springboot响应式编程笔记
目录
- 1. lambda
- 2. Function
- 3. StreamAPI
- 4. Reactive-Stream
- 4.1 响应式编程模型
- 4.2 核心
- 4.3 常用操作
- 4.4 超时与重试
- 4.5 Sinks工具类
- 5. WebFlux
- 6.R2DBC
- 6.1springboot整合R2DBC
教程:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Es4y1q7Bf?spm_id_from=333.788.player.switch&vd_source=7ab9f1a69ec5101ef7a33cf58edb75dd&p=98
96集开始的
1. lambda
package com.atguigu.stream;//函数式接⼝;只要是函数式接⼝就可以⽤Lambda表达式简化
//函数式接⼝: 接⼝中有且只有⼀个未实现的⽅法,这个接⼝就叫函数式接⼝//定义一个接口
//这是一个检查注解,用于检查该接口是否符合函数式接口,不符合就会报错
@FunctionalInterface
interface MyInterface {int sum(int i, int j);//如果加了一个默认实现方法,MyInterface依旧是函数式接口。因为此时依旧只有一个未实现的方法
// default int add(int i, int j) {
// return i + j;
// }
}//自己写一个实现类
class MyInterfaceImpl implements MyInterface {@Overridepublic int sum(int i, int j) {return i + j;}
}public class Lambda {public static void main(String[] args) {//方式1:常规调用MyInterface myInterface = new MyInterfaceImpl();System.out.println(myInterface.sum(1, 2));//方式2:匿名实现类(冗余写法,接口类的名称、方法名、返回值都是固定的,可以简化掉)MyInterface myInterface1 = new MyInterface() {@Overridepublic int sum(int i, int j) {return i + j;}};System.out.println(myInterface1.sum(1, 2));//方式3:Lambda表达式 完整的入参 -> 方法体MyInterface myInterface2 = (int i,int j) -> {return i + j;};System.out.println(myInterface2.sum(1, 2));//方式4:Lambda表达式的简写 简化的入参 -> return后面的表达式//入参只有一个时,(i,j) 可以简化为 iMyInterface myInterface3 = (i, j) -> i + j;System.out.println(myInterface3.sum(1, 2));//方式5:方法引用,将 Integer 类的 sum 静态方法作为 MyInterface 接口 sum 方法的实现MyInterface myInterface4 = Integer::sum;System.out.println(myInterface4.sum(1, 2));}
} public static void main(String[] args) {var names = new ArrayList<String>();names.add("Alice");names.add("Bob");names.add("Charlie");names.add("David");//比较器Collections.sort(names, new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String o1, String o2) {return o1.compareTo(o2);}});//lambda写法1Collections.sort(names, (String o1, String o2) -> o1.compareTo(o2));//写法2Collections.sort(names, (o1, o2) -> o1.compareTo(o2));//写法3Collections.sort( names, String::compareTo);}
以后调⽤某个⽅法传⼊参数,这个参数实例是⼀个接⼝对象,且只定义了⼀个⽅法(函数式接口),就直接⽤lambda简化写法
2. Function
函数式接⼝的出⼊参定义:
函数式接口就认准入参和出参(返回值)就行
1、有⼊参,⽆出参【把入参消费了,称为消费者】: function.accept
public static void main(String[] args) {BiConsumer<String,String> function = (a, b)->{ //能接受两个⼊参System.out.println("哈哈:"+a+";呵呵:"+b);};function.accept("1","2");}
可以看到这俩 T U 都是入参

2、有⼊参,有出参【多功能函数】: function.apply
public static void main(String[] args) {Function<String,Integer> function = (String x) -> Integer.parseInt(x);System.out.println(function.apply("2"));
}
3、⽆⼊参,⽆出参【普通函数】:
Runnable runnable = () -> System.out.println("aaa");
new Thread(runnable).start();
4、⽆⼊参 ,有出参【提供者】: supplier.get()
Supplier<String> supplier = ()-> UUID.randomUUID().toString();
String s = supplier.get();
System.out.println(s);
Supplier 的源码:T是出参,没有入参
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Supplier<T> {/*** Gets a result.** @return a result*/T get();
}
java.util.function包下的所有function定义:
Consumer: 消费者
Supplier: 提供者
Predicate: 断⾔(入参就一个,对入参进行判断,返回boolean)
get / test / apply / accept调⽤的函数⽅法;
3. StreamAPI
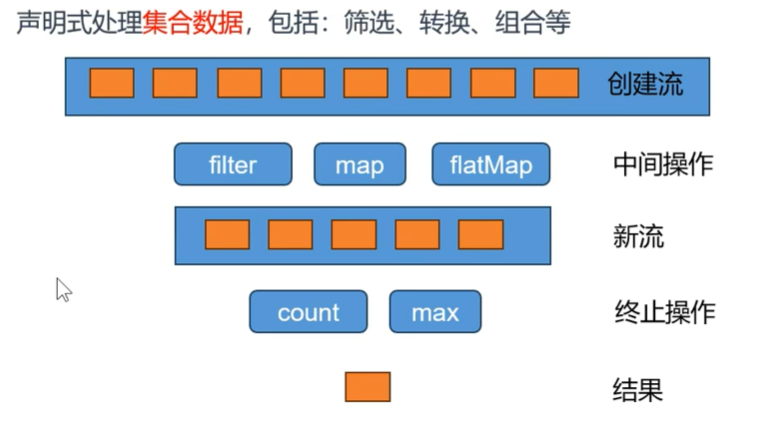
最佳实战:以后凡是你写for循环处理数据的统一全部用StreamAPI进行替换;
Stream所有数据和操作被组合成流管道流管道组成:
- 一个数据源(可以是一个数组、集合、生成器函数、I/O管道)
- 零或多个中间操作(将一个流变形成另一个流)
- 一个终止操作(产生最终结果)
中间操作:Intermediate Operations
- filter:过滤;挑出我们用的元素
- map:映射:–映射,a 变成 b
- mapTolnt、mapToLong、mapToDouble
- flatMap:打散、散列、展开、扩维:一对多映射
filter、
map、mapToInt、mapToLong、mapToDouble
flatMap、flatMapToInt、flatMapToLong、flatMapToDouble
mapMulti、mapMultiToInt、mapMultiToLong、mapMultiToDouble、
parallel、unordered、onClose、sequential
distinct、sorted、peek、limit、skip、takeWhile、dropWhile、
终⽌操作:Terminal Operation
forEach、forEachOrdered、toArray、reduce、collect、toList、min、
max、count、anyMatch、allMatch、noneMatch、findFirst、findAny、iterator
流是惰性的;只有在启动终止操作时才会对源数据进行计算,而且只在需要时才会消耗源元素;
public static void main(String[] args) {//挑出最大的偶数List<Integer> list = List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5,6,7,8,9,10);//传统forint max = 0;for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {if (list.get(i) % 2 == 0) {max = Math.max(max, list.get(i));}}System.out.println(max);/*** 流的特性* 流是lazy 的,不用,方法就不会被调用*///streamAPI//1)、把数据封装成流;要到数据流;集合类.stream 2)、定义流式操作 3)、获取最终结果Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream();Integer max1 = stream.filter(x -> {System.out.println("正在过滤:" + x);return x % 2 == 0;}).max(Integer::compareTo).get();System.out.println(max1);}
public static void main(String[] args) {//1)、创建流Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1,2,3);Stream<Integer> concat =Stream.concat(Stream.of(2,3,4),stream);Stream<Object> build = Stream.builder().add("11").add("22").build();// 2)、从集合容器中获取这个流,List、Set、MapList<Integer> integers = List.of(1,2);Stream<Integer> stream1=integers.stream();Set<Integer> integers1 = Set.of(1,2);integers1.stream();Map<Object,Object> of = Map.of();of.keySet().stream();of.values().stream();}
public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("主线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());//流是并发还是不并发?和for有啥区别?流也是用for循环挨个处理,默认不并发,也可以并发//并发以后,需要自行解决多线程安全问题List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();long count = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).parallel() //中间操作,可以变为并发.filter(i -> { //中间操作System.out.println("filter线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());System.out.println("filter:" + i);//注意这里,流里的数据在外面存储,这种称为有状态数据,会产生并发安全问题,千万不要这么写//推荐流的所有操作都是无状态的,数据状态仅在此函数内有效,不溢出至函数外
// list.add(i); 可以加锁,或者使用线程安全的集合类return i % 2 == 0;}).count(); //终止操作System.out.println("count:" + count);}
public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> people = List.of(new Person("张 三", "女", 16),new Person("王 五", "男", 18),new Person("李 四", "男", 19),new Person("张 七", "女", 17),new Person("赵 八", "男", 20));//挑出所有年龄大于18的//拿到集合流其实就是拿到集合的深拷贝的值,流的所有作都是流的元素引用//流里面的每一个元素都完整走一个流水线,才能轮到下一个元素,people.stream().filter(person -> person.getAge() > 10) //返回的是>18的Person流.peek(person -> System.out.println("过滤:" + person)) //主要用于调试、日志,不要在 peek 中修改元素.map(person -> person.getName()) //返回的是name的String流.distinct() //去重.sorted(String::compareTo) //排序.limit(2).flatMap(name -> { //将 name 拆分成 姓和名 两条 streamString[] s = name.split(" ");return Arrays.stream(s);}).forEach(System.out::println);}
takeWhile
public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> collect = List.of(1,2,3,4,5,6).stream().filter(i -> i > 2) //无条件遍历流中的每一个元素.collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect);List<Integer> collect1 = List.of(1,2,3,4,5,6).stream().takeWhile(i -> i < 2) //当满足条件,拿到这个元素,不满足直接结束流操作.collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect1);}
groupingBy
List<Person> people = List.of(new Person("张 三", "女", 16),new Person("王 五", "男", 18),new Person("李 四", "女", 19),new Person("张 七", "女", 17),new Person("赵 八", "男", 20));Map<String, List<Person>> collect = people.stream().filter(person -> person.age > 10).collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getGender)); //按照性别为 key 分组,返回mapSystem.out.println( collect);
4. Reactive-Stream
Java 9 提供的

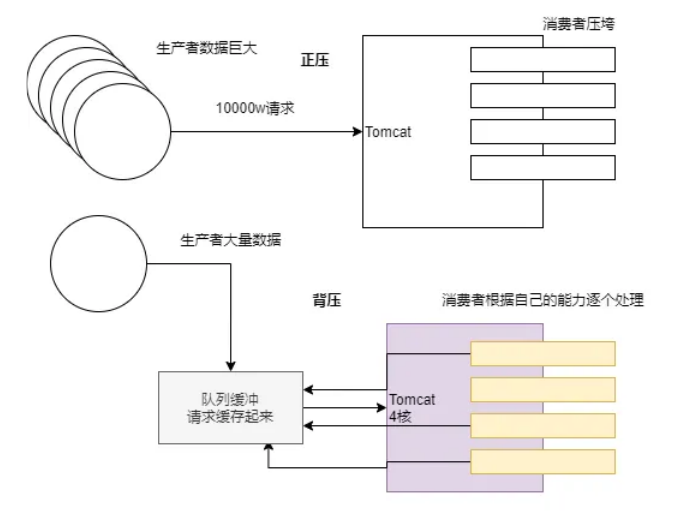
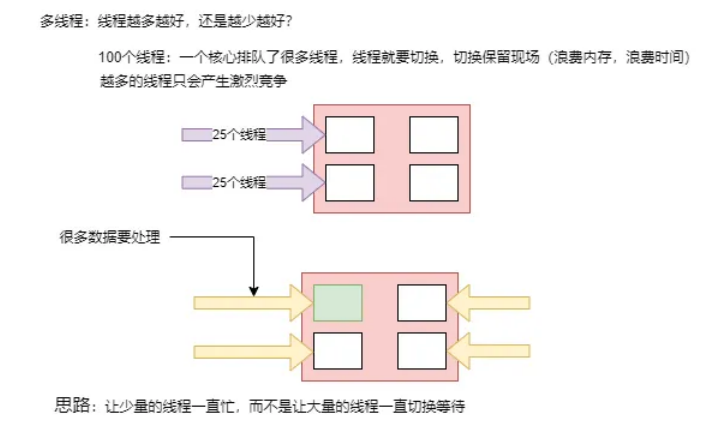
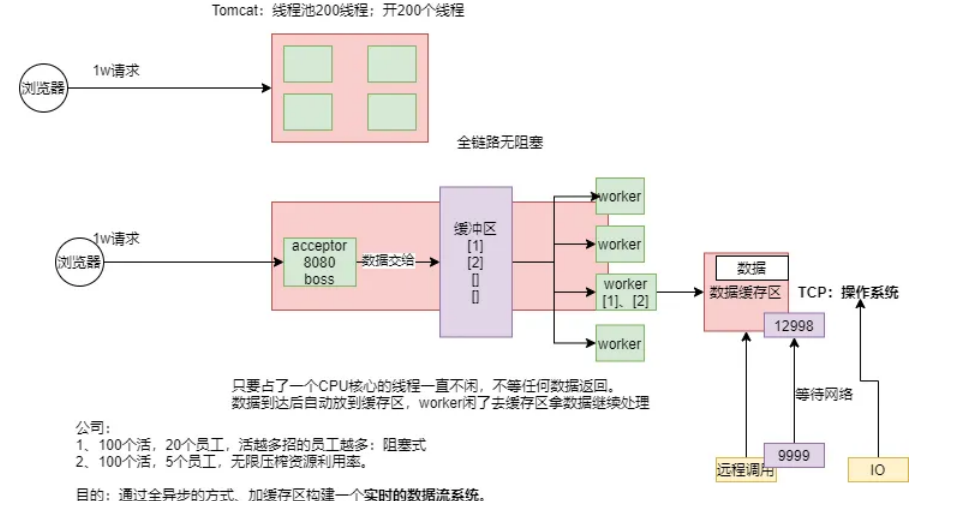
响应式系统的演化背景:
以往生产者和消费者直接通信,一个请求,Tomcat就得开一个线程,而且是阻塞式的,容易造成线程的等待,资源浪费,后来引入了一个队列缓冲

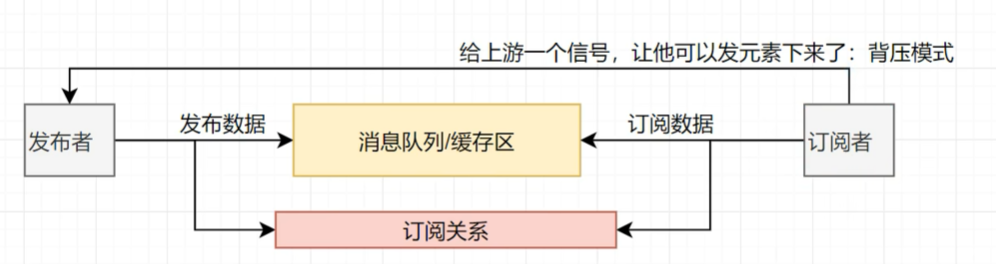
package com.atguigu.stream;import java.util.concurrent.Flow;
import java.util.concurrent.SubmissionPublisher;public class FlowDemo {/*** Publisher 发布者* Subscriber 订阅者* Subscription 订阅关系**/public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {/**//1.定义一个发布者,发布数据Flow.Publisher<String> publisher = new Flow.Publisher<>() {Flow.Subscriber<? super String> subscriber;//订阅者会订阅这个发布者的接口@Overridepublic void subscribe(Flow.Subscriber<? super String> subscriber) {//存一下这个订阅者,这样就能知道是谁订阅了this.subscriber = subscriber;}};*///第二个发布者SubmissionPublisher<String> publisher2 = new SubmissionPublisher<>();//2.定义一个订阅者,订阅者感兴趣发布者的数据Flow.Subscriber<String> subscriber = new Flow.Subscriber<>() {Flow.Subscription subscription;@Override //在订阅时,onXxxx,在xxx事件发生时,会执行这个回调public void onSubscribe(Flow.Subscription subscription) {this.subscription = subscription;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "订阅者开始了" + subscription);//从上游请求1个数据subscription.request(1);}@Override //在下一个数据到达时,会执行这个回调,接收到数据public void onNext(String item) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "订阅者接收到了数据:" + item);//继续请求一个数据subscription.request(1);if (item.equals("p-5")) {//如果接收到p-5,就取消订阅subscription.cancel();}}@Override //在发生错误时,会执行这个回调public void onError(Throwable throwable) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "订阅者发生了错误:" + throwable);}@Override //在完成时,会执行这个回调public void onComplete() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "订阅者接收到完成信号");}};//绑定发布者和订阅者的关系,可以绑定多个订阅者,每个订阅者消费数据都是独立的publisher2.subscribe(subscriber);//建立订阅关系后再发布数据for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {//消息发布到缓冲区publisher2.submit("p-" + i);}//jvm底层对于整个发布订阅关系做好了异步+缓存区处理=响应式系统//发布完成信号publisher2.close();Thread.sleep(20000);}
}下面在中间环节增加几个处理器
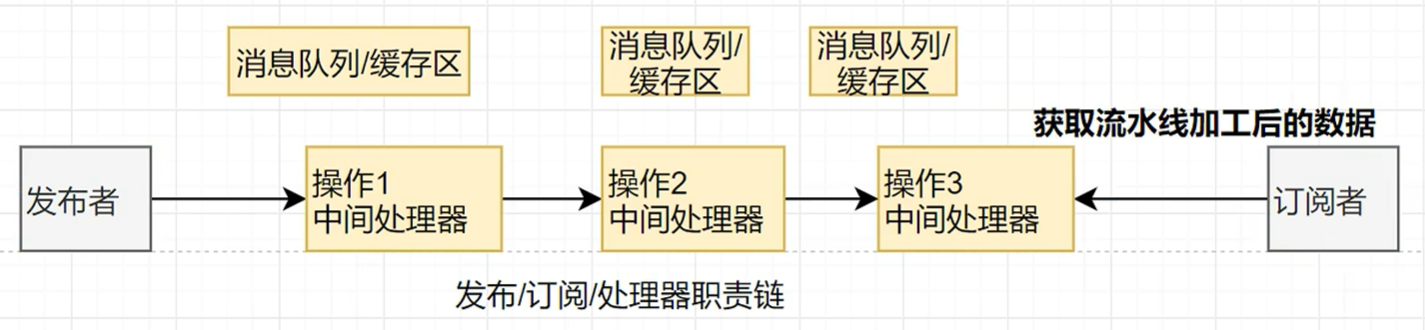
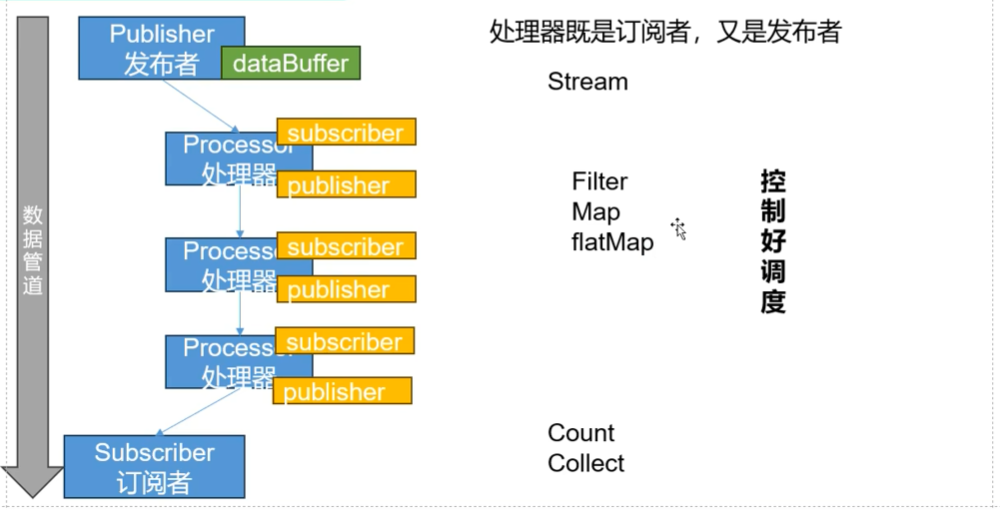
响应式编程:
1、底层:基于数据缓冲队列+消息驱动模型 +异步回调机制
2、编码:流式编程+链式调用+声明式API
3、效果:优雅全异步+消息实时处理+高吞吐量+占用少量资源
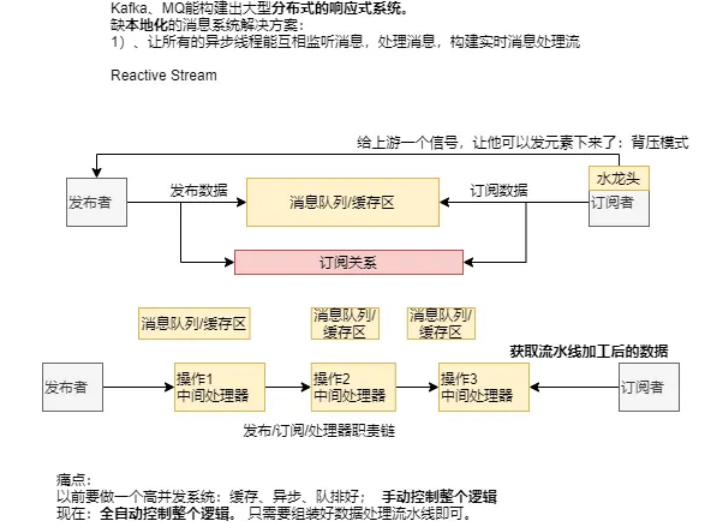
解决的痛点:
以前:要做一个高并发系统:缓存、异步、队排好;手动控制整个逻辑
现在:全自动控制整个逻辑。只需要组装好数据处理流水线即可。
package com.atguigu.stream;import java.util.concurrent.Flow;
import java.util.concurrent.SubmissionPublisher;public class FlowDemo {//定义流中间操作处理器,继承了发布者,只需要写订阅者即可static class MyProcessor extends SubmissionPublisher<String> implements Flow.Processor<String, String> {private Flow.Subscription subscription; //保存绑定关系@Overridepublic void onSubscribe(Flow.Subscription subscription) {System.out.println("processor订阅绑定完成");this.subscription = subscription;subscription.request(1);//找上游要一个数据}@Override //数据到达时,会执行这个回调public void onNext(String item) {System.out.println("processor接收到了数据:" + item);//对数据再加工:加上 哈哈item += "哈哈";submit( item); //把加工后的数据发出去subscription.request(1); //继续找上游要一个数据}@Overridepublic void onError(Throwable throwable) {}@Overridepublic void onComplete() {}}/*** Publisher 发布者* Subscriber 订阅者* Subscription 订阅关系**/public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//1、定义一个发布者SubmissionPublisher<String> publisher2 = new SubmissionPublisher<>();// 2、定义一个中间操作,给每个元素加个 哈哈MyProcessor myProcessor = new MyProcessor();MyProcessor myProcessor2 = new MyProcessor();MyProcessor myProcessor3 = new MyProcessor();//3.定义一个订阅者,订阅者感兴趣发布者的数据Flow.Subscriber<String> subscriber = new Flow.Subscriber<>() {Flow.Subscription subscription;@Override //在订阅时,onXxxx,在xxx事件发生时,会执行这个回调public void onSubscribe(Flow.Subscription subscription) {this.subscription = subscription;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "订阅者开始了" + subscription);//从上游请求1个数据subscription.request(1);}@Override //在下一个数据到达时,会执行这个回调,接收到数据public void onNext(String item) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "订阅者接收到了数据:" + item);//继续请求一个数据subscription.request(1);if (item.equals("p-5")) {//如果接收到p-5,就取消订阅subscription.cancel();}}@Override //在发生错误时,会执行这个回调public void onError(Throwable throwable) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "订阅者发生了错误:" + throwable);}@Override //在完成时,会执行这个回调public void onComplete() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "订阅者接收到完成信号");}};//4、绑定发布者和处理器的关系,此时的处理器相当于订阅者publisher2.subscribe(myProcessor);myProcessor.subscribe(myProcessor2);myProcessor2.subscribe(myProcessor3); //每个处理器既是订阅者,也是发布者,可以链式绑定// 5、绑定处理器和订阅者的关系myProcessor3.subscribe(subscriber);//建立订阅关系后再发布数据for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {//消息发布到缓冲区publisher2.submit("p-" + i);}//jvm底层对于整个发布订阅关系做好了异步+缓存区处理=响应式系统//发布完成信号publisher2.close();Thread.sleep(20000);}
}4.1 响应式编程模型

package com.atguigu.reactor.demo;import reactor.core.publisher.Flux;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;import java.time.Duration;public class FluxDemo {// Mono:0|1个元素的流
// Flux:N个元素的流;
// 发布者发布数据流:源头public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//多元素的流Flux<Integer> just = Flux.just(1,2,3,4,5);//流不消费就没用,消费就是订阅just.subscribe(e -> System.out.println("e1:" + e));just.subscribe(e -> System.out.println("e2:" + e));//一个数据流可以有任意多的消费者
// 对于每个消费者了来说,流都是一样的,广播模式System.out.println("===========================================");Flux<Long> interval = Flux.interval(Duration.ofSeconds(1));//每秒产生一个从0开始的数据interval.subscribe(e -> System.out.println("e3:" + e));//单个元素的流Mono<Integer> mono = Mono.just(1);mono.subscribe(e -> System.out.println("e4:" + e));//空流//事件感知API:当流发生什么事的时候,触发回调,系统调用提前定义好的钩子函数,doOnXxxFlux<Object> empty = Flux.empty().doOnComplete(() -> System.out.println("流结束了...")).doOnCancel(() -> System.out.println("流被取消..."));//编译器根据以下信息进行类型推断:
//subscribe 方法期望接收一个 Consumer 类型的参数
//Lambda表达式 e -> System.out.println("e:" + e) 符合 Consumer 接口的函数描述符
// (T) -> void,有1个入参,无出参
//因此编译器自动推断该Lambda表达式实现了 Consumer 接口empty.subscribe(e -> System.out.println("e5:" + e));
/** 上面的显示写法
empty.subscribe(new Consumer<Integer>() {@Overridepublic void accept(Integer e) {System.out.println("e:" + e);}
});*///代码的演示依赖于主线程,不能让主线程结束的太快了Thread.sleep(10000);}
} public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//链式API中,下面的操作符,操作的是上面的流//下面的这几个API,都是在数据流处理过程中发生对应事件时触发Flux<Integer> f1 = Flux.just(11,22,33,44,55).delayElements(Duration.ofSeconds(1)) //延缓数据流中每个元素的发射时间 1s,效果就是 每秒发射一个元素,而不是立即发射所有元素.doOnComplete(() -> System.out.println("流结束了...")).doOnCancel(() -> System.out.println("流被取消...")).doOnError(throwable -> System.out.println("流出错了...")).doOnNext(e -> System.out.println("doOnNext....." + e)); //下一个元素到来时触发(在数据流中每个元素经过此操作符时触发)//数据源 → doOnNext(元素到来时) → 缓冲区 → hookOnNext(消费者处理时) → 实际消费f1.subscribe(new BaseSubscriber<Integer>() {//下面这几个API都是订阅者在接收到对应的事件时触发@Overrideprotected void hookOnNext(Integer value) {System.out.println("元素到达....." + value); //从缓冲区到达此操作符时触发
// if (value == 33) {
// cancel();
// }if (value == 55) {throw new RuntimeException("出错了...");}request(1);}@Overrideprotected void hookOnComplete() {System.out.println("流结束...");}@Overrideprotected void hookOnError(Throwable throwable) {System.out.println("流出错了..." + throwable);}@Overrideprotected void hookOnCancel() {System.out.println("流被取消...");}@Overrideprotected void hookFinally(SignalType type) {System.out.println("结束信号..." + type);}});//代码的演示依赖于主线程,不能让主线程结束的太快了Thread.sleep(10000);}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {/*doOnXxx API 触发时机:1、doOnNext:每个数据(流的数据)到达的时候触发2、doOnEach:每个元素(流的数据和信号)到达的时候触发3、doOnRequest:消费者请求流元素的时候4、doOnError:流发生错误5、doOnSubscribe:流被订阅的时候6、doOnTerminate: 发送取消/异常信号中断了流7、doOnCancle:流被取消8、doOnDiscard:流中元素被忽路的时候*///doOnXxx 不会产生新流的操作符Flux<Integer> f1 = Flux.just(1,2,3,4,5,6,0) //产生新流.doOnNext(e -> System.out.println("doOnNext....." + e)).map(e -> 10 / e) //产生新流.doOnEach( signal -> System.out.println("doOnEach....." + signal)).doOnComplete(() -> System.out.println("流结束了...")).doOnCancel(() -> System.out.println("流被取消...")).doOnError(throwable -> System.out.println("流出错了...")).map(e -> 100 / e) //产生新流.doOnNext(e -> System.out.println("元素到达....." + e));f1.subscribe(new BaseSubscriber<Integer>() {});/*[输出结果]* doOnNext.....1* doOnEach.....doOnEach_onNext(10)* 元素到达.....10* doOnNext.....2* doOnEach.....doOnEach_onNext(5)* 元素到达.....20* doOnNext.....3* doOnEach.....doOnEach_onNext(3)* 元素到达.....33* doOnNext.....4* doOnEach.....doOnEach_onNext(2)* 元素到达.....50* doOnNext.....5* doOnEach.....doOnEach_onNext(2)* 元素到达.....50* doOnNext.....6* doOnEach.....doOnEach_onNext(1)* 元素到达.....100* doOnNext.....0* doOnEach.....onError(java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero)* 流出错了...*/}
public static void main(String[] args) {//连接两个流
// Flux.concat(Flux.just(1,2,3),Flux.just(4,5,6))
// .subscribe(System.out::println);//日志log 打在不同的地方,onNext 的元素会不一样Flux.range(1,7)
// .log() //记录range 的日志 onNext(1-7).filter(i -> i > 3).log() //只会记录 filter 的日志 onNext(4-7).map(i -> "haha-" + i)//.log() //onNext(haha-4 ---- haha-7).subscribe(System.out::println);}
4.2 核心
subscribe 的一些API
public static void main(String[] args) {/*** subscribe:* 订阅流:没订阅之前流什么也不做* 流的元素开始流动,发生数据变化;* 响应式编程: 数据流 + 变化传播(操作)*/Flux<String> flux = Flux.range(1, 10).map(i -> {System.out.println("map-" + i);// if (i == 5) {
// i = 10 / 0;
// }return "哈哈-" + i;});//======subscribe的一些API=====//订阅时即便什么都不做,也能让数据流动起来
// flux.subscribe();//指定订阅规则:打印
// flux.subscribe(v -> System.out.println("subscribe-" + v));//指定订阅规则:打印 + 错误处理
// flux.subscribe(
// v -> System.out.println("subscribe-" + v),
// throwable -> System.out.println("error:" + throwable));//指定订阅规则:打印 + 错误处理 + 完成处理flux.subscribe(v -> System.out.println("subscribe-" + v),throwable -> System.out.println("error:" + throwable),() -> System.out.println("complete")); //不需要入参}
自定义消费者
订阅者可以随时取消订阅
public static void main(String[] args) {// onErrorXxx、doOnXxxx 是不一样的!// doOnXxx:发生这个事件的时候产生一个回调,通知你(不能改变)// onxxx:发生这个事件后执行一个动作,可以改变元素、信号Flux<String> flux = Flux.range(1, 10).map(i -> {if (i == 5) {i = 10 / 0;}return "哈哈-" + i;}).onErrorComplete(); //流错误的时候,把错误吃掉,转为正常信号//传入自定义的消费者flux.subscribe(new BaseSubscriber<String>() {// 生命周期钩子 1: 订阅关系绑定的时候触发@Overrideprotected void hookOnSubscribe(Subscription subscription) {System.out.println("绑定了...." + subscription);//找发布者要数据request(1); //要1个数据
// requestUnbounded(); //要所有数据}//每个元素都会触发@Overrideprotected void hookOnNext(String value) {System.out.println("数据到达:" + value);// if (value.equals("哈哈-4")) {// cancel(); //订阅者可以随时取消订阅//}request(1); //继续要1个数据}@Overrideprotected void hookOnComplete() {System.out.println("流处理完了");}//flux 的 onErrorComplete 会将错误吃掉,转为正常信号,所以这里就不会执行了,接收到的数据是 哈哈1-4@Overrideprotected void hookOnError(Throwable throwable) {System.out.println("流处理出错了...." + throwable);}@Overrideprotected void hookOnCancel() {System.out.println("流被取消了");}@Overrideprotected void hookFinally(SignalType type) {System.out.println("最终回调...无论正常还是异常结束,一定会被执行");}});}
输出:
绑定了…reactor.core.publisher.FluxOnErrorReturn$ReturnSubscriber@67b6d4ae
数据到达:哈哈-1
数据到达:哈哈-2
数据到达:哈哈-3
数据到达:哈哈-4
流处理完了
最终回调…无论正常还是异常结束,一定会被执行
背压:消费者要多少数据,生产者就发送多少数据
请求重塑
buffer 缓冲
public static void main(String[] args) {new FluxDemo().buffer();}public void buffer() {Flux<List<Integer>> flux = Flux.range(1, 10).buffer(3);//缓冲区缓存3个元素,消费者最多可以一次拿到3个元素,凑满数批量发给消费者//.log()//消费者每次 request(1)拿到的是几个真正的数据 : buffer大小的数据
// flux.subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v的类型:" + v.getClass() + ",内容:" + v)); //v的类型:class java.util.ArrayList,内容:[1, 2, 3]flux.subscribe(new BaseSubscriber<List<Integer>>() {@Overrideprotected void hookOnSubscribe(Subscription subscription) {System.out.println("绑定了");request(2); //请求2次数据,会得到 2个 buffer 大小的数组,一共得到 n * bufferSize 个数据}@Overrideprotected void hookOnNext(List<Integer> value) {System.out.println("数据到达:" + value); //数据到达:[1, 2, 3]}});}
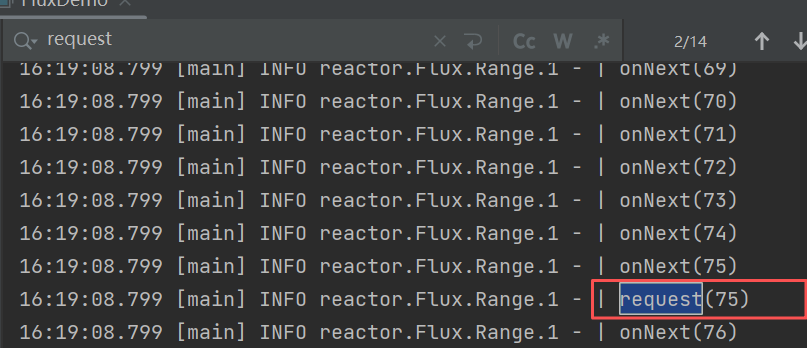
limit 限流
public static void main(String[] args) {new FluxDemo().limit();}//限流public void limit() {Flux.range(1, 1000).log().limitRate(100).subscribe(); //一次预取100个元素// 75% 预取策路:limitRate(100)// 第一次抓取100个数据,如果 75%的元素已经处理了,继续抓取 新的75% 元素}
创建序列
同步的情况下使用 generate
public static void main(String[] args) {new FluxDemo().generate();}//编程方式创建序列public void generate() {
// Flux<Object> flux = Flux.generate(sink -> {
// for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// sink.next("哈哈-" + i); //传递数据;可能会抛出 【不受检异常(运行时异常)、受检异常(编译时异常)】
// }
// });Flux<Object> flux = Flux.generate(()->0, //初始state值(state,sink)->{if (state <= 10) {sink.next(state); //把元素传出去} else {sink.complete(); //完成}if (state == 7) {sink.error(new RuntimeException("我不喜欢7"));}return state + 1; //返回新的迭代 state值});flux.log().doOnError(e-> System.out.println("错误:" + e)).subscribe();}
异步、多线程情况下使用 create
只要用户上线,用户名机会推送到流中
public static void main(String[] args) {new FluxDemo().create();}public void create() {Flux.create(fluxSink -> {MyListener myListener = new MyListener(fluxSink);for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {myListener.onLine("张" + i);}}).log().subscribe();}class MyListener {FluxSink<Object> sink;public MyListener(FluxSink<Object> sink) {this.sink = sink;}public void onLine(String username) {System.out.println("用户上线:" + username);sink.next(username);}}
handle
public static void main(String[] args) {new FluxDemo().handle();}//handle可以自定义流中的元素的处理规则public void handle() {Flux.range(1, 10).handle((i, sink) -> {System.out.println("拿到的值:" + i);//模拟业务处理
// User user = getUserById(i);
// sink.next(user); //next向下传什么数据就不一定了if (i % 2 == 0) {sink.next(i); //sink就是可以向下发送数据的通道}}).log().subscribe(); //空订阅触发数据流动}
线程调度
public static void main(String[] args) {new FluxDemo().thread1();}//响应式:响应式编程: 全异步、消息、事件回调//默认还是⽤当前线程,⽣成整个流、发布流、流操作public void thread1(){/**Schedulers.immediate();//默认:无执行上下文当前线程运行所有操作;Schedulers.single();//使用固定的一个单线程Schedulers.boundedElastic();//有界、弹性调度 不是无限扩充的线程池; 线程池中有 10*CPÙ核心个线程;队列默认100K, keepAliveTime:60s*///调度器:就是线程池Scheduler s = Schedulers.newParallel("parallel-scheduler", 4); //创建一个并发池,池中4个线程final Flux<String> flux = Flux.range(1, 2).map(i -> 10 + i).log().publishOn(s) //在哪个线程池把这个流的数据和操作执行了,改变的是发布者的线程,还有个对应的 subscribeOn//上面改变线程后,后面的所有操作都是在新的线程执行的了.map(i -> "value " + i).log();//只要不指定线程池,默认发布者⽤的线程就是订阅者的线程;new Thread(() -> flux.subscribe(System.out::println)).start();}
输出结果:
20:50:03.908 [Thread-0] INFO reactor.Flux.MapFuseable.1 – | onSubscribe([Fuseable] FluxMapFuseable.MapFuseableSubscriber)
20:50:03.912 [Thread-0] INFO reactor.Flux.MapFuseable.2 – | onSubscribe([Fuseable] FluxMapFuseable.MapFuseableSubscriber)
20:50:03.913 [Thread-0] INFO reactor.Flux.MapFuseable.2 – | request(unbounded)
20:50:03.914 [Thread-0] INFO reactor.Flux.MapFuseable.1 – | request(256)
20:50:03.914 [Thread-0] INFO reactor.Flux.MapFuseable.1 – | onNext(11) 【这一行可以看到publishOn执行前,生产者的线程就是消费者的线程】
20:50:03.915 [Thread-0] INFO reactor.Flux.MapFuseable.1 – | onNext(12)
20:50:03.915 [Thread-0] INFO reactor.Flux.MapFuseable.1 – | onComplete()
20:50:03.915 [parallel-scheduler-1] INFO reactor.Flux.MapFuseable.2 – | onNext(value 11)
value 11
20:50:03.915 [parallel-scheduler-1] INFO reactor.Flux.MapFuseable.2 – | onNext(value 12) 【publishOn执行后,生产者的线程才变了】
value 12
20:50:03.915 [parallel-scheduler-1] INFO reactor.Flux.MapFuseable.2 – | onComplete()
4.3 常用操作
filter、flatMap、concatMap、flatMapMany、transform、defaultIfEmpty、switchIfEmpty、concat、concatWith、merge、mergeWith、mergeSequential、zip、zipWith…
public static void main(String[] args) {new FluxDemo().concatMap();}void concatMap() {//连接操作Flux.concat(Flux.just(1,2),Flux.just(3,4),Flux.just(5,6)).log().subscribe();Flux.just(1,2).concatWith(Flux.just(3,4)).log().subscribe(); //老流连接新流,元素的类型必须一致才行Flux.just(1,2).concatMap(s -> {return Flux.just(s + "-a", "666"); //可以在转换的时候,新加元素}).log().subscribe();}
public static void main(String[] args) {new FluxDemo().transform();}//把流变形成新数据void transform() {//原子整数AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);Flux<String> flux = Flux.just("a", "b", "c").transform(values -> { //无 defer 的情况 (transformDeferred)if (count.incrementAndGet() == 1) {// 如果是第一次调用,则将元素转换成大写return values.map(String::toUpperCase);} else {// 如果不是第一次调用,则不变return values;}});// transform 无 defer ,不会共享外部变量的值,原理,无论多少个订阅者,transform只执行一次// transform 有 defer ,会共享外部变量的值,原理,无论多少个订阅者,每次 transform都会执行一次flux.subscribe(v -> System.out.println("订阅者1==> " + v));flux.subscribe(v -> System.out.println("订阅者2==> " + v));/*** 输出:* 订阅者1==> A* 订阅者1==> B* 订阅者1==> C* 订阅者2==> A* 订阅者2==> B* 订阅者2==> C** transformDeferred* 输出:* 订阅者1==> A* 订阅者1==> B* 订阅者1==> C* 订阅者2==> a* 订阅者2==> b* 订阅者2==> c*/}
public static void main(String[] args) {new FluxDemo().empty();}/*** defaultIfEmpty:兜底数据* switchIfEmpty:空转换,返回新流**/void empty() {//Mono.just(null);//流里面有一个null值元素// Mono.empty();//流里面没有元素,只有完成信号/结束信号haha()//.defaultIfEmpty("haha") //如果发布者元素为null,指定默认值,不为空则用发布者的值.switchIfEmpty(Mono.just("哈哈")) //如果为空,则转换为另一个Mono.subscribe(System.out::println);}Mono<String> haha() {return Mono.empty();}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {new FluxDemo().merge();System.in.read() ;}//与concat不同的是,merge是把多个流中的元素 按照到达顺序 合并成一个流,而concat是把多个流连接成一个流void merge() {//这个就是按照流的先后顺序合并,A流的元素都在前,B流的元素都在后Flux.mergeSequential(Flux.just(1,2,3).delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(1000)),Flux.just("a","b").delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(1500)),Flux.just(7,8,9).delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(2000))).log().subscribe();// Flux.merge(
// Flux.just(1,2,3).delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(1000)),
// Flux.just("a","b").delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(1500)),
// Flux.just(7,8,9).delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(2000))
// ).log().subscribe();}/*** merge 输出:* 21:57:30.383 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Merge.1 -- onSubscribe(FluxFlatMap.FlatMapMain)* 21:57:30.388 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Merge.1 -- request(unbounded)* 21:57:31.407 [parallel-1] INFO reactor.Flux.Merge.1 -- onNext(1)* 21:57:31.902 [parallel-2] INFO reactor.Flux.Merge.1 -- onNext(a)* 21:57:32.397 [parallel-3] INFO reactor.Flux.Merge.1 -- onNext(7)* 21:57:32.413 [parallel-4] INFO reactor.Flux.Merge.1 -- onNext(2)* 21:57:33.407 [parallel-5] INFO reactor.Flux.Merge.1 -- onNext(b)* 21:57:33.422 [parallel-7] INFO reactor.Flux.Merge.1 -- onNext(3)* 21:57:34.400 [parallel-6] INFO reactor.Flux.Merge.1 -- onNext(8)* 21:57:36.404 [parallel-8] INFO reactor.Flux.Merge.1 -- onNext(9)* 21:57:36.407 [parallel-8] INFO reactor.Flux.Merge.1 -- onComplete()** mergeSequential输出:* 22:03:06.071 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.MergeSequential.1 -- onSubscribe(FluxMergeSequential.MergeSequentialMain)* 22:03:06.075 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.MergeSequential.1 -- request(unbounded)* 22:03:07.090 [parallel-1] INFO reactor.Flux.MergeSequential.1 -- onNext(1)* 22:03:08.102 [parallel-4] INFO reactor.Flux.MergeSequential.1 -- onNext(2)* 22:03:09.109 [parallel-7] INFO reactor.Flux.MergeSequential.1 -- onNext(3)* 22:03:09.110 [parallel-7] INFO reactor.Flux.MergeSequential.1 -- onNext(a)* 22:03:09.110 [parallel-7] INFO reactor.Flux.MergeSequential.1 -- onNext(b)* 22:03:09.110 [parallel-7] INFO reactor.Flux.MergeSequential.1 -- onNext(7)* 22:03:10.090 [parallel-6] INFO reactor.Flux.MergeSequential.1 -- onNext(8)* 22:03:12.097 [parallel-8] INFO reactor.Flux.MergeSequential.1 -- onNext(9)* 22:03:12.099 [parallel-8] INFO reactor.Flux.MergeSequential.1 -- onComplete()**/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {new FluxDemo().zip();}/*** Tuple 元组:n个流压缩在一起,就会形成有n个元素的元组 * zipWith 目前最多支持八个流压缩*/void zip() {Flux.just(1,2).zipWith(Flux.just("a","b","c")) //可以不成对,无法成对的元素会被忽略.map(t -> {Integer t1 = t.getT1(); //元组中的第一个元素String t2 = t.getT2(); //此时是2流压缩,所以是没有 getT3的return t1 + t2;}).subscribe(System.out::println);}
错误处理
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {new FluxDemo().error6();}
/*传统方式:捕获异常返回一个静态默认值try {doSomeThingError(10)} catch (Exception e) {return "RECOVERED";}
*//*** onErrorReturn: 实现上面效果,错误的时候返回⼀个值* 1、吃掉异常,消费者无异常感知* 2、返回⼀个兜底默认值* 3、流正常完成;**/void error() {Flux.just(1, 2, 0, 4).map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)).onErrorReturn(NullPointerException.class,"哈哈-6666") //第一个参数:指定异常类型,在遇到"空指针"错误的时候,返回一个默认值.subscribe(v-> System.out.println("v = " + v), //订阅者可以感知正常元素err -> System.out.println("err = " + err), //订阅者可以感知异常,经过 onErrorReturn 处理后,这里就不会感知到异常了()-> System.out.println("流结束")); //订阅者可以感知流结束}/*传统方式:吃掉异常,执⾏⼀个兜底⽅法try {doSomeThingError(10)} catch (Exception e) {return doOtherthing(10);}
*//*** onErrorResume* 1、吃掉异常,消费者⽆异常感知* 2、调⽤⼀个兜底⽅法* 3、流正常完成*/void error2() {Flux<String> map = Flux.just(1, 2, 0, 4).map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i));map.onErrorResume(err -> Mono.just("哈哈-6666")).subscribe(v-> System.out.println("v = " + v),err -> System.out.println("err = " + err),()-> System.out.println("流结束"));}/*根据错误返回⼀个新值try {Value v = erroringMethod();return MyWrapper.fromValue(v);} catch (Throwable error) {return MyWrapper.fromError(error);}*/void error3() {Flux<String> map = Flux.just(1, 2, 0, 4).map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i));map.onErrorResume(err -> haha(err)).subscribe(v-> System.out.println("v = " + v),err -> System.out.println("err = " + err),()-> System.out.println("流结束"));}private Mono<String> haha(Throwable err) {if (err instanceof ArithmeticException) {return Mono.just("哈哈-6666");}return null;}/*捕获并包装成⼀个业务异常,并重新抛出try {return callExternalService(k);} catch (Throwable error) {throw new BusinessException("oops, SLA exceeded", error);}包装重新抛出异常: 推荐⽤ .onErrorMap1、吃掉异常,消费者有感知2、抛新异常3、流异常完成*/void error4() {Flux.just(1, 2, 0, 4).map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)).onErrorMap(err-> new BusinessException(err.getMessage() +": ⼜炸了...")).subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v = " + v),err -> System.out.println("err = " + err), //订阅者可以感知到异常() -> System.out.println("流结束"));}static class BusinessException extends RuntimeException {public BusinessException(String message) {super(message);}}/*捕获异常,记录特殊的错误⽇志,重新抛出try {return callExternalService(k);}catch (RuntimeException error) {//make a record of the errorlog("uh oh, falling back, service failed for key " + k);throw error;}异常被捕获、做⾃⼰的事情不影响异常继续顺着流⽔线传播1、不吃掉异常,只在异常发⽣的时候做⼀件事,消费者有感知
*/void error5() {Flux.just(1, 2, 0, 4).map(i -> "100 / " + i + " = " + (100 / i)).doOnError(err -> {System.out.println("err已被记录 = " + err);}).doFinally(signalType -> {System.out.println("流信号:"+signalType);}).subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v = " + v),err -> System.out.println("err = " + err),() -> System.out.println("流正常结束"));}/*忽略当前异常,仅通知记录,继续推进*/void error6() {Flux.just(1,2,3,0,5).map(i->10/i).onErrorContinue((err,val)->{System.out.println("err = " + err);System.out.println("val = " + val);System.out.println("发现"+val+"有问题了,继续执⾏其他的,我会记录这个问题");}) //发⽣.subscribe(v-> System.out.println("v = " + v),err-> System.out.println("err = " + err));}void error7() {Flux.just(1,2,3,0,5).map(i->10/i).onErrorComplete() //将异常信号转换为 正常结束信号,正常结束.subscribe(v-> System.out.println("v = " + v),err-> System.out.println("err = " + err)); // 不会收到错误Flux<Long> map = Flux.interval(Duration.ofSeconds(1)).map(i -> 10 / (i - 10));//从源头停止流,所有订阅者都会收到错误信号并结束map.onErrorStop() //错误后停止流,是从源头停止,所有监听者全部结束,错误结束.subscribe(v-> System.out.println("v = " + v),err-> System.out.println("err = " + err));// 会收到错误信号}
4.4 超时与重试
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {new Demo2().retryAndTimeout();}void retryAndTimeout() throws IOException {Flux.just(1,2,3).delayElements(Duration.ofSeconds(3)).log().timeout(Duration.ofSeconds(2)) //2s超时.retry(3) // 3次重试,把流从头到尾重新请求一次,如果不传参,默认是无限次.onErrorReturn(2) //报错时返回2.map(i -> i + "哈哈").subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v = " + v));System.in.read() ;}
4.5 Sinks工具类
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {new Demo2().sinks();}void sinks() throws InterruptedException, IOException {//Sinks.many(); // 发送Flux 数据//Sinks.one(); // 发送Mono 数据// sinks: 接受器,数据管道,所有数据顺着这个管道往下走的//Sinks.many().unicast();//单播:这个管道只能绑定单个订阅者(消费者)// Sinks.many().multicast();//多播:这个管道能绑定多个订阅者// Sinks.many().replay();//重放: 这个管道能重放元素。 是否给后来的订阅者把之前的元素依然发给它// 从头消费还是从订阅的那一刻消费Sinks.Many<Object> many = Sinks.many()//.unicast()//单播.multicast() //默认订阅者,从订阅的那一刻开始接元素,如果订阅时已经发送了n个元素,那这n个元素,新的订阅者是收不到的.onBackpressureBuffer();Sinks.Many<Object> many2 = Sinks.many().replay().limit(3); //重放3个元素new Thread(() -> {for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){many.tryEmitNext("a-"+i);try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}).start();many.asFlux().subscribe(v->System.out.println("v1="+ v));
// many.asFlux().subscribe(v->System.out.println("v2="+ v)); unicast单播,不能有俩订阅者new Thread(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}many.asFlux().subscribe(v->System.out.println("v2="+ v));}).start();/*** v1=a-0* v1=a-1* v1=a-2* v2=a-2 可以看到 v2 没有收到 0和1,可以通过 重放 解决这个问题* v1=a-3* v2=a-3* v1=a-4* v2=a-4* v1=a-5* v2=a-5* v1=a-6* v2=a-6* v1=a-7* v2=a-7* v1=a-8* v2=a-8* v1=a-9* v2=a-9*/System.in.read();}
缓存
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {new Demo2().cache();}void cache() throws IOException {Flux<Integer> cache = Flux.range(1, 10).delayElements(Duration.ofSeconds(1)) //不调缓存默认就是缓存所有.cache(3);cache.subscribe();new Thread(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}cache.subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v1=" + v));}).start();/*** v1=2* v1=3* v1=4 2、3、4就是因为缓存了最近的三个元素,所以才会接收到* v1=5 正常来讲会从5开始打印* v1=6* v1=7* v1=8* v1=9* v1=10*/System.in.read();}
阻塞式API
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {new Demo2().block();}void block() {Integer integer = Flux.just(1,2,4).map(i ->i + 10).blockLast(); //获取最后一个元素System.out.println(integer);List<Integer> list = Flux.just(1, 2, 4).map(i -> i + 10).collectList()// Mono<List<Integer>>.block(); //获取listSystem.out.println(list);}批处理+并发
public static void main(String[] args) {new Demo2().parallel();}void parallel() {Flux.range(1, 10000).buffer(100) //100个元素作为一个buffer.parallel(8) //8个线程并行处理.runOn(Schedulers.newParallel("yy")) //指定线程池.log().flatMap(list -> Flux.fromIterable(list)).collectSortedList(Integer::compare).subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v=" + v));}Context API
public static void main(String[] args) {new Demo2().threadlocal();}//ThreadLocal在响应式编程中无法使用//响应式中,数据流期间共享数据,Context API:Context:读写 ContextView:只读void threadlocal() {Flux.just(1,2,3).transformDeferredContextual((flux, context) -> {System.out.println("flux=" + flux);System.out.println("context=" + context);return flux.map(i -> context.get("key") + ":" + i);})//上游能拿到下游的最近一次数据.contextWrite(Context.of("key","value"))//ThreadLocal共享了数据,上游的所有人能看到; Context由下游传播给上游.subscribe(v -> System.out.println("v=" + v));}/***输出* flux=FluxArray* context=Context1{key=value}* v=value:1* v=value:2* v=value:3*/
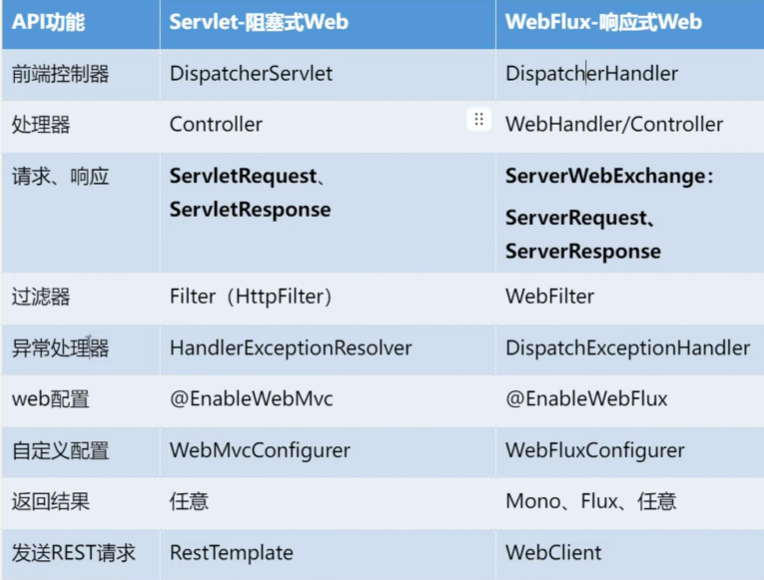
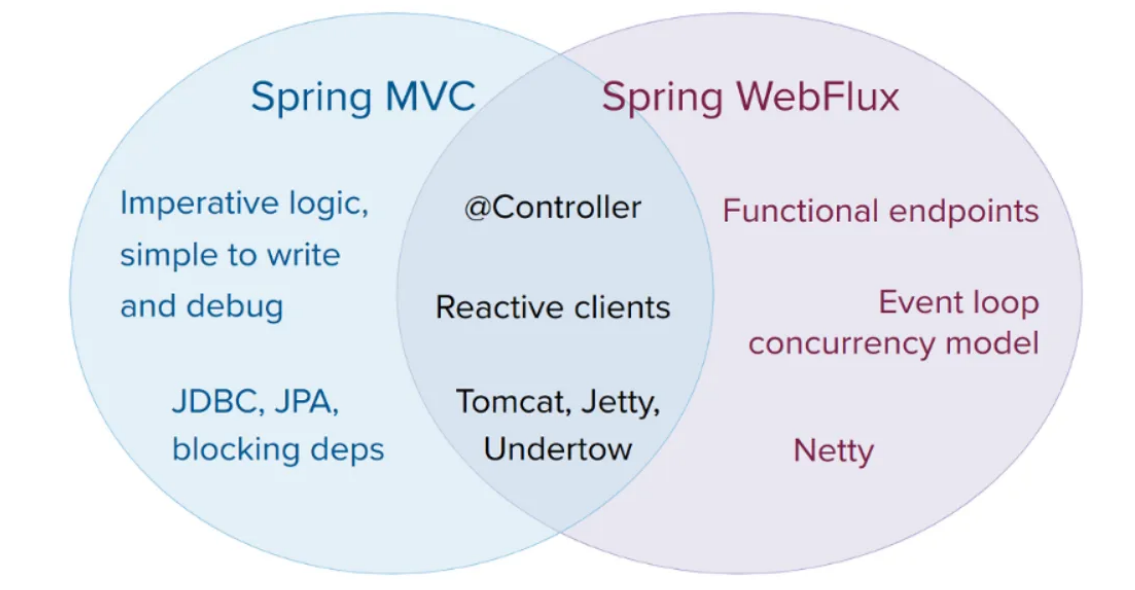
5. WebFlux
底层基于Netty实现的Web容器与请求/响应处理机制
Context 响应式上下⽂数据传递; 由下游传播给上游;
以前: 浏览器 --> Controller --> Service --> Dao: 阻塞式编程
现在: Dao(数据源查询对象【数据发布者】) --> Service --> Controller --> 浏览器: 响应式
package com.atguigu.reactor.webflux;import org.springframework.core.io.buffer.DataBuffer;
import org.springframework.core.io.buffer.DataBufferFactory;
import org.springframework.http.server.reactive.HttpHandler;
import org.springframework.http.server.reactive.ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter;
import org.springframework.http.server.reactive.ServerHttpRequest;
import org.springframework.http.server.reactive.ServerHttpResponse;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import reactor.netty.http.server.HttpServer;import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;public class FluxMainApp {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//快速⾃⼰编写⼀个能处理请求的服务器//1、创建⼀个能处理Http请求的处理器。 参数:请求、响应; 返回值:Mono<Void>:代表处理完成的信号HttpHandler handler = (ServerHttpRequest request,ServerHttpResponse response) -> {URI uri = request.getURI();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "请求进来:" + uri);//编写请求处理的业务,给浏览器写⼀个内容 URL + "Hello~!"// response.getHeaders(); //获取响应头// response.getCookies(); //获取Cookie// response.getStatusCode(); //获取响应状态码;// response.bufferFactory(); //buffer⼯⼚// response.writeWith() //把xxx写出去// response.setComplete(); //响应结束//数据的发布者:Mono<DataBuffer>、Flux<DataBuffer>//创建 响应数据的 DataBufferDataBufferFactory factory = response.bufferFactory();//数据BufferDataBuffer buffer = factory.wrap(new String(uri.toString() +" ==> Hello!").getBytes());// 需要⼀个 DataBuffer 的发布者return response.writeWith(Mono.just(buffer));};//2、启动⼀个服务器,监听8080端⼝,接受数据,拿到数据交给 HttpHandler 进⾏请求处理ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter adapter = new ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter(handler);//3、启动Netty服务器HttpServer.create().host("localhost").port(8080).handle(adapter) //⽤指定的处理器处理请求.bindNow(); //现在就绑定System.out.println("服务器启动完成....监听8080,接受请求");System.in.read();System.out.println("服务器停⽌....");}
}
写个简单的controller
package com.example.streamstudy.controller;import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import reactor.core.publisher.Flux;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;import java.time.Duration;@RestController
public class HelloController {//webFlux:向下兼容原来SpringMVC的大多数注解和API;@GetMapping("/hello")public String hello(@RequestParam(value = "name", defaultValue = "World") String name) {return "hello world:" + name;}@GetMapping("/hello2")public Mono<String> hello2(@RequestParam(value = "name", defaultValue = "World") String name) {return Mono.just("hello world2:" + name);}@GetMapping("/hello3")public Flux<String> hello3() {return Flux.just("h1","h2","h3");}//SSE测试@GetMapping(value = "/sse", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)public Flux<String> sse() {return Flux.range(1, 10).map(i -> "flux data " + i).delayElements(Duration.ofSeconds(1));}
}异常处理
package com.atguigu.reactor.exception;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;@RestControllerAdvice //使该类成为全局异常处理器,可以捕获整个应用中抛出的指定异常
public class GlobalExceptionHandle {@ExceptionHandler(ArithmeticException.class)public String error(ArithmeticException exception){System.out.println("发⽣了数学运算异常"+exception);//返回这些进⾏错误处理;// ProblemDetail: 建造者:声明式编程、链式调⽤// ErrorResponse :return "炸了,哈哈...";}
}注解开发
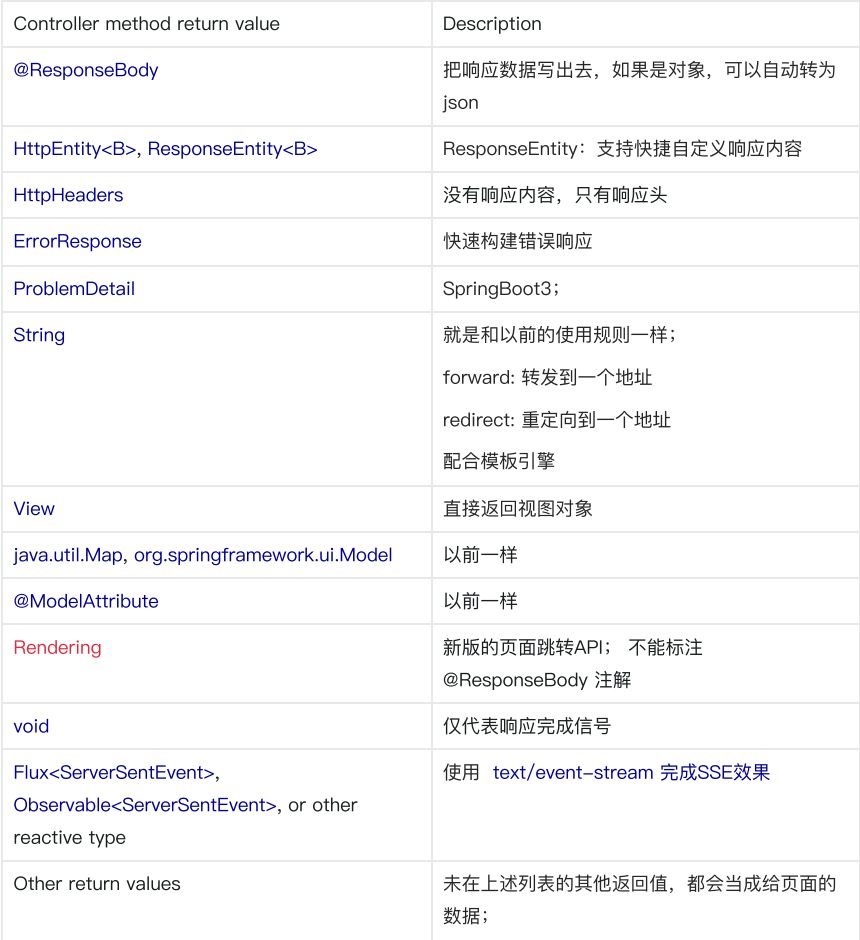
⽬标⽅法传参


2、返回值写法
sse和websocket区别:
SSE:单工;请求过去以后,等待服务端源源不断的数据
websocket:双工;连接建立后,可以任何交互;
@GetMapping("/hello")public String hello(ServerWebExchange exchange, WebSession session,ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {exchange.getResponse();exchange.getRequest();session.getId();request.getHeaders();// 创建Spring的ResponseCookie对象ResponseCookie cookie = ResponseCookie.from("cookieName", "cookieValue").path("/").maxAge(3600).httpOnly(true).build();// 添加Cookieresponse.addCookie(cookie);return "hello world";}
⾃定义Flux配置
WebFluxConfigurer
容器中注⼊这个类型的组件,重写底层逻辑
@Configuration
public class MyWebConfiguration {//配置底层@Beanpublic WebFluxConfigurer webFluxConfigurer(){return new WebFluxConfigurer() {@Overridepublic void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {registry.addMapping("/**") //对所有路径启用CORS.allowedHeaders("*") //允许所有请求头.allowedMethods("*") //允许所有HTTP方法(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等).allowedOrigins("localhost"); //只允许来自localhost的请求}};}
}
这个配置主要用于开发环境,允许本地运行的前端应用访问后端服务,避免跨域问题。在生产环境中,通常会限制具体的域名以提高安全性。
Filter
@Component
public class MyWebFilter implements WebFilter {@Overridepublic Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, WebFilterChain chain) {ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();System.out.println("请求处理放⾏到⽬标⽅法之前...");Mono<Void> filter = chain.filter(exchange); //放⾏//流⼀旦经过某个操作就会变成新流Mono<Void> voidMono = filter.doOnError(err -> {System.out.println("⽬标⽅法异常以后...");}) // ⽬标⽅法发⽣异常后做事.doFinally(signalType -> {System.out.println("⽬标⽅法执⾏以后...");});// ⽬标⽅法执⾏之后//上⾯执⾏不花时间。return voidMono; //看清楚返回的是谁!!!}
}
Spring WebFlux框架会自动订阅Controller或Filter返回的 Mono<Void> 或 Flux<T>
6.R2DBC
Web、网络、10(存储)、中间件(Redis、MySQL)
应用开发:
- 网络
- 存储:MySQL、Redis
- Web: Webflux
- 前端;后端:Controller–Service–Dao(r2dbc;mysql)
数据库:
- 导入驱动;以前:JDBC(jdbc、各大驱动mysql-connector);现在:r2dbc(r2dbc-spi、各大驱动)
1、R2dbc
用法:
1、导入驱动: 导入连接池(r2dbc-pool)、导入驱动(r2dbc-mysql)
2、使用驱动提供的API操作
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.asyncer/r2dbc-mysql --><dependency><groupId>io.asyncer</groupId><artifactId>r2dbc-mysql</artifactId><version>1.0.5</version></dependency><!-- 响应式 Spring Data R2dbc--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-r2dbc</artifactId></dependency>
实体类
@Table("t_author")
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
public class TAuthor {@Idprivate Long id;private String name;//1-N如何封装@Transient //临时字段,并不是数据库表中的一个字段
// @Field(exist=false)private List<TBook> books;
}
@Table("t_book")
@Data
public class TBook {@Idprivate Long id;private String title;private Long authorId;private Instant publishTime; //响应式中日期的映射用 Instant 或者 LocalXxx// private TAuthor author; //每本书有唯一作者;}
@Table("t_book")
@Data
public class TBookAuthor {@Idprivate Long id;private String title;private Long authorId;private Instant publishTime; //响应式中日期的映射用 Instant 或者 LocalXxxprivate TAuthor author; //每本书有唯一作者;
}
测试代码
//思想:// 1、有了r2dbc,我们的应用在数据库层面天然支持高并发、高吞吐量。// 2、并不能提升开发效率@Testvoid connection() throws IOException {// r2dbc基于全异步、响应式、消息驱动// jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test// r2dbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test//0、MySQL配置MySqlConnectionConfiguration configuration = MySqlConnectionConfiguration.builder().host("localhost").port(3306).username("root").password("123456").database("test").build();//1、获取连接工厂MySqlConnectionFactory connectionFactory = MySqlConnectionFactory.from(configuration);//2、获取到连接,发送sql// JDBC: Statement: 封装sql的//3、数据发布者Mono.from(connectionFactory.create()).flatMapMany(connection ->connection.createStatement("select * from t_author where id=?id and name=?name").bind("id", 1L) //具名参数.bind("name", "张三").execute()).flatMap(result -> {return result.map(readable -> {Long id = readable.get("id", Long.class);String name = readable.get("name", String.class);return new TAuthor(id, name, null);});}).subscribe(tAuthor -> System.out.println("tAuthor = " + tAuthor));//背压; 不用返回所有东西,基于请求量返回;System.in.read();}
6.1springboot整合R2DBC
<dependency><groupId>io.asyncer</groupId><artifactId>r2dbc-mysql</artifactId><version>1.0.5</version></dependency><!-- 响应式 Spring Data R2dbc--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-r2dbc</artifactId></dependency><!-- 响应式Web --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId></dependency>
controller
@RestController
public class AuthorController {@GetMapping("/author")public Flux<TAuthor> getAllAuthor(){return null;}
}
/** SpringBoot 对r2dbc的自动配置* 1、R2dbcAutoConfiguration: 主要配置连接工厂、连接池** 2、R2dbcDataAutoConfiguration: 主要给用户提供了 R2dbcEntityTemplate 可以进行CRUD操作* R2dbcEntityTemplate: 操作数据库的响应式客户端;提供CruD api ; RedisTemplate XxxTemplate* 数据类型映射关系、转换器、自定义R2dbcCustomConversions 转换器组件* 数据类型转换:int,Integer; varchar,String; datetime,Instant**** 3、R2dbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration: 开启Spring Data声明式接口方式的CRUD;* mybatis-plus: 提供了 BaseMapper,IService;自带了CRUD功能;* Spring Data: 提供了基础的CRUD接口,不用写任何实现的情况下,可以直接具有CRUD功能;*** 4、R2dbcTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration: 事务管理**/
/*** 告诉Spring Data 怎么封装Book对象*/
@ReadingConverter //读取数据库数据的时候,把row转成 TBook
public class BookConverter implements Converter<Row, TBookAuthor> {//1)、@Query 指定了 sql如何发送//2)、自定义 BookConverter 指定了 数据库返回的一 Row 数据,怎么封装成 TBook//3)、配置 R2dbcCustomConversions 组件,让 BookConverter 加入其中生效@Overridepublic TBookAuthor convert(Row source) {if(source == null) return null;//自定义结果集的封装TBookAuthor tBook = new TBookAuthor();tBook.setId(source.get("id", Long.class));tBook.setTitle(source.get("title", String.class));Long author_id = source.get("author_id", Long.class);tBook.setAuthorId(author_id);tBook.setPublishTime(source.get("publish_time", Instant.class));//让 converter兼容更多的表结构处理(避免单表查询没有返回name字段时的报错问题)//也可以写一个VO专门返回连表查询的结果,再写一个转换器方法返回这个VOif (source.getMetadata().contains("name")) {TAuthor tAuthor = new TAuthor();tAuthor.setId(author_id);tAuthor.setName(source.get("name", String.class));tBook.setAuthor(tAuthor);}return tBook;}
}配置类
@EnableR2dbcRepositories //开启 R2dbc 仓库功能;jpa
@Configuration
public class R2DbcConfiguration {@Bean //替换容器中原来的@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic R2dbcCustomConversions conversions(){//把我们的转换器加入进去; 效果新增了我们的 Converterreturn R2dbcCustomConversions.of(MySqlDialect.INSTANCE,new BookConverter());}
}Repository
@Repository
public interface AuthorRepositories extends R2dbcRepository<TAuthor,Long> {//默认继承了一堆CRUD方法; 像mybatis-plus//QBC: Query By Criteria//QBE: Query By Example//在 AuthorRepositories 接口中声明这样一个符合 Spring Data 命名规则的方法时,框架会自动解析方法名并生成相应的 SQL 语句。//成为一个起名工程师 where id In () and name like ?//仅限单表复杂条件查询Flux<TAuthor> findAllByIdInAndNameLike(Collection<Long> id, String name);//多表复杂查询@Query("select * from t_author") //自定义query注解,指定sql语句Flux<TAuthor> findHaha();// 1-1:关联// 1-N:关联//场景:// 1、一个图书有唯一作者; 1-1// 2、一个作者可以有很多图书: 1-N}
@Repository
public interface BookAuthorRepostory extends R2dbcRepository<TBookAuthor,Long> {// 1-1关联关系; 查出这本图书以及它的作者@Query("select b.*,t.name as name from t_book b" +" LEFT JOIN t_author t on b.author_id = t.id " +" WHERE b.id = :bookId")Mono<TBookAuthor> hahaBook(@Param("bookId")Long bookId);/*
一旦注册了 Converter<Row, TBookAuthor>,所有返回 TBookAuthor的查询(包括简单的单表查询)都会尝试使用前面自定义的转换器。
*/}
@Repository
public interface BookRepostory extends R2dbcRepository<TBook,Long> {// // 1-1关联关系; 查出这本图书以及它的作者
// @Query("select b.*,t.name as name from t_book b" +
// " LEFT JOIN t_author t on b.author_id = t.id " +
// " WHERE b.id = :bookId")
// Mono<TBook> hahaBook(@Param("bookId")Long bookId);}
完整的test
package com.atguigu.r2dbc;import com.atguigu.r2dbc.entity.TAuthor;
import com.atguigu.r2dbc.entity.TBook;
import com.atguigu.r2dbc.repositories.AuthorRepositories;
import com.atguigu.r2dbc.repositories.BookAuthorRepostory;
import com.atguigu.r2dbc.repositories.BookRepostory;
import io.asyncer.r2dbc.mysql.MySqlConnectionConfiguration;
import io.asyncer.r2dbc.mysql.MySqlConnectionFactory;
import io.r2dbc.spi.*;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.reactivestreams.Publisher;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.r2dbc.convert.R2dbcCustomConversions;
import org.springframework.data.r2dbc.core.R2dbcEntityTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.relational.core.query.Criteria;
import org.springframework.data.relational.core.query.Query;
import org.springframework.r2dbc.core.DatabaseClient;
import reactor.core.publisher.Flux;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;import java.beans.Transient;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;@SpringBootTest
/*** @author lfy* @Description* @create 2023-12-23 20:16*/
public class R2DBCTest {//最佳实践: 提升生产效率的做法//1、Spring Data R2DBC,基础的CRUD用 R2dbcRepository 提供好了//2、自定义复杂的SQL(单表): @Query;//3、多表查询复杂结果集: DatabaseClient 自定义SQL及结果封装;//Spring Data 提供的两个核心底层组件@Autowired // join查询不好做; 单表查询用R2dbcEntityTemplate r2dbcEntityTemplate; //CRUD API; 更多API操作示例: https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/relational/reference/r2dbc/entity-persistence.html@Autowired //贴近底层,join操作好做; 复杂查询好用DatabaseClient databaseClient; //数据库客户端@AutowiredAuthorRepositories authorRepositories;@AutowiredBookRepostory bookRepostory;@AutowiredBookAuthorRepostory bookAuthorRepostory;@AutowiredR2dbcCustomConversions r2dbcCustomConversions;@Testvoid oneToN() throws IOException {// databaseClient.sql("select a.id aid,a.name,b.* from t_author a " +
// "left join t_book b on a.id = b.author_id " +
// "order by a.id")
// .fetch()
// .all(row -> {
//
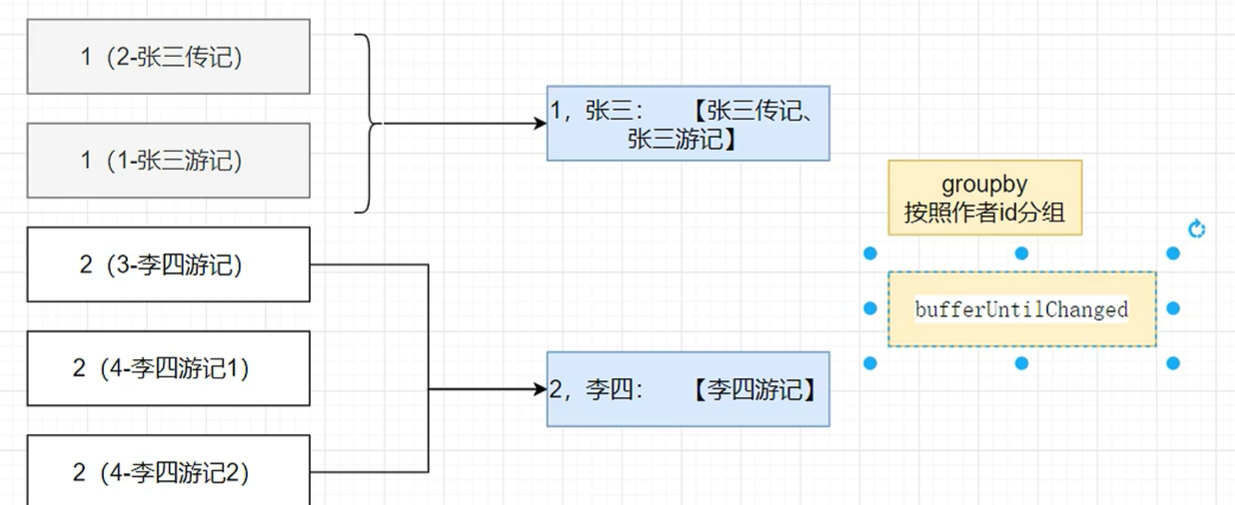
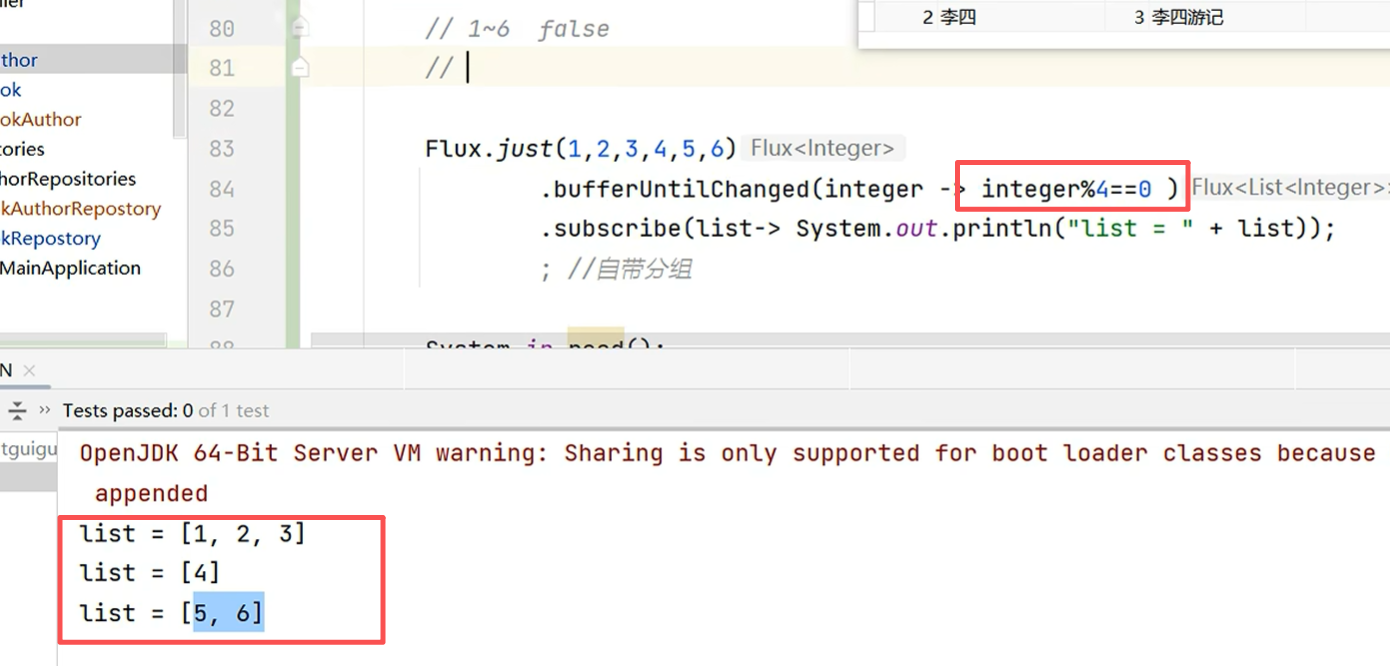
// })// 1~6 integer%4==0 的结果,一旦发生变化,就会产生新的分组// 1%4:false 2:false 3:false ,前三个都是false,没变,所以是一个组,4: true 变化了,所以4是新的分组。8:true 5:false 6:false 7:false 8:true 9:false 10:false// [1,2,3]// [4,8]// [5,6,7]// [8]// [9,10]// bufferUntilChanged:// 如果下一个判定值比起上一个发生了变化就开一个新buffer保存,如果没有变化就保存到原buffer中// Flux.just(1,2,3,4,8,5,6,7,8,9,10)
// .bufferUntilChanged(integer -> integer%4==0 )
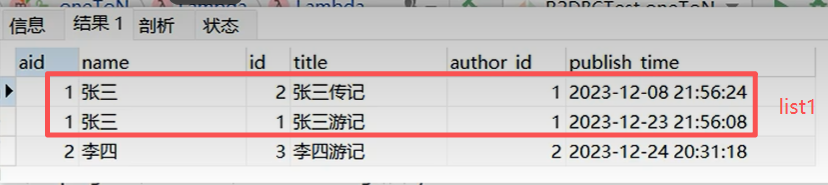
// .subscribe(list-> System.out.println("list = " + list));; //自带分组Flux<TAuthor> flux = databaseClient.sql("select a.id aid,a.name,b.* from t_author a " +"left join t_book b on a.id = b.author_id " +"order by a.id").fetch().all().bufferUntilChanged(rowMap -> Long.parseLong(rowMap.get("aid").toString())) //按照aid分组,前提是将aid排好序了.map(list -> { //对应最下面的图前两条数据是一个list,第三条数据是第二个listTAuthor tAuthor = new TAuthor();Map<String, Object> map = list.get(0);tAuthor.setId(Long.parseLong(map.get("aid").toString()));tAuthor.setName(map.get("name").toString());//查到的所有图书List<TBook> tBooks = list.stream().map(ele -> { //每个list中的元素TBook tBook = new TBook();tBook.setId(Long.parseLong(ele.get("id").toString()));tBook.setAuthorId(Long.parseLong(ele.get("author_id").toString()));tBook.setTitle(ele.get("title").toString());return tBook;}).collect(Collectors.toList());tAuthor.setBooks(tBooks);return tAuthor;});//Long 数字缓存 -127 - 127;// 对象比较需要自己写好equals方法flux.subscribe(tAuthor -> System.out.println("tAuthor = " + tAuthor));System.in.read();}@Testvoid author() throws IOException {authorRepositories.findById(1L).subscribe(tAuthor -> System.out.println("tAuthor = " + tAuthor));System.in.read();}@Testvoid book() throws IOException {
// bookRepostory.findAll()
// .subscribe(tBook -> System.out.println("tBook = " + tBook));// bookRepostory.findBookAndAuthor(1L)
// .map(book-> {
// Long authorId = book.getAuthorId();
// TAuthor block = authorRepositories.findById(authorId).block();
// book.setAuthor(block);
// return book;
// });//1-1: 第一种方式: 自定义转换器封装
// bookRepostory.hahaBook(1L)
// .subscribe(tBook -> System.out.println("tBook = " + tBook));//自定义转换器 Converter<Row, TBook> : 把数据库的row转成 TBook; 所有TBook的结果封装都用这个//工作时机: Spring Data 发现方法签名只要是返回 TBook。 利用自定义转换器进行工作//对以前的CRUD产生影响; 错误:Column name 'name' does not exist//解决办法:// 1)、新VO+新的Repository+自定义类型转化器// 2)、自定义类型转化器 多写判断。兼容更多表类型System.out.println("bookRepostory.findById(1L).block() = "+ bookRepostory.findById(1L).block());System.out.println("================");System.out.println("bookAuthorRepostory.hahaBook(1L).block() = " + bookAuthorRepostory.hahaBook(1L).block());//1-1:第二种方式
// databaseClient.sql("select b.*,t.name as name from t_book b " +
// "LEFT JOIN t_author t on b.author_id = t.id " +
// "WHERE b.id = ?")
// .bind(0, 1L)
// .fetch()
// .all()
// .map(row-> {
// String id = row.get("id").toString();
// String title = row.get("title").toString();
// String author_id = row.get("author_id").toString();
// String name = row.get("name").toString();
// TBook tBook = new TBook();
//
// tBook.setId(Long.parseLong(id));
// tBook.setTitle(title);
//
// TAuthor tAuthor = new TAuthor();
// tAuthor.setName(name);
// tAuthor.setId(Long.parseLong(author_id));
//
// tBook.setAuthor(tAuthor);
//
// return tBook;
// })
// .subscribe(tBook -> System.out.println("tBook = " + tBook));// buffer api: 实现一对N;//两种办法://1、一次查询出来,封装好//2、两次查询// 1-N: 一个作者;可以查询到很多图书System.in.read();}//简单查询: 人家直接提供好接口//复杂条件查询:// 1、QBE API// 2、自定义方法// 3、自定义SQL@Testvoid authorRepositories() throws IOException {
// authorRepositories.findAll()
// .subscribe(tAuthor -> System.out.println("tAuthor = " + tAuthor));//statement// [SELECT t_author.id, t_author.name FROM t_author WHERE t_author.id IN (?, ?)// AND (t_author.name LIKE ?)]//方法起名
// authorRepositories.findAllByIdInAndNameLike(
// Arrays.asList(1L,2L),
// "张%"
// ).subscribe(tAuthor -> System.out.println("tAuthor = " + tAuthor));//自定义@Query注解authorRepositories.findHaha().subscribe(tAuthor -> System.out.println("tAuthor = " + tAuthor));System.in.read();}@Testvoid databaseClient() throws IOException {// 底层操作databaseClient.sql("select * from t_author")
// .bind(0,2L).fetch() //抓取数据.all()//返回所有.map(map -> { //map == bean 属性=值System.out.println("map = " + map);//map ={id=2,name=李四}String id = map.get("id").toString();String name = map.get("name").toString();return new TAuthor(Long.parseLong(id), name, null);}).subscribe(tAuthor -> System.out.println("tAuthor = " + tAuthor));System.in.read();}@Testvoid r2dbcEntityTemplate() throws IOException {// Query By Criteria: QBC//1、Criteria构造查询条件 where id=1 and name=张三Criteria criteria = Criteria.empty().and("id").is(1L).and("name").is("张三");//2、封装为 Query 对象Query query = Query.query(criteria);r2dbcEntityTemplate.select(query, TAuthor.class).subscribe(tAuthor -> System.out.println("tAuthor = " + tAuthor));System.in.read();}//思想:// 1、有了r2dbc,我们的应用在数据库层面天然支持高并发、高吞吐量。// 2、并不能提升开发效率@Testvoid connection() throws IOException {// r2dbc基于全异步、响应式、消息驱动// jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test// r2dbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test//0、MySQL配置MySqlConnectionConfiguration configuration = MySqlConnectionConfiguration.builder().host("localhost").port(3306).username("root").password("123456").database("test").build();//1、获取连接工厂MySqlConnectionFactory connectionFactory = MySqlConnectionFactory.from(configuration);//2、获取到连接,发送sql// JDBC: Statement: 封装sql的//3、数据发布者Mono.from(connectionFactory.create()).flatMapMany(connection ->connection.createStatement("select * from t_author where id=?id and name=?name").bind("id", 1L) //具名参数.bind("name", "张三").execute()).flatMap(result -> {return result.map(readable -> {Long id = readable.get("id", Long.class);String name = readable.get("name", String.class);return new TAuthor(id, name, null);});}).subscribe(tAuthor -> System.out.println("tAuthor = " + tAuthor));//背压; 不用返回所有东西,基于请求量返回;System.in.read();}
}最佳实践: 提升生产效率的做法
1、Spring Data R2DBC,基础的CRUD用 R2dbcRepository 提供好了
2、自定义复杂的SQL(单表):@Query;
3、多表查询复杂结果集:
- DatabaseClient 自定义SQL及结果封装;
- @Query+ 自定义 Converter 实现结果封装