python填充多边形,获取所有内部点
shepely
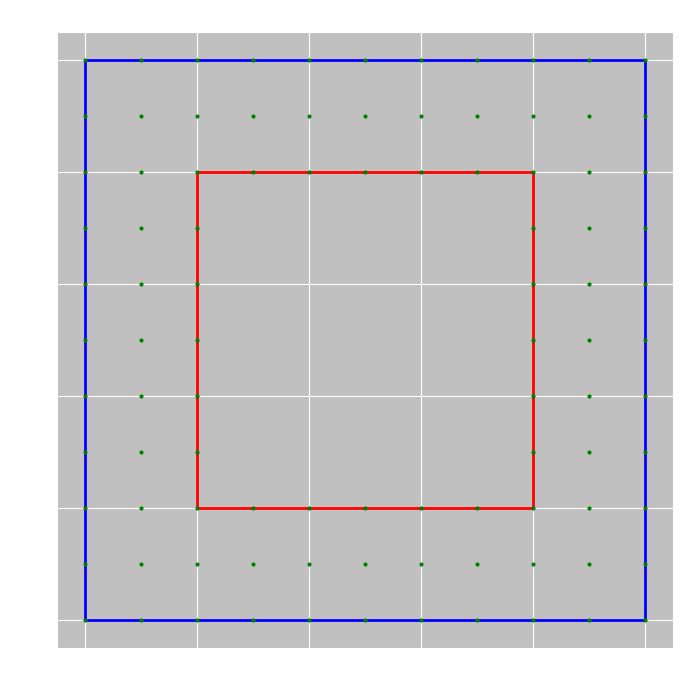
简单示例
from shapely.geometry import Polygon# 创建一个多边形
polygon = Polygon([(0, 0), (0, 5), (5, 5), (5, 0)])# 提取多边形中的点
points = list(polygon.exterior.coords)# 打印结果
print(points)
实际示例
import numpy as np
from shapely.geometry import Polygon, Point, MultiPolygon
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.path import Path
plt.rcParams['figure.facecolor'] = 'white'
plt.rcParams['axes.facecolor'] = 'silver'
# 网格线
plt.rcParams['xtick.direction'] = 'in'
print(plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif"])
# 设置全局字体为黑体
# plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['simhei'] # 替换为其他中文字体如def get_integer_points_in_polygon(polygon, include_boundary=True):"""获取多边形内部的所有整数坐标点参数:polygon: Shapely Polygon对象(可以包含孔洞)include_boundary: 是否包含边界上的点返回:list: 多边形内部的整数坐标点列表 [(x1, y1), (x2, y2), ...]"""# 获取多边形的边界框min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y = polygon.bounds# 将边界框坐标转换为整数min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y = map(int, [min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y])# 生成边界框内的所有整数点x_coords = np.arange(min_x, max_x + 1)y_coords = np.arange(min_y, max_y + 1)# 创建网格点xx, yy = np.meshgrid(x_coords, y_coords)grid_points = np.vstack((xx.flatten(), yy.flatten())).T# 检查每个点是否在多边形内部interior_points = []for point in grid_points:shapely_point = Point(point)if polygon.contains(shapely_point) or (include_boundary and polygon.touches(shapely_point)):interior_points.append(tuple(point))return interior_pointsdef visualize_polygon_and_points(polygon, points):"""可视化多边形和内部点参数:polygon: Shapely Polygon对象points: 点列表"""fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 8), facecolor='white')# 绘制多边形if hasattr(polygon, 'exterior'):# 单个多边形x, y = polygon.exterior.xyax.plot(x, y, 'b-', linewidth=2)# 绘制孔洞for interior in polygon.interiors:x, y = interior.xyax.plot(x, y, 'r-', linewidth=2)else:# 多多边形for poly in polygon.geoms:x, y = poly.exterior.xyax.plot(x, y, 'b-', linewidth=2)for interior in poly.interiors:x, y = interior.xyax.plot(x, y, 'r-', linewidth=2)# 绘制点if points:x_pts, y_pts = zip(*points)ax.plot(x_pts, y_pts, 'go', markersize=2)ax.set_aspect('equal')plt.title('多边形及其内部整数点')plt.xlabel('X坐标')plt.ylabel('Y坐标')plt.grid(True)plt.show()# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":# 创建一个带孔洞的多边形示例exterior = [(0, 0), (10, 0), (10, 10), (0, 10), (0, 0)]interior = [(2, 2), (8, 2), (8, 8), (2, 8), (2, 2)]polygon = Polygon(exterior, [interior])# 获取多边形内部的所有整数点points = get_integer_points_in_polygon(polygon)print(f"找到 {len(points)} 个内部整数点")print("前10个点:", points[:10])# 可视化visualize_polygon_and_points(polygon, points)geopandas
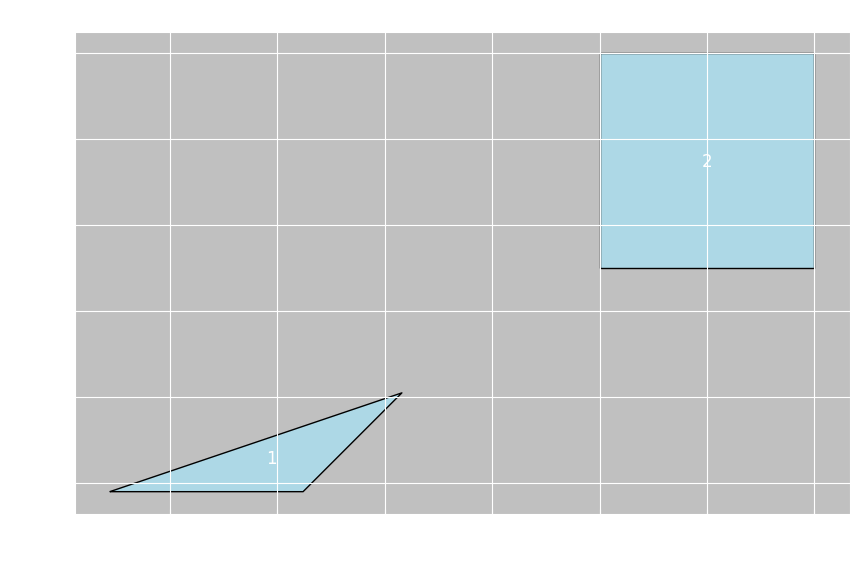
处理非标准geojson
import json
import geopandas as gpd
import pandas as pd
from shapely.geometry import Polygon, GeometryCollection
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 方法1:直接解析GeometryCollection
def parse_geometry_collection(geojson_data):"""解析GeometryCollection格式的GeoJSON"""features = []if geojson_data.get('type') != 'GeometryCollection':raise ValueError("不是GeometryCollection格式")for geom in geojson_data.get('geometries', []):# 提取几何类型和坐标geom_type = geom.get('type')coords = geom.get('coordinates', [])# 提取属性properties = geom.get('properties', {})# 创建对应的shapely几何对象if geom_type == 'Polygon':geometry = Polygon(coords[0]) # 多边形外环elif geom_type == 'Point':from shapely.geometry import Pointgeometry = Point(coords)elif geom_type == 'LineString':from shapely.geometry import LineStringgeometry = LineString(coords)else:continue # 跳过不支持的几何类型features.append({'type': 'Feature','geometry': geometry,'properties': properties})print(features)return features# 方法2:转换为标准GeoJSON格式
def convert_to_standard_geojson(geojson_data):"""将GeometryCollection转换为标准FeatureCollection格式"""features = parse_geometry_collection(geojson_data)return {'type': 'FeatureCollection','features': features}# 方法3:创建GeoDataFrame
def create_geodataframe(geojson_data):"""从GeometryCollection创建GeoDataFrame"""features = parse_geometry_collection(geojson_data)# 提取几何和属性geometries = [f['geometry'] for f in features]properties = [f['properties'] for f in features]# 创建GeoDataFramegdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame(properties, geometry=geometries)return gdf# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":# 示例数据(根据您提供的格式)geojson_data = {"type": "GeometryCollection","geometries": [{"type": "Polygon", "properties": {"uID": 0, "label": "1"}, "coordinates": [[[10436, 6198], [10481, 6198], [10504, 6221], [10436, 6198]]]},{"type": "Polygon", "properties": {"uID": 1, "label": "2"}, "coordinates": [[[10550, 6250], [10600, 6250], [10600, 6300], [10550, 6300], [10550, 6250]]]}]}# 解析GeometryCollectionfeatures = parse_geometry_collection(geojson_data)print("解析出的要素数量:", len(features))# 转换为标准GeoJSONstandard_geojson = convert_to_standard_geojson(geojson_data)print("标准GeoJSON格式已创建")# 创建GeoDataFramegdf = create_geodataframe(geojson_data)print("GeoDataFrame信息:")print(gdf.head())# 可视化fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 8), facecolor='white')gdf.plot(ax=ax, color='lightblue', edgecolor='black')# 添加标签for idx, row in gdf.iterrows():centroid = row.geometry.centroidax.text(centroid.x, centroid.y, row['label'], fontsize=12, ha='center', va='center')plt.title("GeometryCollection中的多边形")plt.xlabel("X坐标")plt.ylabel("Y坐标")plt.grid(True)plt.show()# 保存为标准GeoJSON文件gdf.to_file("converted.geojson", driver="GeoJSON")print("已保存为标准GeoJSON文件: converted.geojson")
处理实际文件
import json# 从文件读取GeometryCollection格式的GeoJSON
def read_geometry_collection_file(file_path):"""从文件读取GeometryCollection格式的GeoJSON"""with open(file_path, 'r') as f:geojson_data = json.load(f)return geojson_data# 使用示例
file_path = "your_file.geojson" # 替换为实际文件路径
geojson_data = read_geometry_collection_file(file_path)# 处理数据
gdf = create_geodataframe(geojson_data)
print(gdf.info())
确保多边形坐标闭合
def ensure_polygon_closed(coordinates):"""确保多边形坐标闭合(首尾点相同)"""if not coordinates:return coordinates# 对于多边形,coordinates是一个列表的列表# 第一个列表是外环,后续列表是内环(孔)closed_coords = []for ring in coordinates:if len(ring) < 3:continue # 跳过无效环(至少需要3个点)# 检查是否闭合(第一个点和最后一个点相同)first_point = ring[0]last_point = ring[-1]if first_point != last_point:# 添加第一个点作为最后一个点以闭合环closed_ring = ring + [first_point]else:closed_ring = ringclosed_coords.append(closed_ring)return closed_coords
提取坐标信息
def extract_coordinates_from_geometry_collection(geojson_data):"""从GeometryCollection中提取所有坐标"""coordinates = []if geojson_data.get('type') != 'GeometryCollection':return coordinatesfor geom in geojson_data.get('geometries', []):geom_type = geom.get('type')coords = geom.get('coordinates', [])properties = geom.get('properties', {})if geom_type == 'Polygon':# 多边形坐标 - 第一个列表是外环,后续列表是内环(孔)for ring in coords:coordinates.extend(ring)elif geom_type == 'Point':coordinates.append(coords)elif geom_type == 'LineString':coordinates.extend(coords)elif geom_type == 'MultiPolygon':for polygon in coords:for ring in polygon:coordinates.extend(ring)return coordinates# 使用示例
all_coords = extract_coordinates_from_geometry_collection(geojson_data)
print(f"提取到 {len(all_coords)} 个坐标点")
print("前10个坐标:", all_coords[:10])
生成mask
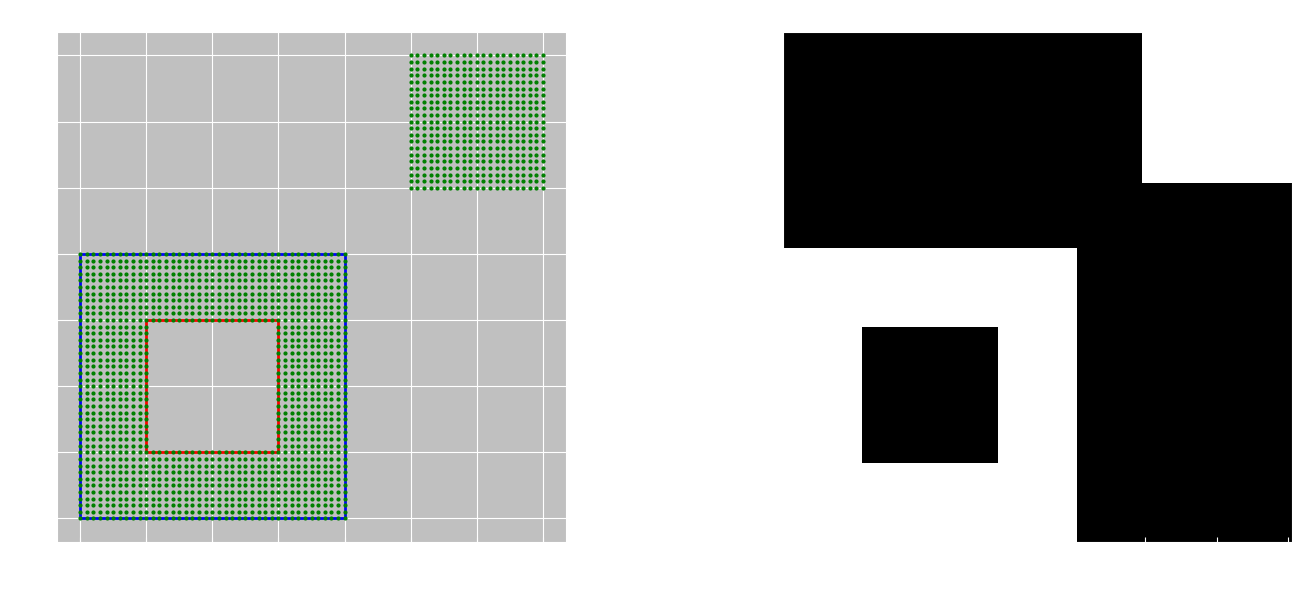
import numpy as np
from shapely.geometry import Polygon, MultiPolygon, Point
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.path import Path
import matplotlib.patches as patches
import jsondef get_integer_points_from_geometry_collection(geojson_data):"""从GeometryCollection中提取所有多边形内部的整数坐标点参数:geojson_data: GeometryCollection格式的GeoJSON数据返回:set: 所有多边形内部的整数坐标点集合"""interior_points = set()if geojson_data.get('type') != 'GeometryCollection':return interior_pointsfor geom in geojson_data.get('geometries', []):geom_type = geom.get('type')coords = geom.get('coordinates', [])properties = geom.get('properties', {})if geom_type == 'Polygon':# 创建Shapely多边形对象polygon = Polygon(coords[0], coords[1:])# 获取多边形内部的整数点points = get_integer_points_in_polygon(polygon)interior_points.update(points)elif geom_type == 'MultiPolygon':# 处理多多边形for polygon_coords in coords:polygon = Polygon(polygon_coords[0], polygon_coords[1:])points = get_integer_points_in_polygon(polygon)interior_points.update(points)return interior_pointsdef get_integer_points_in_polygon(polygon):"""获取多边形内部的所有整数坐标点参数:polygon: Shapely Polygon对象返回:set: 多边形内部的整数坐标点集合"""# 获取多边形的边界框min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y = polygon.bounds# 将边界框坐标转换为整数min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y = map(int, [np.floor(min_x), np.floor(min_y), np.ceil(max_x), np.ceil(max_y)])# 生成边界框内的所有整数点x_coords = np.arange(min_x, max_x + 1)y_coords = np.arange(min_y, max_y + 1)# 创建网格点xx, yy = np.meshgrid(x_coords, y_coords)grid_points = np.vstack((xx.flatten(), yy.flatten())).T# 检查每个点是否在多边形内部include_boundary = Trueinterior_points = []for point in grid_points:shapely_point = Point(point)if polygon.contains(shapely_point) or (include_boundary and polygon.touches(shapely_point)):interior_points.append(tuple(point))return interior_points# # 修正后的路径创建方法 - 确保代码数组是一维且长度匹配# exterior = np.array(polygon.exterior.coords)# # 创建路径代码 - 确保是一维数组# n_points = len(exterior)# codes = np.ones(n_points, dtype=Path.code_type) * Path.LINETO# codes[0] = Path.MOVETO# # 创建路径# path = Path(exterior, codes)# # 检查每个点是否在多边形内部# contains = path.contains_points(grid_points)# interior_points = set(tuple(map(int, point)) for point, inside in zip(grid_points, contains) if inside)# return interior_pointsdef create_mask_from_points(points, shape=None):"""从点集合创建二值mask参数:points: 点集合shape: mask的形状 (height, width)。如果为None,则根据点坐标自动确定返回:numpy.array: 二值mask"""if not points:return np.array([]), (0, 0)# 如果没有指定形状,则根据点坐标确定if shape is None:all_x = [p[0] for p in points]all_y = [p[1] for p in points]min_x, max_x = min(all_x), max(all_x)min_y, max_y = min(all_y), max(all_y)width = max_x - min_x + 1height = max_y - min_y + 1origin = (min_x, min_y)else:height, width = shapeorigin = (0, 0)# 创建空的maskmask = np.zeros((height, width), dtype=np.uint8)# 填充maskfor point in points:x, y = pointmask_y = y - origin[1]mask_x = x - origin[0]if 0 <= mask_y < height and 0 <= mask_x < width:mask[mask_y, mask_x] = 1return mask, origindef visualize_polygon_and_mask(polygon, mask, origin, points=None):"""可视化多边形和mask参数:polygon: Shapely Polygon对象mask: 二值maskorigin: mask的原点坐标points: 点集合(可选)"""fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 6))# 绘制多边形if hasattr(polygon, 'exterior'):# 单个多边形x, y = polygon.exterior.xyax1.plot(x, y, 'b-', linewidth=2)# 绘制孔洞for interior in polygon.interiors:x, y = interior.xyax1.plot(x, y, 'r-', linewidth=2)else:# 多多边形for poly in polygon.geoms:x, y = poly.exterior.xyax1.plot(x, y, 'b-', linewidth=2)for interior in poly.interiors:x, y = interior.xyax1.plot(x, y, 'r-', linewidth=2)# 绘制点if points:x_pts, y_pts = zip(*points)ax1.plot(x_pts, y_pts, 'go', markersize=2)ax1.set_aspect('equal')ax1.set_title('多边形及其内部整数点')ax1.set_xlabel('X坐标')ax1.set_ylabel('Y坐标')ax1.grid(True)# 绘制maskax2.imshow(mask, cmap='gray', origin='lower')ax2.set_title('生成的Mask')ax2.set_xlabel(f'X (原点: {origin[0]})')ax2.set_ylabel(f'Y (原点: {origin[1]})')plt.tight_layout()plt.show()def process_geojson_data(geojson_data):"""处理GeoJSON数据并生成mask参数:geojson_data: GeoJSON数据返回:mask: 二值maskorigin: mask的原点坐标interior_points: 内部点集合"""# 提取多边形内部的所有整数点interior_points = get_integer_points_from_geometry_collection(geojson_data)print(f"找到 {len(interior_points)} 个内部整数点")# 创建maskmask, origin = create_mask_from_points(interior_points)print(f"Mask形状: {mask.shape}, 原点: {origin}")# 可视化# 注意:这里简化处理,只可视化第一个多边形if geojson_data.get('type') == 'GeometryCollection' and geojson_data.get('geometries'):first_geom = geojson_data['geometries'][0]if first_geom.get('type') == 'Polygon':polygon = Polygon(first_geom['coordinates'][0], first_geom['coordinates'][1:])visualize_polygon_and_mask(polygon, mask, origin, interior_points)return mask, origin, interior_points# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":# 示例GeometryCollection数据geojson_data = {"type": "GeometryCollection","geometries": [{"type": "Polygon", "properties": {"uID": 0, "label": "1"}, "coordinates": [[[10, 10], [50, 10], [50, 50], [10, 50], [10, 10]], # 外环[[20, 20], [40, 20], [40, 40], [20, 40], [20, 20]] # 内环(孔洞)]},{"type": "Polygon", "properties": {"uID": 1, "label": "2"}, "coordinates": [[[60, 60], [80, 60], [80, 80], [60, 80], [60, 60]]]}]}# 处理数据mask, origin, interior_points = process_geojson_data(geojson_data)# 保存mask为图像plt.imsave('mask.png', mask, cmap='gray')print("Mask已保存为 mask.png")# 保存点坐标到文件with open('interior_points.txt', 'w') as f:for point in sorted(interior_points):f.write(f"{point[0]}, {point[1]}\n")print("点坐标已保存为 interior_points.txt")
