【数据结构】顺序表,ArrayList
文章目录
- 前言
- ArrayList简介
- ArrayList使用
- 构造方法
- ArrayList常见操作
- remove
- subList
- 遍历ArrayList
- ArrayList中的二维数组
- 总结
前言
在上一篇博文中,我们尝试自己实现了一下ArrayList类。不过,在实际应用中,ArrayList有着更灵活、更便捷的使用方法。在这一篇博文中,让我们更加深入的了解一下吧。
ArrayList简介
在集合框架中,ArrayList是一个普通的类,实现了List接口,具体框架图如下:
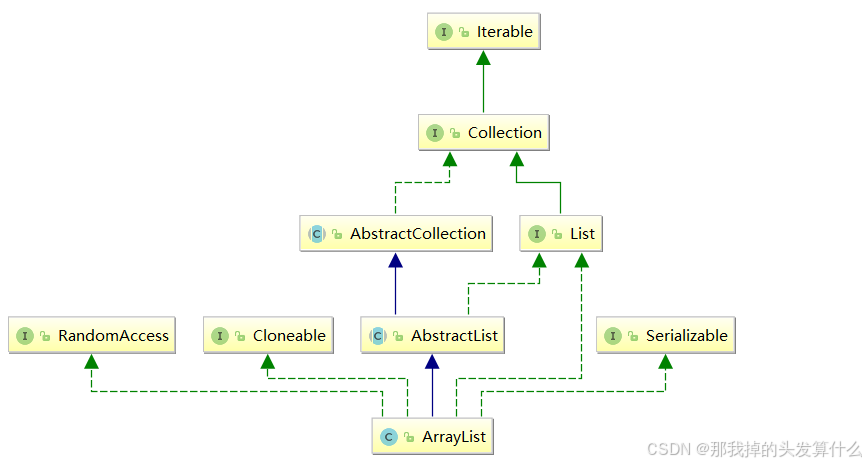
【说明】
-
ArrayList是以泛型方式实现的,使用时必须要先实例化
-
ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,表明ArrayList支持随机访问
-
ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口,表明ArrayList是可以clone的
-
ArrayList实现了Serializable接口,表明ArrayList是支持序列化的
-
和Vector不同,ArrayList不是线程安全的,在单线程下可以使用,在多线程中可以选择Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList
-
ArrayList底层是一段连续的空间,并且可以动态扩容,是一个动态类型的顺序表
ArrayList使用
构造方法
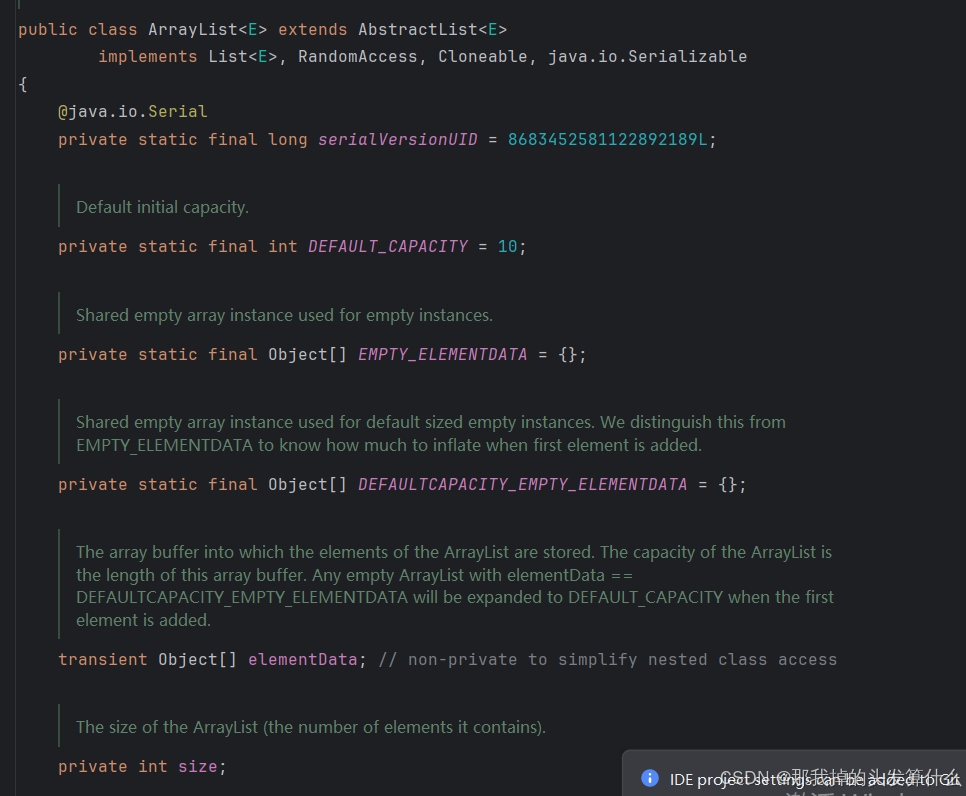
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {if (initialCapacity > 0) {this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;} else {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);}}/*** Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.*/public ArrayList() {this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}/*** Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's* iterator.** @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null*/public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {Object[] a = c.toArray();if ((size = a.length) != 0) {if (c.getClass() == ArrayList.class) {elementData = a;} else {elementData = Arrays.copyOf(a, size, Object[].class);}} else {// replace with empty array.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}}
我们如果去看源码,会发现ArratList有三个构造方法。首先第一个不必多说,第二个其实是创建一个空表,详情请看下图:
我们主要来讲第三个:
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
首先Collection是这些表类的父类,“?”指的是通配符,参数的意思是:给参数时要保证首先类型是Collection或者它的子类,<>里面的得是E的子类。举例说明一下大家就很快明白了。
import java.util.ArrayList;//TIP To <b>Run</b> code, press <shortcut actionId="Run"/> or
// click the <icon src="AllIcons.Actions.Execute"/> icon in the gutter.
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(1);System.out.println(list);ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>(list);System.out.println(list1);}}
首先List< Integer>肯定是Collection类的子类,而Integer与ArrayList list1 = new ArrayList<>(list);所代表的Integer包装类又是相同的,所以,可以这样定义一个新表。
但是!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!到这里构造方法还没完。
上一个博文中我们实现add方法时会扩容。此时,在第一个和第二个构造方法中,我们可能会建立空表,如果是空表,照我们的代码来看,似乎没办法扩容以及插入数据啊?我们来看java具体是怎么实现的吧!


我们可以看到,其实是java先给原来的size + 1之后,才进行的扩容操作,并且扩容是按照1.5倍进行扩容的。
ArrayList常见操作
ArrayList虽然提供的方法比较多,但是常用方法如下所示
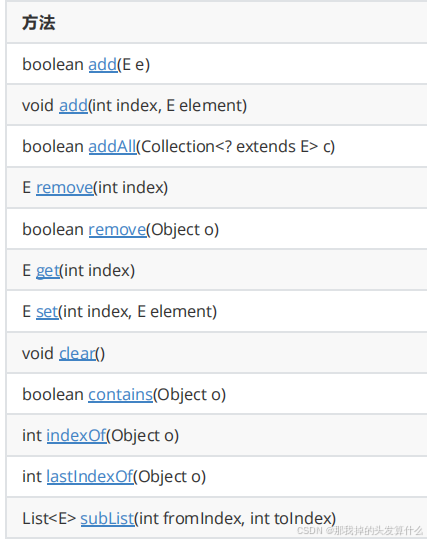
这些方法我们大多数都实现了,这里讲两个没提到的。
remove
我们能注意到,remove既可以传数据,又可以传下标。那么问题来了:我们传入一个“1”,那我指的是下标还是数据呢?
import java.util.ArrayList;//TIP To <b>Run</b> code, press <shortcut actionId="Run"/> or
// click the <icon src="AllIcons.Actions.Execute"/> icon in the gutter.
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);list.add(4);list.add(5);System.out.println(list);
// ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>(list);
// System.out.println(list1);list.remove(1);System.out.println(list);}}
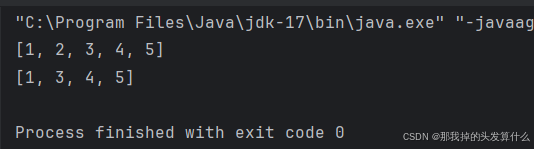
是下标!
那怎么才能传数据呢?
list.remove(new Integer(1));System.out.println(list);
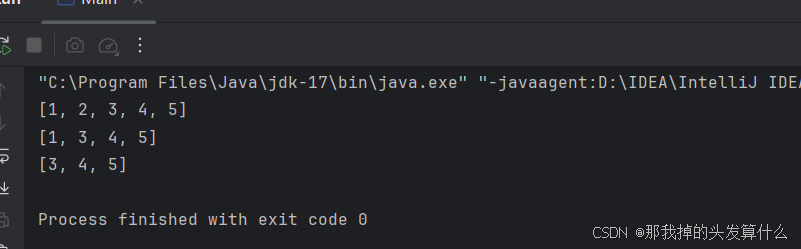
但是自从java9以来,这种写法变得过时了,编译器会报错。
subList
subList在截取过程中有一个有意思的现象:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;//TIP To <b>Run</b> code, press <shortcut actionId="Run"/> or
// click the <icon src="AllIcons.Actions.Execute"/> icon in the gutter.
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);list.add(4);list.add(5);System.out.println(list);List<Integer> list1 = list.subList(1,3);list1.set(1,999);System.out.println(list);System.out.println(list1);}}
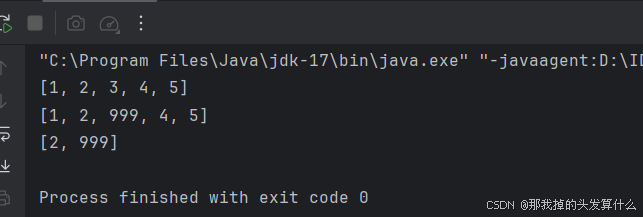
可以看到我们修改list1的内容时,list的内容也改变了,这是因为subList不是建立一个新对象,而是建立一个新索引,仍然指向原表。
遍历ArrayList
我们有四种方法来遍历ArrayList,其中有两种为使用迭代器遍历,这是一个新增的知识:
public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);list.add(4);list.add(5);System.out.println("for下标遍历");for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("foreach遍历");for (Integer x : list){System.out.print(x + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("使用迭代器Iterator输出");Iterator<Integer> it = list.iterator();while(it.hasNext()){System.out.print(it.next() + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("使用迭代器ListIterator输出");ListIterator<Integer> it2 = list.listIterator();while(it2.hasNext()){System.out.print(it2.next() + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("使用迭代器ListIterator输出====扩展(反向输出)");ListIterator<Integer> it3 = list.listIterator(list.size());while(it3.hasPrevious()){System.out.print(it3.previous() + " ");}System.out.println();}
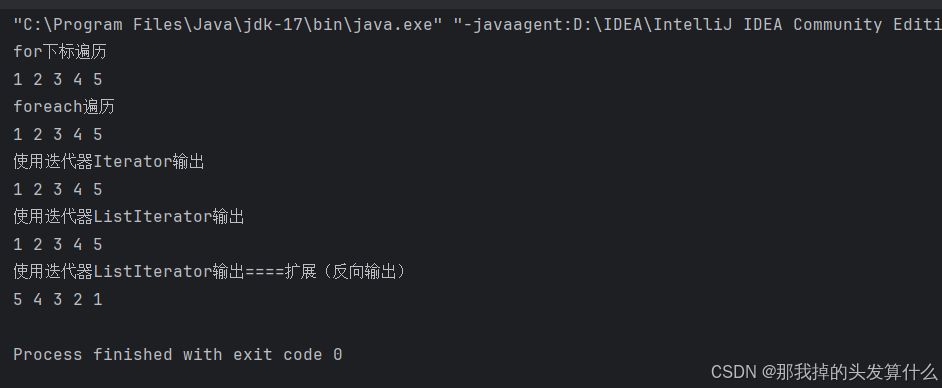
注意:
- ArrayList最长使用的遍历方式是:for循环+下标 以及 foreach
- 迭代器是设计模式的一种,后序容器接触多了再给大家铺垫
ArrayList中的二维数组
大家来看一道简单的杨辉三角的题目,看上去似乎很简单,但是请看这里:
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
List<List< Integer >>这啥玩意儿?????
在这之前确实没见过这种写法,但我们可以拆开理解一下。
先看里面:
List< Integer>
这个都认识,数据类型为Integer的List表。
那这个List<List< Integer>>是不是就是类型为List< Integer>的List表了呢?
或者我来这样说,这是不是就是一个二维数组呢??
没错,这样的写法代表的就是List的一个类似于二维数组的表示,即:List表中的每一个数据都是一个list表
这一题的代码也很简单:
public static List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> list0 = new ArrayList<>();list0.add(1);ret.add(list0);//从第2行开始 进行求每个元素for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {//处理第一个元素List<Integer> curRow = new ArrayList<>();curRow.add(1);//中间List<Integer> preRow = ret.get(i-1);for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {int val1 = preRow.get(j);int val2 = preRow.get(j-1);curRow.add(val1+val2);}//尾巴curRow.add(1);ret.add(curRow);}return ret;}
总结
顺序表作为最基础的数据结构之一,是理解更复杂结构的基石。它通过连续的内存空间和索引机制,实现了高效的元素访问,但在插入删除操作上存在性能瓶颈。
掌握顺序表的设计思想,不仅能帮助我们更好地理解编程语言中的内置集合(如 Java 的 ArrayList),也能为后续学习链表、栈、队列等结构打下坚实基础。
在实际开发中,应根据具体场景选择合适的数据结构 —— 需要频繁访问时选顺序表,需要频繁插入删除时可考虑链表,平衡二者优缺点的结构(如跳表)则适用于更复杂的场景。
