identity mapping kernel image mapping
create_table_entry
这个宏定义主要是用来创建一个中间level的translation table中的描述符。如果用linux的术语,就是创建PGD、PUD或者PMD的描述符。如果用ARM64术语,就是创建L0、L1或者L2的描述符。具体创建哪一个level的Translation table descriptor是由tbl参数指定的,tbl指向了该translation table的内存。virt参数给出了要创建地址映射的那个虚拟地址,shift参数以及ptrs参数是和具体在哪一个entry中写入描述符有关。我们知道,在定位页表描述的时候,我们需要截取虚拟地址中的一部分做为offset(index)来定位描述符,实际上,虚拟地址右移shift,然后截取ptrs大小的bit field就可以得到entry index了。tmp1和tmp2是临时变量。 create_table_entry的代码如下:
/*
* Macro to create a table entry to the next page.
*
* tbl: page table address
* virt: virtual address
* shift: #imm page table shift
* ptrs: #imm pointers per table page
*
* Preserves: virt
* Corrupts: ptrs, tmp1, tmp2
* Returns: tbl -> next level table page address
*/
.macro create_table_entry, tbl, virt, shift, ptrs, tmp1, tmp2
add \tmp1, \tbl, #PAGE_SIZE
phys_to_pte \tmp2, \tmp1
orr \tmp2, \tmp2, #PMD_TYPE_TABLE // address of next table and entry type
lsr \tmp1, \virt, #\shift
sub \ptrs, \ptrs, #1
and \tmp1, \tmp1, \ptrs // table index
str \tmp2, [\tbl, \tmp1, lsl #3]
add \tbl, \tbl, #PAGE_SIZE // next level table page
.endm
初始阶段页表
初始阶段的页表地址定义在链接脚本中,如下:
. = ALIGN(PAGE_SIZE);
init_pg_dir = .;
. += INIT_DIR_SIZE;
init_pg_end = .;
其中,INIT_DIR_SIZE定义了内核初始化阶段,用于映射内核镜像的,各级页目录所需要的内存大小之和。其定义如下:
#define EARLY_PAGES(vstart, vend) ( 1 /* PGDIR page */ \
+ EARLY_PGDS((vstart), (vend)) /* each PGDIR needs a next level page table */ \
+ EARLY_PUDS((vstart), (vend)) /* each PUD needs a next level page table */ \
+ EARLY_PMDS((vstart), (vend))) /* each PMD needs a next level page table */
#define INIT_DIR_SIZE (PAGE_SIZE * EARLY_PAGES(KIMAGE_VADDR, _end))
解释一下EARLY_PAGES这个宏定义:
- 首先,需要一个PGDIR的page,也就是第一行最后的“1”;
- 然后,每个PGDIR的entry会对应下一level的一个page,所以,第二行“EARLY_PGDS”计算的是虚拟地址区间 [vstart,vend]所需要的PGDIR entry条目数,也就下一级(PUD)所需要的page数
- 接着,计算虚拟地址区间 [vstart,vend]所需要的PUD entry条目数,也就下一级(PMD)所需要的page数
- 最后,计算虚拟地址区间 [vstart,vend]所需要的PMD entry条目数,也就下一级(PTE)所需要的page数
需要说明的是,对于内核镜像所需要的几十MB的虚拟地址空间来说:PGD条目数肯定是1;PUD条目数也肯定是1;PMD条目数可能有多个(对于4KB的pagesize,1个PMDentry对应2MB),也就是PTE会有多个page。假设内核镜像占用的虚拟地址区间是38MB,则需要19个PTE pages;这样,INIT_DIR_SIZE就等于1+1+1+19=22pages。
初始阶段的页表(PGD/PUD/PMD/PTE)都是排列在一起的,页目录(PGD/PUD/PMD)每一个占用一个page。也就是说,如果create_table_entry当前操作的是PGD,那么tmp2这时候保存了下一level的页表,也就是PUD了。
PMD_TYPE_TABLE
接上一节,tmp2存储了指向下一level页表的页表项。但是这还不够,还需要在该页表项中明确下一个页表的类型(bit1)以及设置该页表项为valid(bit0),对于中间level的页表,该描述符不可能是block entry,只能是table type的描述符,因此该描述符的最低两位是0b11。如下面的PMD_TYPE_TABLE和PUD_TYPE_TABLE:
/*
* Hardware page table definitions.
*
* Level 1 descriptor (PUD).
*/
#define PUD_TYPE_TABLE (_AT(pudval_t, 3) << 0)
#define PUD_TABLE_BIT (_AT(pudval_t, 1) << 1)
#define PUD_TYPE_MASK (_AT(pudval_t, 3) << 0)
#define PUD_TYPE_SECT (_AT(pudval_t, 1) << 0)
#define PUD_SECT_RDONLY (_AT(pudval_t, 1) << 7) /* AP[2] */
/*
* Level 2 descriptor (PMD).
*/
#define PMD_TYPE_MASK (_AT(pmdval_t, 3) << 0)
#define PMD_TYPE_TABLE (_AT(pmdval_t, 3) << 0)
#define PMD_TYPE_SECT (_AT(pmdval_t, 1) << 0)
#define PMD_TABLE_BIT (_AT(pmdval_t, 1) << 1)
需要注意PMD_TYPE_TABLE和PUD_TYPE_TABLE值是相等的,所以create_table_entry中直接使用了#PMD_TYPE_TABLE 来统一代表中间levlel页目录项的属性。
map_memory
新版的linux内核(主要是head.s),基本使用map_memory宏来创建各级页表项,而不是上一小节的create_table_entry宏。
/*
* Map memory for specified virtual address range. Each level of page table needed supports
* multiple entries. If a level requires n entries the next page table level is assumed to be
* formed from n pages.
*
* tbl: location of page table
* rtbl: address to be used for first level page table entry (typically tbl + PAGE_SIZE)
* vstart: virtual address of start of range
* vend: virtual address of end of range - we map [vstart, vend - 1]
* flags: flags to use to map last level entries
* phys: physical address corresponding to vstart - physical memory is contiguous
* order: #imm 2log(number of entries in PGD table)
*
* If extra_shift is set, an extra level will be populated if the end address does
* not fit in 'extra_shift' bits. This assumes vend is in the TTBR0 range.
*
* Temporaries: istart, iend, tmp, count, sv - these need to be different registers
* Preserves: vstart, flags
* Corrupts: tbl, rtbl, vend, istart, iend, tmp, count, sv
*/
.macro map_memory, tbl, rtbl, vstart, vend, flags, phys, order, istart, iend, tmp, count, sv, extra_shift
如其注释所说,map_memory宏就是为指定虚拟地址范围创建页表映射,并根据需要填充多级页表。其在代码中,多次调用populate_entries宏,来分别创建extra(按需)、PGD、PUD(按需)、PMD(按需)和PTE。
- The mapping at the final table level uses one of two methods, depending on the kernel configuration.
- 1) When using page mapping in units of PAGE_SIZE (16K or 64K)
- 2) When using PMD (2M) unit block mapping using 4K page setting
- If you use PMD mapping, you might find it strange to see the PTRS_PER_PTE constant in the entry count. You might wonder why PTRS_PER_PTE is used instead of PTRS_PER_PMD. This is because both PTE mapping and PMD mapping use the same code in this code, depending on the kernel option settings, so we only use PTRS_PER_PTE of the last unit. Note that this is possible because PTRS_PER_PTE and PTRS_PER_PMD use the same value.
最后一级页表采用PTE还是到PMD就结束,依赖用户配置。如果配置了CONFIG_ARM64_4K_PAGES,即使用4KB为页大小,则init阶段页表会开启section map,即最后一级页表是PMD。
/*
* The linear mapping and the start of memory are both 2M aligned (per
* the arm64 booting.txt requirements). Hence we can use section mapping
* with 4K (section size = 2M) but not with 16K (section size = 32M) or
* 64K (section size = 512M).
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM64_4K_PAGES
#define ARM64_SWAPPER_USES_SECTION_MAPS 1
#else
#define ARM64_SWAPPER_USES_SECTION_MAPS 0
#endif
/* Initial memory map size */
#if ARM64_SWAPPER_USES_SECTION_MAPS
#define SWAPPER_BLOCK_SHIFT SECTION_SHIFT
#define SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE SECTION_SIZE
#define SWAPPER_TABLE_SHIFT PUD_SHIFT
#else
#define SWAPPER_BLOCK_SHIFT PAGE_SHIFT
#define SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE PAGE_SIZE
#define SWAPPER_TABLE_SHIFT PMD_SHIFT
#endif
The following figure shows how to use a table expanded by one level.
- When using the extra page table, the page table is created in the order of extra -> pgd -> pud -> pmd.
-
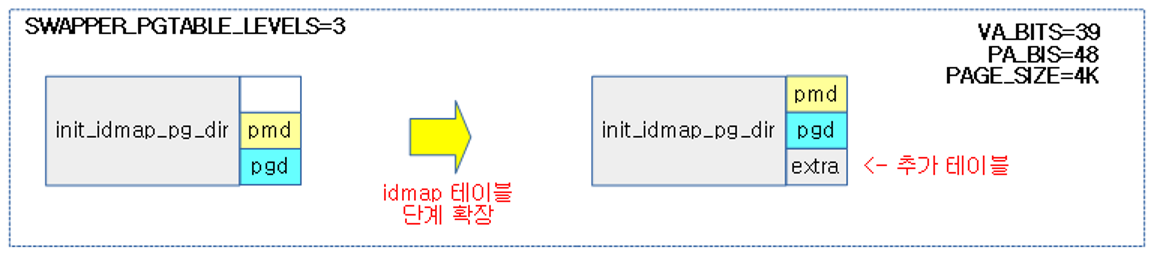
The following figure shows how the kernel image area is mapped to init_idmap_pg_dir via the map_memory macro.
- For reference, the following figure shows an example when the extra page table is not used.
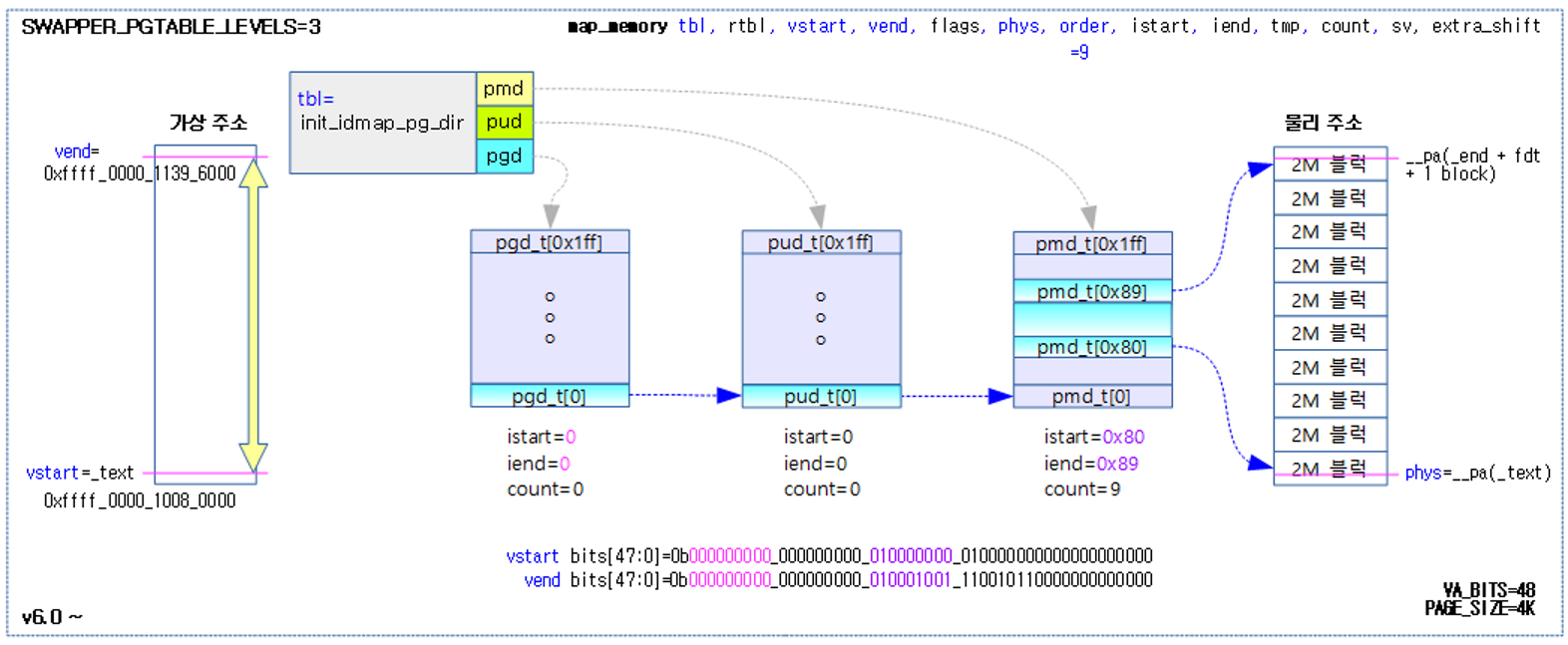
注:上图中的init_idmap_pg_dir,在linux v6.1中已经改为了init_pg_dir。
__create_page_tables
/*
* Setup the initial page tables. We only setup the barest amount which is
* required to get the kernel running. The following sections are required:
* - identity mapping to enable the MMU (low address, TTBR0)
* - first few MB of the kernel linear mapping to jump to once the MMU has
* been enabled
*/
SYM_FUNC_START_LOCAL(__create_page_tables)
如上注释描述,__create_page_tables宏主要是两个功能:
- 创建identity mapping,为MMU使能的相关代码创建页表映射
- 为内核镜像的最开始几MB空间创建线性映射,为内核早期初始化代码赋能
注:
__create_page_tables宏是老版本内核提供的(如v5.10),在新版本中(如v6.1)arm64已经没有了该宏。Identity mapping和kernel mapping已经大大改动了。其中,Identity mapping不只是为MMU使能的小块代码创建1:1映射,而是直接给整个kernel镜像+fdt镜像构建了1:1映射!
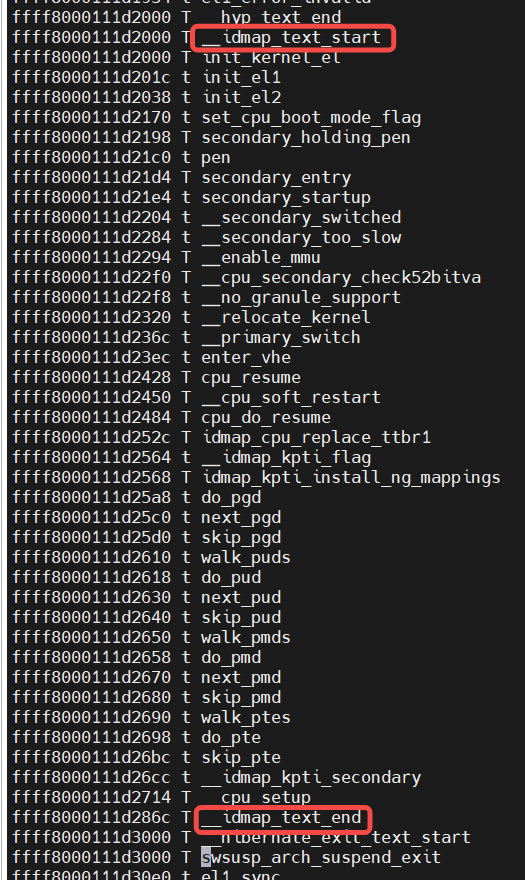
identity mapping
下图可以直观的看出有哪些函数符号包含在identity mapping中(老版本有效):
/*
* The ID map carries a 1:1 mapping of the physical address range
* covered by the loaded image, which could be anywhere in DRAM. This
* means that the required size of the VA (== PA) space is decided at
* boot time, and could be more than the configured size of the VA
* space for ordinary kernel and user space mappings.
*
* There are three cases to consider here:
* - 39 <= VA_BITS < 48, and the ID map needs up to 48 VA bits to cover
* the placement of the image. In this case, we configure one extra
* level of translation on the fly for the ID map only. (This case
* also covers 42-bit VA/52-bit PA on 64k pages).
*
* - VA_BITS == 48, and the ID map needs more than 48 VA bits. This can
* only happen when using 64k pages, in which case we need to extend
* the root level table rather than add a level. Note that we can
* treat this case as 'always extended' as long as we take care not
* to program an unsupported T0SZ value into the TCR register.
*
* - Combinations that would require two additional levels of
* translation are not supported, e.g., VA_BITS==36 on 16k pages, or
* VA_BITS==39/4k pages with 5-level paging, where the input address
* requires more than 47 or 48 bits, respectively.
*/
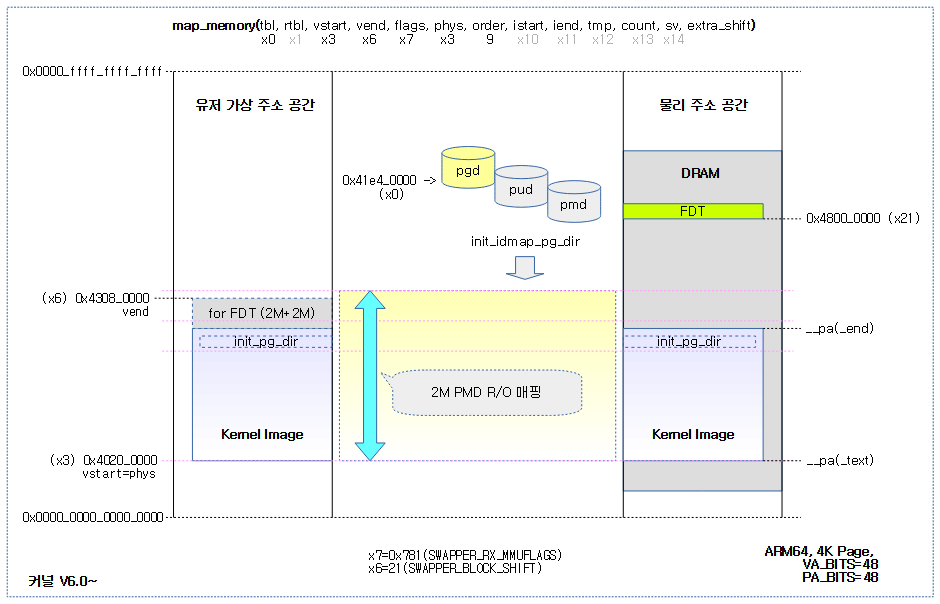
The kernel image and FDT area loaded into the memory are mapped to the init_idmap_pg_dir table with the Read Only attribute so that the physical and virtual addresses are converted 1:1 (VA = PA). Then, the init_pg_dir page table area within the kernel image and the FDT area located above the kernel image are remapped separately with the Read/Write attribute.
整个内核镜像和fdt都被readonly的1:1映射到identity mapping(PGD页表:init_idmap_pg_dir),如下:
adrp x0, init_idmap_pg_dir
adrp x3, _text
adrp x6, _end + MAX_FDT_SIZE + SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE
mov x7, SWAPPER_RX_MMUFLAGS
map_memory x0, x1, x3, x6, x7, x3, IDMAP_PGD_ORDER, x10, x11, x12, x13, x14, EXTRA_SHIFT
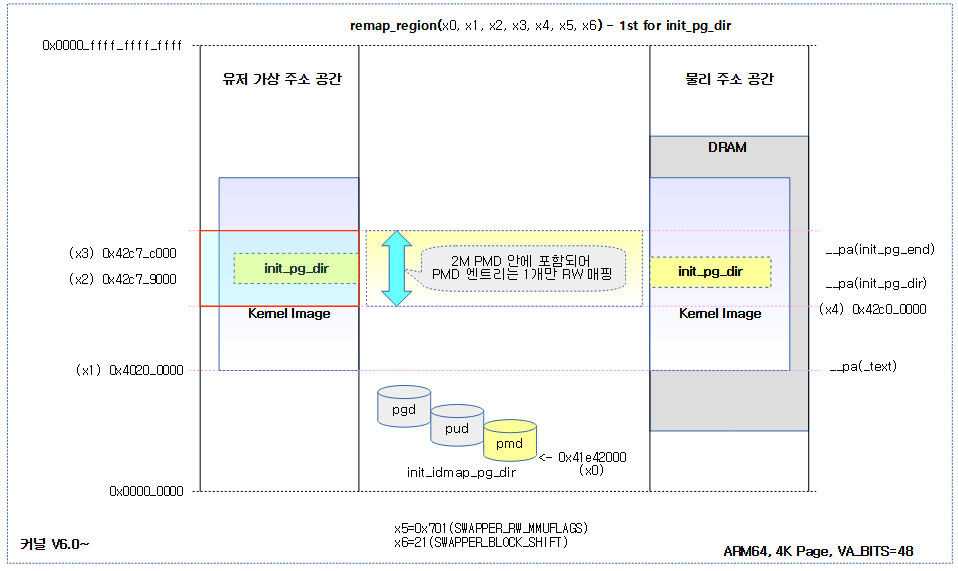
然后,将内核镜像中的init_pg_dir~init_pg_end区域(用于初始化内核的页表区域),映射为RW
/* Remap the kernel page tables r/w in the ID map */
adrp x1, _text
adrp x2, init_pg_dir
adrp x3, init_pg_end
bic x4, x2, #SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE - 1
mov x5, SWAPPER_RW_MMUFLAGS
mov x6, #SWAPPER_BLOCK_SHIFT
bl remap_region
接着,FDT区域也映射为RW,如下:
/* Remap the FDT after the kernel image */
adrp x1, _text
adrp x22, _end + SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE
bic x2, x22, #SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE - 1
bfi x22, x21, #0, #SWAPPER_BLOCK_SHIFT // remapped FDT address
add x3, x2, #MAX_FDT_SIZE + SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE
bic x4, x21, #SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE - 1
mov x5, SWAPPER_RW_MMUFLAGS
mov x6, #SWAPPER_BLOCK_SHIFT
bl remap_region
The following figure shows the 1:1 identity mapping with the R/O attribute in the init_idmap_pg_dir page table for the kernel image + FDT area.
The following figure shows the remapping of the init_pg_dir page table area inside the kernel image to the init_idmap_pg_dir page table with the R/W attribute.
The following figure shows the remapping of the FDT area outside the kernel image to the init_idmap_pg_dir page table with the R/W attribute.
- Note: Since the FDT is separate from the kernel image, you will notice that it does not provide a 1:1 identity mapping even if you use the init_idmap_pg_dir page table.
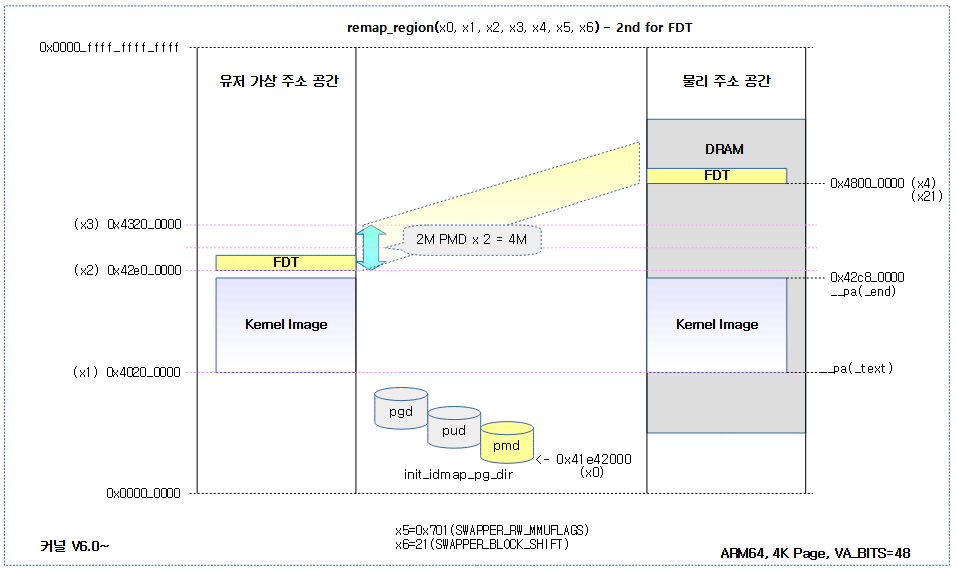
如上图,fdt的identity mapping并不是1:1的映射!不过其也复用了init_idmap_pg_dir的页表。
Kernel mapping
SYM_FUNC_START_LOCAL(clear_page_tables)
/*
* Clear the init page tables.
*/
adrp x0, init_pg_dir
adrp x1, init_pg_end
sub x2, x1, x0
mov x1, xzr
b __pi_memset // tail call
SYM_FUNC_END(clear_page_tables)
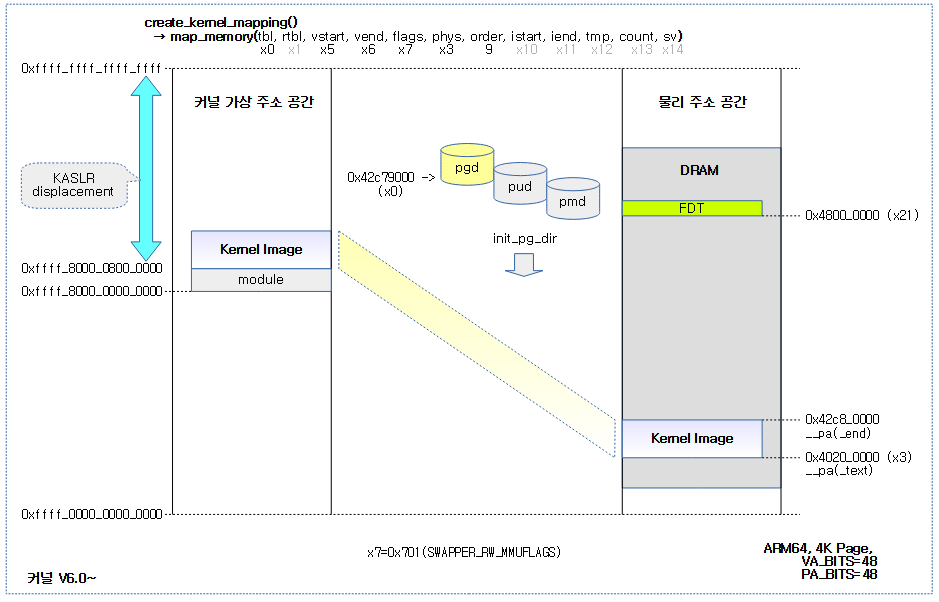
SYM_FUNC_START_LOCAL(create_kernel_mapping)
adrp x0, init_pg_dir
mov_q x5, KIMAGE_VADDR // compile time __va(_text)
#ifdef CONFIG_RELOCATABLE
add x5, x5, x23 // add KASLR displacement
#endif
adrp x6, _end // runtime __pa(_end)
adrp x3, _text // runtime __pa(_text)
sub x6, x6, x3 // _end - _text
add x6, x6, x5 // runtime __va(_end)
mov x7, SWAPPER_RW_MMUFLAGS
map_memory x0, x1, x5, x6, x7, x3, (VA_BITS - PGDIR_SHIFT), x10, x11, x12, x13, x14
dsb ishst // sync with page table walker
ret
SYM_FUNC_END(create_kernel_mapping)
Kernel mapping就非常简单了。就是将kernel镜像在物理内存中的加载地址__pa(_text)~__pa(_end),线性映射到编译器虚拟地址_text~_end(可能需要加上一个random的kaslr offset),如下图: