基于AIS动态数据与AI结合得经纬度标示算法
目标和场景应用
摄像头可以拍到港口,船舶有ais系统,如何和AI结合起来,在摄像头画面中将每个船得经纬度地址标示在视频上. 使用协议接收AIS船舶动态数据结合,通过AI技术实现在画面上实时标注每艘船的经纬度(甚至船名、航速等),可以用于港口监控、智能海事、船舶调度等场景。
一、系统架构概览
1 [摄像头视频流] → [AI目标检测] → [船舶检测+跟踪]
2 [AIS数据流] → [船舶ID匹配] → [地理坐标→图像坐标映射] → [叠加标注到视频]
3 [输出带标注的实时视频流]
二、关键技术步骤详解
1. 获取并解析AIS数据
AIS数据包含每艘船的:
- MMSI(船舶唯一ID)
- 经纬度 航向、
- 航速 船名、
- 呼号等
获取方式包括:
本地AIS接收机(如USB AIS dongle + 软件如 OpenCPN, ShipPlotter)
网络AIS服务(如 MarineTraffic API、AISHub、VesselFinder)
自建AIS基站 + 解码器(如 rtl-ais)
//json 数据示例
{"MMSI": "412123456","LAT": 31.2345,"LON": 121.6789,"SOG": 12.5,"COG": 90.0,"NAME": "COSCO SHANGHAI"
}
2. 摄像头视频中检测船舶(AI目标检测)
使用目标检测模型识别画面中的船舶:
使用模型:
1 YOLOv11 (速度快,适合实时)
2 Faster R-CNN(精度高,速度慢)
3 自定义训练 (用港口船舶数据集微调)
标注内容:
检测框(bounding box)
跟踪ID(使用 FASTREID实现跨帧跟踪)
船舶匹配(视频目标 ↔ AIS船舶)
将画面中的“船舶目标”与AIS中的“船舶实体”匹配。
3. 船舶匹配算法(视频目标 ↔ AIS船舶)
算法1 基于位置投影匹配
- 将AIS经纬度 → 投影到图像坐标(需相机标定)
- 计算每个AIS船投影点与视频检测框中心的距离
- 最近邻匹配(可加阈值过滤)
- 使用排序方法来确定船只之间得关系
算法2 基于运动轨迹匹配 多船、遮挡场景
- 视频中跟踪船舶运动方向/速度
- 与AIS船舶的COG/SOG匹配
调试方式
- 人工校准 + MMSI显示
- 人工指定某检测框对应某MMSI 调试小范围
4. 相机标定与地理坐标映射
建立 经纬度 → 像素坐标 的映射关系,步骤为:
1 相机标定(内参+外参):
使用棋盘格标定相机内参(OpenCV)
获取相机位置(经纬度、高度、俯仰角、偏航角)
2 建立投影模型:
使用 透视投影 + 地球曲面近似平面
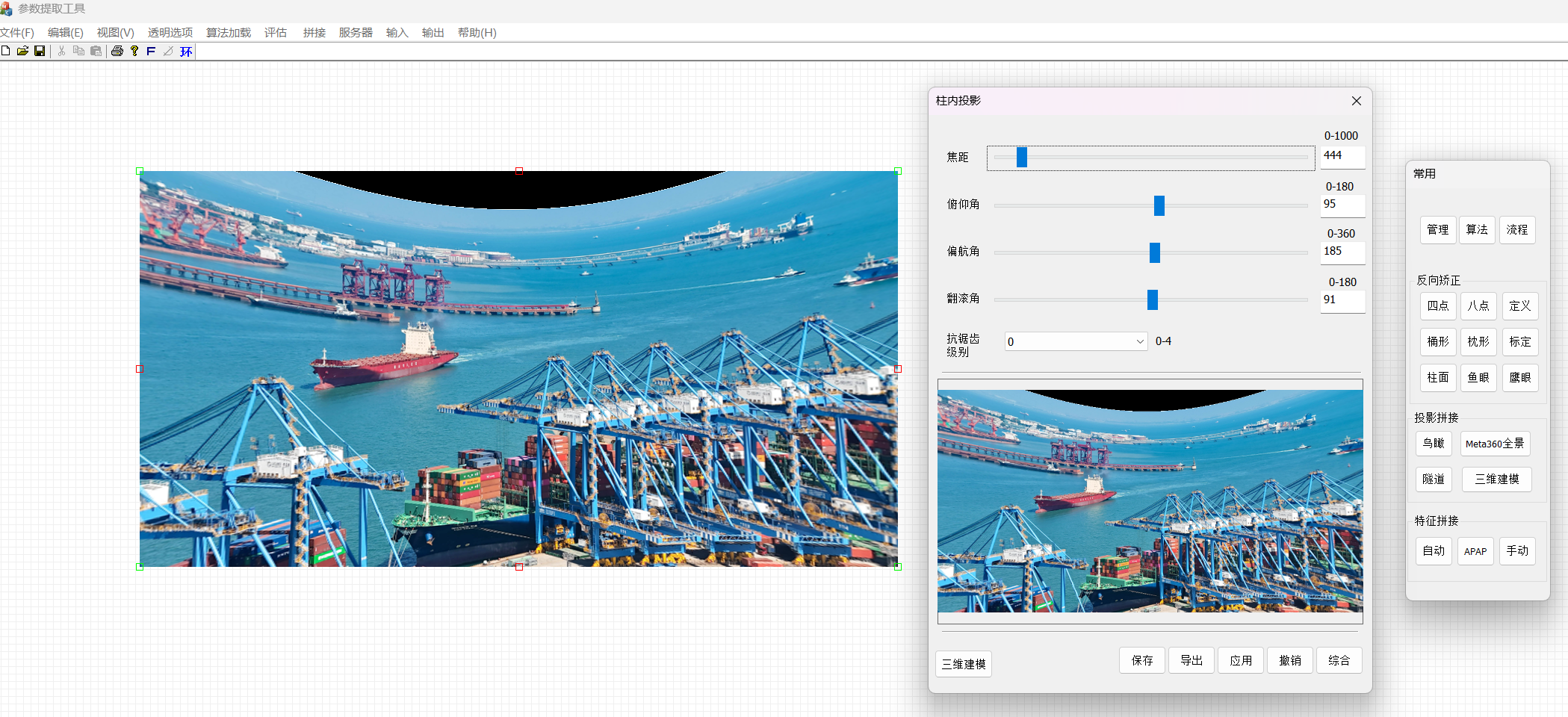
通过调整俯仰,焦距,偏航,翻滚等角度矫正得矩阵运算以后得到经度拉直得画面
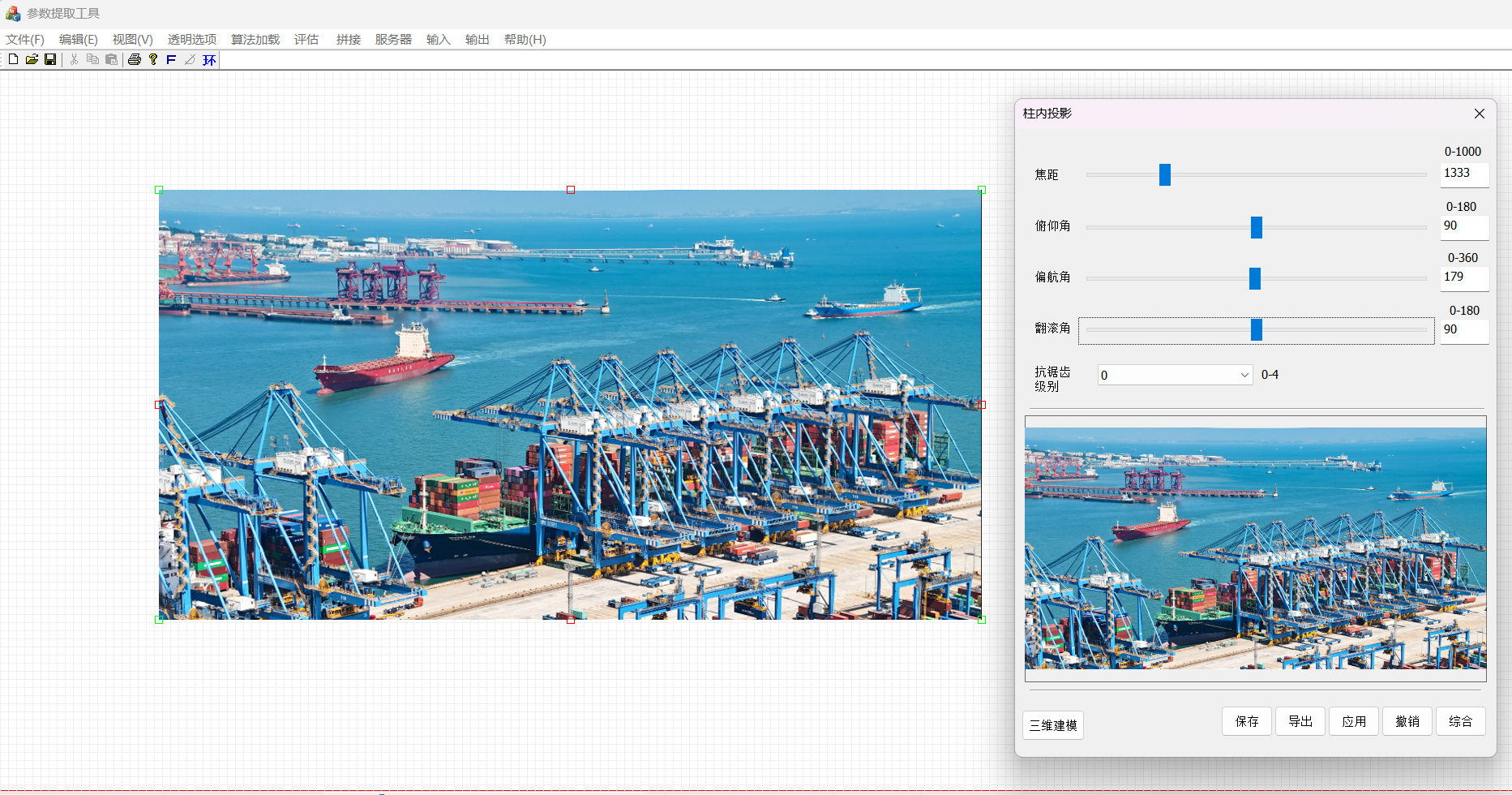
以上只是示例,实际画面根据摄像头得类型会比较复杂,可以使用我们得工具来进行各种矫正,包括鹰眼矫正
3 地理坐标 → 图像坐标公式(简化平面投影):
代码示例
import mathdef latlon_to_pixel(lat, lon, cam_lat, cam_lon, cam_yaw_deg, cam_height, img_width, img_height, fov_h_deg):# 计算相对位置(米)dy = (lat - cam_lat) * 111320 # 纬度差转米dx = (lon - cam_lon) * 111320 * math.cos(math.radians(cam_lat)) # 经度差转米# 转为相机局部坐标系(假设相机朝向 cam_yaw)angle = math.atan2(dy, dx) - math.radians(cam_yaw_deg)distance = math.sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy)# 投影到图像平面(简单针孔模型)if distance == 0: return Nonepixel_x = img_width / 2 + (math.tan(angle) * cam_height / distance) * (img_width / 2 / math.tan(math.radians(fov_h_deg)/2))pixel_y = img_height - (cam_height / distance) * (img_height / 2 / math.tan(math.radians(fov_h_deg)/2))return pixel_x, pixel_y
其他
1 可以使用OpenCV + 地理投影库 pyproj + 3D旋转矩阵 加辅助计算翻滚,偏航,俯仰关系
2 校准技巧:
手动选取画面中几艘已知AIS位置的船,反推相机参数
使用 GIS 工具(如 QGIS)辅助标定
5. 实时叠加标注到视频
cv2.putText(frame, f"{ship_name} ({lat:.4f}, {lon:.4f})", (int(x), int(y)-10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0,255,255), 2)
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1,y1), (x2,y2), (0,255,0), 2)
可标注内容:
- 船名
- MMSI
- 经纬度
- 航速/航向
- 匹配置信度
三 、开发步骤
1 获取AIS数据并解析(打印到控制台)
2 用YOLO检测视频中的船(不匹配,只画框)
3 手动输入相机经纬度、朝向、高度,写死几个AIS船位置,投影到画面验证
4 实现简单最近邻匹配(距离<50像素则匹配)
5 加入跟踪ID,实现跨帧稳定匹配
6 优化投影模型(考虑镜头畸变、地球曲率)
7 部署为实时系统(flv 输出 或 RTSP输出)
四 、优化方向
1 多摄像头融合(扩大覆盖范围)
2 时间同步(AIS和视频帧时间戳对齐)
3 遮挡处理(预测船舶位置)
4 异常船舶报警(AIS关闭、偏离航道等)
5 3D可视化(结合数字孪生港口)
五 配置
{
“camera_lat”: 31.2345,
“camera_lon”: 121.6789,
“camera_height_m”: 30.0,
“camera_yaw_deg”: 90.0,
“camera_fov_horizontal_deg”: 60.0,
“image_width”: 1920,
“image_height”: 1080
}
ais 数据接收样例
[
{
“MMSI”: “412123456”,
“LAT”: 31.2350,
“LON”: 121.6795,
“SOG”: 12.5,
“COG”: 90.0,
“NAME”: “COSCO SHANGHAI”
},
{
“MMSI”: “412654321”,
“LAT”: 31.2340,
“LON”: 121.6780,
“SOG”: 8.2,
“COG”: 270.0,
“NAME”: “MAERSK HOUSTON”
}
]
import cv2
import numpy as np
import json
import math
from ultralytics import YOLO
from collections import defaultdict# --------------------------
# 1. 加载配置
# --------------------------
with open('camera_config.json', 'r') as f:cam_cfg = json.load(f)with open('ais_data.json', 'r') as f:ais_ships = json.load(f) # 后续改为实时流# --------------------------
# 2. 初始化YOLO模型(检测船舶)
# --------------------------
# 首次运行会自动下载 yolov8n.pt
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt") # 可换为 yolov8s.pt 或自定义训练模型
# 如果你有船舶专用模型,替换为: model = YOLO("ship_yolov8.pt")# --------------------------
# 3. 地理坐标 → 图像像素坐标 转换函数(简化平面投影)
# --------------------------
def latlon_to_pixel(lat, lon, cam_lat, cam_lon, cam_yaw_deg, cam_height, img_w, img_h, fov_h_deg):"""将经纬度投影到图像坐标(简化模型,适合小范围港口)"""# 纬度差 → 米(近似)dy = (lat - cam_lat) * 111320# 经度差 → 米(考虑纬度缩放)dx = (lon - cam_lon) * 111320 * math.cos(math.radians(cam_lat))# 转为相机局部坐标系(相机朝向 cam_yaw_deg)angle_rad = math.atan2(dy, dx) - math.radians(cam_yaw_deg)distance = math.sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy)if distance < 1: # 避免除零return None# 简化针孔投影(无畸变)# 水平方向:根据角度和FOV计算像素偏移pixel_x = img_w / 2 + (math.tan(angle_rad) * cam_height / distance) * (img_w / 2 / math.tan(math.radians(fov_h_deg)/2))# 垂直方向:距离越近,y值越大(画面底部)pixel_y = img_h - (cam_height / distance) * (img_h / 2 / math.tan(math.radians(fov_h_deg)/2))return pixel_x, pixel_y# --------------------------
# 4. 匹配函数:AIS船 ↔ 视频检测框(最近邻)
# --------------------------
def match_ais_to_detections(ais_list, detections, frame_shape):"""简单匹配:计算AIS投影点与检测框中心的欧氏距离,取最近且<阈值者"""img_h, img_w = frame_shape[:2]matches = []for ais in ais_list:proj = latlon_to_pixel(ais['LAT'], ais['LON'],cam_cfg['camera_lat'], cam_cfg['camera_lon'],cam_cfg['camera_yaw_deg'], cam_cfg['camera_height_m'],img_w, img_h, cam_cfg['camera_fov_horizontal_deg'])if proj is None:continuepx, py = projbest_dist = float('inf')best_det = Nonefor det in detections:x1, y1, x2, y2 = det['bbox']cx = (x1 + x2) / 2cy = (y1 + y2) / 2dist = math.sqrt((cx - px)**2 + (cy - py)**2)if dist < best_dist:best_dist = distbest_det = det# 设定匹配阈值(像素)if best_dist < 100 and best_det is not None:matches.append({'ais': ais,'detection': best_det,'projected_point': (int(px), int(py)),'distance': best_dist})return matches# --------------------------
# 5. 主循环:视频处理
# --------------------------
def main():# 打开摄像头或视频文件cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) # 改为 0 为摄像头,或 'port.mp4' 为视频文件if not cap.isOpened():print("❌ 无法打开摄像头/视频")returnframe_id = 0while True:ret, frame = cap.read()if not ret:break# YOLO检测船舶(class 8 = 'boat' 或 'ship',COCO中船是 class 8)# 注意:COCO数据集中 'boat' 是 class 8,但可能漏检货轮,建议微调模型results = model(frame, classes=[8], conf=0.3, verbose=False) # 只检测 boat 类detections = []for r in results:boxes = r.boxesfor box in boxes:x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, box.xyxy[0].tolist())conf = box.conf[0].item()cls_id = int(box.cls[0].item())detections.append({'bbox': [x1, y1, x2, y2],'conf': conf,'class_id': cls_id})# 画检测框(无匹配时)cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)# 匹配AIS船舶与检测框matches = match_ais_to_detections(ais_ships, detections, frame.shape)# 在画面上标注匹配结果for match in matches:ais = match['ais']det = match['detection']px, py = match['projected_point']x1, y1, x2, y2 = det['bbox']# 画匹配框(蓝色)cv2.rectangle(frame, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (255, 0, 0), 3)# 标注船名 + 经纬度label = f"{ais['NAME']} ({ais['LAT']:.4f}, {ais['LON']:.4f})"cv2.putText(frame, label, (x1, y1 - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (255, 255, 0), 2)# 画投影点(红色圆点)cv2.circle(frame, (px, py), 5, (0, 0, 255), -1)# 显示帧数cv2.putText(frame, f"Frame: {frame_id}", (10, 30), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 255), 2)cv2.imshow("Ship AIS Overlay", frame)frame_id += 1if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):breakcap.release()cv2.destroyAllWindows()if __name__ == "__main__":main()
实时AIS流
用socket或requests轮询API,或监听串口/UDP
精确投影
使用 OpenCV solvePnP+ 地面控制点标定
船舶跟踪
加入ByteTrack或DeepSORT,多船稳定匹配 加入匈牙利算法或卡尔曼滤波预测
Web可视化
用 Flask + WebSocket 推流到浏览器
报警功能
检测AIS缺失或位置异常
调试完成以后改成c++
