树的遍历方式总结
以此树为demo
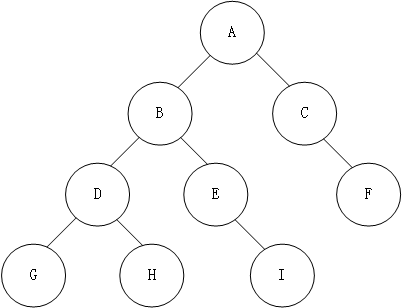
先序遍历
定义:优先访问根节点,然后访问左子树,最后访问右子树,根节点->左子树->右子树
按照定义,那么上述demo的结果可以很好得出来:A->B->D->G->H->E->I->C->F
那么算法怎么实现呢?这里使用递归方法:
public static void nlr(TreeNode rootNode) {TreeNode leftChild;TreeNode rightNode;if (rootNode != null) {System.out.print(rootNode.data+" ");leftChild = rootNode.leftChild;nlr(leftChild);rightNode = rootNode.rightChild;nlr(rightNode);}
}
运行结果如下:
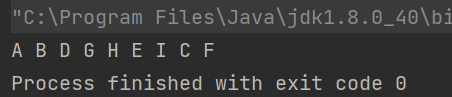
中序遍历
定义:优先访问左子树,然后访问根节点,然后访问右子树,左子树->根节点->右子树
按照定义,那么上述demo的结果可以很好得出来:G->D->H->B->E-I->A->C->F
public static void lnr(TreeNode rootNode) {TreeNode leftChild;TreeNode rightNode;if (rootNode != null) {leftChild = rootNode.leftChild;lnr(leftChild);System.out.print(rootNode.data+" ");rightNode = rootNode.rightChild;lnr(rightNode);}
}
运行结果如下:
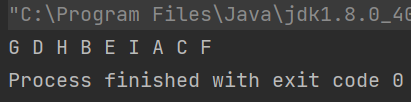
后续遍历
定义:优先访问左子树,然后访问右子树,然后访问根节点,左子树->右子树->根节点
按照定义,那么上述demo的结果可以很好得出来:G->H->D->I->E->B->F->C->A
public static void lrn(TreeNode rootNode) {TreeNode leftChild;TreeNode rightNode;if (rootNode != null) {leftChild = rootNode.leftChild;lrn(leftChild);rightNode = rootNode.rightChild;lrn(rightNode);System.out.print(rootNode.data+" ");}
}
运行结果如下:
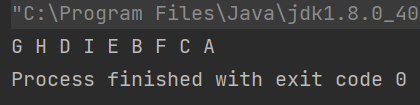
按层遍历
定义:广度优先遍历,优先访问节点的左子树和右子树
使用队列方式来,每个节点判断一下有没有左右子树,有的话直接offer进队列,然后不停的输出队列即可
public static void storey(TreeNode rootNode) {//使用队列,先进先出Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(rootNode);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode t = queue.poll();System.out.print(t.data+" ");if (t.leftChild != null) {queue.offer(t.leftChild);}if (t.rightChild != null) {queue.offer(t.rightChild);}}
}
运行结果:
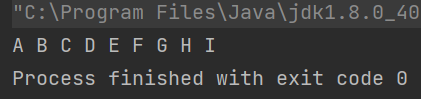
获取层数(获取二叉树最大深度)
相当于按层遍历的进阶了
public static void storey2(TreeNode rootNode) {//使用队列,先进先出Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(rootNode);int n;int levelN = 1;int count = 0;System.out.print(rootNode.data);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {n = levelN; //上一层的节点数量赋值给nlevelN = 0; //清空leveN,开始重新计算当前行的节点数,给下一层使用System.out.println();for (int i=0;i<n;i++) { //n表示这一行的所有节点数量,n的值依赖于上一层的levelN的值TreeNode t = queue.poll();if (t.leftChild != null) {queue.offer(t.leftChild);levelN++; //节点数量+1System.out.print(t.leftChild.data+" ");}if (t.rightChild != null) {queue.offer(t.rightChild);levelN++; //节点数量+1System.out.print(t.rightChild.data+" ");}}count++; //开始换行}System.out.print("行数:"+count);
}
运行结果如下:
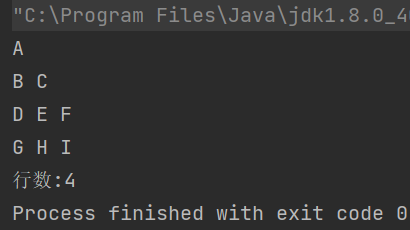
优化写法:leftchild和rightchild offer进队列的时候,不急着poll出来,等到当前层的所有节点的左右子树都offer进去的时候,再进行下一次循环,这时候队列数量就是当前层的节点数量,然后继续下一层遍历,本质上和上文写的逻辑一样,只不过不需要额外的变量了。
public static void storey2(TreeNode rootNode) {//使用队列,先进先出Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(rootNode);int count = 0;System.out.print(rootNode.data);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int n = queue.size(); //临时保存队列数量,队列数量就是当前层节点数量System.out.println();for (int i=0;i<n;i++) { //循环当前层的节点数量TreeNode t = queue.poll();if (t.leftChild != null) {queue.offer(t.leftChild);System.out.print(t.leftChild.data+" ");}if (t.rightChild != null) {queue.offer(t.rightChild);System.out.print(t.rightChild.data+" ");}}count++;}System.out.print("行数:"+count);
}
其他二叉树的进阶算法,后续记录在leetcode分类栏目中
