北航计算机保研机试题+解答
北航计院每年都是两/三道题,大模拟,考查各种数据结构(尤其是树和链表)的使用。
参考资料:GitHub - Muyiyunzi/BUAA-CS-Codes: 北京航空航天大学计算机学院研究生考试复试上机部分往年试题及解答
2021:
第一题:
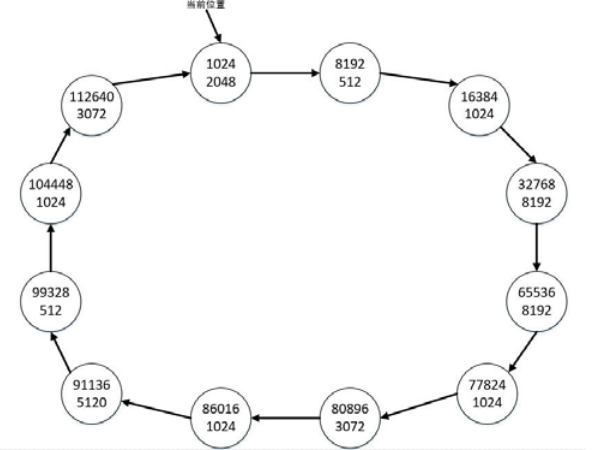
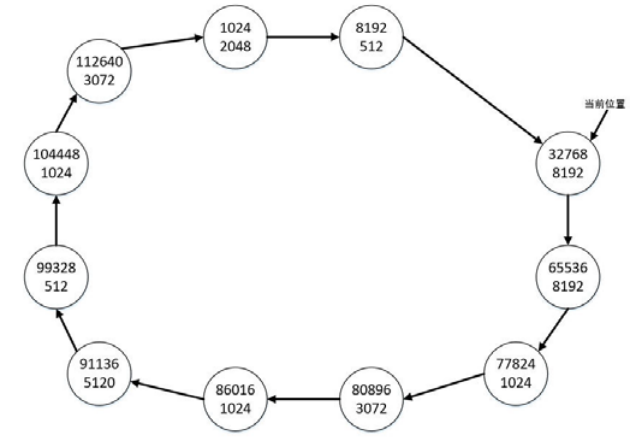
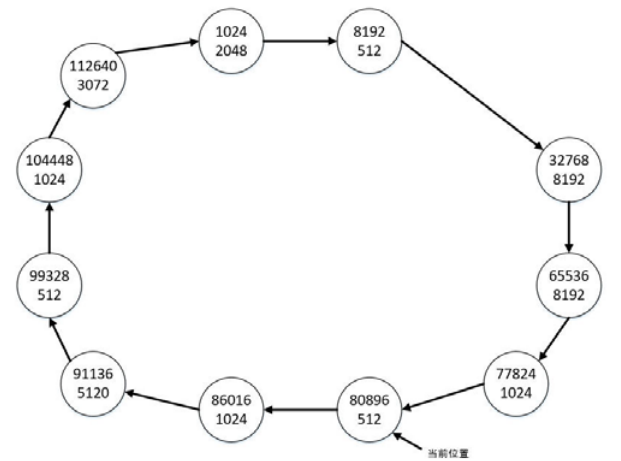
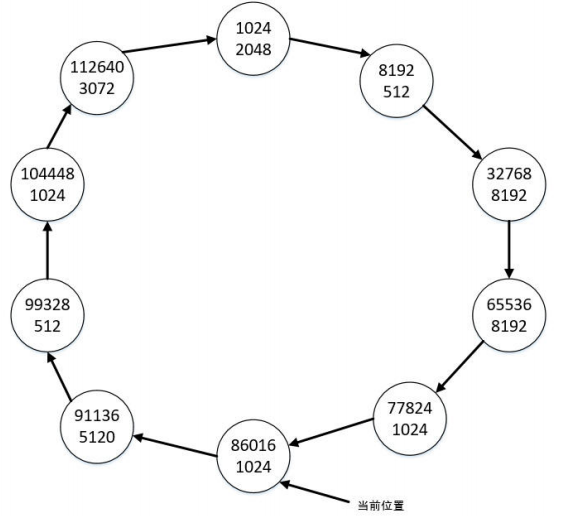
12
1024 2048
8192 512
16384 1024
32768 8192
65536 8192
77824 1024
80896 3072
86016 1024
91136 5120
99328 512
104448 1024
112640 3072
1024 2560 10240 512 1024 6400 512 -1104448 1024
112640 3072
1024 2048
8192 512
32768 1792
65536 8192
77824 1024
91136 5120#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
struct Node
{int sta;int capa;Node *pre = nullptr;Node *next = nullptr;Node(int sta, int capa) : sta(sta), capa(capa) {}
};int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);cin >> n;int a, b;Node *head = nullptr;Node *cur;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){cin >> a >> b;if (head == nullptr){head = new Node(a, b);head->next = head;head->pre = head;cur = head;}else{Node *p = new Node(a, b);// 尾插法p->pre = cur;p->next = head;head->pre = p;cur->next = p;cur = p;}}int require;Node *p = head;while (cin >> require && require != -1){int tempmin = INT_MAX;Node *t = head;Node *x = p->pre;do{if (p->capa >= require){if (p->capa < tempmin){tempmin = p->capa;t = p;}}p = p->next;} while (p != x);if (tempmin == INT_MAX){p = p->next;continue;}else if (tempmin == require){Node *z = t->next;Node *y = t->pre;y->next = z;z->pre = y;p = z;delete (t);}else if (tempmin > require){p = t;p->capa -= require;}}Node *x = p->pre;do{cout << p->sta << " " << p->capa << endl;p = p->next;} while (p != x);cout << p->sta << " " << p->capa << endl;return 0;
}第二题:
12
100 101 102 103
103 14 108 13
101 5 104 6
104 7 8 -1
102 105 106 107
106 1 110 2
108 16 15 -1
107 18 111 17
110 3 4 -1
105 9 109 10
111 20 19 -1
109 11 12 -1
17 865
5 668
20 3000
13 1020
11 980
8 2202
15 1897
6 1001
14 922
7 2178
19 2189
1 1267
12 3281
2 980
18 1020
10 980
3 1876
9 1197
16 980
4 576
-1 -1输出:
12 5
20 6
8 14
19 13
7 7
15 8
3 9
1 10
9 1
13 2
18 18
6 17
2 16
10 15
11 11
16 12
14 3
17 4
5 20
4 19比第一题简单,主要考查哈希表和树的层序遍历。
几个tips:首先是结构体部分,之前写的时候在 vector<Node> store(100); 这一句里,试图用无参构造函数去初始化 100 个 Node,但 Node 只有一个自己定义的带参构造函数,于是编译器不会合成默认构造函数,导致
error: no matching function for call to ‘Node::Node()’
改为这样就好:
struct Node
{int par = -1;int c1 = -1;int c2 = -1;int c3 = -1;Node() = default; // <-- 补上Node(int p, int a, int b, int c) // 原来的: par(p), c1(a), c2(b), c3(c) {}
};#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;struct TreeNode
{int c1 = -1;int c2 = -1;int c3 = -1;
};int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int n;cin >> n;// 使用map存储树节点:编号->子节点信息map<int, TreeNode> treeMap;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){int r, s1, s2, s3;cin >> r >> s1 >> s2 >> s3;treeMap[r] = {s1, s2, s3};}vector<pair<int, int>> flows;int gate, flowVal;while (cin >> gate >> flowVal){if (gate == -1 && flowVal == -1)break;flows.push_back({gate, flowVal});}// 按流量排序:流量降序,流量相同按编号升序sort(flows.begin(), flows.end(), [](const auto &a, const auto &b){if (a.second != b.second) return a.second > b.second;return a.first < b.first; });// 层次遍历获取登机口位置顺序vector<int> gatePositions; // 存储层次遍历得到的登机口位置queue<int> q;q.push(100); // 从根节点开始while (!q.empty()){int nodeId = q.front();q.pop();// 当前节点必须在树图中if (treeMap.find(nodeId) == treeMap.end())continue;TreeNode node = treeMap[nodeId];// 处理三个子节点:按c1->c2->c3顺序vector<int> children = {node.c1, node.c2, node.c3};for (int child : children){if (child == -1)continue;if (child < 100){ // 登机口gatePositions.push_back(child);}else{ // 分叉节点q.push(child);}}}// 输出调整结果for (int i = 0; i < flows.size(); i++){cout << flows[i].first << " " << gatePositions[i] << endl;}return 0;
}2019:
第一题:
比较简单,核心在于如何高效的求解素数,这里显然是筛法!
埃拉托色尼筛法(Sieve of Eratosthenes),它是一种批量找出某个上限以内所有素数的算法,而不是单独判断一个数是否为素数。
核心思想
从 2 开始,把当前最小未被划掉的数视为素数,然后划掉它的所有倍数;重复这一过程,直到处理完 √n 为止。剩下的未被划掉的数就是素数。
第二题:
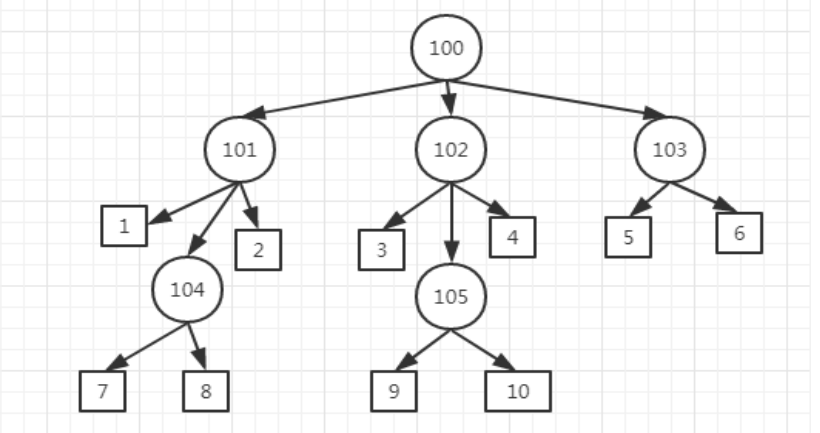
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);int n;if (!(cin >> n))return 0;unordered_map<int, array<int, 3>> children;unordered_map<int, int> parent; // child -> parentchildren.reserve(n);parent.reserve(n * 3);int r, a, b, c;int root = -1;for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){cin >> r >> a >> b >> c;if (i == 0)root = r;children[r] = {a, b, c};if (a != -1)parent[a] = r;if (b != -1)parent[b] = r;if (c != -1)parent[c] = r;}int m;cin >> m;vector<pair<int, int>> req;req.reserve(m);for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i){int des, pri;cin >> des >> pri;req.emplace_back(des, pri);}sort(req.begin(), req.end(), [](const pair<int, int> &x, const pair<int, int> &y){ return x.second < y.second; });auto is_leaf = [&](int x) -> bool{auto it = children.find(x);if (it == children.end())return true; // 没有孩子条目 -> 叶子auto &arr = it->second;return (arr[0] == -1 && arr[1] == -1 && arr[2] == -1);};auto get_ancestors = [&](int x){vector<int> anc;int cur = x;anc.push_back(cur);while (parent.find(cur) != parent.end()){cur = parent[cur];anc.push_back(cur);}return anc; // 从 x 到 root};auto path_between = [&](int u, int v){if (u == v)return vector<int>{u};vector<int> ancU = get_ancestors(u);vector<int> ancV = get_ancestors(v);unordered_set<int> setU;setU.reserve(ancU.size() * 2);for (int x : ancU)setU.insert(x);int lca = -1;for (int x : ancV){if (setU.count(x)){lca = x;break;}}// 拼 u -> ... -> lcavector<int> path;for (int x : ancU){path.push_back(x);if (x == lca)break;}// 拼 lca -> ... -> v (不重复 lca)vector<int> down;for (int x : ancV){if (x == lca)break;down.push_back(x); // v -> ... -> child_of_lca}for (auto it = down.rbegin(); it != down.rend(); ++it)path.push_back(*it);return path;};int sta = root;for (auto &p : req){int des = p.first;vector<int> pth = path_between(sta, des); // 包含 sta 和 des// 如果起点是叶子,则按照样例要求省略起点(即不打印 sta)int start_idx = 0;if (is_leaf(sta) && !pth.empty())start_idx = 1;for (int i = start_idx; i < (int)pth.size(); ++i){cout << pth[i] << (i + 1 == (int)pth.size() ? "" : " ");if (i + 1 == (int)pth.size())cout << ""; // 保持格式if (i < (int)pth.size() - 1)cout << " ";}cout << "\n";sta = des;}// 送完后返回 root(也按样例省略起点若为叶子)vector<int> finalPath = path_between(sta, root);int start_idx = 0;if (is_leaf(sta) && !finalPath.empty())start_idx = 1;for (int i = start_idx; i < (int)finalPath.size(); ++i){cout << finalPath[i];if (i + 1 < (int)finalPath.size())cout << " ";}cout << "\n";return 0;
}
2018:
第一题:

#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
struct Node
{int ch1 = -1;int ch2 = -1;int ch3 = -1;Node() = default;Node(int ch1, int ch2, int ch3) : ch1(ch1), ch2(ch2), ch3(ch3) {};
};
unordered_map<int, Node> mmap;
int t, ansnode, ansdep;void dfs(int root, int depth, vector<int> &count)
{if (root == -1)return;int b = mmap[root].ch1;int c = mmap[root].ch2;int d = mmap[root].ch3;int k = 0;if (b != -1)k++;if (c != -1)k++;if (d != -1)k++;if (k > t){t = k;ansnode = root;ansdep = depth;}else if (k == t && depth > ansdep){ansnode = root;ansdep = depth;}count.push_back(root);dfs(b, depth + 1, count);dfs(c, depth + 1, count);dfs(d, depth + 1, count);return;
}int main()
{cin >> n;int a, b, c, d;int root = -1;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){cin >> a >> b >> c >> d;mmap[a] = Node(b, c, d);if (root == -1)root = a;}using pii = pair<int, int>;t = 0;ansnode = root;ansdep = 0;vector<int> count;dfs(root, 0, count);int time = 0;for (int i = 0; i < count.size(); i++){if (count[i] == ansnode){time = i + 1;break;}}cout << ansnode << " " << time << endl;return 0;
}2017:
第一题:
对于实现稳定排序,c++里面的sort只需要把比较符定义好就行:
struct node {int x, t; //输入的数值和次序
}num[maxn];
bool cmp(node a, node b) {if(a.x == b.x) return a.t < b.t;return a.x < b.x;
}还有一个做法是直接套用稳定排序std:
stable_sort(store.begin(), store.end(), [](const Node& A, const Node& B) {return A.num < B.num; // stable_sort 保证相等时前者先于后者});对于归并排序,c++中的稳定排序,实现:
在实现上,正确、鲁棒的做法是对每个 left 明确算出 mid = min(left+s-1,n-1) 和 right = min(left+2*s-1,n-1),并且只在 left + s < n 时合并(条件明晰,这样就省去了复杂且易出错的判断)
注意:合并的时候下标要对齐:store[i] = temp[i - le];
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
struct Node
{int num;int pos;Node() = default;Node(int num, int pos) : num(num), pos(pos) {}
};
vector<Node> store;// 把 [le..mid] 和 [mid+1..ri] 合并到有序
void merge_segment(int le, int mid, int ri)
{vector<Node> temp;int a = le;int b = mid + 1;while (a <= mid && b <= ri){if (store[a].num <= store[b].num){temp.push_back(store[a++]);}else{temp.push_back(store[b++]);}}while (a <= mid)temp.push_back(store[a++]);while (b <= ri)temp.push_back(store[b++]);for (int i = le; i <= ri; ++i)store[i] = temp[i - le];
}void iterative_merge_sort()
{if (n <= 1)return;for (int s = 1; s < n; s <<= 1){// 每次处理长度为 s 的一对对区间for (int left = 0; left < n - s; left += 2 * s){int mid = left + s - 1;int right = min(left + 2 * s - 1, n - 1);merge_segment(left, mid, right);}}
}int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cin >> n;store.reserve(n);for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){int a;cin >> a;store.emplace_back(a, i);}iterative_merge_sort();if (n % 2 == 1){cout << store[n / 2].num << " " << store[n / 2].pos << "\n";}else{cout << store[n / 2 - 1].num << " " << store[n / 2 - 1].pos << "\n";cout << store[n / 2].num << " " << store[n / 2].pos << "\n";}return 0;
}
再次强调主归并的标准写法:
for (int s = 1; s < n; s <<= 1){// 每次处理长度为 s 的一对对区间for (int left = 0; left < n - s; left += 2 * s){int mid = left + s - 1;int right = min(left + 2 * s - 1, n - 1);merge_segment(left, mid, right);}}第二题:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;int findlca(int a, int u, int v, const vector<pair<int, int>> &childs)
{if (a == -1)return -1;if (a == u || a == v)return a;int left = childs[a].first;int right = childs[a].second;int k1 = -1, k2 = -1;if (left != -1)k1 = findlca(left, u, v, childs);if (right != -1)k2 = findlca(right, u, v, childs);if (k1 != -1 && k2 != -1)return a;return (k1 != -1) ? k1 : k2;
}int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);int n;if (!(cin >> n))return 0;unordered_map<string, int> mmap;vector<string> id2name;vector<int> parents; // parents[i] = parent id or -1vector<pair<int, int>> childs; // childs[i] = {left, right}, -1 表示无子int cnt = 0;auto ensure = [&](const string &s) -> int{auto it = mmap.find(s);if (it != mmap.end())return it->second;int id = cnt++;mmap[s] = id;id2name.push_back(s);parents.push_back(-1);childs.push_back({-1, -1});return id;};for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){string a, b, c;cin >> a >> b >> c;int pa = ensure(a);int pb = ensure(b);int pc = ensure(c);parents[pb] = pa;parents[pc] = pa;childs[pa] = {pb, pc};}string s1, s2;cin >> s1 >> s2;if (!mmap.count(s1) || !mmap.count(s2))return 0;int u = mmap[s1];int v = mmap[s2];// 找 rootint root = -1;for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i)if (parents[i] == -1){root = i;break;}if (root == -1)return 0;int lca = findlca(root, u, v, childs);if (lca == -1){// 理论上不该发生(输入保证在同一棵树),但防御性输出cout << "-1 0\n";return 0;}auto dist = [&](int node, int anc){int steps = 0;while (node != anc){node = parents[node];steps++;if (node == -1)break; // 防御性}return steps;};int du = dist(u, lca);int dv = dist(v, lca);cout << id2name[lca] << " " << abs(du - dv) << "\n";return 0;
}#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;int findlca(int a, int u, int v, const vector<pair<int, int>> &childs)
{if (a == -1)return -1;if (a == u || a == v)return a;int left = childs[a].first;int right = childs[a].second;int k1 = -1, k2 = -1;if (left != -1)k1 = findlca(left, u, v, childs);if (right != -1)k2 = findlca(right, u, v, childs);if (k1 != -1 && k2 != -1)return a;return (k1 != -1) ? k1 : k2;
}此外,上面的是给了输入数量N的写法,如果没有给n?
使用getline(cin, line)读一整行的输入!然后利用空格划分字符串。
2016:
第一题:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;int main()
{cin >> n;string ori = to_string(n);string change = ori;reverse(change.begin(), change.end());int m = stoi(change);// cout << change << endl;// cout << m << endl;if (m > 0 && m % n == 0){cout << n << '*' << m / n << '=' << m << endl;}elsecout << ori << " " << change << endl;return 0;
}第二题:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string s;
int main()
{getline(cin, s);int len = s.size();int pos = -1;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){if (s[i] != '{')continue;else{pos = i;break;}}int k = pos + 1;vector<string> ori;string t = "";while (k < len - 2){if (s[k] != ','){t += s[k];k++;}else{ori.push_back(t);t.clear();k++;}}ori.push_back(t);using psi = pair<string, int>;vector<psi> ans;for (string str : ori){int len = str.size();int n_pos = -1;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){if (str[i] == '='){n_pos = i;break;}}if (n_pos == -1)ans.push_back(make_pair(str, n_pos));else{int z = stoi(str.substr(n_pos + 1));ans.push_back(make_pair(str.substr(0, n_pos), z));}}int pre = 0;for (auto ele : ans){auto [name, num] = ele;if (num == -1)ele.second = pre++;else if (num != -1)pre = num + 1;cout << ele.first << " " << ele.second << endl;}return 0;
}2015:
第一题:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a, b;void count(int x, vector<int> &store)
{for (int i = 1; i <= x / 2 + 1; i++){if (x % i == 0)store.push_back(i);}return;
}int main()
{cin >> a >> b;vector<int> numa;vector<int> numb;count(a, numa);count(b, numb);string outa = "";int len = numa.size();for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++){outa = outa + to_string(numa[i]) + '+';}outa = outa + to_string(numa[len - 1]) + '=';int tota = accumulate(numa.begin(), numa.end(), 0);outa += to_string(tota);string outb = "";len = numb.size();for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++){outb = outb + to_string(numb[i]) + '+';}outb = outb + to_string(numb[len - 1]) + '=';int totb = accumulate(numb.begin(), numb.end(), 0);outb += to_string(totb);cout << a << ", " << outa << endl;cout << b << ", " << outb << endl;cout << int(tota == b && totb == a) << endl;return 0;
}第二题:
new Node() 创建临时 pre,导致删除首节点时形成自环(p->next = head 把自己指向自己)。——所以引入哨兵节点做统一真的很重要!#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using t4i = tuple<int, int, int, int>;
struct Node
{int id = -1;t4i pos = {0, 0, 0, 0};Node *next = nullptr;Node() = default;
};
int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);int n, m;cin >> n;int id, a, b, c, d;Node *head = nullptr;Node *tail = nullptr;for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){cin >> id >> a >> b >> c >> d;Node *p = new Node();p->id = id;p->pos = {a, b, c, d};if (!head){head = tail = p;}else{tail->next = p;tail = p;}}cin >> m;int x, y;for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i){cin >> x >> y;Node dummy; // 使用栈上的哨兵dummy.next = head;Node *pre = &dummy;Node *p = head;while (p != nullptr){auto [rix, riy, lex, ley] = p->pos;if (lex <= x && x <= rix && riy <= y && y <= ley){pre->next = p->next;head = dummy.next;p->next = head;head = p;break;}else{pre = p;p = p->next;}}}Node *cur = head;while (cur){cout << cur->id << " ";cur = cur->next;}cout << "\n";return 0;
}
第三题:
std::getline 在 读到换行符 和 读到 EOF 时的行为:-
std::getline(istream& is, string& str)会一直从流is中读字符,直到遇到换行符 或 EOF 为止。 -
当遇到换行符:
-
换行符本身 不会存入
str。 -
getline会丢弃这个换行符(把它从输入流里读走,但不放到结果字符串里)。 -
函数返回后,
str中存的就是该行的内容(不包含行尾的\n)。
-
-
返回值:成功读取到一行 →
getline返回一个非空的istream&,在布尔上下文中为 true。
还有就是在结尾要判断一下有没有多余的还没放进去
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;int main() {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);set<string> mset;string s;while (getline(cin, s)) {string t;for (char ch : s) {// 题目保证都是小写字母,但用 islower 更通用一点if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {t.push_back(ch);} else {if (!t.empty()) {mset.insert(t);t.clear();}}}// 行结尾后,若有缓存的单词也要插入if (!t.empty()) {mset.insert(t);}}for (const auto &w : mset) {cout << w << '\n';}return 0;
}
