000) { // 阈值根据实际情况调整alert("High thread count: " + threadCount);generateDiagnosticReport();}// 检查死锁long[] deadlockedThreads = threadBean.findDeadlockedThreads();if (deadlockedThreads != null && deadlockedThreads.length > 0) {alert("Deadlock detected in " + deadlockedThreads.length + " threads");generateDeadlockReport(deadlockedThreads);}}private void generateDiagnosticReport() {// 生成详细的诊断报告ThreadDumpGenerator.generateDump("high_thread_count_diagnostic");ConnectionPoolAnalyzer.analyzePoolStatus();MemoryAnalyzer.analyzeMemoryUsage();}
}总结
多线程调试是处理现代高并发应用的必备技能。通过系统性地验证SqlSession的线程安全性,以及熟练运用线程转储分析连接池问题,我们能够:
-
预防并发bug:在开发阶段发现潜在的线程安全问题
-
快速诊断问题:在生产环境快速定位连接池相关问题
-
优化系统性能:基于线程分析结果优化资源使用
-
提升系统稳定性:建立完善的线程监控和告警机制
掌握这些高级调试技巧,不仅能够解决眼前的问题,更能培养系统性思考和预防性编程的能力,这是在分布式和高并发场景下不可或缺的核心竞争力。
🥂(❁´◡`❁)您的点赞👍➕评论📝➕收藏⭐是作者创作的最大动力🤞
💖📕🎉🔥 支持我:点赞👍+收藏⭐️+留言📝欢迎留言讨论
🔥🔥🔥(源码 + 调试运行 + 问题答疑)
🔥🔥🔥 有兴趣可以联系我。文末有免费源码
💖学习知识需费心,
📕整理归纳更费神。
🎉源码免费人人喜,
🔥码农福利等你领!💖常来我家多看看,
📕网址:扣棣编程,
🎉感谢支持常陪伴,
🔥点赞关注别忘记!💖山高路远坑又深,
📕大军纵横任驰奔,
🎉谁敢横刀立马行?
🔥唯有点赞+关注成!
往期文章推荐:
基于Springboot + vue实现的学生宿舍信息管理系统
免费获取宠物商城源码--SpringBoot+Vue宠物商城网站系统
【2025小年源码免费送】
