Unity数据持久化操作——二进制篇
2 进制是什么?
2 进制是计算技术中广泛采用的一种数制。2 进制数据是用 0 和 1 两个数码来表示的数。它的基数为 2,进位规则是 “逢二进一”。
计算机中存储的数据本质上都是 2 进制数的存储,在计算机中位(bit)是最小的存储单位。1 位就是一个 0 或者一个 1。
也就是说一个文件的数据本质上都是由 n 个 0 和 1 组合而成的,通过不同的解析规则最终呈现在我们的眼前。
2进制的好处
1.安全性较高
2.效率较高
3.为网络通信做铺垫
各类型数据转字节数组
不同变量类型
有符号 sbyte int short long
无符号 byte uint ushort ulong
浮点型 float double decimal
特殊 bool char string2 进制文件读写的本质
它就是通过将各类型变量转换为字节数组
将字节数组直接存储到文件中
一般人是看不懂存储的数据的
不仅可以节约存储空间,提升效率
还可以提升安全性
而且在网络通信中我们直接传输的数据也是字节数据(2 进制数据)
各类型数据和字节数据相互转换
C#提供了一个公共类帮助我们进行转化
类名:BitConverter
命名空间:using System
//将各类型转字节byte[] bytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(99);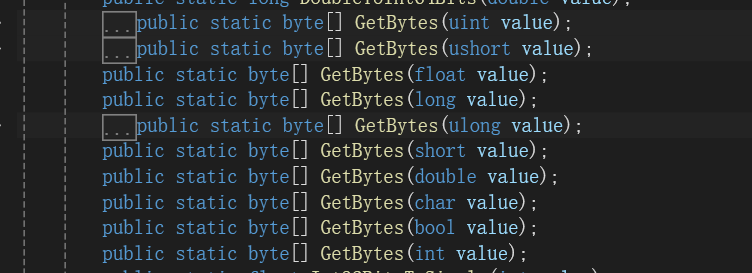
//字节数组转各类型int i = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes,0);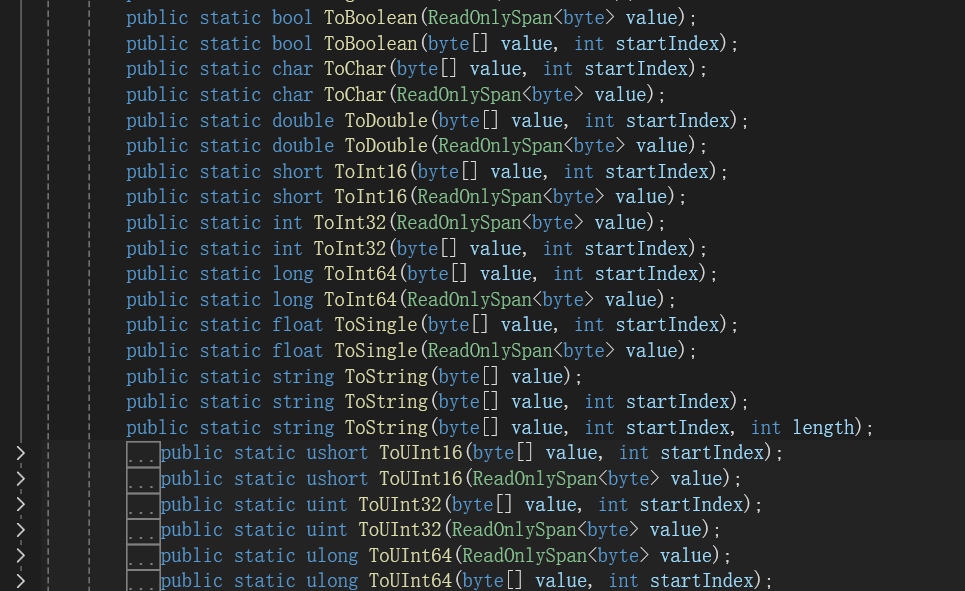
编码格式
C#中有一个专门的编码格式类,来帮助我们将字符串和字节数组进行转换
类名:Encoding
需要引用命名空间:using System.Text
//将字符串以指定编码格式转字节byte[] bytes1 = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("你好");//字节数组以指定编码格式转字符串string s = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes1);文件操作相关
代码中的文件操作是做什么
在电脑上我们可以在操作系统中创建删除修改文件
可以增删查改各种各样的文件类型
代码中的文件操作就是通过代码来做这些事情
文件相关操作公共类
C#提供了一个名为File(文件)的公共类,让我们可以快捷的通过代码操作文件相关
类名:File
命名空间:System.IO
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using UnityEngine;public class lesson2 : MonoBehaviour
{// Start is called before the first frame updatevoid Start(){//判断文件是否存在if (File.Exists(Application.dataPath + "/xxxx.txt")) { }//创建文件//FileStream fs = File.Create(Application.dataPath + "/xxxx.txt");//写入文件//将指定字节数组 写入到指定路径的文件中byte[] bytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(256);File.WriteAllBytes(Application.dataPath + "/xxxx.txt",bytes);//将指定的string数组内容 一行行写入到指定路径中string[] strs = new string[] {"123","234","345","456" };File.WriteAllLines(Application.dataPath +"/num.txt", strs);//将指定的字符串写入指定路径File.WriteAllText(Application.dataPath+"/string.txt" , "HelloWorld");//读取文件//读取字节数据bytes = File.ReadAllBytes(Application.dataPath + "/xxxx.txt");print(BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes));//读取所有行信息strs = File.ReadAllLines(Application.dataPath + "/num.txt");for (int i = 0; i < strs.Length; i++){print(strs[i]);}//读取所有行信息strs[0] = File.ReadAllText(Application.dataPath + "/string.txt");print(strs[0]);//删除文件//注意 如果删除打开着的文件会报错File.Delete(Application.dataPath + "/string.txt");//复制文件//参数一:现有文件 需要是流关闭状态//参数二:目标文件File.Copy(Application.dataPath + "/num.txt",Application.dataPath + "/num(2).txt",true);//文件替换//参数一:用来替换的路径//参数二:被替换的路径//参数三:备份路径File.Replace(Application.dataPath + "/xxxx.txt", Application.dataPath + "/num.txt", Application.dataPath + "/xxxx.txt");//以流的形式 打开文件并写入或读取//参数一:路径//参数二:打开模式//参数三:访问模式FileStream fs = File.Open(Application.dataPath + "/xxxx.txt",FileMode.OpenOrCreate,FileAccess.ReadWrite);}// Update is called once per framevoid Update(){}
}
文件操作相关文件流
在C#中提供了一个文件流类 FileStream类
主要作用是用于读写文件的细节,之前学习的File只能整体读写文件
而FileStream可以以读写字节的形式处理文件
打开或创建指定文件
方法一: new Filestream
参数一:路径
参数二:打开模式
CreateNew: 创建新文件 如果文件存在 则报错
Create: 创建文件,如果文件存在 则覆盖
Open: 打开文件,如果文件不存在 报错
OpenOrCreate: 打开或者创建文件根据实际情况操作
Append: 若存在文件,则打开并查找文件尾,或者创建 个新文件
Truncate: 打开并清空文件内容
参数三:访问模式
参数四:共享权限
None 谢绝共享
Read 允许别的程序读取当前文件
Write 允许别的程序写入该文件
ReadWrite 允许别的程序读写该文件
FileStream fs = new FileStream(Application.dataPath+"/xxx.txt",FileMode.Create,FileAccess.ReadWrite,FileShare.None);
方法二: File.Create
参数一:路径
参数二:缓存大小
参数三:描述如何创建或覆盖该文件 (不常用)
Asynchronous 可用于异步读写
DeleteOnClose 不使用时,自动删除
Encrypted 加密
None 不应用其它选项
RandomAccess 随机访问文件
SequentialScan 从头到尾顺序访问文件
WriteThrough 通过中间缓存直接写入磁盘FileStream fs2 = File.
FileStream fs2 = File.Create(Application.dataPath + "/xxx.txt",2048);方法三: File.Open
参数一:路径
参数二:打开模式
FileStream fs3 = File.Open(Application.dataPath + "/xxx.txt",FileMode.Open);重要属性和方法
//文本字节长度print(fs.Length);//是否可写if (fs.CanWrite) { }//是否可读if (fs.CanRead) { }//将字节写入文件 当写入后 一定执行一次fs.Flush();//关闭流 当文件读写完毕后 一定执行fs.Close();//缓存资源销毁回收fs.Dispose();写入字节
/**方法:write参数一: 写入的字节数组参数二: 数组中的开始索引参数三:写入多少个字节*/byte[] bytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(999);fs.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);//写入字符串时 先写入长度 再写入字符串具体内容bytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("HelloWorld");int length = bytes.Length;fs.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(length), 0, 4);fs.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);//避免数据丢失 一定写入后要执行fs.Flush();fs.Dispose();读取字节
挨个读取字节数组
fs = File.Open(Application.dataPath + "/xxx.txt", FileMode.Open);//读取第一个整形byte[] bytes1 = new byte[4];//方法一:挨个读取字节数组//参数一:用于存储读取的字节数组的容器//参数二:容器中开始的位置//参数三:读取多少个字节装入容器//返回值:当前流索引前进了几个位置int index = fs.Read(bytes1, 0, bytes1.Length);int i = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes1,0);print(i);//读取第二个字符串//先读取长度index = fs.Read(bytes1, 0, 4);int length2 = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes1);//再读取字符串bytes1 = new byte[length];index = fs.Read(bytes1, 0, length);Debug.Log(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes1));//避免数据丢失 一定写入后要执行fs.Flush();fs.Dispose();一次性读取字节数组
fs = File.Open(Application.dataPath + "/xxx.txt", FileMode.Open);//一开始声明一个和文件字节数组长度一样的容器byte[] bytes2 = new byte[fs.Length];fs.Read(bytes2,0, (int)fs.Length);fs.Dispose();//读取整数print(BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes2,0));//读取字符串字节数组长度int temp = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes2, 4);//读取字符串print(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes2, 8, temp));更加安全的使用文件流对象
using 关键字重要用法
using (申明一个引用对象)
{
使用对象
}
无论发生什么情况 当 using 语句块结束后
会自动调用该对象的销毁方法 避免忘记销毁或关闭流
using 是一种更安全的使用方法
强调:
目前我们对文件流进行操作 为了文件操作安全 都用 using 来进行处理最好
using (fs = File.Open(Application.dataPath + "/xxx.txt", FileMode.Open)){//一开始声明一个和文件字节数组长度一样的容器byte[] bytes2 = new byte[fs.Length];fs.Read(bytes2, 0, (int)fs.Length);fs.Dispose();//读取整数print(BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes2, 0));//读取字符串字节数组长度int temp = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes2, 4);//读取字符串print(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes2, 8, temp));}文件夹操作
平时我们可以在操作系统的文件管理系统中通过一些操作增删改查文件夹
通过代码的形式来对文件夹进行增删改查的操作
//判断文件夹是否存在if (Directory.Exists(Application.dataPath+"/xxx")){}//创建文件夹DirectoryInfo info = Directory.CreateDirectory(Application.dataPath + "/xxx");//删除文件夹//参数一:路径//参数二:是否删除非空目录,如果为true,将删除整个目录,如果为false,仅当该目录为空时才可删除Directory.Delete(Application.dataPath + "/xxx",false);//查找文件夹和文件//得到指定路径下所有文件夹名Directory.GetDirectories(Application.dataPath + "/xxx");//得到指定路径下所有文件名Directory.GetFiles(Application.dataPath);//移动文件夹Directory.Move(Application.dataPath + "/xxx", Application.dataPath + "/xxx(2)");DirectoryInfo和FileInfo
DirectoryInfo目录信息类
我们可以通过它获取文件夹的更多信息
//创建文件夹方法的返回值DirectoryInfo info = Directory.CreateDirectory(Application.dataPath + "/xxxx");//全路径print(info.FullName);//文件名print(info.Name);//查找上级文件夹信息info = Directory.GetParent(Application.dataPath + "/xxxx");//全路径print(info.FullName);//文件名print(info.Name);//得到所有子文件夹的目录信息DirectoryInfo[] infos = info.GetDirectories();//FileInfo文件信息类//我们可以通过DirectoryInfo得到该文件下所有文件信息FileInfo[] finfos = info.GetFiles();for (int i = 0; i < finfos.Length; i++){print(finfos[i].Name);//文件名print(finfos[i].FullName);//路径print(finfos[i].Length);//字节长度print(finfos[i].Extension);//后缀名}如何存储Student类
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using UnityEngine;public class lesson2_3 : MonoBehaviour
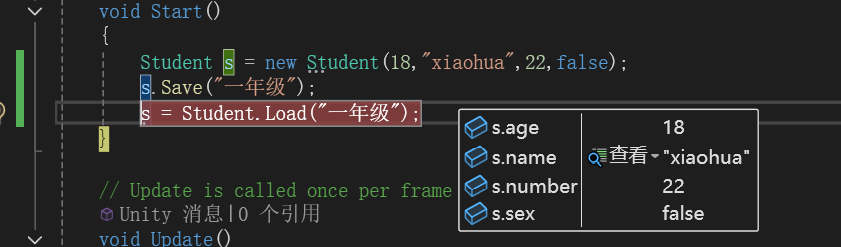
{// Start is called before the first frame updatevoid Start(){Student s = new Student(18,"xiaohua",22,false);s.Save("一年级");s = Student.Load("一年级");}// Update is called once per framevoid Update(){}
}
public class Student
{public int age;public string name;public int number;public bool sex;public Student() { }public Student(int age,string name,int number,bool sex) {this.age = age;this.name = name;this.number = number;this.sex = sex;}public void Save(string fileName){Debug.Log(Application.persistentDataPath);//如果不存在指定路径 则创建一个文件夹if (!Directory.Exists(Application.persistentDataPath+"/Student")){Directory.CreateDirectory(Application.persistentDataPath + "/Student");}//新建一个指定名字的文件 并返回文件流 进行存储using (FileStream fs = new FileStream(Application.persistentDataPath + "/Student/"+fileName+".han",FileMode.OpenOrCreate,FileAccess.Write)){//写agebyte[] bytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(age);fs.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);//写namebytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(name);fs.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(name.Length), 0, 4);fs.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);//写numberbytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(number);fs.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);//写sexbytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(sex);fs.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);fs.Flush();fs.Dispose();}}public static Student Load(string fileName){//判断文件是否存在if (!File.Exists(Application.persistentDataPath + "/Student/" + fileName + ".han")){Debug.Log("没有对应文件");return null;}//声明对象Student s = new Student();//加载2进制文件 进行赋值using (FileStream fs = File.Open(Application.persistentDataPath + "/Student/" + fileName + ".han",FileMode.Open,FileAccess.Read)){//把文件中的字节全部读取byte[] bytes = new byte[fs.Length];fs.Read(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);fs.Close();//挨个读取其中的内容s.age = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes,0);int length = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes,4);s.name = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes, 8, length);s.number = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes, 8 + length);s.sex = BitConverter.ToBoolean(bytes,12+length);}return s;}
}
C#类对象的序列化和反序列化
序列化
序列化类对象第一步声明类对象
注意:如果要使用C#自带的序列化2进制方法,声明类时需要添加[System.Serializeable]特性
[System.Serializable]
public class Person
{public int age = 1; public string name = "xiaohei"; public int[] ints = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; public List<int> list = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; public Dictionary<int, string> dic = new Dictionary<int, string>() { { 1, "123" }, { 2,"234" } };public StructTest st = new StructTest(2,"123");public ClassTest ct = new ClassTest();
}
[System.Serializable]
public struct StructTest
{public int i;public string s;public StructTest(int i,string s) {this.i = i;this.s = s;}
}
[System.Serializable]
public class ClassTest
{public int i = 1;public string s = "yinianji";
}序列化类对象第二步 - 将对象进行 2 进制序列化
方法一:使用内存流得到 2 进制字节数组
主要用于得到字节数组 可以用于网络传输
内存流对象 类名:MemoryStream 命名空间:System.IO
进制格式化对象 类名:BinaryFormatter 命名空间:System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary
主要方法:序列化方法 Serialize
Person p = new Person();using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream()){//2进制格式化程序BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();//序列化对象 生成2进制字节数组 写入到内存流当中bf.Serialize(ms,p);//得到对象的2进制字节数组byte[] bytes = ms.GetBuffer();//存储字节File.WriteAllBytes(Application.dataPath+"/person.txt",bytes);//关闭内存流ms.Close();}方法二:使用文件流进行存储
主要用于存储到文件中
using (FileStream fs =new FileStream(Application.dataPath + "/person.txt", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write)){//2进制格式化程序BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();//序列化对象 生成2进制字节数组 写入到文件流中bf.Serialize(fs,p);fs.Flush();fs.Dispose();}反序列化
文件流反序列化
//通过文件流打开指定的2进制数据文件using (FileStream fs = new FileStream(Application.dataPath + "/person.txt",FileMode.Open,FileAccess.Read) ){//声明一个 2进制格式化类BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();//反序列化p = bf.Deserialize(fs) as Person;fs.Close();}内存流反序列化
byte[] bytes = File.ReadAllBytes(Application.dataPath + "/person.txt");//声明内存流对象 一开始就把字节数组传输进去using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(bytes)){//声明一个 2进制格式化类BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();//反序列化p = bf.Deserialize(ms) as Person;ms.Close();}加密解密
何时加密?何时解密?
当我们将类对象转换为二进制数据时进行加密
当我们将二进制数据转换为类对象时进行解密
这样如果第三方获取到我们的二进制数据
当他们不知道加密规则和解密秘钥时就无法获取正确的数据
起到保证数据安全的作用
异或加密的思想:
加密 :0001 异或 key:0010 等于 0011
解密: 0011 异或 key:0010 等于 0001
加密
Person p = new Person();byte key = 199;using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream()){BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();bf.Serialize(ms, p);byte[] bytes = ms.GetBuffer();//异或加密for (int i = 0; i < bytes.Length; i++){bytes[i] ^= key;}File.WriteAllBytes(Application.dataPath + "/person.txt",bytes);}解密
byte[] bytes2 = File.ReadAllBytes(Application.dataPath + "/person.txt");//解密for (int i = 0; i < bytes2.Length; i++){bytes2[i] ^= key;}using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(bytes2)){BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();Person p2 = bf.Deserialize(ms) as Person;ms.Close();}实现一个二进制数据序列化和反序列化控制类
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using UnityEngine;public class lesson3_1
{private string path = Application.persistentDataPath + "/test";private byte key = 120;private static lesson3_1 instance = new lesson3_1();public static lesson3_1 Instance => instance;private lesson3_1() { }/// <summary>/// 存储类对象数据/// </summary>/// <param name="obj">要存储的类对象</param>/// <param name="fileName">文件名</param>public void Save(object obj, string fileName){if (!Directory.Exists(Application.persistentDataPath + "/test"))Directory.CreateDirectory(Application.persistentDataPath + "/test");using (FileStream fs = new FileStream(path+"/"+fileName+".han",FileMode.OpenOrCreate,FileAccess.Write)){BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();bf.Serialize(fs, obj);fs.Flush();fs.Dispose();}}/// <summary>/// 读取2进制数据转换成对象/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>/// <param name="fileName"></param>/// <returns></returns>public T Load<T>(string fileName) where T : class{//如果没有这个文件,就返回这个对象的默认值if (!File.Exists(path + "/" + fileName+".han")){return default(T);}T obj;using (FileStream fs = new FileStream(path + "/" + fileName + ".han",FileMode.Open,FileAccess.Read)){BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();obj = bf.Deserialize(fs) as T;fs.Close();}return obj;}
}读取Excel表中的数据
打开Excel表格
[MenuItem("GameTool/打开Excel表")]
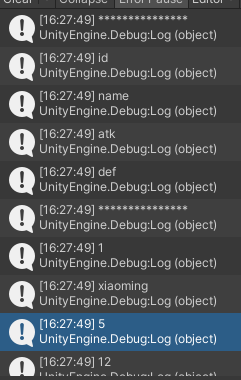
private static void OpenExcel(){using (FileStream fs =File.Open(Application.dataPath+"/Arts/PlayerInfo.xlsx",FileMode.Open,FileAccess.Read)){//通过我们的文件流获取ExcelIExcelDataReader excelDataReader = ExcelReaderFactory.CreateOpenXmlReader(fs);//将excel表中的数据转换为DataSet数据类型 方便我们获取其中的内容DataSet result = excelDataReader.AsDataSet();//得到Excel文件中的所有表信息for (int i = 0; i < result.Tables.Count; i++){Debug.Log("表名: " + result.Tables[i].TableName);Debug.Log("行数:" + result.Tables[i].Rows.Count);Debug.Log("列数:" + result.Tables[i].Columns.Count);}fs.Close();}}获取Excel表中单元格的信息
[MenuItem("GameTool/读取Excel表")]private static void ReadExcel(){using (FileStream fs = File.Open(Application.dataPath + "/Arts/PlayerInfo.xlsx", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read)){//通过我们的文件流获取ExcelIExcelDataReader excelDataReader = ExcelReaderFactory.CreateOpenXmlReader(fs);//将excel表中的数据转换为DataSet数据类型 方便我们获取其中的内容DataSet result = excelDataReader.AsDataSet();for (int i = 0; i < result.Tables.Count; i++){//得到其中一张表的具体数据DataTable table = result.Tables[i];//得到其中一行的数据//DataRow row = table.Rows[0];//得到行中某一列的信息//Debug.Log(row[1].ToString());DataRow row;for ( int j = 0; j < table.Rows.Count; j++){//得到每一行的信息row = table.Rows[j];Debug.Log("***************");for (int k = 0; k < table.Columns.Count;k++){Debug.Log(row[k].ToString());}}}fs.Close();}}结果: