1.System类常见方法和案例
- exit:退出当前程序
- arraycopy:复制数组元素,比较适合底层调用,一般使用 Arrays.copyOf 完成复制数组
- int[] src={1,2,3};int[] dest = new int[3]; System.arraycopy(src, 0, dest, 0, 3);
- currentTimeMilens:返回当前时间距离1970-1-1 的毫秒数
- gc:运行垃圾回收机制 System.gc();
package com.logic.system_;import java.util.Arrays;public class System01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//exit 退出当前程序// System.out.println("ok1");
// //1. exit(0) 表示程序退出
// //2. 0 表示一个状态 , 正常的状态
// System.exit(0);//
// System.out.println("ok2");//arraycopy :复制数组元素,比较适合底层调用,// 一般使用Arrays.copyOf完成复制数组int[] src = {1, 2, 3};int[] dest = new int[3];// dest 当前是 {0,0,0}//1. 主要是搞清楚这五个参数的含义//2.// 源数组// * @param src the source array.// srcPos: 从源数组的哪个索引位置开始拷贝// * @param srcPos starting position in the source array.// dest : 目标数组,即把源数组的数据拷贝到哪个数组// * @param dest the destination array.// destPos: 把源数组的数据拷贝到 目标数组的哪个索引// * @param destPos starting position in the destination data.// length: 从源数组拷贝多少个数据到目标数组// * @param length the number of array elements to be copied.System.arraycopy(src, 0, dest, 0, src.length);// int[] src={1,2,3};System.out.println("dest=" + Arrays.toString(dest));//[1, 2, 3]//currentTimeMillis:返回当前时间距离1970-1-1 的毫秒数System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());}
}
2.BigInteger和BigDecimal介绍
- Biglnteger适合保存比较大的整型
- BigDecimal适合保存精度更高的浮点型(小数)
3.BigInteger和BigDecimal
package com.logic.bignum;import java.math.BigInteger;public class BigInteger_ {public static void main(String[] args) {//当我们编程中,需要处理很大的整数,long 不够用//可以使用BigInteger的类来搞定//long l = 23788888899999999999999999999l;//System.out.println("l=" + l);BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger("23788888899999999999999999999");BigInteger bigInteger2 = new BigInteger("10099999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999");System.out.println(bigInteger);//1. 在对 BigInteger 进行加减乘除的时候,需要使用对应的方法,不能直接进行 + - * ///2. 可以创建一个 要操作的 BigInteger 然后进行相应操作BigInteger add = bigInteger.add(bigInteger2);System.out.println(add);//BigInteger subtract = bigInteger.subtract(bigInteger2);System.out.println(subtract);//减BigInteger multiply = bigInteger.multiply(bigInteger2);System.out.println(multiply);//乘BigInteger divide = bigInteger.divide(bigInteger2);System.out.println(divide);//除}
}
package com.logic.bignum;public class BigDecimal {public static void main(String[] args) {//当我们需要保存一个精度很高的数时,double 不够用//可以是 BigDecimal
// double d = 1999.11111111111999999999999977788d;
// System.out.println(d);java.math.BigDecimal bigDecimal = new java.math.BigDecimal("1999.11");java.math.BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = new java.math.BigDecimal("3");System.out.println(bigDecimal);//1. 如果对 BigDecimal进行运算,比如加减乘除,需要使用对应的方法//2. 创建一个需要操作的 BigDecimal 然后调用相应的方法即可System.out.println(bigDecimal.add(bigDecimal2));System.out.println(bigDecimal.subtract(bigDecimal2));System.out.println(bigDecimal.multiply(bigDecimal2));//System.out.println(bigDecimal.divide(bigDecimal2));//可能抛出异常ArithmeticException//在调用divide 方法时,指定精度即可. BigDecimal.ROUND_CEILING//如果有无限循环小数,就会保留 分子 的精度System.out.println(bigDecimal.divide(bigDecimal2, java.math.BigDecimal.ROUND_CEILING));}}
4.第一代日期类
- Date:精确到毫秒,代表特定的瞬间
- SimpleDateFormat:格式和解析日期的类 SimpleDateFormat 格式化和解析日期的具体类 它允许进行格式化(日期->文本)、解析(文本->日期)和规范化
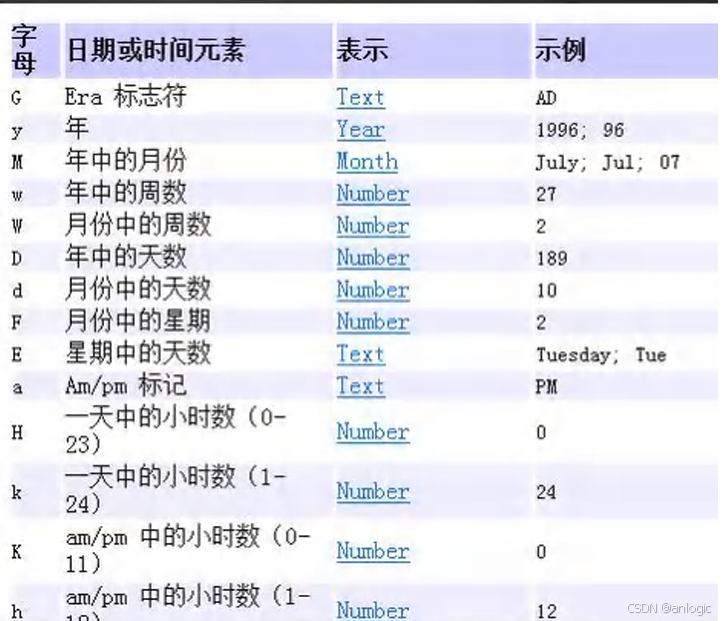
package com.logic.date_;import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;public class Date01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//1. 获取当前系统时间//2. 这里的Date 类是在java.util包//3. 默认输出的日期格式是国外的方式, 因此通常需要对格式进行转换Date d1 = new Date(); //获取当前系统时间System.out.println("当前日期=" + d1);Date d2 = new Date(9234567); //通过指定毫秒数得到时间System.out.println("d2=" + d2); //获取某个时间对应的毫秒数//1. 创建 SimpleDateFormat对象,可以指定相应的格式//2. 这里的格式使用的字母是规定好,不能乱写SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 hh:mm:ss E");String format = sdf.format(d1); // format:将日期转换成指定格式的字符串System.out.println("当前日期=" + format);//1. 可以把一个格式化的String 转成对应的 Date//2. 得到Date 仍然在输出时,还是按照国外的形式,如果希望指定格式输出,需要转换//3. 在把String -> Date , 使用的 sdf 格式需要和你给的String的格式一样,否则会抛出转换异常String s = "1996年01月01日 10:20:30 星期一";Date parse = null;try {parse = sdf.parse(s);} catch (ParseException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println("parse=" + sdf.format(parse));}
}
5.第二代日期类
- 第二代日期类,主要是Calender类(日历)
- Calendar 类是一个抽象类,它为特定瞬间与一组诸如 YEAR、MONTH、DAY_OF_MONTH、HOUR 等日历字段之间的转换提供了一些方法,并为操作日历字段(例如获得下星期的日期)提供了一些方法。
package com.logic.date_;import java.util.Calendar;public class Calender_ {public static void main(String[] args) {//1. Calendar是一个抽象类, 并且构造器是private//2. 可以通过 getInstance() 来获取实例//3. 提供大量的方法和字段提供给程序员//4. Calendar没有提供对应的格式化的类,因此需要程序员自己组合来输出(灵活)//5. 如果我们需要按照 24小时进制来获取时间, Calendar.HOUR ==改成=> Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAYCalendar c = Calendar.getInstance(); //创建日历类对象//比较简单,自由System.out.println("c=" + c);//2.获取日历对象的某个日历字段System.out.println("年:" + c.get(Calendar.YEAR));// 这里为什么要 + 1, 因为Calendar 返回月时候,是按照 0 开始编号System.out.println("月:" + (c.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1));System.out.println("日:" + c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));System.out.println("小时:" + c.get(Calendar.HOUR));System.out.println("分钟:" + c.get(Calendar.MINUTE));System.out.println("秒:" + c.get(Calendar.SECOND));//Calender 没有专门的格式化方法,所以需要程序员自己来组合显示System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR) + "-" + (c.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1) + "-" + c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH) +" " + c.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY) + ":" + c.get(Calendar.MINUTE) + ":" + c.get(Calendar.SECOND));}
}

