golang面经——context模块
面试题相关
1、context 结构是什么样的?
分析:
关于context要清楚具体是什么,context其实是一个接口,提供了四种方法,而在官方go语言中对context接口提供了四种基本类型的实现,回答的时候,要答出接口以及几种实现结构。
回答:
一、go语言里的context实际上是一个接口,提供了四种方法:
type Context interface {Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool) // Deadline方法的第一个返回值表示还有多久到期,第二个返回值表示是否被超时时间控制;Done() <-chan struct{} // Done()返回一个 只读channel,当这个channel被关闭时,说明这个context被取消;Err() error // Err()返回一个错误,表示channel被关闭的原因,例如是被取消,还是超时关闭;Value(key interface{}) interface{} // value方法返回指定key对应的value,这是context携带的值。
}Deadline的两个返回值:
deadline
含义:表示这个 Context 应该被取消的绝对时间点
类型:time.Time 类型的时间值
作用:
当设置了截止时间时,返回具体的时间点
当没有设置截止时间时,返回 time.Time 的零值(0001-01-01 00:00:00 +0000 UTC)
ok bool - 是否设置了截止时间
含义:指示这个 Context 是否设置了截止时间
类型:布尔值
可能值:
true:Context 设置了截止时间(如通过 WithDeadline 或 WithTimeout 创建)
false:Context 没有设置截止时间(如通过 Background() 或 WithCancel 创建)
二、有emptyCtx、cancelCtx、timerCtx、valueCtx四种实现:
A. emptyCtx:emptyCtx 虽然实现了context接口,但是不具备任何功能,因为实现很简单,基本都是直接返回空值。我们一般调用context.Background()和context.TODO()都是返回一个 *emptyctx的动态类型(通过静态类型context.Context传递)。
B. cancelCtx:cancelCtx同时实现Context和canceler接口,通过取消函数cancelFunc实现退出通知。注意其退D出通知机制不但通知自己,同时也通知其children节点。我们一般调用context.WithCancel()就会返回一个*cancelCtx 和cancelFunc
C. timerCtx:timerCtx是一个实现了Context接口的具体类型,其内部封装了cancelctx类型实例,同时也有个C.deadline变量,用来实现定时退出通知。
我们一般调用context,WithTimeout()就会返回一个*timerCtx和cancelFunc,不仅可以定时通知,也可以调用cancelFunc进行通知。
调用context.WithDeadline()也可以,WithTimeout是多少秒后进行通知,WithDeadline是在某个时间点通知,本质上,WithTimeout会转而WithDeadline。
- valueCtx: valueCtx是一个实现了Context接口的具体类型,其内部封装了Context接口类型,同时也封装了-个k/v的存储变量,其是一个实现了数据传递
我们一般context.WithValue()来得到一个*valueCtx,valuectx可以继承它的parent valuectx中的{key,value}。
2、context 使用场景和用途?(基本必问)
分析:
这个问题其实可以可以上一个问题的补充提问,在明确了context是什么之后,即context接口提供了哪些哪些方法,以及有哪些实践之后,看似联想出这些实现是为了解决什么问题,主要突出两点:上下文信息传递和协程的取消控制。
回答:
- context 主要用来在 goroutine 之间传递上下文信息,比如传递请求的trace id,以便于追踪全局唯一请求
- 另一个用处是可以用来做取消控制,通过取消信号和超时时间来控制子goroutine的退出,防止goroutine泄漏。包括:取消信号、超时时间、截止时间、k-v 等。
知识点总结
1、context的用法总结
在 Go 语言中,context 是一个核心包,用于在 API 边界之间传递请求作用域的值、取消信号和超时控制。它特别适用于管理跨多个 goroutine 的请求生命周期。
Context 的核心用途:
取消传播:向所有相关 goroutine 广播取消信号
超时控制:设置请求的最大执行时间
值传递:在调用链中安全传递请求相关的数据
截止时间:设置操作的绝对截止时间点
type Context interface {Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool) // 获取截止时间Done() <-chan struct{} // 返回取消信号通道Err() error // 返回取消原因Value(key interface{}) interface{} // 获取关联值
}1.1 context创建的几种方式
在 Go 语言的 context 包中,有几种主要的 Context 创建方式,每种都代表不同的使用场景和控制机制。以下是各种创建方式及其含义的详细解释:
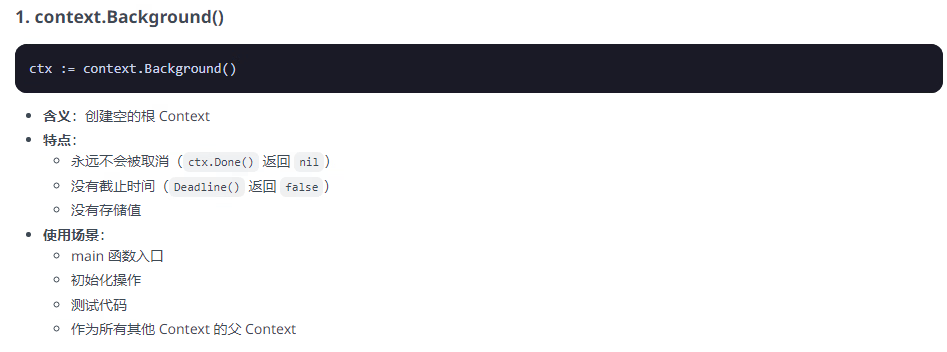

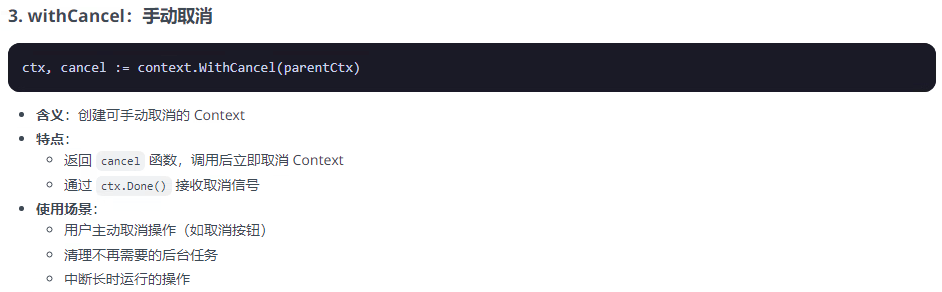
// 示例:用户取消下载
func downloadFile(ctx context.Context) {for {select {case <-ctx.Done():fmt.Println("下载取消")returndefault:// 继续下载...}}
}// 调用
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
go downloadFile(ctx)// 用户点击取消时调用
cancel()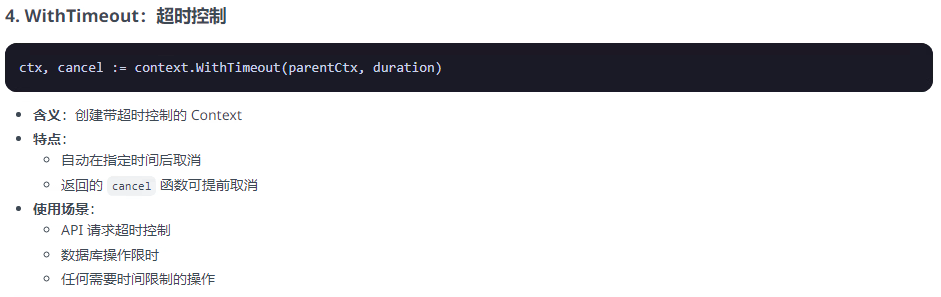
// 示例:HTTP请求超时
func fetchData() {ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 3*time.Second)defer cancel() // 确保资源释放req, _ := http.NewRequestWithContext(ctx, "GET", url, nil)resp, err := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)if errors.Is(err, context.DeadlineExceeded) {fmt.Println("请求超时")}
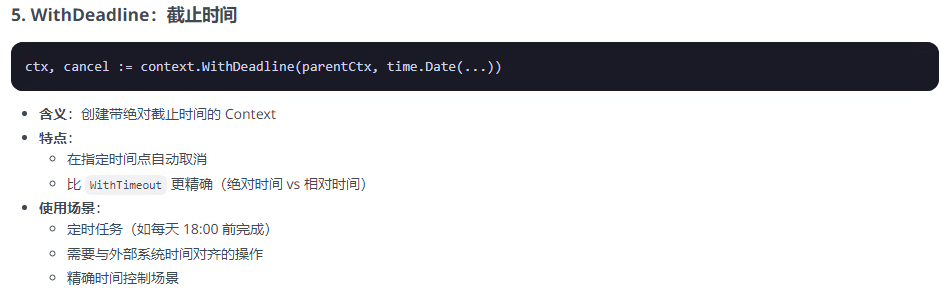
}
// 示例:每日报告生成
func generateDailyReport() {// 设置今天23:59:59为截止时间deadline := time.Date(2025, 9, 24, 23, 59, 59, 0, time.Local)ctx, cancel := context.WithDeadline(context.Background(), deadline)defer cancel()// 生成报告...
}
// 定义安全的key类型
type userKey struct{}func authMiddleware(next http.Handler) http.Handler {return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {// 验证用户并获取用户信息user := authenticate(r) // 将用户信息存入Contextctx := context.WithValue(r.Context(), userKey{}, user)next.ServeHTTP(w, r.WithContext(ctx))})
}// 在业务逻辑中获取
func handleRequest(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {user := r.Context().Value(userKey{}).(*User)fmt.Fprintf(w, "欢迎, %s", user.Name)
}(1)一个上下文的节点只能存放一组kv
(2)使用以下方式可以读取ctx值内容:
debugMode, _ := ctx.Value(debugKey).(bool)
timeout, _ := ctx.Value(timeoutKey).(time.Duration)
1.2 context 父子之间的关系,为什么要有父子关系?
在 Go 的 context 包中,父子关系是 context 体系的核心设计,理解这种层级关系对于编写健壮的并发程序至关重要。以下是 context 父子关系的详细解析:

1)取消信号传播(核心价值)
级联取消:当父 Context 被取消时,所有派生出的子 Context 会自动收到取消信号
示例场景:
func main() {parent, cancelParent := context.WithCancel(context.Background())child, _ := context.WithCancel(parent)// 取消父ContextcancelParent()// 子Context会立即收到信号<-child.Done() // 此通道会立即关闭fmt.Println("子Context已取消")
}实际应用:HTTP 服务器中,当客户端断开连接时,自动取消所有关联的数据库查询和下游服务调用。
2) 超时/截止时间继承
子 Context 的截止时间不会超过父 Context 的设置
自动取最短时间:
parent, _ := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 5*time.Second)
child, _ := context.WithTimeout(parent, 3*time.Second) // 实际超时:3秒deadline, _ := child.Deadline()
fmt.Println(deadline) // 显示3秒后的时间设计意义:防止子操作意外延长整体执行时间
3)值传递的隔离与继承
值继承:子 Context 继承父 Context 的所有键值对
隔离性:在子 Context 中添加新值不会影响父 Context
示例:
parent := context.WithValue(context.Background(), "key", "parentValue")
child := context.WithValue(parent, "childKey", "childValue")fmt.Println(parent.Value("key")) // parentValue
fmt.Println(child.Value("key")) // parentValue (继承)
fmt.Println(child.Value("childKey")) // childValue
fmt.Println(parent.Value("childKey")) // nil (隔离)4)资源生命周期管理
自动清理:当父 Context 取消时,所有关联资源(goroutine、连接等)可通过 defer cancel() 统一释放。
防泄漏机制:
func process(ctx context.Context) {// 忘记此调用会导致goroutine泄漏!defer cancel() go func() {select {case <-ctx.Done(): // 依赖父子传播自动终止return}}()
}一个较为全面的例子:
package mainimport ("context""fmt""math/rand""net/http""sync""time"
)// 模拟服务依赖
type UserService struct{}
type OrderService struct{}
type NotificationService struct{}// 模拟用户信息
type User struct {ID intName stringRole string
}// 模拟订单信息
type Order struct {ID intUserID intAmount float64Status string
}// 全局服务实例
var (userService = &UserService{}orderService = &OrderService{}notificationService = &NotificationService{}
)func main() {// 启动HTTP服务器http.HandleFunc("/batch-process", batchProcessHandler)http.HandleFunc("/user-orders", userOrdersHandler)fmt.Println("服务器启动在 :8080")http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
}// 批量处理订单接口 - 展示复杂的父子Context使用
func batchProcessHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {// 父Context:设置整体超时和请求IDparentCtx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 10*time.Second)defer cancel()// 添加请求标识和用户信息parentCtx = context.WithValue(parentCtx, "requestID", generateRequestID())parentCtx = context.WithValue(parentCtx, "user", User{ID: 123, Name: "admin", Role: "admin"})fmt.Printf("[%s] 开始批量处理订单\n", parentCtx.Value("requestID"))// 并发处理多个订单orderIDs := []int{1001, 1002, 1003, 1004, 1005}results := processOrdersConcurrently(parentCtx, orderIDs)// 汇总结果successCount := 0for _, result := range results {if result.Success {successCount++}}response := fmt.Sprintf("批量处理完成: 成功 %d/%d 个订单", successCount, len(orderIDs))fmt.Fprintln(w, response)fmt.Printf("[%s] %s\n", parentCtx.Value("requestID"), response)
}// 并发处理订单
func processOrdersConcurrently(ctx context.Context, orderIDs []int) []ProcessResult {var wg sync.WaitGroupresults := make(chan ProcessResult, len(orderIDs))// 为每个订单创建独立的子Contextfor _, orderID := range orderIDs {wg.Add(1)// 创建子Context,设置更严格的超时childCtx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 3*time.Second)childCtx = context.WithValue(childCtx, "orderID", orderID)go func(ctx context.Context, cancel context.CancelFunc, orderID int) {defer wg.Done()defer cancel() // 确保子Context资源释放// 模拟处理单个订单result := processSingleOrder(ctx)results <- result}(childCtx, cancel, orderID)}// 等待所有订单处理完成go func() {wg.Wait()close(results)}()// 收集结果var finalResults []ProcessResultfor result := range results {finalResults = append(finalResults, result)}return finalResults
}// 处理单个订单
func processSingleOrder(ctx context.Context) ProcessResult {orderID := ctx.Value("orderID").(int)requestID := ctx.Value("requestID").(string)fmt.Printf("[%s] 开始处理订单 %d\n", requestID, orderID)// 步骤1: 验证订单 - 创建孙子ContextvalidateCtx, validateCancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 1*time.Second)defer validateCancel()if err := validateOrder(validateCtx, orderID); err != nil {return ProcessResult{OrderID: orderID,Success: false,Error: fmt.Sprintf("验证失败: %v", err),}}// 检查父Context是否已取消select {case <-ctx.Done():return ProcessResult{OrderID: orderID,Success: false,Error: fmt.Sprintf("处理被取消: %v", ctx.Err()),}default:}// 步骤2: 处理支付 - 创建孙子ContextpaymentCtx, paymentCancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 2*time.Second)defer paymentCancel()if err := processPayment(paymentCtx, orderID); err != nil {return ProcessResult{OrderID: orderID,Success: false,Error: fmt.Sprintf("支付失败: %v", err),}}// 检查父Context是否已取消select {case <-ctx.Done():return ProcessResult{OrderID: orderID,Success: false,Error: fmt.Sprintf("处理被取消: %v", ctx.Err()),}default:}// 步骤3: 发送通知 - 创建孙子ContextnotifyCtx, notifyCancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 1*time.Second)defer notifyCancel()if err := sendNotification(notifyCtx, orderID); err != nil {// 通知失败不影响整体成功fmt.Printf("[%s] 订单 %d 通知发送失败: %v\n", requestID, orderID, err)}fmt.Printf("[%s] 订单 %d 处理完成\n", requestID, orderID)return ProcessResult{OrderID: orderID,Success: true,Error: "",}
}// 查询用户订单接口 - 展示更复杂的依赖关系
func userOrdersHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {// 父Context:设置整体超时parentCtx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 5*time.Second)defer cancel()// 添加请求信息parentCtx = context.WithValue(parentCtx, "requestID", generateRequestID())parentCtx = context.WithValue(parentCtx, "userID", 456)fmt.Printf("[%s] 开始查询用户 %d 的订单\n", parentCtx.Value("requestID"), parentCtx.Value("userID"))// 创建多个并行查询任务var wg sync.WaitGroupresults := make(chan interface{}, 3)// 查询用户信息wg.Add(1)go func() {defer wg.Done()// 为用户查询创建子ContextuserCtx, userCancel := context.WithTimeout(parentCtx, 2*time.Second)defer userCancel()user, err := getUserInfo(userCtx)if err != nil {results <- fmt.Sprintf("用户查询失败: %v", err)} else {results <- user}}()// 查询订单列表wg.Add(1)go func() {defer wg.Done()// 为订单查询创建子ContextorderCtx, orderCancel := context.WithTimeout(parentCtx, 3*time.Second)defer orderCancel()orders, err := getUserOrders(orderCtx)if err != nil {results <- fmt.Sprintf("订单查询失败: %v", err)} else {results <- orders}}()// 查询统计信息wg.Add(1)go func() {defer wg.Done()// 为统计查询创建子ContextstatsCtx, statsCancel := context.WithTimeout(parentCtx, 2*time.Second)defer statsCancel()stats, err := getUserStats(statsCtx)if err != nil {results <- fmt.Sprintf("统计查询失败: %v", err)} else {results <- stats}}()// 等待所有查询完成go func() {wg.Wait()close(results)}()// 聚合结果response := make([]interface{}, 0)for result := range results {response = append(response, result)}fmt.Fprintf(w, "查询完成,返回 %d 个结果\n", len(response))fmt.Printf("[%s] 查询完成\n", parentCtx.Value("requestID"))
}// 模拟服务实现
func (us *UserService) GetUser(ctx context.Context, userID int) (*User, error) {select {case <-time.After(time.Duration(rand.Intn(500)) * time.Millisecond): // 模拟网络延迟if rand.Intn(10) == 0 { // 10%失败率return nil, fmt.Errorf("用户服务暂时不可用")}return &User{ID: userID, Name: fmt.Sprintf("User%d", userID), Role: "customer"}, ctx.Err()case <-ctx.Done():return nil, ctx.Err()}
}func (os *OrderService) GetOrders(ctx context.Context, userID int) ([]Order, error) {select {case <-time.After(time.Duration(rand.Intn(800)) * time.Millisecond): // 模拟网络延迟if rand.Intn(20) == 0 { // 5%失败率return nil, fmt.Errorf("订单服务暂时不可用")}return []Order{{ID: 2001, UserID: userID, Amount: 99.99, Status: "completed"},{ID: 2002, UserID: userID, Amount: 149.50, Status: "pending"},}, ctx.Err()case <-ctx.Done():return nil, ctx.Err()}
}func (ns *NotificationService) SendOrderConfirmation(ctx context.Context, orderID int) error {select {case <-time.After(time.Duration(rand.Intn(300)) * time.Millisecond): // 模拟网络延迟if rand.Intn(15) == 0 { // 约6.7%失败率return fmt.Errorf("通知服务暂时不可用")}return ctx.Err()case <-ctx.Done():return ctx.Err()}
}// 辅助函数
func validateOrder(ctx context.Context, orderID int) error {// 模拟验证过程select {case <-time.After(200 * time.Millisecond):if rand.Intn(20) == 0 { // 5%验证失败return fmt.Errorf("订单验证失败")}return nilcase <-ctx.Done():return ctx.Err()}
}func processPayment(ctx context.Context, orderID int) error {// 模拟支付过程select {case <-time.After(500 * time.Millisecond):if rand.Intn(10) == 0 { // 10%支付失败return fmt.Errorf("支付处理失败")}return nilcase <-ctx.Done():return ctx.Err()}
}func sendNotification(ctx context.Context, orderID int) error {// 模拟发送通知select {case <-time.After(100 * time.Millisecond):return notificationService.SendOrderConfirmation(ctx, orderID)case <-ctx.Done():return ctx.Err()}
}func getUserInfo(ctx context.Context) (*User, error) {userID := ctx.Value("userID").(int)return userService.GetUser(ctx, userID)
}func getUserOrders(ctx context.Context) ([]Order, error) {userID := ctx.Value("userID").(int)return orderService.GetOrders(ctx, userID)
}func getUserStats(ctx context.Context) (map[string]interface{}, error) {select {case <-time.After(300 * time.Millisecond):return map[string]interface{}{"total_orders": 15,"total_spent": 1250.75,}, nilcase <-ctx.Done():return nil, ctx.Err()}
}func generateRequestID() string {return fmt.Sprintf("REQ-%d", time.Now().UnixNano()%100000)
}// 处理结果结构
type ProcessResult struct {OrderID intSuccess boolError string
}
