Bean的生命周期(二)
Bean的生命周期主要围绕对象的创建、依赖注入、对象的初始化、对象的销毁展开的。除了这几个主要的阶段,其它的都是围绕着这四个阶段前后通过Bean后处理器作拓展。我们可以自定义一个Bean的后处理器进行调试。
1.自定义Bean后处理器
通过实现下面两个接口并重写里面的方法,便可以对容器里面的Bean作拓展,为测试方便,只对我们自己写的类作拓展。
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
package com.example.demo2;import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** @author zhou* @version 1.0* @description TODO* @date 2025/9/30 21:06*/
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyBeanPostProcessor.class);@Overridepublic Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {if(beanName.equals("lifeCycleBean")){log.info("<<<<<<<实例化之前执行,返回的对象会替换掉原本的bean");}return null;}@Overridepublic boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {if(beanName.equals("lifeCycleBean")){log.info("<<<<<<<实例化之后执行,如果返回false会跳过依赖注入阶段");}return true;}@Nullablepublic PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {if(beanName.equals("lifeCycleBean")){log.info("<<<<<<<依赖注入阶段执行,如@Autowired,@Value,@Resource");}return pvs;}@Overridepublic void postProcessBeforeDestruction(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {if(beanName.equals("lifeCycleBean")){log.info("<<<<<<<销毁之前执行,效果类似@PreDestroy");}}@Overridepublic Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {if(beanName.equals("lifeCycleBean")){log.info("<<<<<<<初始化之前执行,返回的对象会替换掉原本的bean,如@PostConstruct、@ConfigurationProperties");}return bean;}@Overridepublic Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {if(beanName.equals("lifeCycleBean")){log.info("<<<<<<<初始化后执行,返回的对象会替换掉原本的bean,如代理增强");}return bean;}
}
2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//package org.springframework.beans.factory.config;import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;public interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {@Nullabledefault Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {return null;}default boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {return true;}@Nullabledefault PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {return pvs;}
}
3.DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor接口
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//package org.springframework.beans.factory.config;import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;public interface DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {void postProcessBeforeDestruction(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;default boolean requiresDestruction(Object bean) {return true;}
}
4.BeanPostProcessor接口
上面两个接口都继承自这个接口。
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//package org.springframework.beans.factory.config;import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;public interface BeanPostProcessor {@Nullabledefault Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {return bean;}@Nullabledefault Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {return bean;}
}
5.主类调用
package com.example.demo2;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;@SpringBootApplication
public class Demo2Application {public static void main(String[] args) {ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(Demo2Application.class, args);context.close();}}
package com.example.demo2;import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;/*** @author zhou* @version 1.0* @description TODO* @date 2025/9/29 21:48*/
@Component
public class LifeCycleBean {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LifeCycleBean.class);public LifeCycleBean(){log.info("构造方法");}@Autowiredpublic void autowire(@Value("${JAVA_HOME}") String home){log.info("依赖注入: {}",home);}@PostConstructpublic void init(){log.info("初始化");}@PreDestroypublic void destroy(){log.info("销毁");}
}
6.结果输出
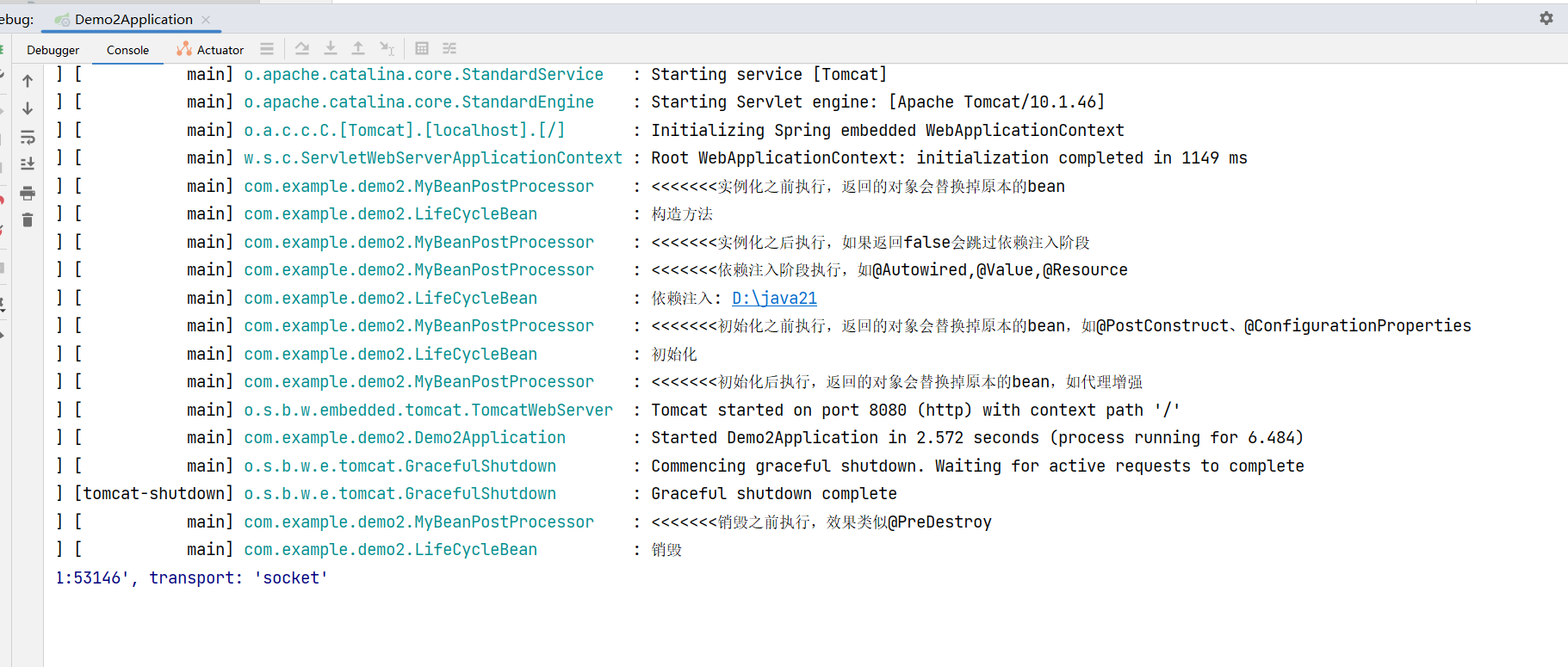
通过结果可以看到我们重写的各个方法执行的时机,上面输出的调试顺序也代表着Bean的生命周期。
