人工智能机器学习——逻辑回归
一、分类问题(Classification)
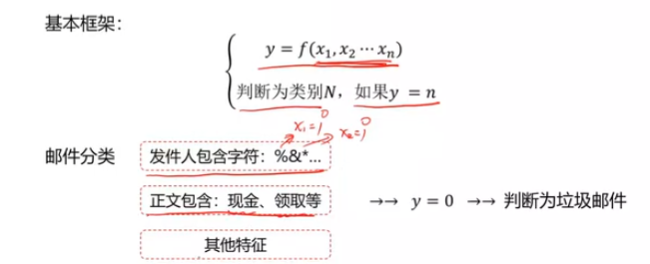
垃圾邮件检测

流程
- 标注样本邮件未垃圾/普通邮件(人)
- 获取批量的样本邮件及其标签,学习其特征(计算机)
- 针对新的邮件,自动判断其类别(计算机)

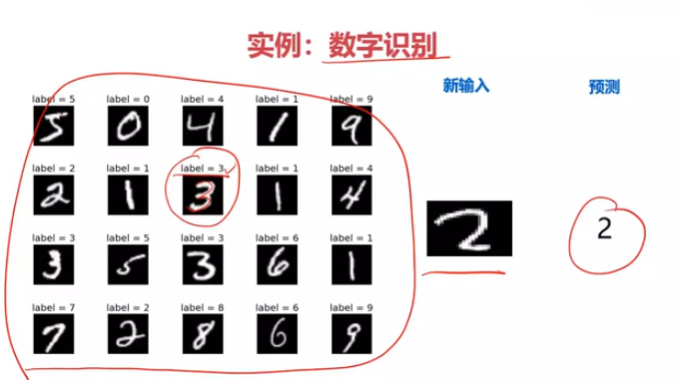
图像分类

数字识别
分类
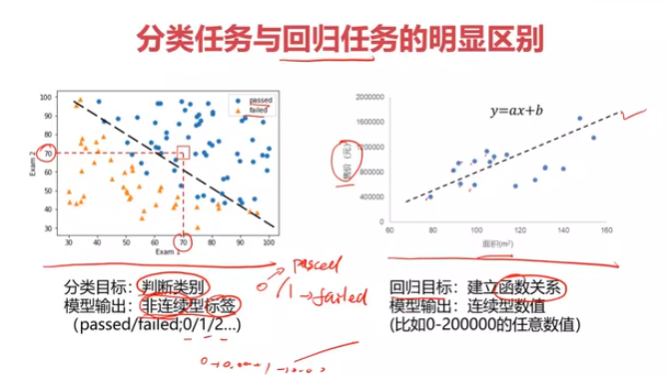
分类:根据已知样本的某些特征,判断一个新的样本属于哪种已知的样本类
二、分类方法
- 逻辑回归
- KNN近邻模型
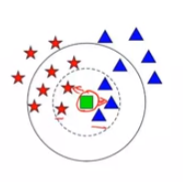
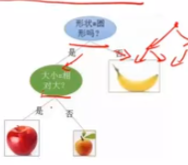
- 决策树
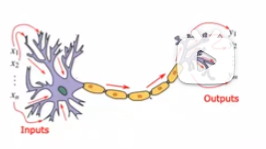
- 神经网络
逻辑回归
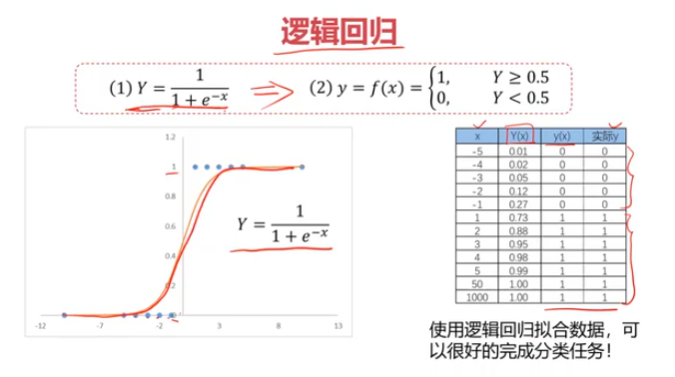
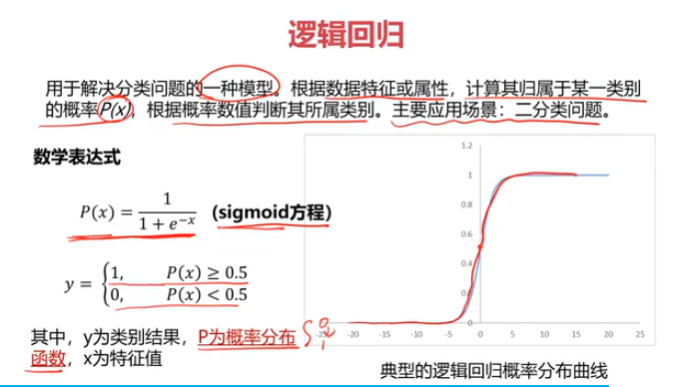
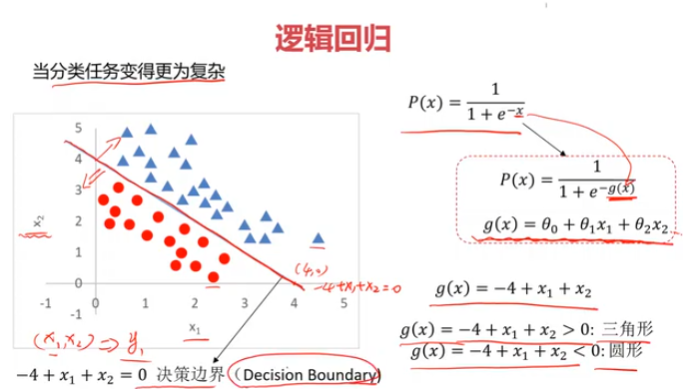
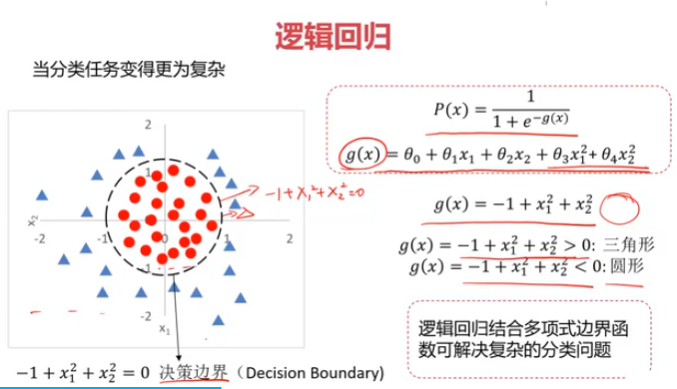

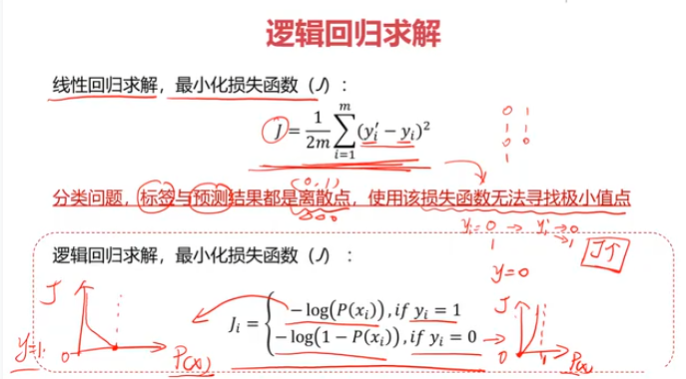
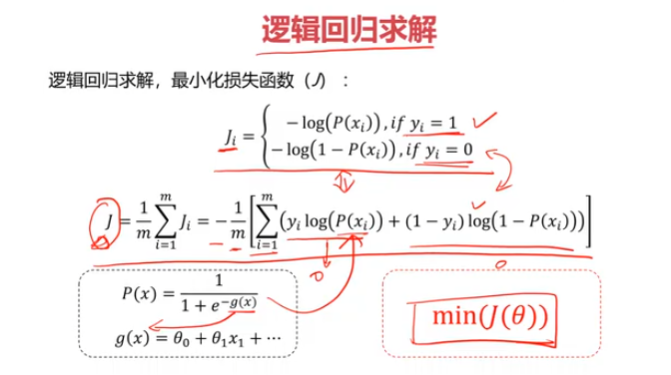
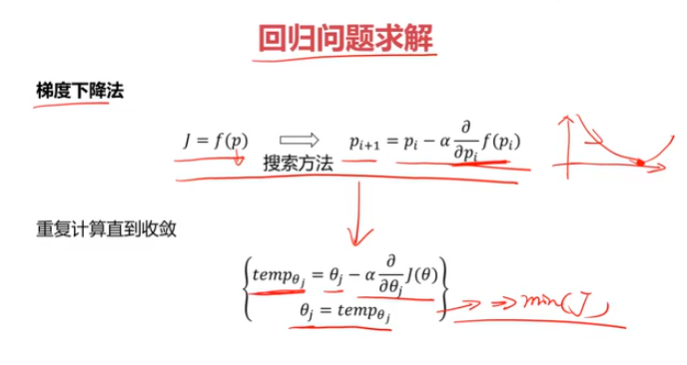
三、考试通过预测,使用数据集examdata.csv
#加载数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
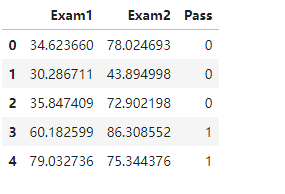
data = pd.read_csv('examdata.csv')
data.head()
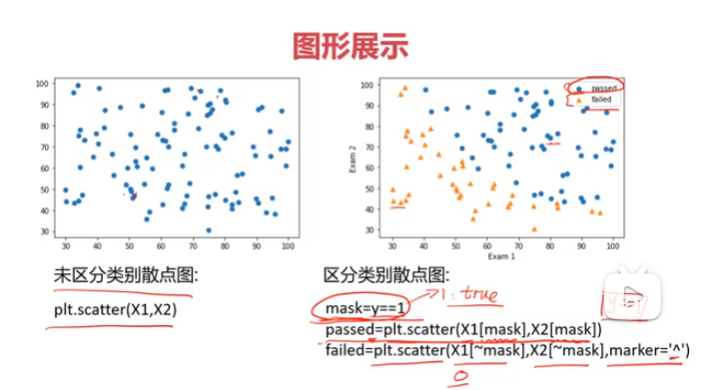
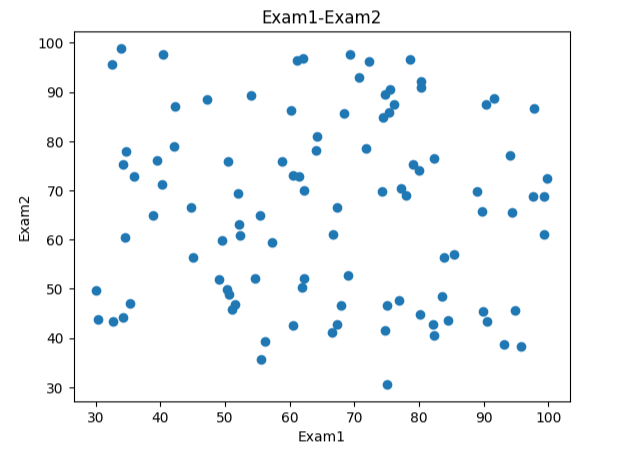
#画散点图
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
fig1 = plt.figure()
plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'],data.loc[:,'Exam2'])
plt.title("Exam1-Exam2")
plt.xlabel("Exam1")
plt.ylabel("Exam2")
plt.show()
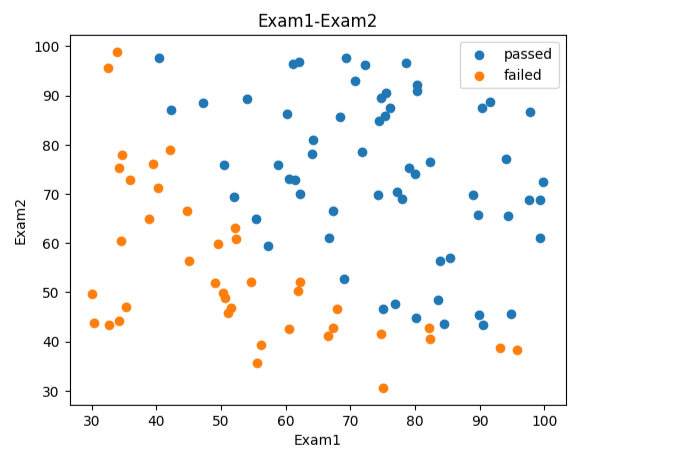
#区分数据
mask = data.loc[:,'Pass']==1
print(mask)

fig2 = plt.figure()
passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][mask])
failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][~mask])
plt.title("Exam1-Exam2")
plt.xlabel("Exam1")
plt.ylabel("Exam2")
plt.legend((passed,failed),("passed","failed"))
plt.show()
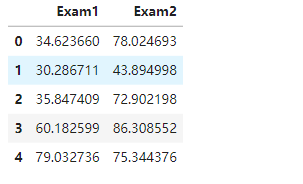
#赋值x,y
x = data.drop(['Pass'],axis=1)
x.head()
x1 = data.loc[:,'Exam1']
x2 = data.loc[:,'Exam2']
y = data.loc[:,'Pass']
y.head()
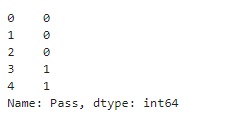
#打印x,y维度
print(x.shape,y.shape)
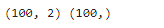
#训练逻辑回归模型
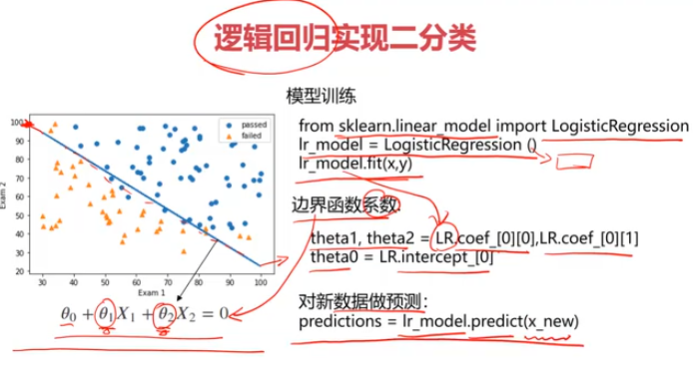
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
LR = LogisticRegression()
LR.fit(x,y)
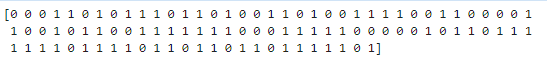
#预测结果
y_predict = LR.predict(x)
print(y_predict)
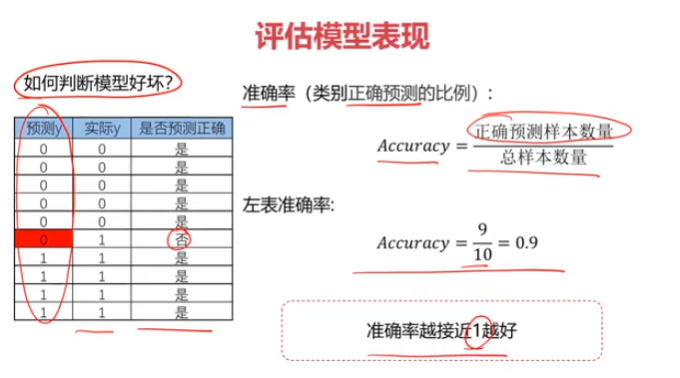
#打印预测准确率
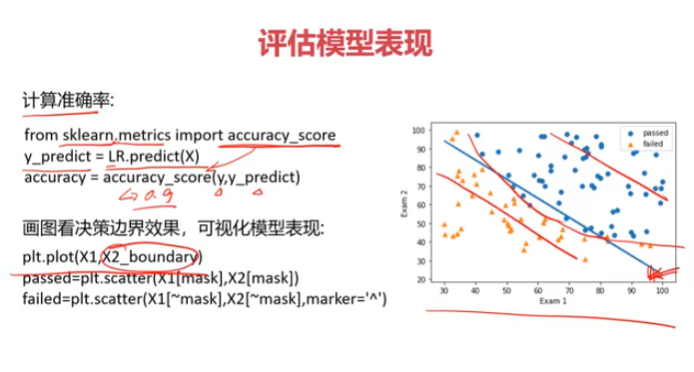
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy = accuracy_score(y,y_predict)
print(accuracy)

#预测新数据
X_test = pd.DataFrame([[70,65]],columns=['Exam1','Exam2'])
y_test = LR.predict(X_test)
print('passed' if y_test==1 else 'failed')
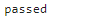
#边界曲线
LR.coef_
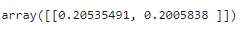
LR.intercept_
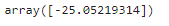
theta0 = LR.intercept_
theta1,theta2 = LR.coef_[0][0],LR.coef_[0][1]
print(theta0,theta1,theta2)
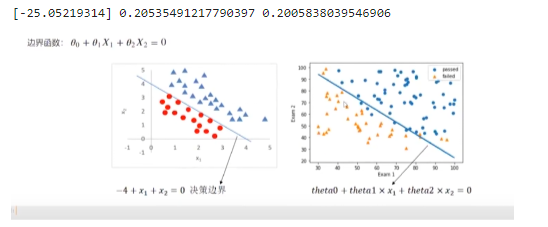
X2_new = -(theta0+theta1*x1)/theta2
print(X2_new)
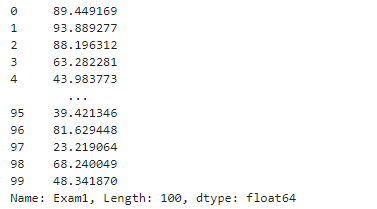
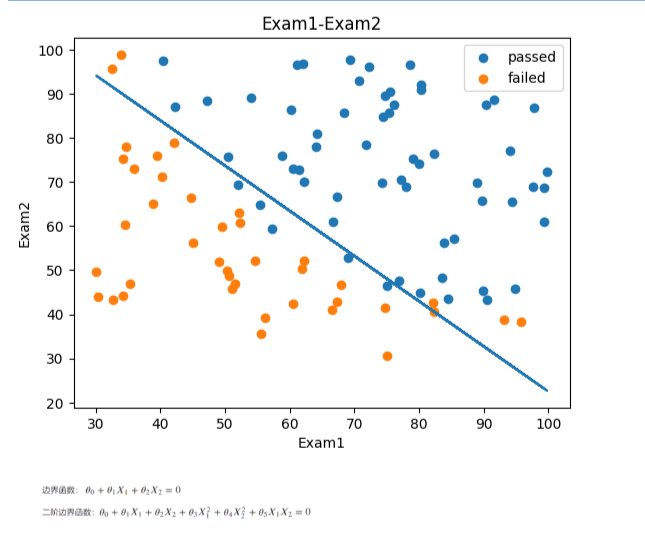
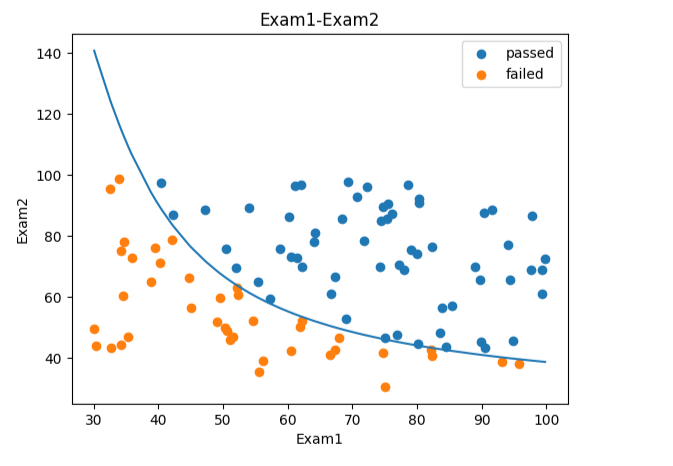
fig3 = plt.figure()
passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][mask])
failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][~mask])
plt.plot(x1,X2_new)
plt.title("Exam1-Exam2")
plt.xlabel("Exam1")
plt.ylabel("Exam2")
plt.legend((passed,failed),("passed","failed"))
plt.show()
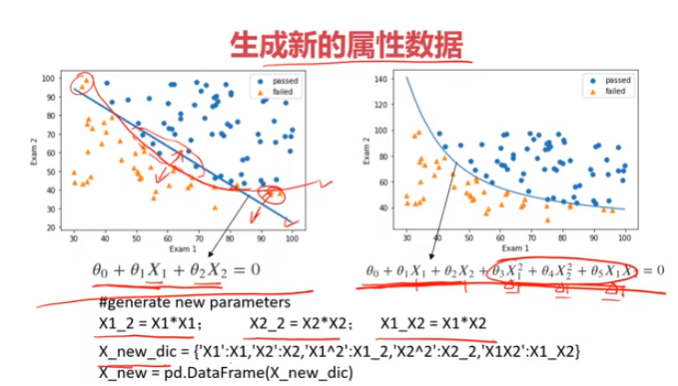
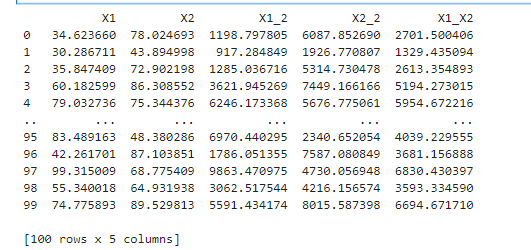
#使用二阶边界函数
X1_2 = x1*x1
X2_2 = x2*x2
X1_X2 = x1*x2
X_new = {'X1':x1,'X2':x2,'X1_2':X1_2,'X2_2':X2_2,'X1_X2':X1_X2}
X_new = pd.DataFrame(X_new)
print(X_new)
#创建模型2
LR2 = LogisticRegression(solver='liblinear', max_iter=1000)# solver='saga', # 最通用的求解器 max_iter=1000, # 足够的迭代次数
LR2.fit(X_new,y)
#预测结果
y_2_predict = LR2.predict(X_new)
print(y_2_predict)

#打印预测准确率
accuracy = accuracy_score(y,y_2_predict)
print(accuracy)
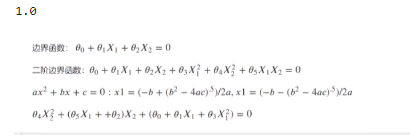
#对x1排序
X1_new = x1.sort_values()
print(x1,X1_new)
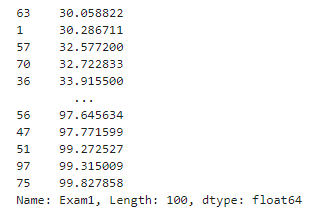
LR2.coef_

theta0 = LR2.intercept_
theta1,theta2,theta3,theta4,theta5 = LR2.coef_[0][0],LR2.coef_[0][1],LR2.coef_[0][2],LR2.coef_[0][3],LR2.coef_[0][4]
a = theta4
b = theta5*X1_new+theta2
c = theta0+theta1*X1_new+theta3*X1_new*X1_new
X2_new_boundary = (-b+np.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/(2*a)print(theta0,theta1,theta2,theta3,theta4,theta5)
print(X2_new_boundary)
fig4 = plt.figure()
plt.plot(x1,X2_new_boundary)
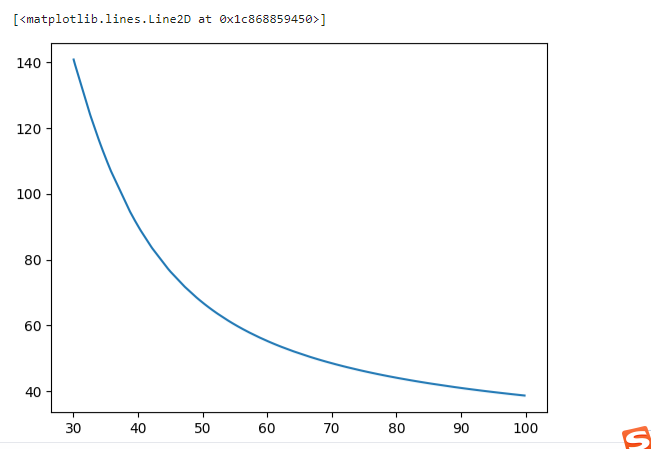
fig5 = plt.figure()
passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][mask])
failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'Exam1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'Exam2'][~mask])
plt.plot(x1,X2_new_boundary)
plt.title("Exam1-Exam2")
plt.xlabel("Exam1")
plt.ylabel("Exam2")
plt.legend((passed,failed),("passed","failed"))
plt.show()
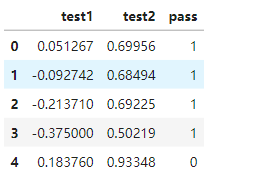
四、芯片质量预测实战,使用数据集chip_test.csv
#加载数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = pd.read_csv('chip_test.csv')
data.head()
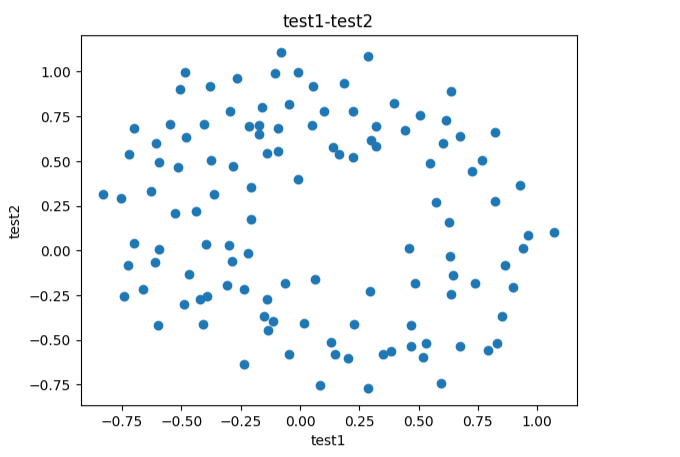
#画散点图
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
fig6 = plt.figure()
plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'],data.loc[:,'test2'])
plt.title("test1-test2")
plt.xlabel("test1")
plt.ylabel("test2")
plt.show()
#区分数据
mask = data.loc[:,'pass']==1
print(mask)
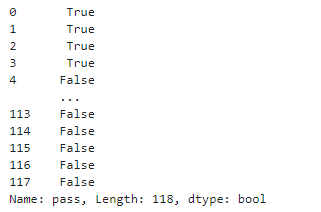
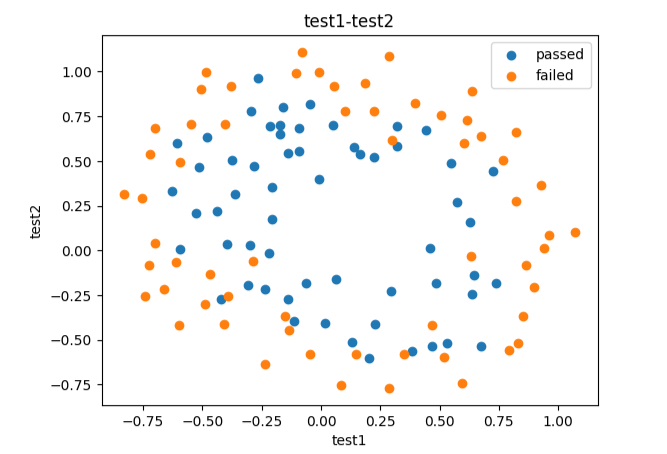
fig7 = plt.figure()
passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][mask])
failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][~mask])
plt.title("test1-test2")
plt.xlabel("test1")
plt.ylabel("test2")
plt.legend((passed,failed),("passed","failed"))
plt.show()
#赋值x,y
x = data.drop(['pass'],axis=1)
x1 = data.loc[:,'test1']
x2 = data.loc[:,'test2']
y = data.loc[:,'pass']
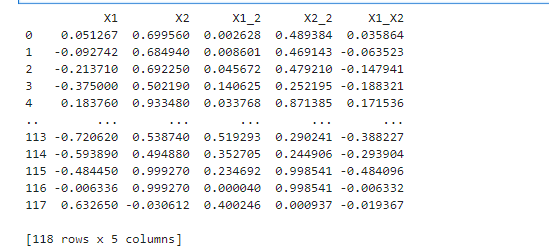
#使用二阶边界函数
X1_2 = x1*x1
X2_2 = x2*x2
X1_X2 = x1*x2X_new = {'X1':x1,'X2':x2,'X1_2':X1_2,'X2_2':X2_2,'X1_X2':X1_X2}
X_new = pd.DataFrame(X_new)
print(X_new)
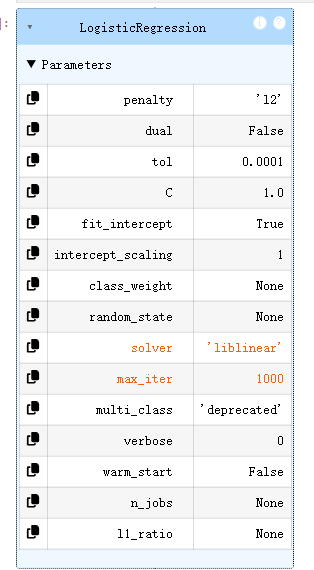
#创建模型2
LR2 = LogisticRegression(solver='liblinear', max_iter=1000)# solver='saga', # 最通用的求解器 max_iter=1000, # 足够的迭代次数
LR2.fit(X_new,y)
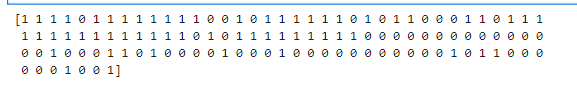
#预测结果
y_2_predict = LR2.predict(X_new)
print(y_2_predict)
#打印预测准确率
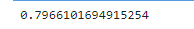
accuracy = accuracy_score(y,y_2_predict)
print(accuracy)
#对x1排序
X1_new = x1.sort_values()
print(x1,X1_new)
LR2.coef_
theta0 = LR2.intercept_
theta1,theta2,theta3,theta4,theta5 = LR2.coef_[0][0],LR2.coef_[0][1],LR2.coef_[0][2],LR2.coef_[0][3],LR2.coef_[0][4]print(theta0,theta1,theta2,theta3,theta4,theta5)

a = theta4
b = theta5*X1_new+theta2
c = theta0+theta1*X1_new+theta3*X1_new*X1_new
X2_new_boundary = (-b+np.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/(2*a)
print(X2_new_boundary)
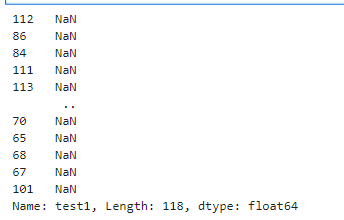
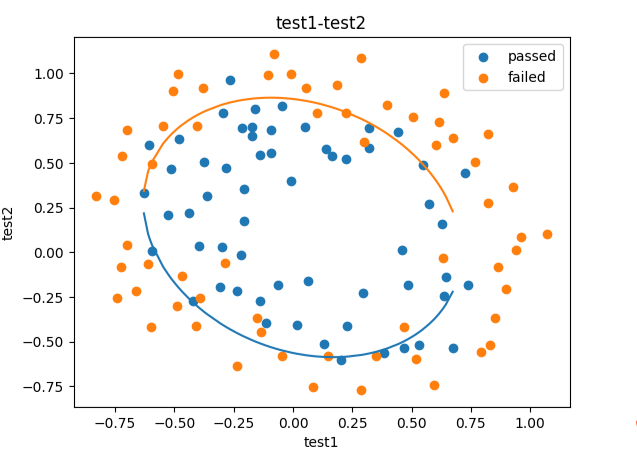
fig8 = plt.figure()
plt.plot(X1_new,X2_new_boundary)
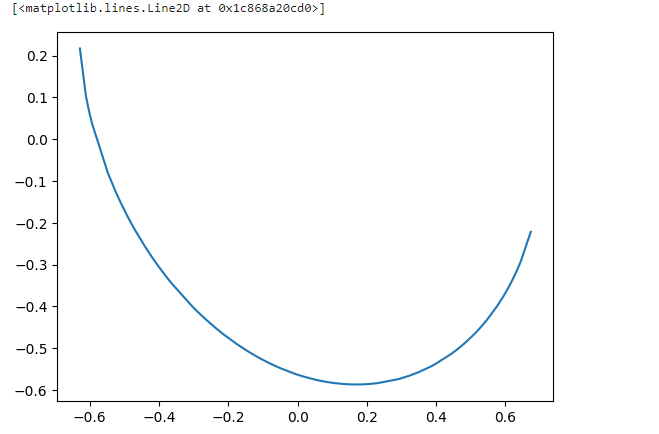
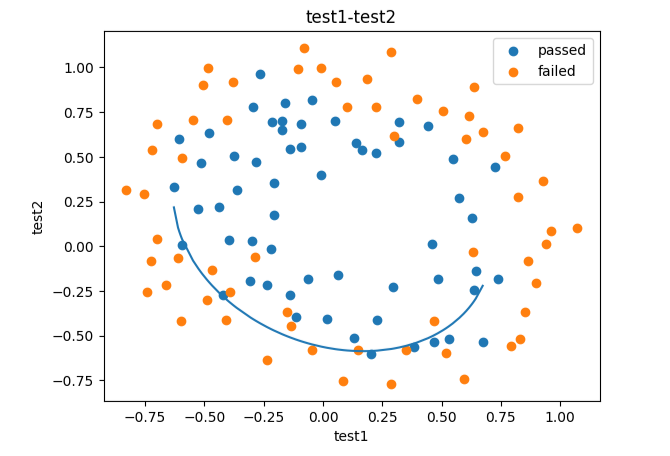
fig9 = plt.figure()
passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][mask])
failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][~mask])
plt.plot(X1_new,X2_new_boundary)
plt.title("test1-test2")
plt.xlabel("test1")
plt.ylabel("test2")
plt.legend((passed,failed),("passed","failed"))
plt.show()
#定义边界函数
def f(x):a = theta4b = theta5*x+theta2c = theta0+theta1*x+theta3*x*xX2_new_boundary1 = (-b+np.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/(2*a)X2_new_boundary2 = (-b-np.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/(2*a)return X2_new_boundary1,X2_new_boundary2
X2_new_boundary1 = []
X2_new_boundary2 = []
for x in X1_new:X2_new_boundary1.append(f(x)[0])X2_new_boundary2.append(f(x)[1])
print(X2_new_boundary1,X2_new_boundary2)
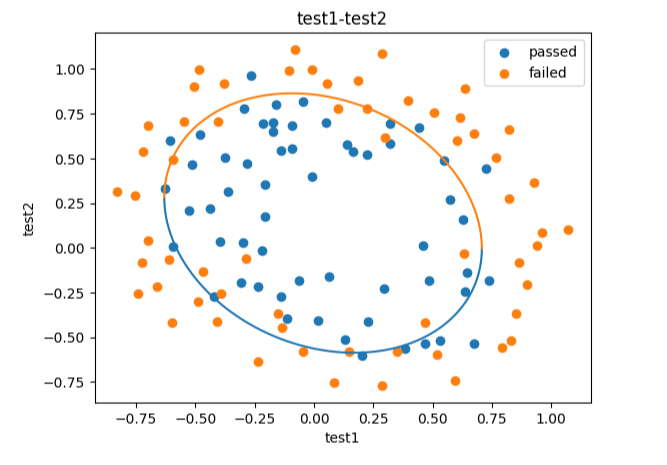
fig10 = plt.figure()
passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][mask])
failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][~mask])
plt.plot(X1_new,X2_new_boundary1)
plt.plot(X1_new,X2_new_boundary2)
plt.title("test1-test2")
plt.xlabel("test1")
plt.ylabel("test2")
plt.legend((passed,failed),("passed","failed"))
plt.show()
X1_range = [-0.9+x/10000 for x in range(0,19000)]
X1_range = np.array(X1_range)
X2_new_boundary1 = []
X2_new_boundary2 = []
for x in X1_range:X2_new_boundary1.append(f(x)[0])X2_new_boundary2.append(f(x)[1])
print(X2_new_boundary1,X2_new_boundary2)
fig11 = plt.figure()
passed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][mask])
failed = plt.scatter(data.loc[:,'test1'][~mask],data.loc[:,'test2'][~mask])
plt.plot(X1_range,X2_new_boundary1)
plt.plot(X1_range,X2_new_boundary2)
plt.title("test1-test2")
plt.xlabel("test1")
plt.ylabel("test2")
plt.legend((passed,failed),("passed","failed"))
plt.show()