数据库造神计划第八天---增删改查(CRUD)(4)

🔥个人主页:寻星探路
🎬作者简介:Java研发方向学习者
📖个人专栏:《从青铜到王者,就差这讲数据结构!!!》、 《JAVA(SE)----如此简单!!!》、《数据库那些事!!!》
⭐️人生格言:没有人生来就会编程,但我生来倔强!!!

目录
一、插入查询结果
1、语法
2、示例
二、聚合函数
1、常用函数
2、示例
2.1COUTN(有多少记录)
2.2SUM(和)
2.3AVG(平均)
2.4MAX(最大)
2.5MIN(最小)
三、group by分组查询
1、语法
2、示例
3、having子句
4、Having与Where的区别
续接上一话:
一、插入查询结果
把一个查询语句的结果,作为另一个插入语句的插入的数据
1、语法
INSERT INTO table_name [(column [, column ...])] SELECT ...2、示例
删除表中的重复记录,重复的数据只能有⼀份
# 创建测试表,并构造数据
CREATE TABLE t_recored (id int, name varchar(20));
# 插⼊测试数据
INSERT INTO t_recored VALUES(100, 'aaa'),(100, 'aaa'),(200, 'bbb'),(200, 'bbb'),(200, 'bbb'),(300, 'ccc');
# 查看结果
select * from t_recored;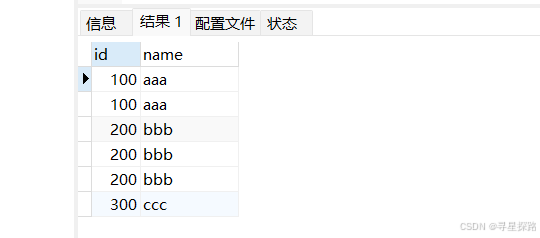
实现思路:原始表中的数据⼀般不会主动删除,但是真正查询时不需要重复的数据,如果每次查询都使用DISTINCT进行去重操作,会严重效率。可以创建⼀张与 t_recored 表结构相同的表,把去重的记录写⼊到新表中,以后查询都从新表中查,这样真实的数据不丢失,同时又能保证查询效率
# 创建⼀张新表,表结构与t_recored相同
create table t_recored_new like t_recored;
# 新表中没有记录
selec * from t_recored_new;
# 原表中的记录去重后写⼊到新表
insert into t_recored_new select distinct * from t_recored;
# 查询新表中的记录,实现去重
select * from t_recored_new;
# 新表与原来重命名
rename table t_recored to t_recored_old, t_recored_new to t_recored;
# 查询重命名后表中的记录,实现需求且原来中的记录不受影响
select * from t_recored;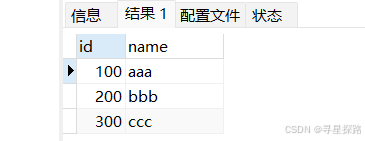
select * from t_recored_old;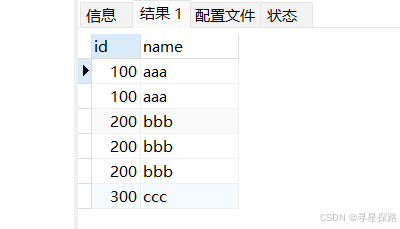
二、聚合函数
针对查询结果进行一些行级别的"统计"!!!
先查询,再聚合!!!
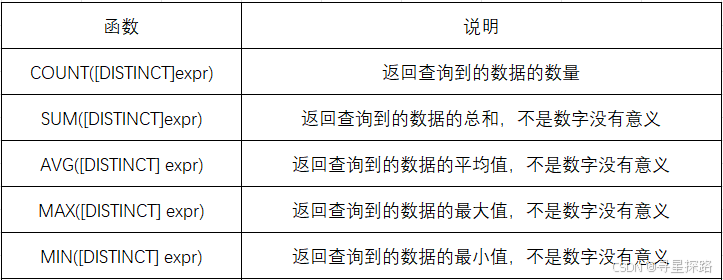
1、常用函数
2、示例
#创建表结构
CREATE TABLE exam (id BIGINT,name VARCHAR(20) COMMENT '同学姓名',chinese float COMMENT '语⽂成绩',math float COMMENT '数学成绩',english float COMMENT '英语成绩'
);#插⼊测试数据
INSERT INTO exam (name, chinese, math, english) VALUES(1, '唐三藏', 134, 98, 56),(3, '猪悟能', 176, 98, 90),(4, '曹孟德', 140, 90, 67),(5, '刘⽞德', 110, 115, 45),(6, '孙权', 140, 73, 78),(7, '宋公明', 150, 95, 30),(8, '张飞', 54 ,0 ,NULL);2.1COUTN(有多少记录)
(1)统计exam表中有多少记录
# 使⽤ * 做统计
select count(*) from exam;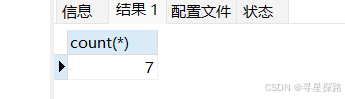
# 使⽤常量做统计
select count(1) from exam;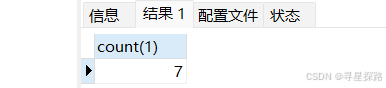
(2)统计有多少学生参加数学考试
# 使⽤指定列做统计
select count(math) from exam;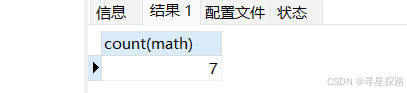
(3)统计有多少学生参加英语考试
# 查看表中的记录
select * from exam;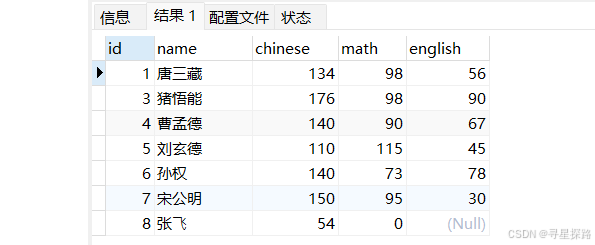
(张飞没参加英语考试)
# NULL 的数据不会计⼊结果
select count(english) from exam;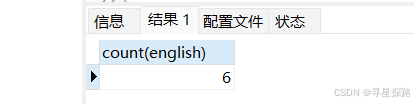
(4)统计语文成绩小于50分的学生个数
# 加⼊where条件
select count(chinese) from exam where chinese < 10;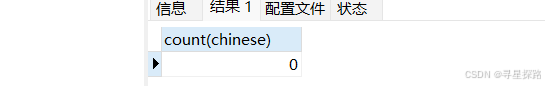
一个 sq| 中有条件,有 order by,有 limit 有聚合函数执行顺序如何的??
1)遍历表的每一行
2)执行 where,把每一行代入条件
3)获取到列, 表达式求值,定义别名操作,
4)执行 order by 对结果排序
5)执行 limit 进行限制长度
6)再进行聚合
2.2SUM(和)
#注:sum 操作会直接排除 null 值!!!
(1)统计所有学生数学成绩总分
select sum(math) from exam;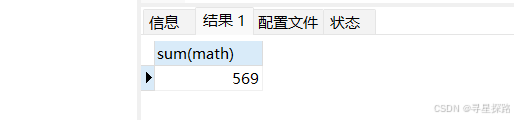
(2)统计所有学生英语成绩总分
# 值为NULL的列不参与统计
select sum(english) from exam;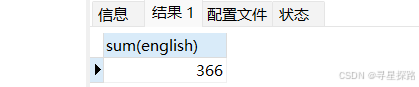
(3)不能统计非数值的列
select sum(name) from exam;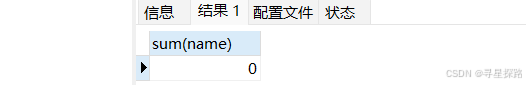
2.3AVG(平均)
(1)统计英语成绩的平均分
# NULL值不参与统计
select avg(english) from exam;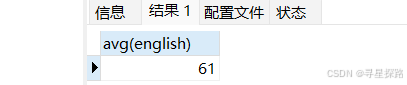
(2)统计平均总分
select avg(chinese + math + english) as 总分 from exam;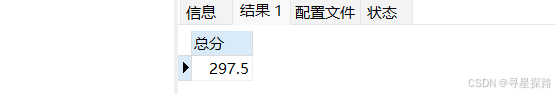
2.4MAX(最大)
(1)查询英语最高分
select max(english) from exam;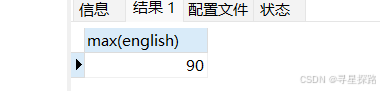
2.5MIN(最小)
(1)查询>70分以上的数学最低分
select min(math) from exam where math > 70;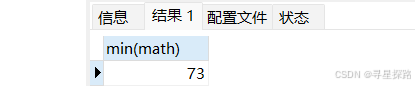
(2)查询数据成绩的最高分与英语成绩的最低分
# 可以使⽤多个聚合函数
select max(math), min(english) from exam;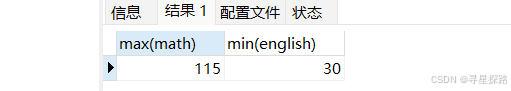
三、group by分组查询
group by子句的作用是通过⼀定的规则将⼀个数据集划分成若干个小的分组,然后针对若干个分组进行数据处理,比如使用聚合函数对分组进行统计。
1、语法
SELECT {col_name | expr} ,... , aggregate_function (aggregate_expr)FROM table_referencesGROUP BY { col_name | expr}, ...[H AVING where_condition]col_name|expr:要查询的列或表达式,可以有多个,必须在 据 GROUP BY 子句中作为分组的依
aggregate_function:聚合函数,比如COUNT(),SUM(),AVG(),MAX(),MIN()
aggregate_expr:聚合函数传入的列或表达式,如果列或表达式不在 GOURP BY 子句中,必须包含中聚合函数中
2、示例
准备测试表及数据职员表emp,列分别为:id(编号),name(姓名),role(角色),salary(薪水)
drop table if exists emp;create table emp (id bigint primary key auto_increment,name varchar(20) not null,role varchar(20) not null,salary decimal(10, 2) not null);insert into emp values (1, '⻢云', '⽼板', 1500000.00);insert into emp values (2, '⻢化腾', '⽼板', 1800000.00);insert into emp values (3, '张三', '程序员', 10000.00);insert into emp values (4, '李四', '程序员', 12000.00);insert into emp values (5, '王五', '程序员', 9000.00);insert into emp values (6, '赵六', '程序员', 8000.00);insert into emp values (7, '孙悟空', '游戏⻆⾊', 956.8);insert into emp values (8, '猪悟能', '游戏⻆⾊', 700.5);insert into emp values (9, '沙和尚', '游戏⻆⾊', 333.3);select * from emp;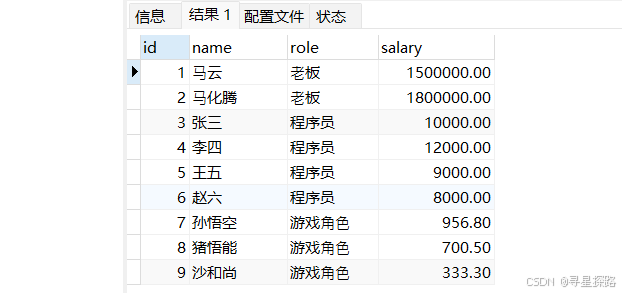
统计每个角色的人数
select role, count(*) from emp group by role;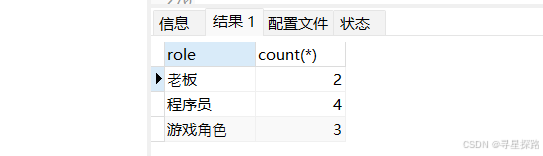
统计每个角色的平均工资,最高工资,最低工资
select role, ROUND(avg(salary),2) as 平均⼯资, ROUND(max(salary),2) as 最⾼⼯资, ROUND(min(salary),2) as 最低⼯资 from emp group by role;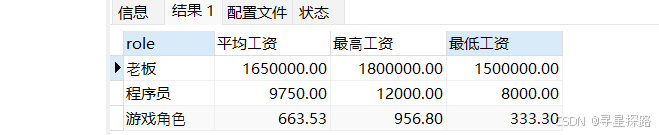
3、having子句
使用GROUPBY对结果进行分组处理之后,对分组的结果进行过滤时,不能使用WHERE 子句,而要使用 HAVING 子句
显示平均工资低于1500的角色和它的平均工资
select role, avg(salary) from emp group by role having avg(salary) < 1500;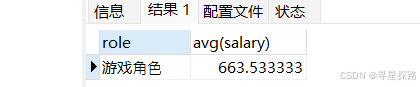
where 同样可以使用
where 的条件是在聚合之前使用的条件
having 的条件是在聚合之后使用的条件
4、Having与Where的区别
(1)Having用于对分组结果的条件过滤
(2)Where用于对表中真实数据的条件过滤
由于内容较多,会分为多篇讲解,预知后续内容,请看后续博客!!!
