Arduino+AD9833测试!DDS
提示:本文内容仅供学习参考。Author: Jonnie Walker CGC
目录
前言
二、使用步骤
1.硬件
2.软件
1.Demo_1
2.Demo_2
3.测试数据
总结
前言
你好! 本文我们将使用AD9833指定输出不同波形的测试过程。从目录中你大概已经知道内容在讲什么了!这里我就不废话了!对于小白建议仔细往下看。
一、AD9833是什么?
AD9833是一种低功耗、可编程波形发生器,能产生正弦、三角形和正方形波形输出。输出频率和相位为软件可编程,允许轻松调整。没有外部组件是必需的。频率寄存器是28位宽:时钟频率为25MHz,分辨率可达0.1 Hz实现;时钟频率为1mhz时,AD9833可调至0.004 Hz分辨率。通过3线串行接口写入AD9833。这个系列接口工作在时钟频率高达40MHz,是兼容DSP和微控制器标准。
......。
主要性能参数:
1.工作电压: 2.3V 至 5.5V (兼容 3.3V 和 5V 系统)
2.输出波形: 正弦波、三角波、方波
3.最大输出频率: 理论上为参考时钟频率的一半(奈奎斯特定律),但实际上受限于内部DAC 的性能,纯净的正弦波输出通常推荐在 0 到 12 MHz。
4.频率分辨率: 28位(取决于频率调谐字的位数),在 25 MHz 时钟下,分辨率约为 0.1 Hz。
5.功耗: 非常低,在 3V 电压下约 5mW,非常适合电池供电设备。
6.控制接口: SPI 兼容的 3 线串行接口。
7.工作温度:−40℃~ +105℃
8.封装: MSOP-10
缺点:
1.输出幅度固定:如果需要调整幅度,需要外接放大器或数字电位器。
2.输出波形纯度:在较高频率时会下降,谐波分量会增加。
3.无法产生任意波形:只能产生内置的三种波形。
二、使用步骤
1.硬件
图1
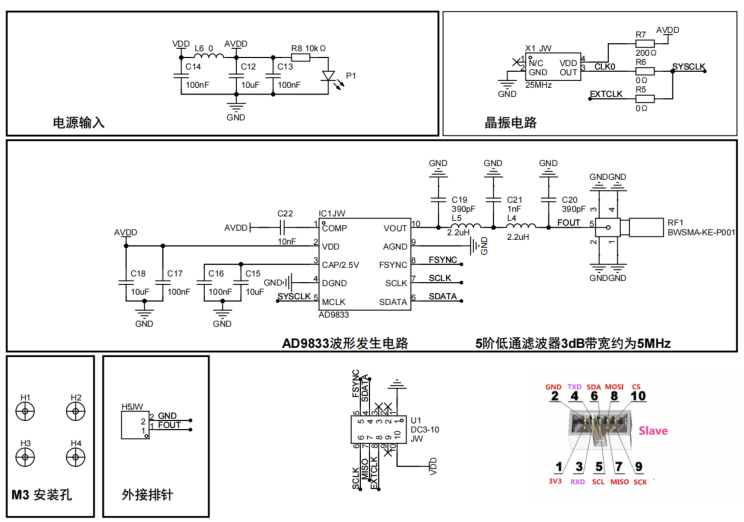
图2
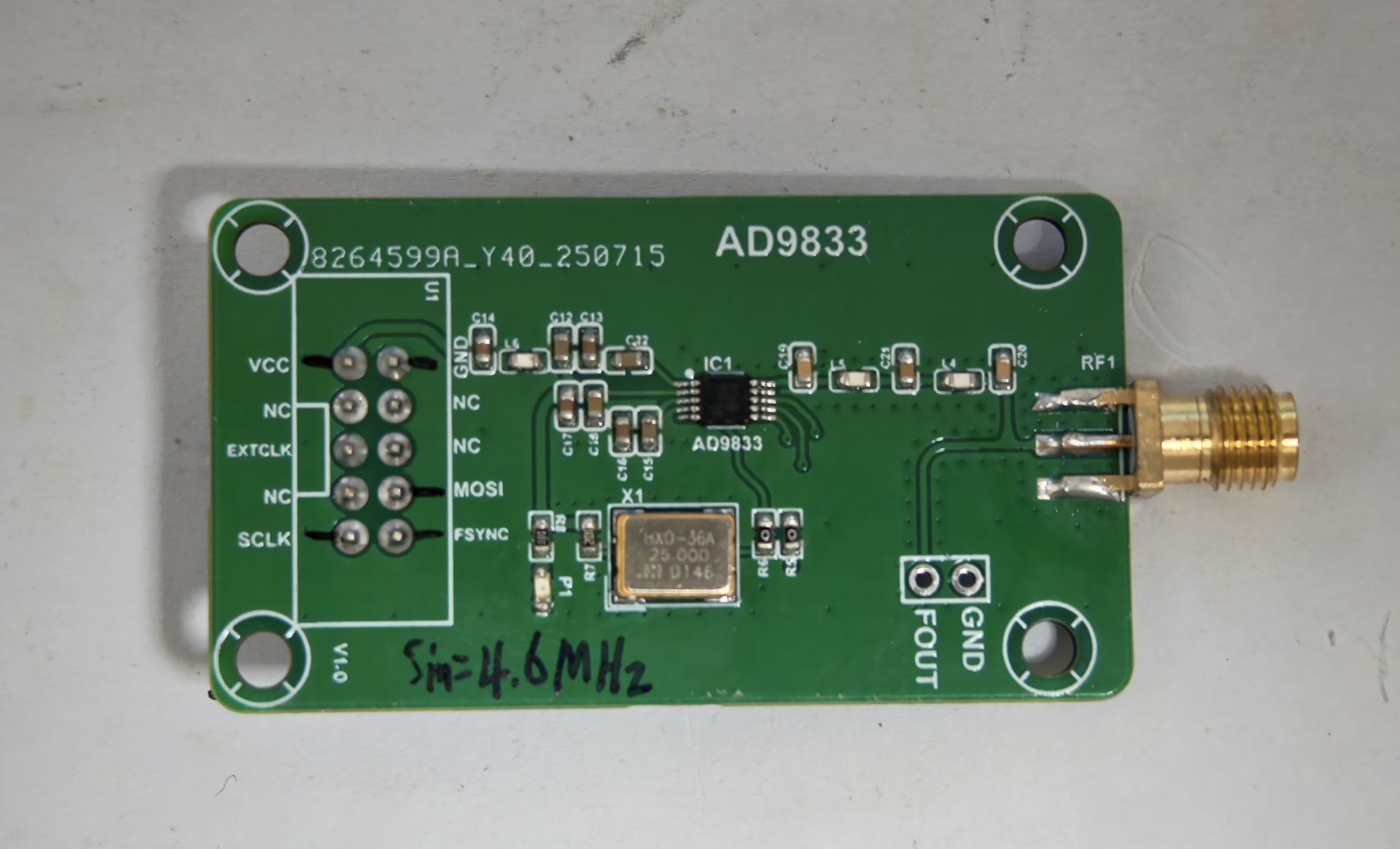

图2为本次测试的实物图,此硬件的带宽5MHz。
硬件通信引脚连接说明:
ArduinoUNO ------------ AD9833
SCK --13 --------------- CLK
MOSI--11 --------------- DAT
PIN4--4 ---------------- FNC
GND ----------------- GND
3.3V-5V ----------------- VCC
图3
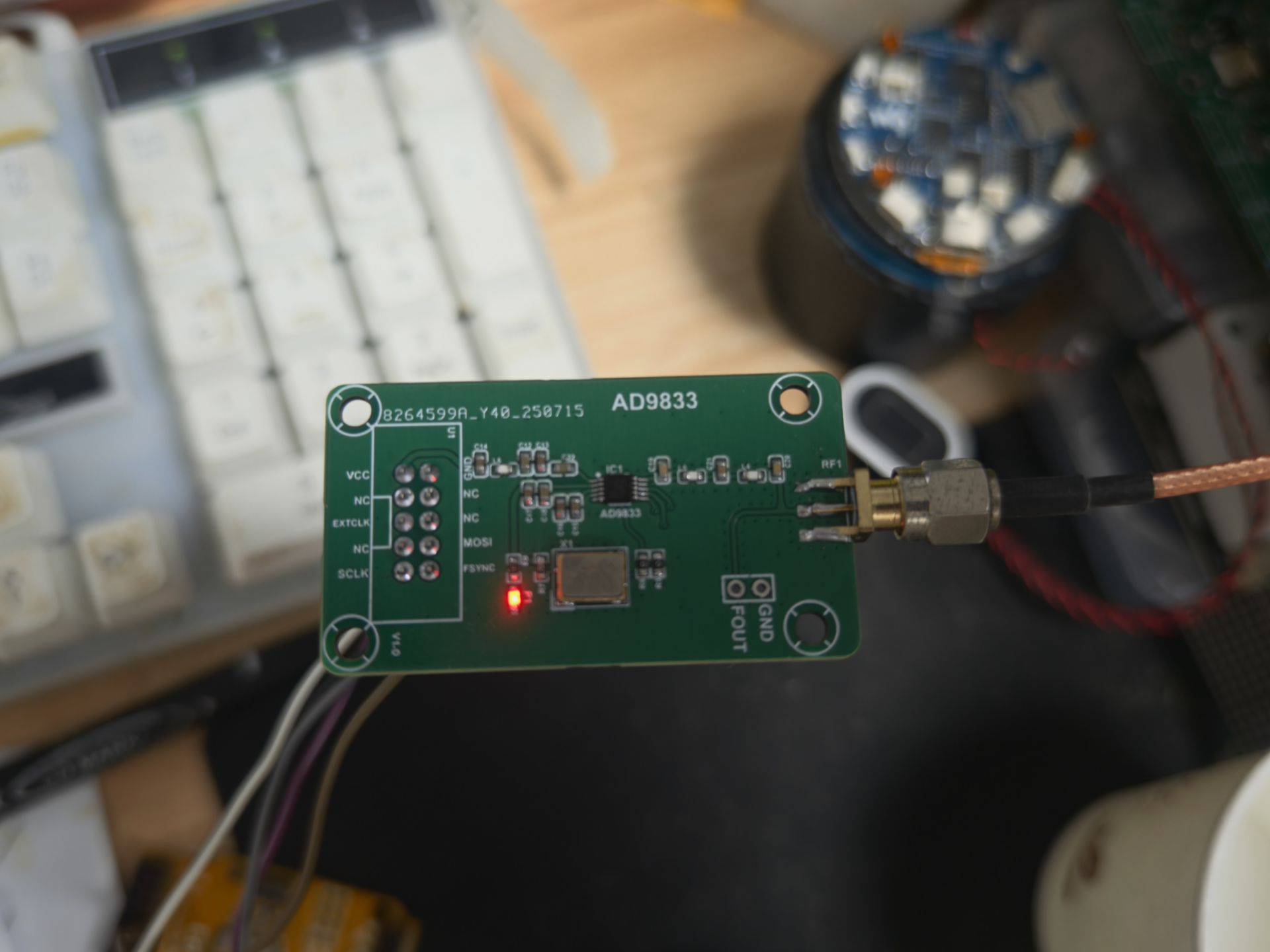

图3为实物测试连接图。
2.软件
测试条件:1.示波器 ,2.AD9833模块(图2)3.Arduino UNO开发板(不固定)
编译环境ArduinoIDE。在编译下面例程时需要安装:AD9833-Library-Arduino-master库文件。
要不然编译出错误!!!!
1.Demo_1
此程序需要结合串口工具,本次使用都是:XCOM V2.0。
比如:自定义频率需要通过串口工具发送5 指令,然后继续发送你需要设定的频率参数比如:1MHz,2MHz,3MHz。
/*** @file AD9833_test_suite.ino* @author Jonnie Wlaker CGC* @brief AD9833_Test2* @version 0.1* @date 2025-10-02* * @copyright Copyright (c) 2025* * ------------------------------------------------/* * 此例程需要结合串口工具,通过串口工具发送简单指令实现不同的功能,具体看一下loop()函数内容。* 在程序中我做了注释说明。* 在编译前先安装AD9833-Library-Arduino-master库。如果运行功能函数不知道起什么功能,可以去这 * 个库文件中查看具体封装函数信息!* * *//*ArduinoUNO AD9833-----------------SCK --13 CLKMOSI--11 DATPIN4--4 FNCGND GND3.3V-5V VCC*/#include <AD9833.h> #define RUNNING F("\tRUNNING")
#define NOT_RUNNING F("")
#define ON F("ON")
#define OFF F("OFF")
#define LED_PIN 13 // I'm alive blinker
#define FNC_PIN 4 // Any digital pin. Used to enable SPI transfers (active LO // Some macros to 'improve' readability
#define BLINK_LED digitalWrite(LED_PIN,millis()%1000 > 500);/** We need to manually call serialEventRun since we're not returning through the loop()* function while inside the test functions. If a character is in the receive buffer,* exit the test function. We also blink the I'm Alive LED to give a visual indication* that the program is not hung up.*/
#define YIELD_ON_CHAR if ( serialEventRun ) serialEventRun(); \if ( Serial.available() ) return; \BLINK_LED#define DELAY_WITH_YIELD for ( uint8_t i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) { \YIELD_ON_CHAR \delay(100); \}#define FLUSH_SERIAL_INPUT if ( serialEventRun ) serialEventRun(); \do { Serial.read(); delay(100); } while ( Serial.available() > 0 );//--------------- Create an AD9833 object ----------------
// Note, SCK and MOSI must be connected to CLK and DAT pins on the AD9833 for SPI
// ----- AD9833 ( FNCpin, referenceFrequency = 25000000UL )
AD9833 gen(FNC_PIN); // Defaults to 25MHz internal reference frequencyvoid setup() { pinMode(LED_PIN,OUTPUT);while (!Serial); // Delay until terminal opensSerial.begin(9600);// This MUST be the first command after declaring the AD9833 objectgen.Begin(); // The loaded defaults are 1000 Hz SINE_WAVE using REG0// The output is OFF, Sleep mode is disabledgen.EnableOutput(false); // Turn ON the outputPrintMenu(0,true); // Display menu for the first time
}void loop() { static bool outputOn = false;BLINK_LEDif ( Serial.available() ) {char ch = Serial.read();FLUSH_SERIAL_INPUTPrintMenu(ch,outputOn);//通过串口工具发送数据,控制一下功能!switch ( ch ) {case '1':IncrementFrequencyTest(); //将选择的频率寄存器增加freqIncHzbreak;case '2':CycleWaveformsTest(); //波形切换实现,循环切换所有波形类型break; case '3':SwitchFrequencyRegisterTest();break; case '4':PhaseTest();break;case '5':RequestedvsProgrammedValues(); //设置自定义频率break;case '6':outputOn = ! outputOn; //开启/关闭输出gen.EnableOutput(outputOn); // Turn off outputbreak;default:Serial.println(F("*** Invalid command ***"));break; } }
}/** Setup a manual ramp from a Start frequency to a Stop frequency in some increment* over a ramp time. */
void IncrementFrequencyTest ( void ) {float startHz = 1000, stopHz = 5000, incHz = 1, sweepTimeSec = 5.0;// Calculate the delay between each increment.uint16_t numMsecPerStep = (sweepTimeSec * 1000.0) / ((uint16_t)((stopHz - startHz) / incHz) + 1);if ( numMsecPerStep == 0 ) numMsecPerStep = 1;// Apply a signal to the output. If phaseReg is not supplied, then// a phase of 0.0 is applied to the same register as freqReggen.ApplySignal(SINE_WAVE,REG1,startHz);while ( true ) {gen.SetFrequency(REG1,startHz-incHz);for ( float i = startHz ; i <= stopHz; i += incHz ) {YIELD_ON_CHARgen.IncrementFrequency(REG1,incHz);delay(numMsecPerStep); }}
}/** Cycle through all of the waveform types. Also cycle the * frequency registers.*/
void CycleWaveformsTest ( void ) {WaveformType waveType = SINE_WAVE;// 设置两个寄存器为相同波形gen.SetFrequency(REG0,10000.0); // Load valuesgen.SetFrequency(REG1,1000.0);// We don't care about phase for this testwhile ( true ) {gen.SetWaveform(REG1,waveType); // Next waveform , 设置波形类型(核心函数)gen.SetWaveform(REG0,waveType);gen.SetOutputSource(REG1); // Output 1000 Hz waveform// Hack to allow I'm alive lamp a chance to blink and give a better// response to user inputDELAY_WITH_YIELDgen.SetOutputSource(REG0); // Output 10000 Hz waveformDELAY_WITH_YIELD// 切换波形类型switch ( waveType ) { // Cycle through all the waveform typescase SINE_WAVE:waveType = TRIANGLE_WAVE;break;case TRIANGLE_WAVE:waveType = SQUARE_WAVE;break;case SQUARE_WAVE:waveType = HALF_SQUARE_WAVE;break;case HALF_SQUARE_WAVE:waveType = SINE_WAVE;break; }}
}/** Fast switching example.* I use the FFT display capability on my scope*/
void SwitchFrequencyRegisterTest ( void ) {gen.ApplySignal(SINE_WAVE,REG0,500000);gen.ApplySignal(SINE_WAVE,REG1,100000);gen.SetPhase(REG1,180); // Offset second freq by 180 deggen.Reset();while ( true ) { // This takes timeYIELD_ON_CHAR // This takes more timegen.SetOutputSource(REG0); // This takes about 18 usecgen.SetOutputSource(REG1); // This takes about 18 usec // What ends up is REG0 frequency is active a shorter amount of time// then REG1 frequency. In the sepctrum, the duty cycle differences will// show up (power is lower by 10log(DC))}
}/** Phase shift between REG0 and REG1. Use a oscilloscope set to Normal* triggering, AC coupling, 500usec/div, 100 mV/div. This will display* about two cycles for register 0, 4 cycle for register 1, plus dead * time for the Reset.* Use Normal triggering so the display remains even when triggering is * lost. Can use any waveform for this test. Remember that the square * wave is about 5v-pp while sine and triangle are about 600 mv-pp*/
void PhaseTest ( void ) {gen.ApplySignal(TRIANGLE_WAVE,REG0,1000);gen.ApplySignal(SINE_WAVE,REG1,2000);bool reverse = true;while ( true ) {reverse = ! reverse;for ( int16_t i = 0; i <= 360; i += 1 ) {if ( ! reverse )gen.IncrementPhase(REG1,-1);elsegen.IncrementPhase(REG1,1);YIELD_ON_CHAR/** Display ~ 2 cycles using REG0 phase. If no REG is supplied for phase,* defaults to REG specified for frequency. RESET is removed during this* function call.*/gen.SetOutputSource(REG0); /** This is just a wag to try to get exactly 2 cycles of the waveform. * It makes the phase alignments easier to verify.*/delayMicroseconds(1900);YIELD_ON_CHAR/* This also works if you keep using REG1 for frequency* Now display ~ 4 cycles using REG1*/gen.SetOutputSource(REG1);delayMicroseconds(1950);/** Turn off for remaining trace. Reset the registers so triggering occurs * on the start of REG0 signal. Reset() includes 15 msec delay which is good * to ensure sweep is completed. * I tried using EnableOutput(true) then EnableOutput(false) in this* loop but could not get reliable triggering on the scope.* * The difference between Reset() and EnableOutput(false) is that EnableOutput(false)* keeps the AD9833 in RESET until you specifically remove the RESET using * EnableOutput(true). However, after a call to Reset(), calls to ANY function * EXCEPT Set/Increment Phase will also remove the RESET.* */gen.Reset(); if ( i % 90 == 0 )delay(1000); // Stop and show phase alignment between REG0 REG1}}
}/** Show the requested versus actual programmed values for frequency and phase* Also show resolution, max frequency (based on refFrequency)*/
void RequestedvsProgrammedValues ( void ) {float requestedFrequency, programmedFrequency;char buffer[20]; // 14 characters actually needed for display gen.ApplySignal(SINE_WAVE,REG0,1000.0); //产生正弦波,//产生方波// gen.ApplySignal(SQUARE_WAVE, REG0, 2000.0); // 2kHz方波//产生三角波//gen.SetWaveform(REG1, TRIANGLE_WAVE); // 设置波形//gen.SetFrequency(REG1, 500.0); // 500Hz频率//gen.SetOutputSource(REG1); // 选择寄存器while ( true ) {FLUSH_SERIAL_INPUTSerial.println(F("\nEnter frequency ('Q' to quit) >"));while ( !Serial.available() ) BLINK_LEDif ( toupper(Serial.peek()) == 'Q' ) {// Need an extra <CR> ?FLUSH_SERIAL_INPUT // why isn't this flushing input?return;}requestedFrequency = Serial.parseFloat();gen.SetFrequency(REG0,requestedFrequency);programmedFrequency = gen.GetActualProgrammedFrequency(REG0);Serial.print(F("Requested :"));dtostrf(requestedFrequency,14,5,buffer); Serial.print(buffer);Serial.print(F(" Actual :"));dtostrf(programmedFrequency,14,5,buffer); Serial.println(buffer); }
}/* * Display the command menu*/
void PrintMenu ( char ch, bool outputOn ) {Serial.println(); Serial.println();Serial.println(F("****** AD9833 Test Menu ******\n"));Serial.print(F("'1' IncrementFrequencyTest"));Serial.println(ch == '1' ? RUNNING : NOT_RUNNING);Serial.print(F("'2' CycleWaveformsTest\t"));Serial.println(ch == '2' ? RUNNING : NOT_RUNNING);Serial.print(F("'3' SwitchFrequencyRegisterTest"));Serial.println(ch == '3' ? RUNNING : NOT_RUNNING);Serial.print(F("'4' PhaseTest\t\t"));Serial.println(ch == '4' ? RUNNING : NOT_RUNNING);Serial.print(F("'5' RequestedvsProgrammedValues"));Serial.println(ch == '5' ? RUNNING : NOT_RUNNING);Serial.print(F("'6' Output ")); if ( ch == '6' ) { if ( outputOn ) Serial.println(OFF);else Serial.println(ON);}else {if ( outputOn ) Serial.println(ON);else Serial.println(OFF); }Serial.println(F("Enter a number 1 to 6 >"));
}
2.Demo_2
/*** @file ApplySignal-3T.ino* @author Jonnie Wlaker CGC* @brief AD9833_Test1* @version 0.1* @date 2025-10-02* * @copyright Copyright (c) 2025* * -----------------------------------------------------------/* * 此程序测试硬件Arduino UNO。如果你使用的其他硬件请你修改SPI通信引脚,在这个程序中没有看到引 * 脚定义是因为默认硬件为UNO开发板引脚定义被封装,* 所以你需要去查看SPI通信封装内容或调用SPI的API函数重新定义引脚。* * 在编译前先安装AD9833-Library-Arduino-master库。如果运行功能函数不知道起什么功能,可以去这 * 个库文件中查看具体封装函数信息!* * */
/*ArduinoUNO AD9833----------------------SCK --13 CLKMOSI--11 DATPIN4--4 FNCGND GND3.3V-5V VCC*/#include <AD9833.h> // Include the library#define FNC_PIN 4 // Can be any digital IO pin//--------------- Create an AD9833 object ----------------
// Note, SCK and MOSI must be connected to CLK and DAT pins on the AD9833 for SPI
AD9833 gen(FNC_PIN); // Defaults to 25MHz internal reference frequencyvoid setup() {// This MUST be the first command after declaring the AD9833 objectgen.Begin(); //产生正弦波gen.ApplySignal(SINE_WAVE,REG0,1000); // 1kHz正弦波//产生三角波//gen.SetWaveform(REG1, TRIANGLE_WAVE); // 设置波形//gen.SetFrequency(REG1, 500.0); // 500Hz频率//gen.SetOutputSource(REG1); // 选择寄存器//产生方波// gen.ApplySignal(SQUARE_WAVE, REG0, 2000.0); // 2kHz方波gen.EnableOutput(true); // Turn ON the output - it defaults to OFF// There should be a 1000 Hz sine wave on the output of the AD9833
}void loop() {// To change the signal, you can just call ApplySignal again with a new frequency and/or signal// type.
}
在Demo_2程序中分别有3处地方需要你自己去修改:
1.产生正弦波
2.产生三角波
3.产生方波
通过添加或取消注释符分别开启相应的功能,程序中已经有说明了!
3.测试数据
图4
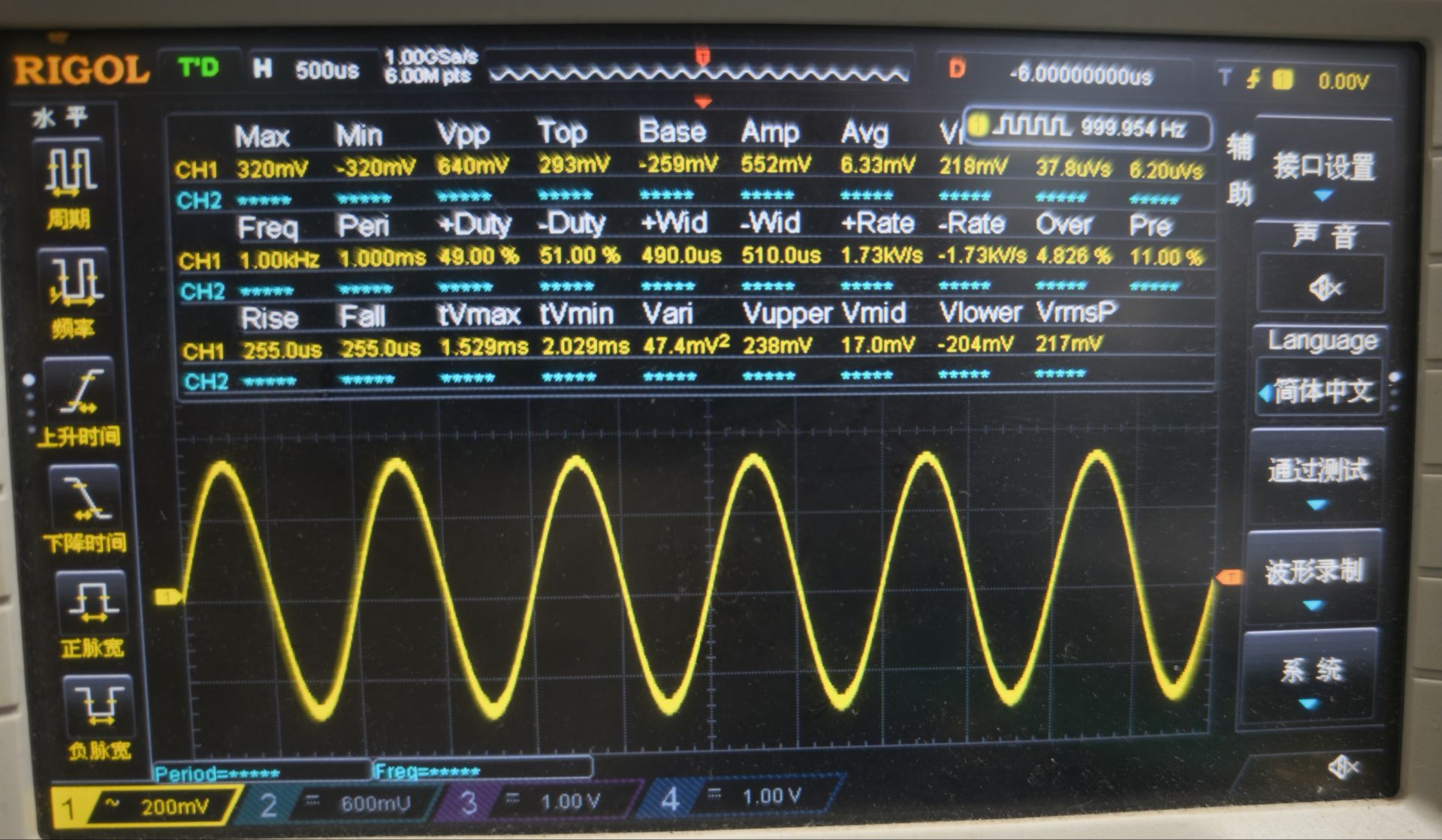
图4中测试频率:1KHz ,输出正弦波 。
图5
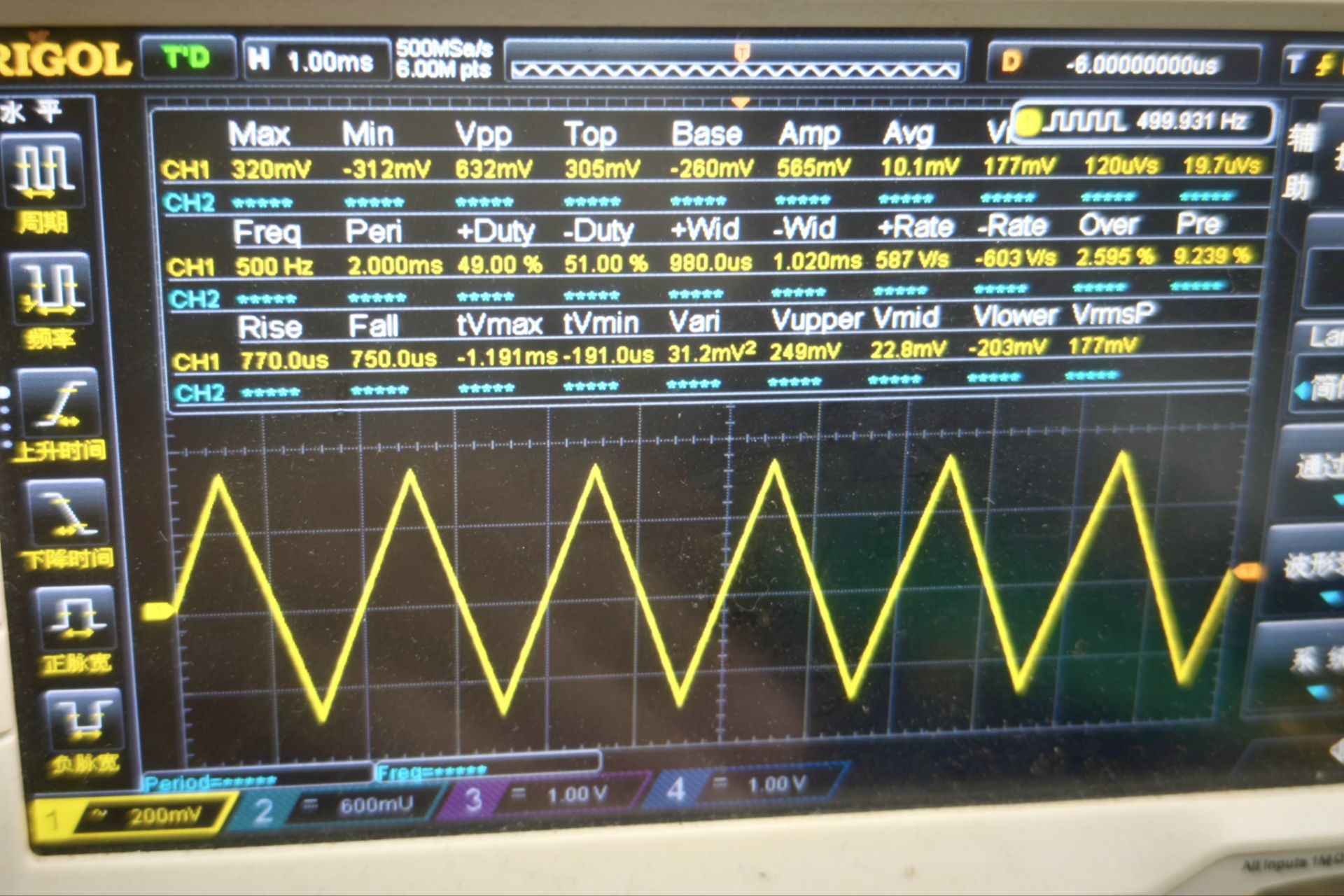
图5中测试频率:500Hz ,输出三角波 。
图6
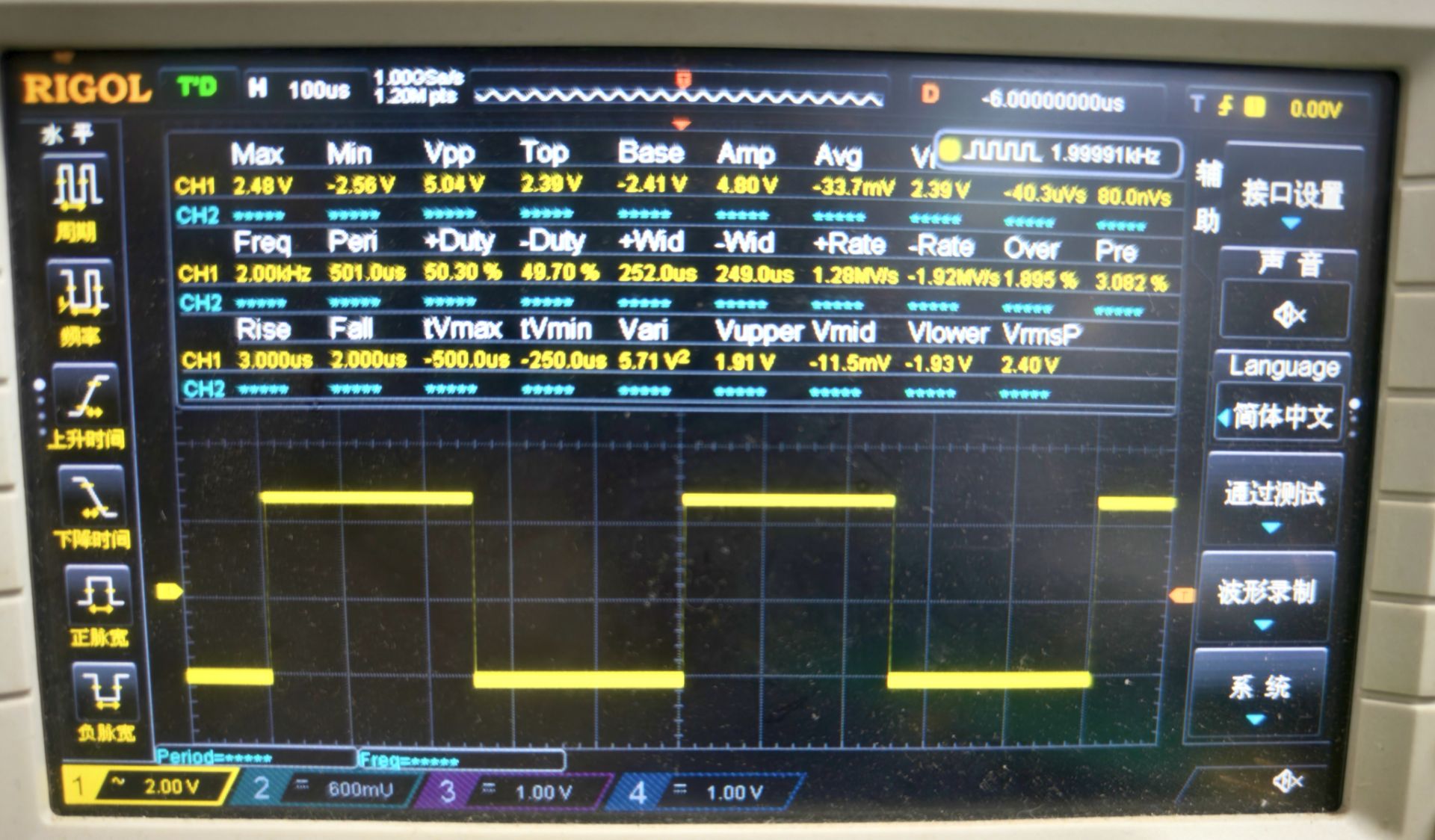
图6中测试率:2KHz ,输出方波 。
图7
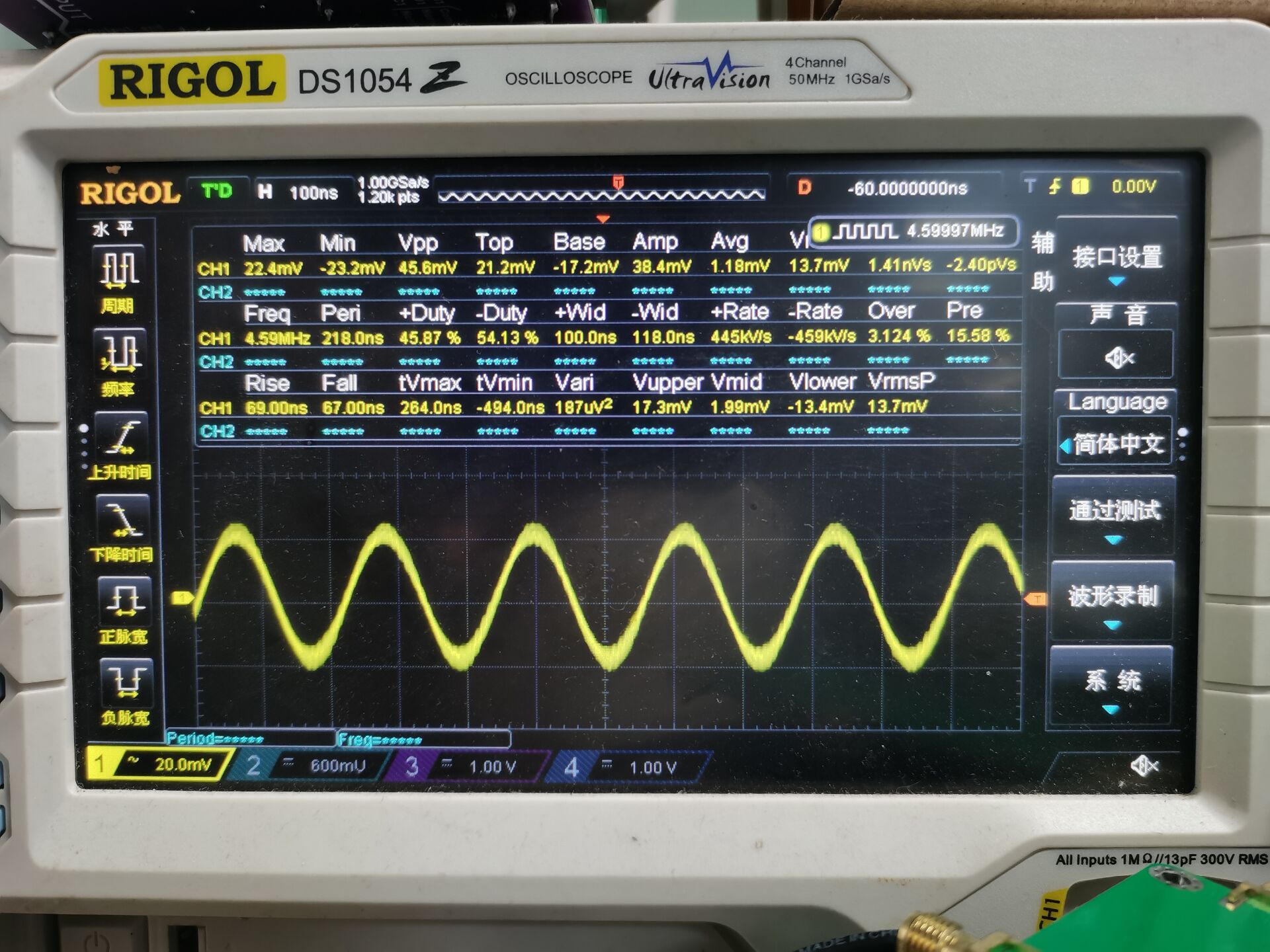
图7中波形是本次测试硬件最大频率稳定波形图,带宽频率:4.59MHz.,输出正弦波。
下面是超出硬件带宽5MHz,测试数据图形:
图8
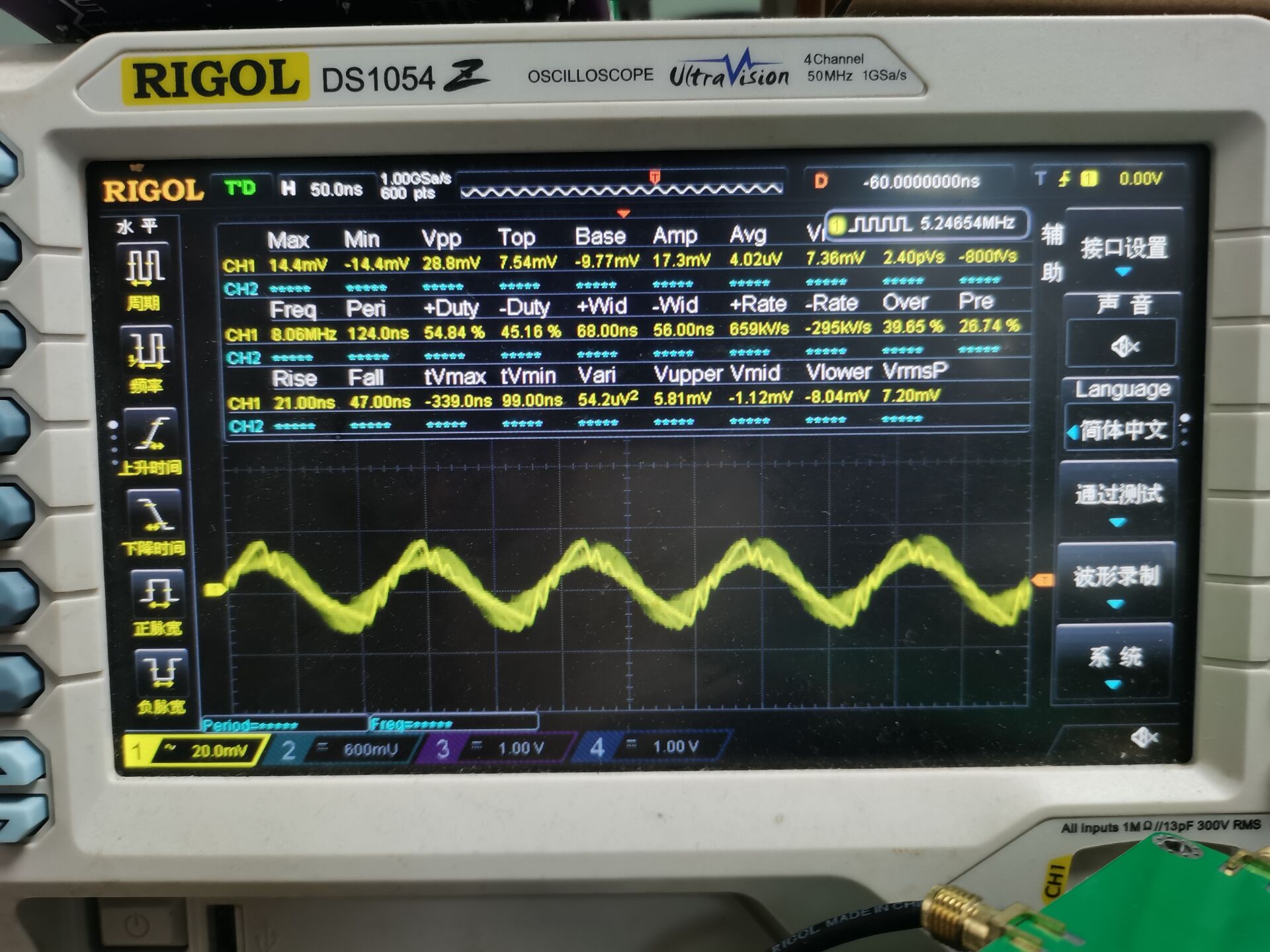
图9
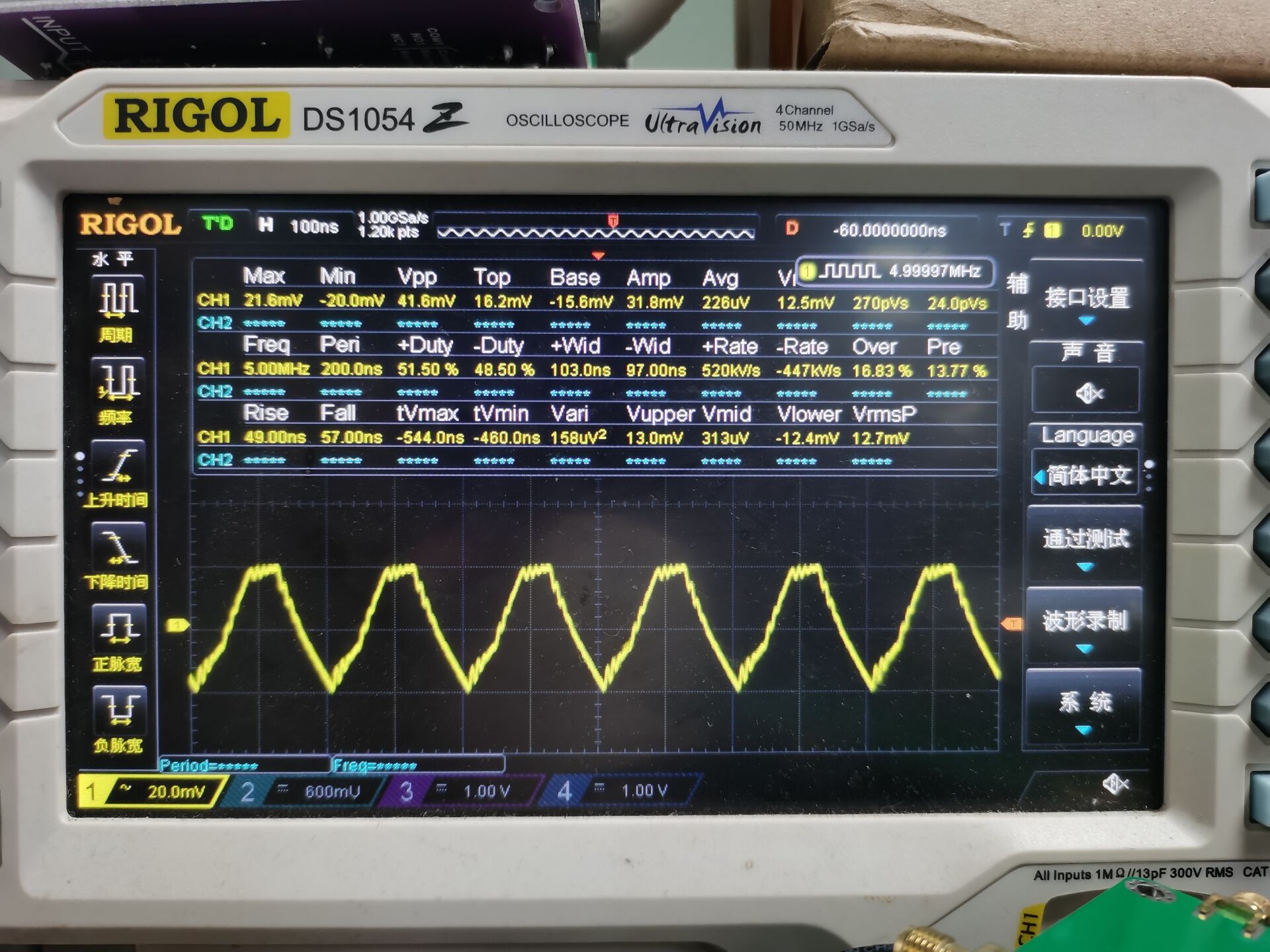
图10
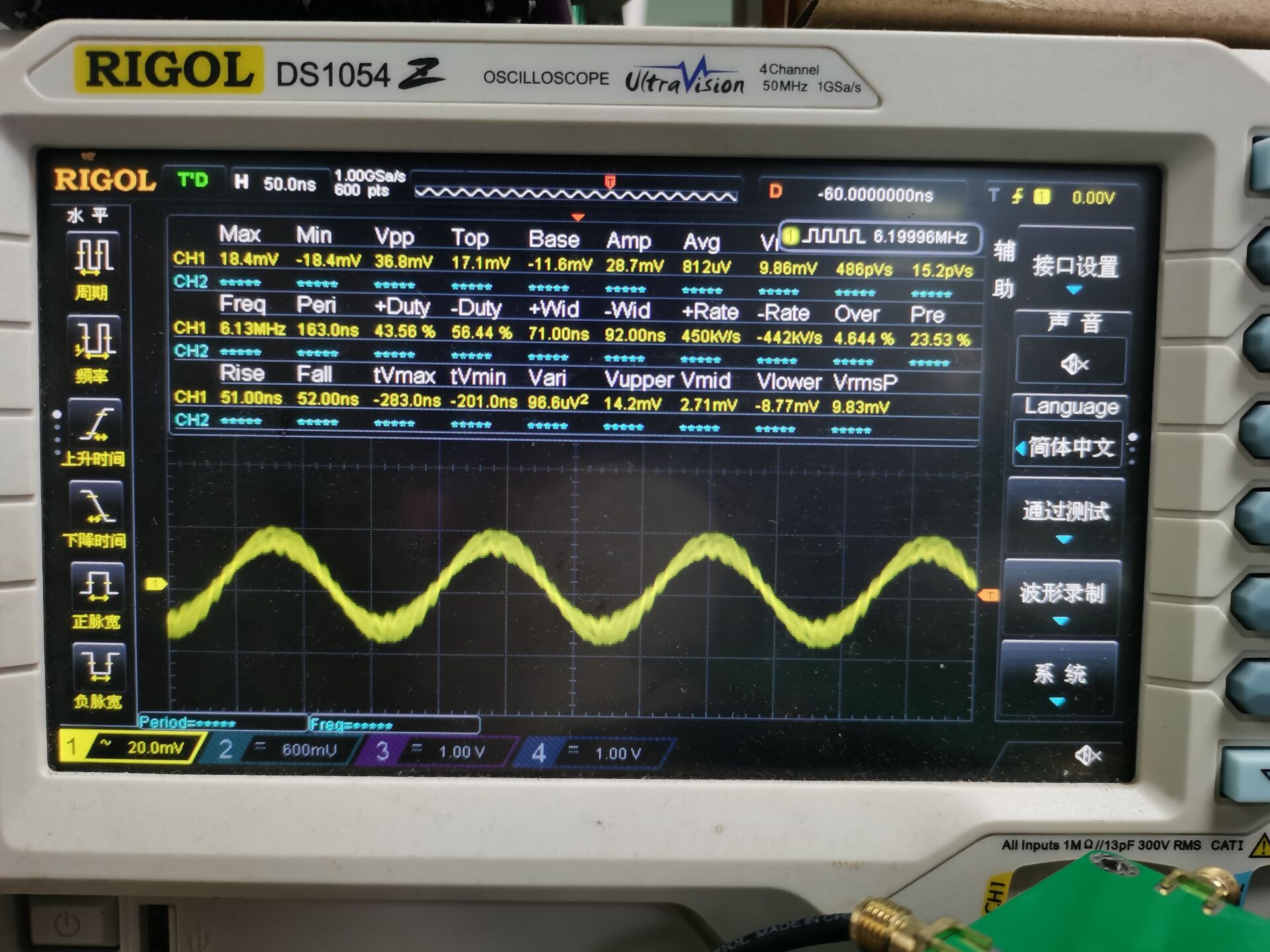
从图8,图9,图10波形图中可以看出测试的波形已经突变了!
总结
AD9833 是一款将数字世界的精确性与模拟世界连接起来的桥梁芯片。 它让用户能够以极低的成本和简单的操作,生成一个在传统模拟电路中需要复杂、昂贵且不稳定的元器件才能产生的精密波形。对于任何需要可编程信号源的项目来说,它都是一个非常出色的选择。
所以本文通过结合硬件和软件简单测试 ,展示AD9833基本功能使用步骤。
感谢你能看到这里!CGC
