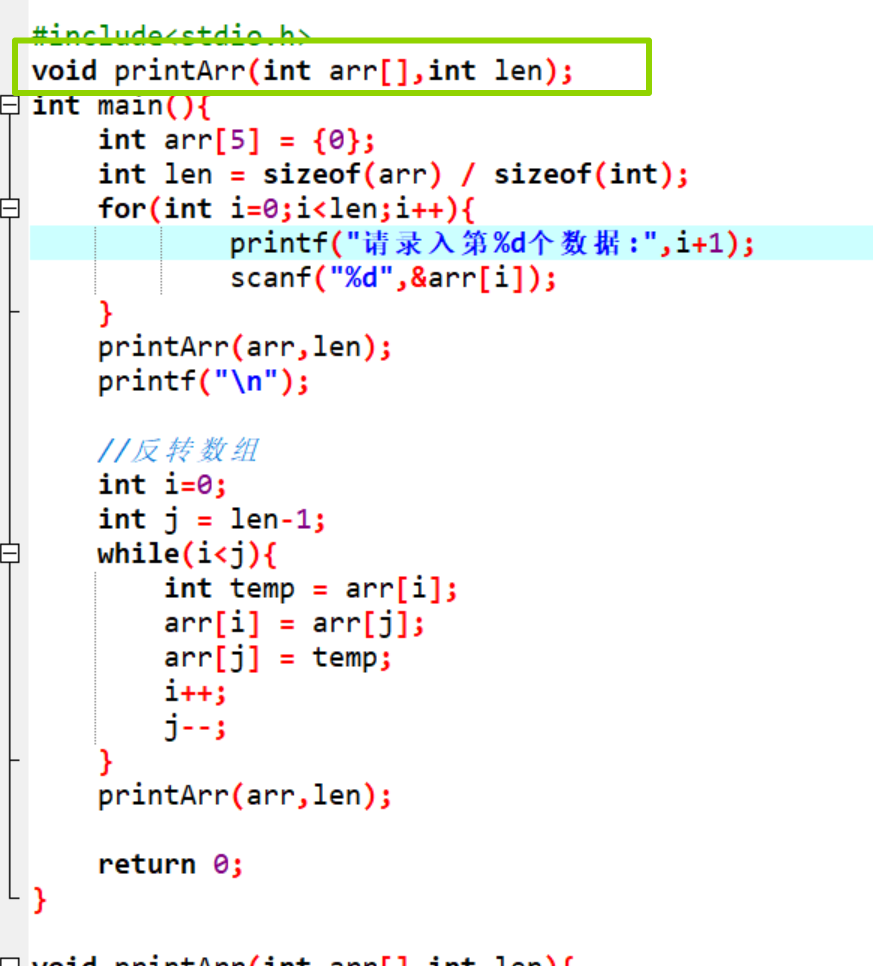
C语言易错点大总结
笔记
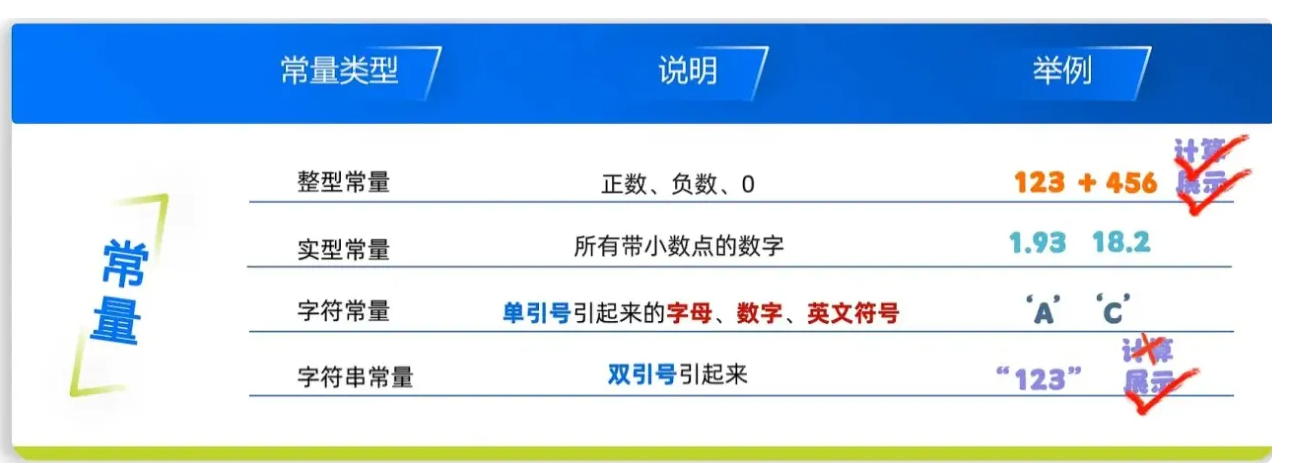
🏙️常量和占位符
熟悉各个常量实例

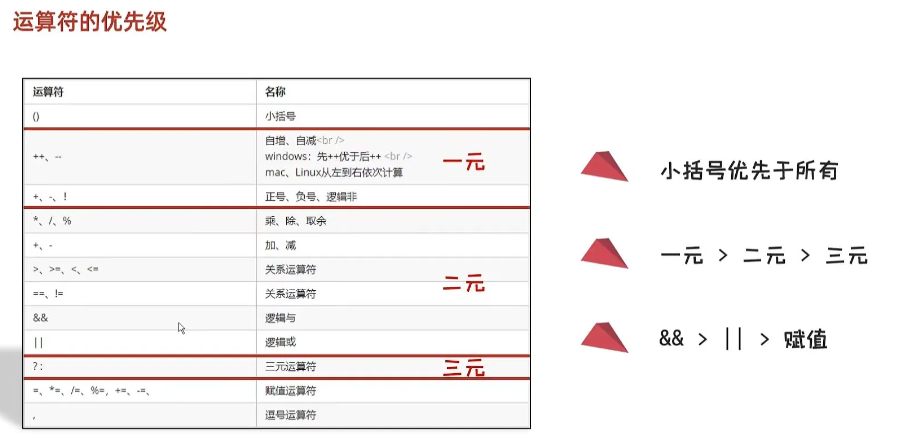
🏙️运算符优先级



🏙️整数,小数,字符串类型
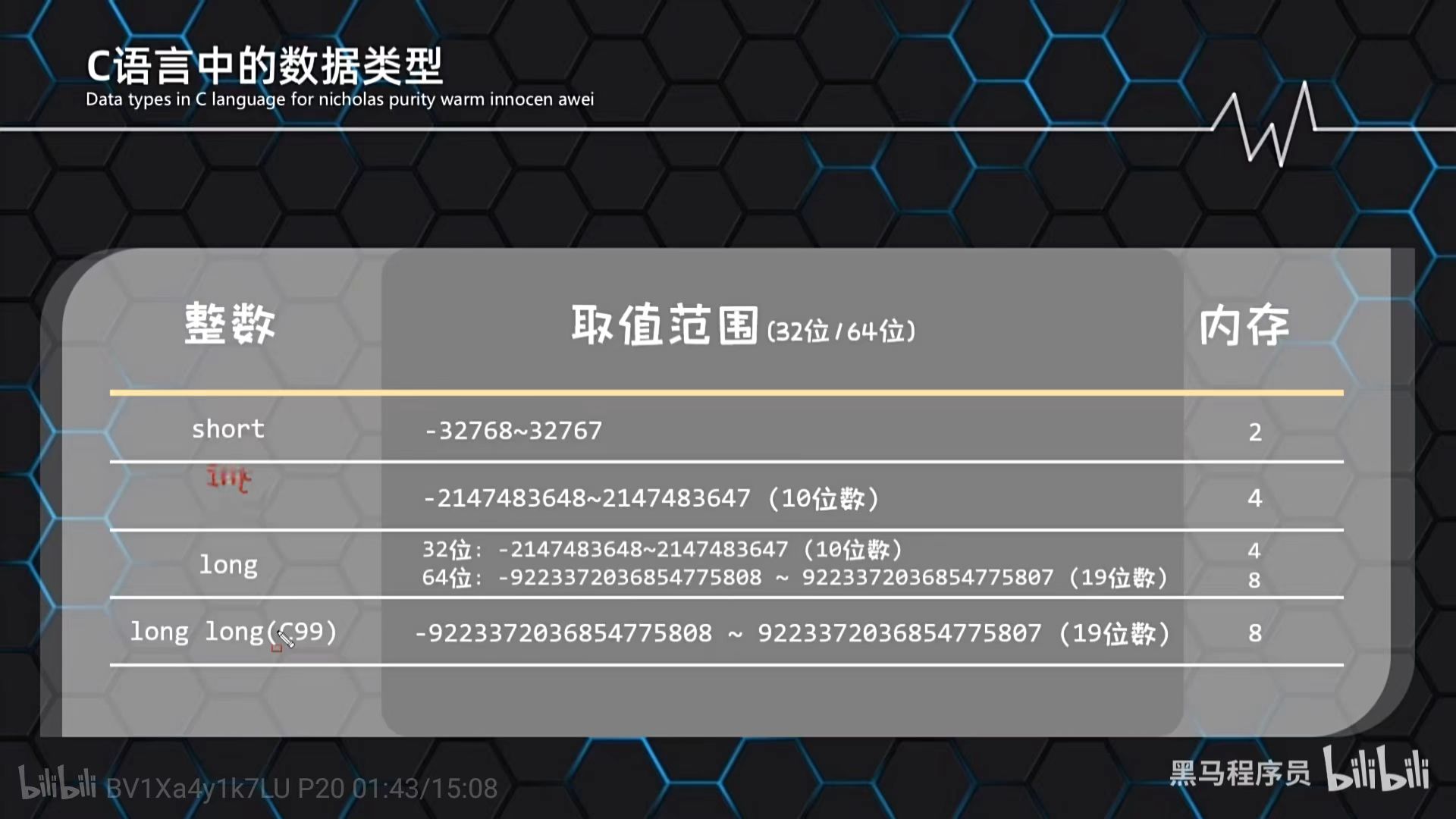
整数类型
有无符号
signed 有符号整数 正数,负数
unsigned 无符号整数 正数
signed int e=-100;
printf("%d\n",e);// 定义一个变量表示序号
unsigned int f = 20;
printf("%u\n",f);return 0;小数类型

#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//1.定义short,int,long,long long4种数据类型的变量
//格式:数据类型 变量名=数据值;//short 短整型 windows 2个字节(-32768~32767)
short a = 10;
printf("%d\n", a);//int整数 windows 4个字节(-2147483648~2147483647)
int b = 100;
printf("%d\n", b);//long 长整数 windows 4个字节 (-2147483648~2147483647)
// Linux 32位 4个字节 64位 8位
long c = 1000L;
printf("%ld\n,c");//long long(C99)超长整型 windows 8个字节 (19位数)
long long d = 10000LL;
printf("%lld\n", d);//2.利用sizeof测量每一种数据类型占用多少字节
//short
printf("%zu\n", sizeof(short));
printf("%zu\n", sizeof(a));//int
printf("%zu\n", sizeof(int));
printf("%zu\n", sizeof(b));//long
printf("%zu\n", sizeof(long));
printf("%zu\n", sizeof(c));//long long
printf("%zu\n", sizeof(long long));
printf("%zu\n", sizeof(d));return 0;
}字符类型

总结

🏙️函数
⚽函数的基本格式
void 函数名() {
函数体;
}
//函数的调用方式
函数名();
#include <stdio.h>
void playGame()
{printf("选择任务\n");printf("准备开局\n");printf("开始对线\n");printf("下把继续\n");
}int main(){//调用playGame这个函数playGame();return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>void sum(){int num1 = 10;int num2=20;int sum = num1 + num2;printf("%d\n",sum);
}int main(){sum();return 0;
} 
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{char* str1 = "abc";char str2[100] = "abc";char str3[5] = { 'q','w','e','r' ,'\0' };printf("---------------------strlen(长度)---------------------------\n");////细节:strlen这个函数在统计长度的时候,是不计算结束标记的////细节:在window中,默认情况下,一个中文占2个字节//int len1 = strlen(str1);//3//int len2 = strlen(str2);//3//int len3 = strlen(str3);//4////想要调用这个函数,直接把对应的字符串直接传递给他就行了,这个函数会给我们返回一个整数,就是当前字符串的长度//printf("%d\n", len1);//printf("%d\n", len2);//printf("%d\n", len3);//第一个数组要留足够的位置,因为要拼接第二个数组的内容,也需要位置printf("---------------------strcat(拼接)---------------------------\n");////细节:把第二个字符串中全部的内容,拷贝到 第一个字符串的末尾// //前提1:第一个字符串的内容是可以被修改的// //前提2:第2个字符串中剩余的空间可以容纳拼接的字符串//strcat_s(str2, str3);//abcqwer//printf("%s\n", str2);//qwer//printf("%s\n", str3);////现在是把str2和str3给传递过去了,也就是说现在要把qwer拼在abc后面printf("---------------------strcpy(拷贝)---------------------------\n");//strcat_s(str2, sizeof(str2), str3);////细节:把第2个字符串所有的内容,拷贝到第一个字符串中,把第一个字符串里面原有的内容给覆盖了//// 前提1:第一个字符串是可以被修改的//// 前提2:第一个字符串中空间可以容纳第二个字符串的完整内容//printf("%s\n", str2);//qwer//printf("%s\n", str3);//qwerprintf("---------------------strcmp(比较)---------------------------\n");//细节:在比较的时候,要求顺序和内容完全一样,才叫做字符串一样////完全一样:0////只要有一个不一样:非0//int res = strcmp(str1, str2);//printf("%d\n", res);//printf("---------------------strlwr(变小写)---------------------------\n");//细节:只能转换英文的大小写,不能修改中文的大小写——1壹//_strlwr(str2) ;//printf("%s\n",str2);//printf("---------------------strupr(变大写)---------------------------\n");//细节:只能转换英文的大小写,不能修改中文的大小写_strupr_s(str2, sizeof(str2));printf("%s\n",str2);return 0;
}⚽带形参的函数

#include<stdio.h>void sum(int num1,int num2){int sum = num1 + num2;printf("%d\n",sum);
}
int main(){sum(10,20);return 0;
}⚽带返回值的函数


#include<stdio.h>int sum(int base,int additional){int sum = base + additional;return sum;
}
int main(){int score1 = sum(93,10);int score2 = sum(78,9);if(score1>score2){printf("小明的成绩更高");}else if(score1<score2){printf("小黑的成绩更高");}else{printf("两个人的成绩一样高"); } return 0;
}⚽函数注意事项

🏙️C语言中的常见函数#include<math.h>\<stdio.h>\<time.h>
C语言中的常见函数(math)

#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>int main()
{/*math.h:poww() 幂sprt() 平方根ceil() 向上取整floor() 向下取整abs() 绝对值*///1.powdouble res1 = pow(2, 3);printf("%lf\n", res1);//2.sqrtdouble res2 = sqrt(9);printf("%lf\n", res2);//3.ceildouble res3 = ceil(13.2);printf("%lf\n", res3);//4.floordouble res4 = floor(13.2);printf("%lf\n", res4);//5.absint res5= abs(-45);printf("%d\n", res5);return 0;
}C语言的常见函数(time)

#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>int main()
{/*time.h:time() 获取当前时间*///time() 获取当前时间//形参:表示获取的当前时间是否需要在其他地方进行存储// 一般来讲,不需要在其他地方进行存储的,MULL(大写)//返回值:long long//结果是什么呢//从1970.1.1 0:0:0 开始过了1709817925秒的那个时间点long long res = time(NULL);printf("%lld\n", res);//1709817925return 0;
}🏙️随机数<stdlib.h>
笔记

#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{//1.设置种子//初始值,因为每一个随机数都是通过前一个数字再结合一系列复杂的计算得到的srand(1);//2.获取随机数int num = rand();//3.输出打印printf("%d\n", num);return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(){srand(90);//2.获取随机数
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{//2.获取随机数int num = rand();//3.输出打印printf("%d\n", num);
}
}随机数的两个小弊端

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{//1.设置种子//种子:不能固定不变,结果就不变//用一个变化的数据去充当种子 时间srand(time(NULL));for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){//2.获取随机数int num = rand();//3.输出打印printf("%d\n", num);}return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{/*默认范围:0~32767任意的范围之内获取一个随机数:1~1007~238~49绝招:用于生产任意范围之内的随机数1.把这个范围变成包头不包尾,包左不包右 1-1012.拿着尾巴-开头 101-13.修改代码*/srand(time(NULL));//2.获取随机数int num = rand() % 100 + 1;//3.输出打印printf("%d\n", num);return 0;
}猜数字小游戏
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>int main()
{/*生成1-100之间的随机数使用键盘录入去猜,猜中为止*///1.生成1-100之间的随机数srand(time(NULL));int number = rand() % 100 + 1;//2.利用循环 + 键盘录入去猜int guess;while (1){printf("请输入要猜的数字:\n");scanf_s("%d", &guess);//拿着guess跟随机数进行比较if (guess < number){printf("小了\n");}else if (guess > number){printf("大了\n");}else{printf("中了\n");break;}}}🏙️字符串的常见函数<string.h>

strlen
//细节:strlen这个函数在统计长度的时候,是不计算结束标记的
//细节:在window中,默认情况下,一个中文占2个字节
//想要调用这个函数,直接把对应的字符串直接传递给他就行了,这个函数会给我们返回一个整数,就是当前字符串的长度
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{char* str1 = "abc";char str2[100] = "abc";char str3[8] = { 'q','w','e','r' ,'\0' };printf("---------------------strlen(长度)---------------------------\n");int len1 = strlen(str1);//3int len2 = strlen(str2);//3int len3 = strlen(str3);//4printf("%d\n", len1);printf("%d\n", len2);printf("%d\n", len3);return 0;
}strcat
//把第二个字符串中全部的内容,拷贝到 第一个字符串的末尾
//前提1:第一个字符串的内容是可以被修改的
//前提2:第2个字符串中剩余的空间可以容纳拼接的字符串

#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(){char* str1 = "abc";char str2[100] = "abc";char str3[8] = { 'q','w','e','r' ,'\0' };printf("---------------------strcat(拼接)---------------------------\n");strcat(str2, str3);//abcqwerprintf("%s\n", str2);//qwerprintf("%s\n", str3);return 0;//现在是把str2和str3给传递过去了,也就是说现在要把qwer拼在abc后面
}strcpy 用于字符串赋值
//把第二个字符串中全部的内容,拷贝到第一个字符串中,把第一个字符串里面原有的内容给覆盖了
前提1:第一个字符串是可以被修改的
前提2:第一个字符串中空间可以容纳第二个字符串的完整内容
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{char* str1 = "abc";char str2[100] = "abc";char str3[5] = { 'q','w','e','r' ,'\0' };printf("---------------------strcpy(拷贝)---------------------------\n");strcpy(str2,str3);printf("%s\n", str2);//qwerprintf("%s\n", str3);//qwerreturn 0;
}strcmp
//细节:在比较的时候,要求顺序和内容完全一样,才叫做字符串一样
//完全一样:0
//只要有一个不一样:非0
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{char* str1 = "abc";char str2[100] = "abc";char str3[5] = { 'q','w','e','r' ,'\0' };printf("---------------------strcmp(比较)---------------------------\n");int res = strcmp(str1, str2);printf("%d\n", res);return 0;
}
strlwr/strupr
只能转换英语的大小写,不能转换中文大小写
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{char* str1 = "abc";char str2[100] = "Abc";char str3[5] = { 'q','w','e','r' ,'\0' };printf("---------------------strlwr(变小写)---------------------------\n");//细节:只能转换英文的大小写,不能修改中文的大小写——1壹strlwr(str2) ;printf("%s\n",str2);
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{char* str1 = "abc";char str2[100] = "Abc";char str3[5] = { 'q','w','e','r' ,'\0' };printf("---------------------strupr(变大写)---------------------------\n");//细节:只能转换英文的大小写,不能修改中文的大小写strupr(str2);printf("%s\n",str2);return 0;
}🏙️指针
笔记
指针变量定义格式

获取了变量a的内存地址,再存储到指针p当中

指针使用细节
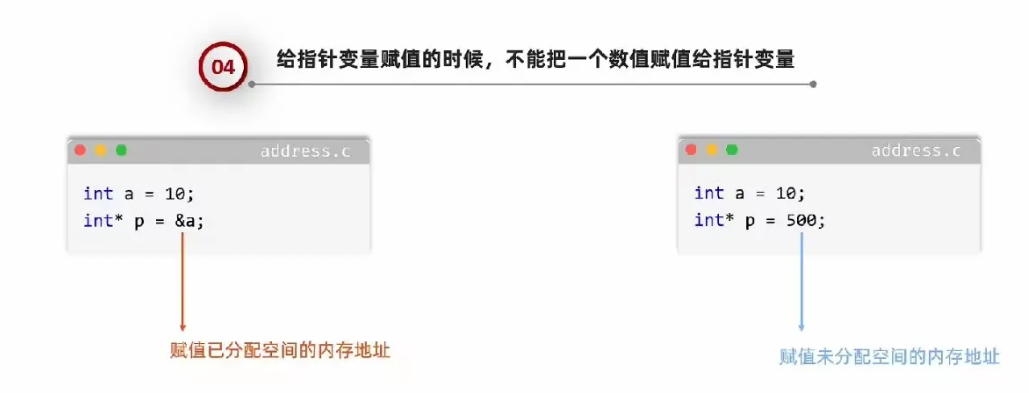
2个*是不一样的意思,
标记:表示只是一个指针,里面记录的是内存地址
查询时用到的*是解引用运算符,表示通过后面的内存地址去获取对应的数据
可以吧*p写在输出语句中,就可以看到程序运行结果

可以把*P写在等号左边,表示存储数据或者是修改数据

指针的作用


指针的第二个作用(函数返回多个值)
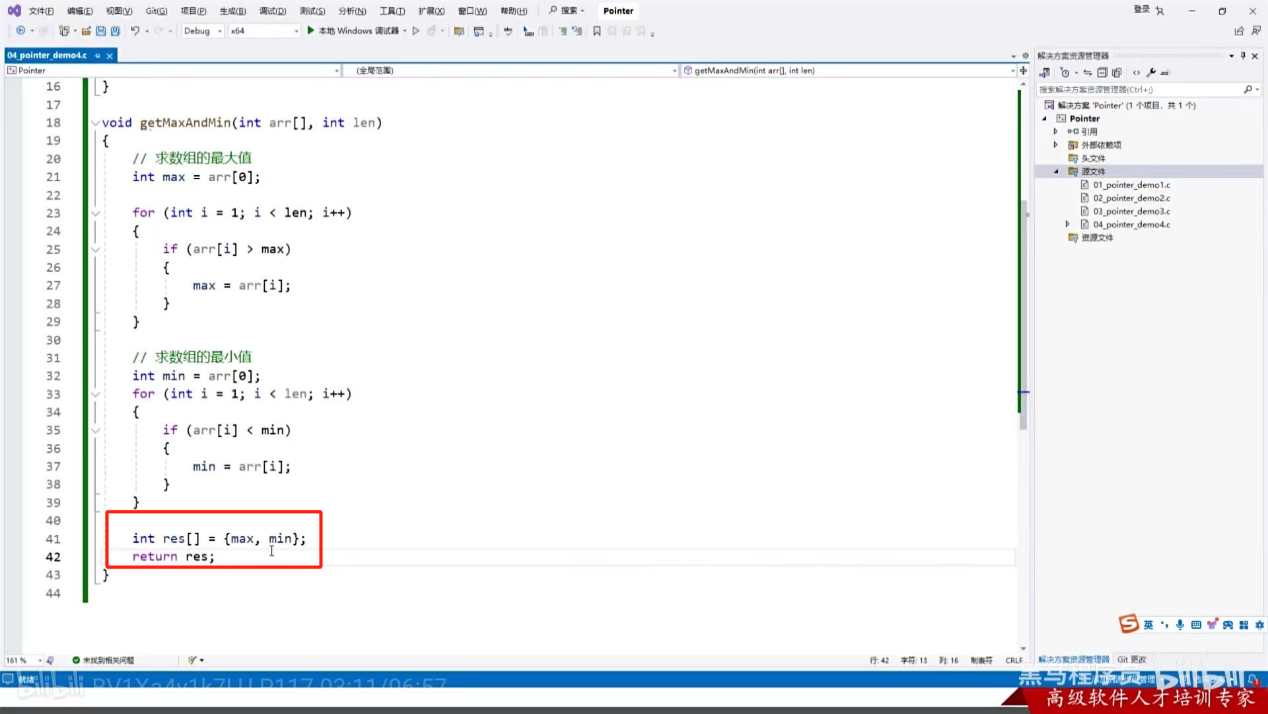
按照之前所学,我们在这个下面,不管写max还是min都是有问题的,按照以前所学,只能返回一个值
以上的那个方法是可行的,但是会给方法的调用者会有一个误解,他也不知道是零索引是最大还是最小,还得看下面的逻辑才能知道
数组指针
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{/*练习:利用指针遍历数组*///1.定义数组int arr[] = { 10,20,30,40,50 };int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int);//2.获取数组的指针//实际上获取的:数组的首地址int* p1 = arr;int* p2 = &arr[0];printf("%d\n", *p1);printf("%d\n", *(p1 + 1));//要是不加( ),相当于先获取到10,再拿着10+1,结果是11//改进:利用循环和指针遍历数组获取里面的每一个元素for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){printf("%d\n", *p1);p1++;//或者改成printf("%d\n",*p1++);}return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{//1.定义数组int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };//2.sizeof运算的时候,不会退化,arr还是整体printf("%zu\n", sizeof(arr));//40//3.&arr获取地址的时候,不会退化,记录的内存地址第一个元素的首地址,也是数组的首地址,步长:数据类型*数组的长度 40//arr参与计算的时候,也会退化为第一个元素的指针,记录的内存地址是第一个元素的首地址,也是数组的首地址,步长:数据类型 int 4printf("%p\n", arr);//000000000062FE20printf("%p\n", &arr);//000000000062FE20printf("%p\n", arr + 1);printf("%p\n", &arr + 1);return 0;}结构体
结构体格式

#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
struct GirlFriend {char name[100];int age;char gender;double height;
};
int main(){struct GirlFriend gf1;strcpy(gf1.name,"jjj");gf1.age = 18;gf1.gender = 'F';gf1.height = 1.78;printf("名字为:%s\n",gf1.name);printf("年龄为:%d\n",gf1.age);printf("性别为:%c\n",gf1.gender);printf("身高为:%.2lf",gf1.height);return 0 ;
}结构体数组
#include <stdio.h>
struct Student {char name[100];int age;
};int main(){//1.定义3个学生,同时进行赋值struct Student stu1 = { "zhangsan" ,23};struct Student stu2 = { "lisi",24 };struct Student stu3 = { "wangwu",25 };//2.把三个学生放入数组当中struct Student stuArr[3] = {stu1,stu2,stu3 };//stuArr为名字,容易看的名字//struct Student 是自己定义的类型//3.遍历数组得到每一个元素for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){struct Student temp = stuArr[i];//StuArr[i]这样就能获取数组里的每一个元素,其实就是每一个学生0,然后再把他赋值给一个临时变量printf("学生的信息为:姓名%s,年龄%d\n", temp.name, temp.age);}return 0;
}起别名
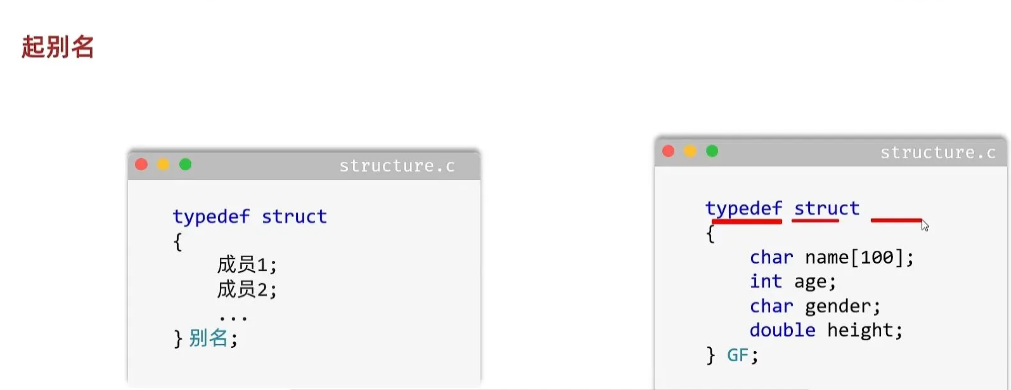
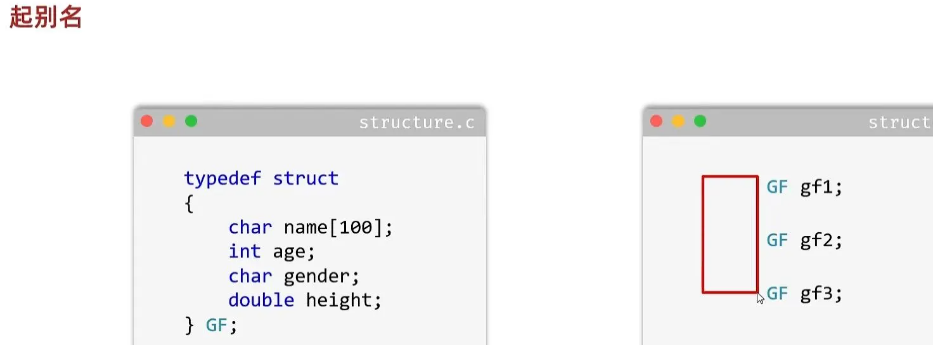
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct {char name[100];int attack;int defense;int blood;
}M;int main(){//1.定义奥特曼M taro = { "泰罗",100,90,500 };M rem = { "迪迦",90,80,500 };M daina = { "戴拿",100,99,599 };//2.定义数组M arr[3] = { taro,rem,daina };//3.遍历数组for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){M temp = arr[i];printf("奥特曼的名字为%s,攻击力是%d,防御力是%d,血量是%d\n", temp.name, temp.attack, temp.defense, temp.blood);}return 0;}结构体嵌套
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>struct Message{char phone[12];char mail[100];
};struct Student{char name[100];int age;char gender;double heigth;//因为此时还没有起别名,所以只要用到结构体前面必须要写structstruct Message msg;
};
int main(){/*定义一个结构体表示表示学生studentstudent成员如下:名字,年龄,性别,身高,联系方式联系方式Message也是一个结构体,成员如下手机号,电子邮箱*///1. 定义学生类型的变量struct Student stu;//2.给里面的每一个成员进行赋值strcpy(stu.name, "zhangtao");stu.age = 23;stu.gender = 'M';stu.heigth = 1.78;strcpy(stu.msg.phone, "13112345678");strcpy(stu.msg.mail, "12345678@qq.com");//3.输出打印printf("学生的信息为:\n");printf("姓名为:%s\n", stu.name);printf("年龄为:%d\n", stu.age );printf("性别为:%c\n", stu.gender);printf("身高为:%lf\n", stu.heigth);printf("手机号为:%s\n", stu.msg.phone);printf("邮箱为:%s\n", stu.msg.mail);printf("------------------------\n");//批量进行赋值struct Student stu2 = { "lixiang",24,'F',1.65,{"1311234567","5678@qq.com"} };//3.输出打印printf("学生的信息为:\n");printf("姓名为:%s\n", stu2.name);printf("年龄为:%d\n", stu2.age);printf("性别为:%c\n", stu2.gender);printf("身高为:%lf\n", stu2.heigth);printf("手机号为:%s\n", stu2.msg.phone);printf("邮箱为:%s\n", stu2.msg.mail);return 0;
}动态内存分配
常用函数

经验
1.字符串变量的定义关系char str[] = ""
2.计算次数,需要定义,给初始值”0“
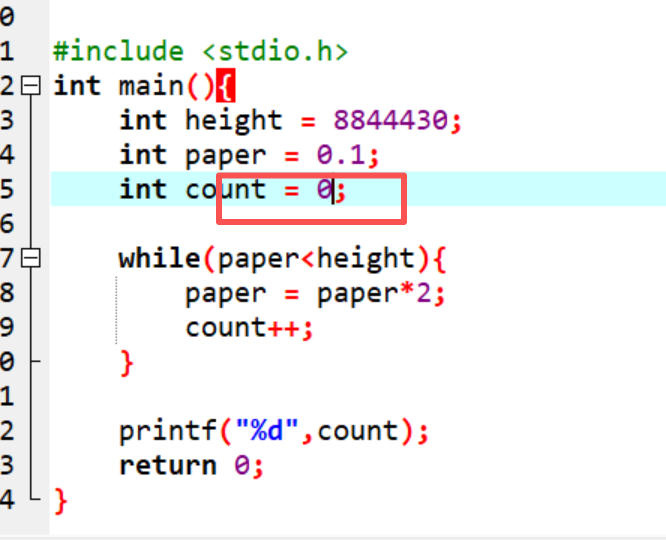
赋值赋值 ***
3.scanf,需要加”&“
4.数据类型的错误
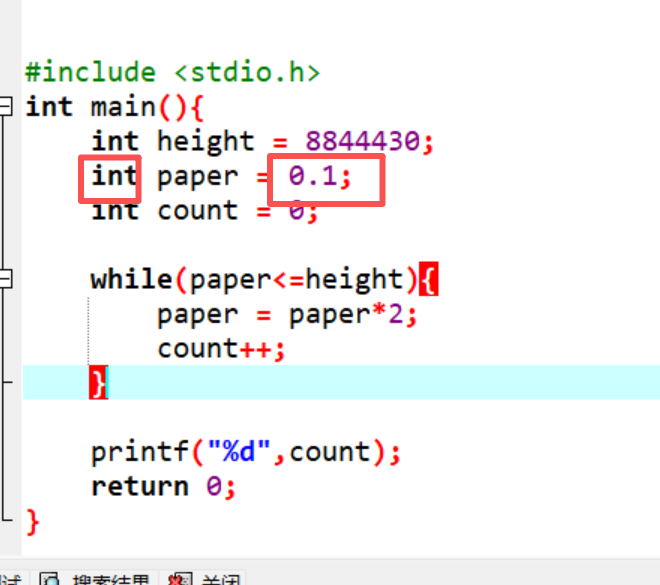
5.占位符用错
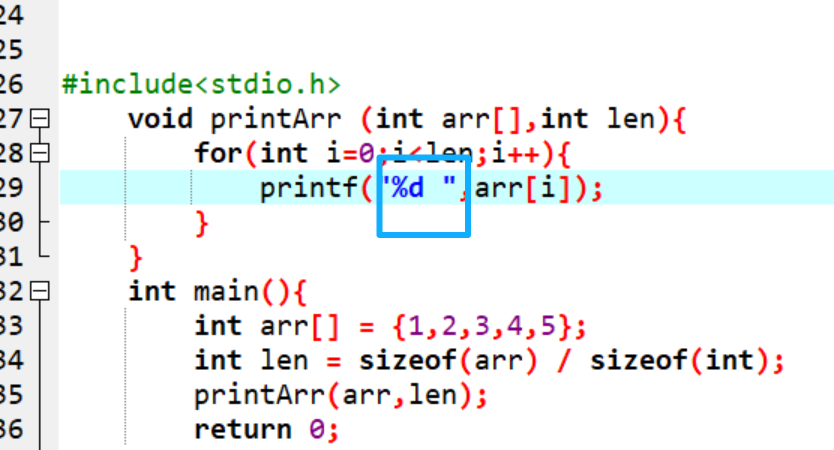
6.记得输出和输出的位置不要放错,***
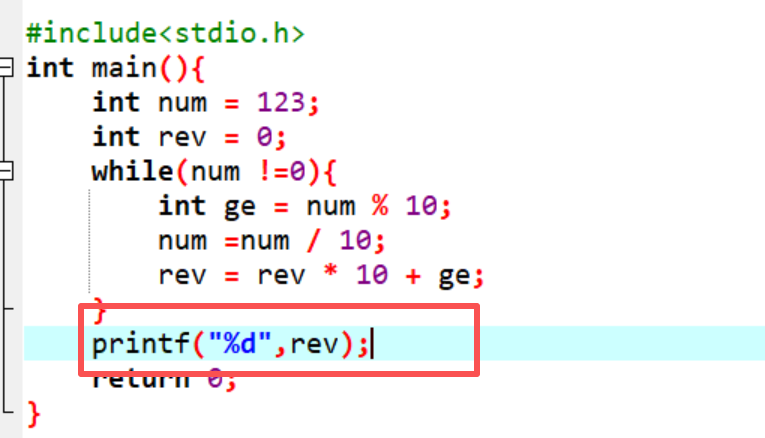
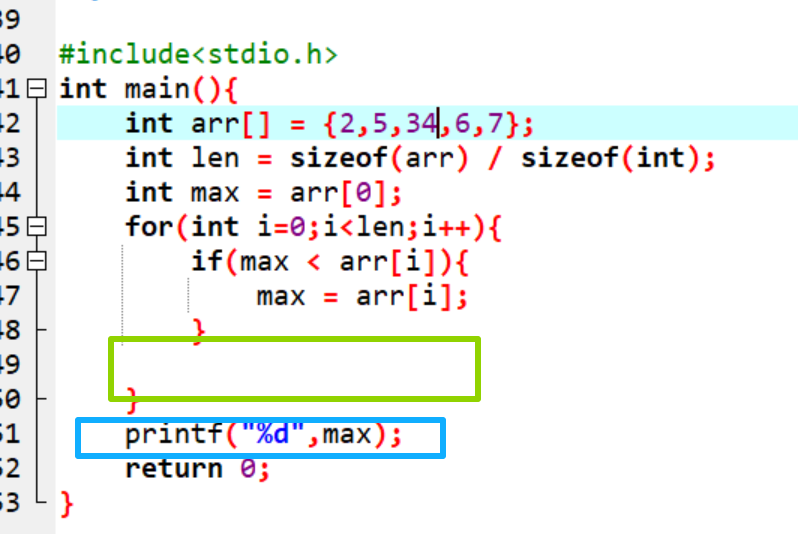
7.数组,记得加[ ],数组的大小设置**

8.函数声明