1.泛型的引入
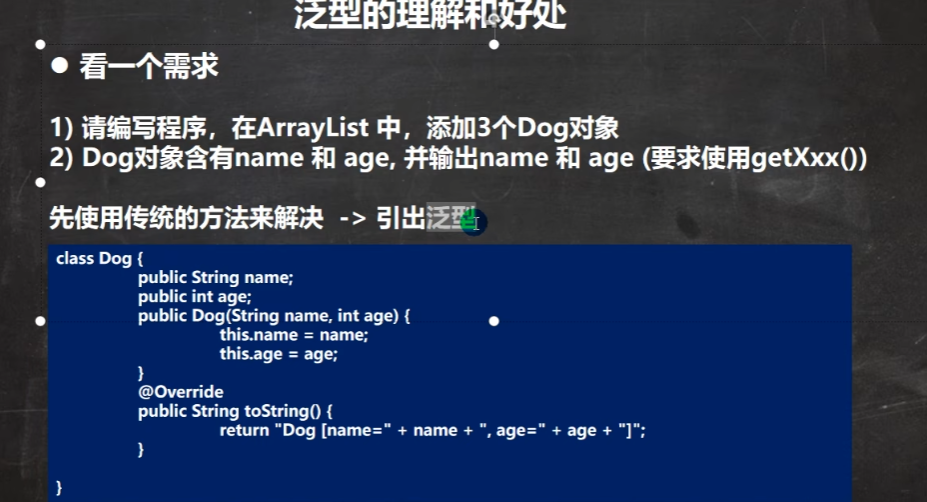

package com.hspedu.generic;import java.util.ArrayList;@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Generic01 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 使用传统方法来解决ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();arrayList.add(new Dog("旺财", 10));arrayList.add(new Dog("发财", 1));arrayList.add(new Dog("小黄", 5));// 假如不小心,添加了一只猫arrayList.add(new Cat("招财猫", 8));// 遍历for (Object o : arrayList) {// 向下转型 Object -> DogDog dog = (Dog) o;System.out.println(dog.getName() + "-" + dog.getAge());}}
}class Dog {private String name;private int age;public Dog(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}
}class Cat { // Cat 类private String name;private int age;public Cat(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}
}
2.泛型的入门

package com.hspedu.generic.imporve;import java.util.ArrayList;//@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Generic02 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 使用传统方法来解决 ===> 使用泛型//解读//1.当我们 ArrayList<Dog> 表示存放到 ArrayList 集合中的元素是 Dog 类型(细节后面说...)//2.如果编译器发现添加的类型,不满足要求,就会报错//3.在遍历的时候,可以直接取出 Dog 类型而不是 Object//4. public class ArrayList<E> {} E称为泛型,那么 Dog -> EArrayList<Dog> arrayList = new ArrayList<Dog>();arrayList.add(new Dog("旺财", 10));arrayList.add(new Dog("发财", 1));arrayList.add(new Dog("小黄", 5));// 假如不小心,添加了一只猫//arrayList.add(new Cat("招财猫", 8));// 遍历for (Object o : arrayList) {// 向下转型 Object -> DogDog dog = (Dog) o;System.out.println(dog.getName() + "-" + dog.getAge());}System.out.println("===使用泛型后进行遍历===");// 遍历for (Dog dog : arrayList) {System.out.println(dog.getName() + "-" + dog.getAge());}}
}/*
1.请编写程序,在 ArrayList 中,添加 3 个 Dog 对象
2.Dog 对象含有 name 和 age , 并输出 name 和 age (要求使用 getXXX())
3.使用泛型来完成代码*//*
旺财-10
发财-1
小黄-5
===使用泛型后进行遍历===
旺财-10
发财-1
小黄-5*/class Dog {private String name;private int age;public Dog(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}
}class Cat { // Cat 类private String name;private int age;public Cat(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}
}
3.泛型说明

对 4 的说明

package com.hspedu.generic;public class Generic03 {public static void main(String[] args) {//注意,特别强调: E 具体的数据类型在定义 Person 对象的时候指定,即在编译期间,就确定 E 是什么类型Person<String> stringPerson = new Person<String>("我是地球的");stringPerson.show(); // class java.lang.String/*可以这样理解,上面的 Person 类class Person {String s; // E 表示 s 的数据类型,该数据类型在定义 Person 对象的时候指定,即在编译期间,就确定 E 是什么类型public Person(String s) { // E 也可以是在参数类型this.s = s;}public String f() { // 返回类型使用 Ereturn s;}}*/Person<Integer> person2 = new Person<Integer>(100);person2.show(); // class java.lang.Integer/*class Person {Integer s; // E 表示 s 的数据类型,该数据类型在定义 Person 对象的时候指定,即在编译期间,就确定 E 是什么类型public Person(Integer s) { // E 也可以是在参数类型this.s = s;}public Integer f() { // 返回类型使用 Ereturn s;}}*/}
}class Person<E> {E s; // E 表示 s 的数据类型,该数据类型在定义 Person 对象的时候指定,即在编译期间,就确定 E 是什么类型public Person(E s) { // E 也可以是在参数类型this.s = s;}public E f() { // 返回类型使用 Ereturn s;}public void show() {System.out.println(s.getClass()); // 显示 s 的运行类型}
}
4.泛型应用实例

package com.hspedu.generic;import java.util.*;@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class GenericExercise {public static void main(String[] args) {// 使用泛型方式给 HashSet 放入 3 个学生对象HashSet<Student> students = new HashSet<Student>();students.add(new Student("jack", 18));students.add(new Student("tom", 28));students.add(new Student("mary", 19));// 遍历for (Student student : students) {System.out.println(student);}// 使用泛型给 HashMap 放入 3 个学生对象// k -> String v -> StudentHashMap<String, Student> hm = new HashMap<String, Student>();/*public class HashMap<K,V> {}*/hm.put("milan", new Student("milan", 38));hm.put("smith", new Student("smith", 48));hm.put("swk", new Student("swk", 10000));System.out.println("======");//迭代器 EntrySet/*public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es;return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new EntrySet()) : es;}*/Set<Map.Entry<String, Student>> entries = hm.entrySet();/*public final Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {return new EntryIterator();}*/Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Student>> iterator = entries.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Map.Entry<String, Student> next = iterator.next();System.out.println(next.getKey() + next.getValue());}}
}/*
Student{name='tom', age=28}
Student{name='jack', age=18}
Student{name='mary', age=19}
======
smithStudent{name='smith', age=48}
swkStudent{name='swk', age=10000}
milanStudent{name='milan', age=38}*/class Student {private String name;private int age;public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
5.泛型使用细节1
package com.hspedu.generic;import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;public class GenericDetail {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.给泛型指定数据类型时,要求是引用类型,不能是基本数据类型List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); // ok
// List<int> list2 = new ArrayList<int> (); // 错误//2.说明// 因为 E 指定了 A 类型,构造器传入了 new A()// 在给泛型指定具体类型后,可以传入该类型或者其子类型Pig<A> aPig = new Pig<A>(new A());aPig.f(); // class com.hspedu.generic.APig<A> aPig2 = new Pig<A>(new B());aPig2.f(); // class com.hspedu.generic.B//3.泛型的使用形式ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<Integer>();List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();//在实际开发中,往往简写//编译器会进行类型推断,推荐使用下面写法ArrayList<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> list4 = new ArrayList<>();ArrayList<Pig> pigs = new ArrayList<>();}
}class A {}
class B extends A{}class Pig<E> {E e;public Pig(E e) {this.e = e;}public void f() {System.out.println(e.getClass());}
}
6.泛型使用细节2
package com.hspedu.generic;import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class GenericDetail {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.给泛型指定数据类型时,要求是引用类型,不能是基本数据类型List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); // ok
// List<int> list2 = new ArrayList<int> (); // 错误//2.说明// 因为 E 指定了 A 类型,构造器传入了 new A()// 在给泛型指定具体类型后,可以传入该类型或者其子类型Pig<A> aPig = new Pig<A>(new A());aPig.f(); // class com.hspedu.generic.APig<A> aPig2 = new Pig<A>(new B());aPig2.f(); // class com.hspedu.generic.B//3.泛型的使用形式ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<Integer>();List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();//在实际开发中,往往简写//编译器会进行类型推断,推荐使用下面写法ArrayList<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> list4 = new ArrayList<>();ArrayList<Pig> pigs = new ArrayList<>();//4.如果是这样写 泛型默认是 ObjectArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList(); // 等价 ArrayList<Object> arrayList = new ArrayList();arrayList.add("xx");/*public boolean add(Object e) {modCount++;add(e, elementData, size);return true;}*/Tiger tiger = new Tiger();/*class Tiger { // 类Object e;public Tiger() {}public Tiger(Object e) {this.e = e;}}*/}
}class Tiger<E> { // 类E e;public Tiger() {}public Tiger(E e) {this.e = e;}
}class A {}
class B extends A{}class Pig<E> {E e;public Pig(E e) {this.e = e;}public void f() {System.out.println(e.getClass());}
}
7.泛型课堂练习

package com.hspedu.generic;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class GenericExercise02 {public static void main(String[] args) {Employee employee1 = new Employee("tom", 500, new MyDate(1999, 1, 1));Employee employee = new Employee("jack", 1000, new MyDate(2000, 1, 1));Employee employee2 = new Employee("tom", 2000, new MyDate(1000, 2, 2));ArrayList<Employee> employees = new ArrayList<>();employees.add(employee);employees.add(employee1);employees.add(employee2);for (Employee employee_ : employees) {System.out.println(employee_);}System.out.println("===对雇员进行排序===");employees.sort(new Comparator<Employee>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Employee emp1, Employee emp2) {// 先对传入的参数进行验证if (!(emp1 instanceof Employee && emp2 instanceof Employee)) {System.out.println("类型不正确..");return 0;}//比较 nameint i = emp1.getName().compareTo(emp2.getName());if (i != 0) {return i;}//下面对 birthday 的比较,因此,我们最好把这个比较,放在 MyDate 类完成//封装后,将来可维护性和复用性,就大大增强return emp1.getBirthday().compareTo(emp2.getBirthday());}});System.out.println("===排序后的结果===");for (Employee employee_ : employees) {System.out.println(employee_);}}
}/*
Employee{name='jack', sal=1000.0, birthday=MyDate{month=1, day=1, year=2000}}
Employee{name='tom', sal=500.0, birthday=MyDate{month=1, day=1, year=1999}}
Employee{name='tom', sal=2000.0, birthday=MyDate{month=2, day=2, year=1000}}
===对雇员进行排序===
===排序后的结果===
Employee{name='jack', sal=1000.0, birthday=MyDate{month=1, day=1, year=2000}}
Employee{name='tom', sal=2000.0, birthday=MyDate{month=2, day=2, year=1000}}
Employee{name='tom', sal=500.0, birthday=MyDate{month=1, day=1, year=1999}}*/class Employee {private String name;private double sal;private MyDate birthday;public Employee(String name, double sal, MyDate birthday) {this.name = name;this.sal = sal;this.birthday = birthday;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public double getSal() {return sal;}public void setSal(double sal) {this.sal = sal;}public MyDate getBirthday() {return birthday;}public void setBirthday(MyDate birthday) {this.birthday = birthday;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Employee{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", sal=" + sal +", birthday=" + birthday +'}';}
}class MyDate implements Comparable<MyDate>{private int month;private int day;private int year;public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) {this.month = month;this.day = day;this.year = year;}public int getMonth() {return month;}public void setMonth(int month) {this.month = month;}public int getDay() {return day;}public void setDay(int day) {this.day = day;}public int getYear() {return year;}public void setYear(int year) {this.year = year;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "MyDate{" +"month=" + month +", day=" + day +", year=" + year +'}';}@Overridepublic int compareTo(MyDate o) { // 把对 year - month - day 比较放在这里int yearMinus = year - o.getYear();if (yearMinus != 0) {return yearMinus;}//如果 year 相同 就比较 monthint monthMinus = month - o.getMonth();if (monthMinus != 0) {return monthMinus;}//如果 year 和 month 相同return day - o.getDay();}
}







