h3笔记:polygon
- h3-py使用抽象基类
H3Shape及其具体子类LatLngPoly和LatLngMultiPoly来表示多边形 (polygon) 和多多边形 (multipolygon)- 任何涉及 “H3Shape” 的引用或函数名,都同时适用于
LatLngPoly和LatLngMultiPoly对象
- 任何涉及 “H3Shape” 的引用或函数名,都同时适用于
1 LatLngPoly
- 通过提供一组 经纬度 (latitude/longitude) 坐标对 来创建一个简单的
LatLngPoly对象,这些坐标描述了多边形的外边界。
import h3
import foliumouter = [(37.804, -122.412),(37.778, -122.507),(37.733, -122.501)
]poly = h3.LatLngPoly(outer)
print(poly)
#<LatLngPoly: [3]># folium 地图
m = folium.Map(location=[37.77, -122.45], zoom_start=12, tiles="cartodbpositron")folium.GeoJson(poly.__geo_interface__
).add_to(m)
m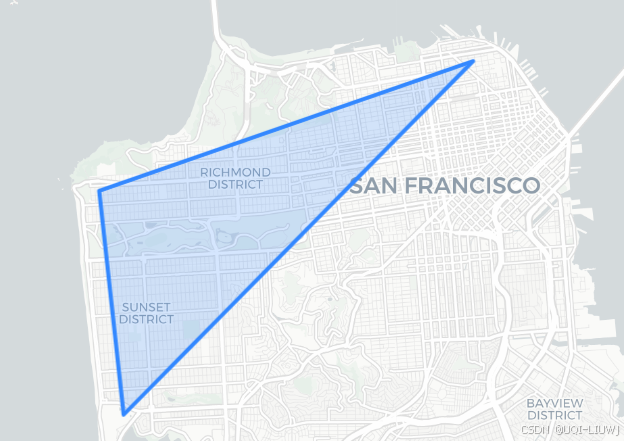
- 还可以选择性地在多边形中添加 “孔洞 (holes)” —— 只需再追加一些经纬度坐标列表,用来描述这些孔洞即可
hole1 = [(37.782, -122.449),(37.779, -122.465),(37.788, -122.454),
]poly = h3.LatLngPoly(outer, hole1)
print(poly)
#<LatLngPoly: [3/(3,)]># folium 地图
m = folium.Map(location=[37.77, -122.45], zoom_start=12, tiles="cartodbpositron")folium.GeoJson(poly.__geo_interface__
).add_to(m)
m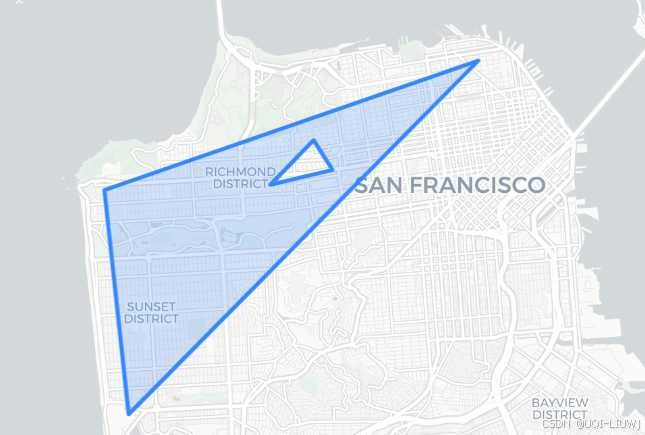
hole2 = [(37.771, -122.484),(37.761, -122.481),(37.758, -122.494),(37.769, -122.496),
]poly = h3.LatLngPoly(outer, hole1, hole2)
print(poly)
# folium 地图
m = folium.Map(location=[37.77, -122.45], zoom_start=12, tiles="cartodbpositron")folium.GeoJson(poly.__geo_interface__
).add_to(m)
m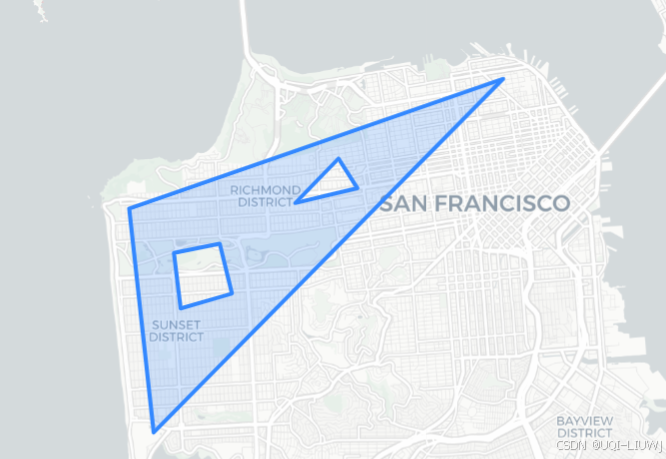
1.1 字符串表示与属性
LatLngPoly 的字符串表示(通过它的 __repr__ 方法给出)会显示:
外环(outer loop)顶点的数量;
以及每个孔洞(hole)顶点的数量。
<LatLngPoly: [3/(3, 4)]>表示一个多边形:
外边界由 3 个顶点组成;
内部有 2 个孔洞,第一个孔洞由 3 个顶点组成,第二个孔洞由 4 个顶点组成。
1.2 坐标访问
可以通过属性来访问构成多边形的坐标:
LatLngPoly.outer
返回外环的经纬度点列表(外边界)。LatLngPoly.holes
返回一个列表,其中每个元素又是一个经纬度点列表,分别描述每个孔洞。
poly = h3.LatLngPoly(outer, hole1, hole2)
poly.outer
#((37.804, -122.412), (37.778, -122.507), (37.733, -122.501))poly.holes
'''
([(37.782, -122.449), (37.779, -122.465), (37.788, -122.454)],[(37.771, -122.484),(37.761, -122.481),(37.758, -122.494),(37.769, -122.496)])
'''2 __geo_interface__
LatLngPoly.__geo_interface__会返回该多边形的 GeoJSON 表示-
LatLngPoly.__geo_interface__等价于对该对象调用h3.h3shape_to_geo():
-
需要注意以下区别:
点的顺序:GeoJSON 中的点是 (lng, lat)(经度在前,纬度在后),而
LatLngPoly构造函数需要 (lat, lng)。首尾点重复:GeoJSON 中的多边形,最后一个顶点会重复第一个顶点,以闭合环路。
d = poly.__geo_interface__
d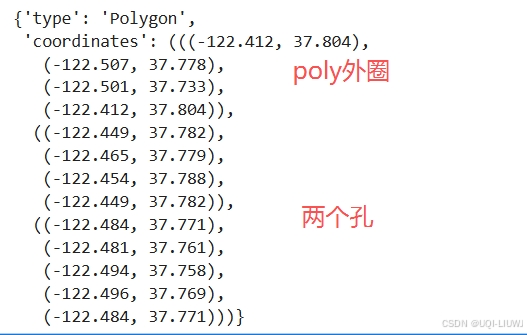
h3.h3shape_to_geo(poly)
'''
{'type': 'Polygon','coordinates': (((-122.412, 37.804),(-122.507, 37.778),(-122.501, 37.733),(-122.412, 37.804)),((-122.449, 37.782),(-122.465, 37.779),(-122.454, 37.788),(-122.449, 37.782)),((-122.484, 37.771),(-122.481, 37.761),(-122.494, 37.758),(-122.496, 37.769),(-122.484, 37.771)))}
'''2.1 从 GeoJSON 创建 LatLngPoly
可以通过 h3.geo_to_h3shape() 从 GeoJSON 字典或任何实现了 __geo_interface__ 的对象来创建一个 LatLngPoly
d = poly.__geo_interface__
d
'''
{'type': 'Polygon','coordinates': (((-122.412, 37.804),(-122.507, 37.778),(-122.501, 37.733),(-122.412, 37.804)),((-122.449, 37.782),(-122.465, 37.779),(-122.454, 37.788),(-122.449, 37.782)),((-122.484, 37.771),(-122.481, 37.761),(-122.494, 37.758),(-122.496, 37.769),(-122.484, 37.771)))}
'''h3.geo_to_h3shape(d)
#<LatLngPoly: [3/(3, 4)]>3 多边形转 H3 单元格
- 可以通过
h3.h3shape_to_cells()获取某个多边形 (LatLngPoly) 内部所有 H3 单元格(cell) - 具体来说,它会返回所有质心 (centroid) 落在该多边形内部的单元格索引
- 调用时需要指定 分辨率 (resolution)。
hole1 = [(37.782, -122.449),(37.779, -122.465),(37.788, -122.454),
]poly = h3.LatLngPoly(outer, hole1)
print(poly)h3.h3shape_to_cells(poly, res=7)
'''
<LatLngPoly: [3/(3,)]>
['872830958ffffff', '87283095bffffff', '87283095affffff', '872830829ffffff']
'''
from shapely.geometry import shape as shapely_shape
# folium 地图
m = folium.Map(location=[37.77, -122.45], zoom_start=12, tiles="cartodbpositron")folium.GeoJson(poly.__geo_interface__
).add_to(m)cells = h3.h3shape_to_cells(poly,9)
boundary = h3.cells_to_h3shape(cells)
print(boundary)folium.GeoJson(boundary.__geo_interface__
).add_to(m)m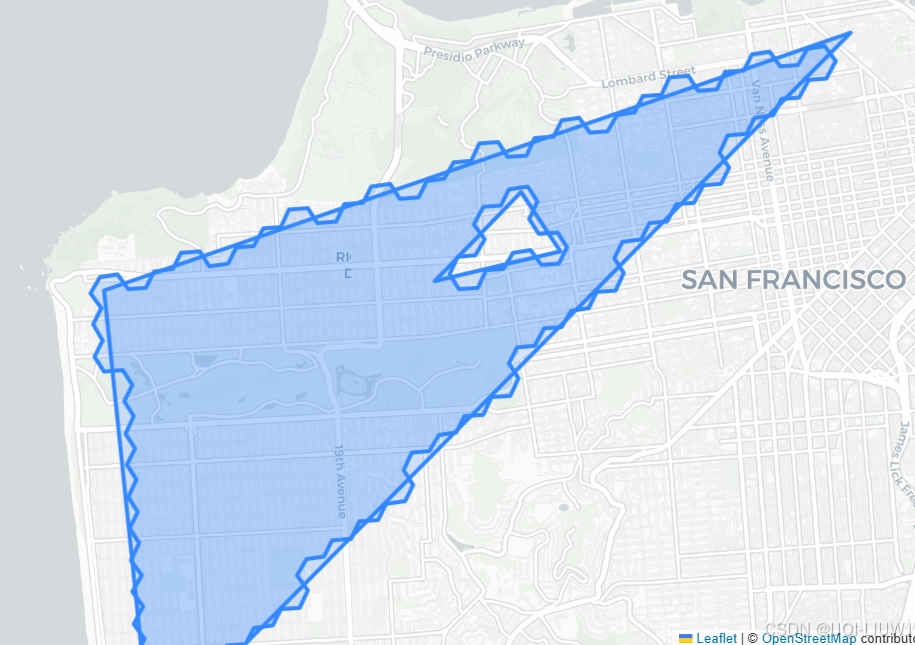
3.1 H3 多边形不要求遵循“右手法则”
- 与 GeoJSON Polygon 不同,
LatLngPoly对象 不需要遵循“右手法则”。 右手法则 的要求是:
外环(outer loop)顶点必须按 逆时针 (counterclockwise) 顺序排列;
孔洞(holes)顶点必须按 顺时针 (clockwise) 顺序排列。
在
h3-py中:顶点顺序可以随意,通常都会按你期望的方式解析,例如在转换为 H3 cell 集合时。
但是:
h3-py并不会自动调整顶点顺序来符合右手法则。所以如果你用
__geo_interface__去画图,可能出现渲染错误。
4 LatLngMultiPoly
一个 LatLngMultiPoly 可以由多个 LatLngPoly 对象创建。
它的字符串表示会显示:
每个
LatLngPoly外环的顶点数量;以及每个孔洞(如果存在)的顶点数量。
poly1 = h3.LatLngPoly([(37.804, -122.412), (37.778, -122.507), (37.733, -122.501)])
poly2 = h3.LatLngPoly([(37.803, -122.408), (37.736, -122.491), (37.738, -122.380), (37.787, -122.39)],[(37.760, -122.441), (37.772, -122.427), (37.773, -122.404), (37.758, -122.401), (37.745, -122.428)]
)
mpoly = h3.LatLngMultiPoly(poly1, poly2)print(poly1)
print(poly2)
print(mpoly)'''
<LatLngPoly: [3]>
<LatLngPoly: [4/(5,)]>
<LatLngMultiPoly: [3], [4/(5,)]>
'''
m = folium.Map(location=[37.77, -122.45], zoom_start=12, tiles="cartodbpositron")folium.GeoJson(mpoly.__geo_interface__
).add_to(m)
m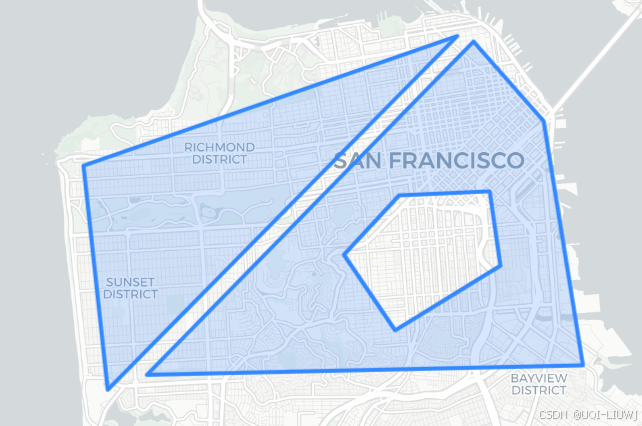
5 从 Cells 转换为 LatLngPoly 或 LatLngMultiPoly
如果你手里有一组 H3 单元格 (cells) 想要可视化,有两种常用做法:
转换为
LatLngPoly/LatLngMultiPoly使用
h3.cells_to_h3shape(cells)。得到的结果可以通过
__geo_interface__拿到 GeoJSON 表示,方便绘图(比如在folium或geopandas中)。
直接获取 GeoJSON
使用
h3.cells_to_geo(cells)。直接返回一个 GeoJSON 风格的字典,可以立即丢给
folium.GeoJson()使用。
